The global G terminal manufacturing industry is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for reliable connectivity in industrial automation, telecommunications, and transportation sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global terminal blocks and connectors market—under which G terminals fall—was valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing investments in smart infrastructure, renewable energy installations, and the automation of manufacturing processes. As critical components for secure electrical connections, G terminals are witnessing heightened adoption across automotive, energy, and industrial equipment applications. With stringent safety regulations and the need for high-performance electrical systems, manufacturers are focusing on innovation in materials, miniaturization, and durability. In this evolving landscape, a select group of global suppliers stands out for their technological expertise, quality compliance, and scalable production—shaping the future of electrical terminal solutions.
Top 10 G Terminal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 International Transportation Service – Pier G
Domain Est. 1996
Website: polb.com
Key Highlights: Facilities information for the International Transportation Service – ITS – terminal at Pier G in the Port of Long Beach….
#2 Turkish Airlines
Domain Est. 1996
#3 Long Beach Container Terminal
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lbct.com
Key Highlights: LBCT is at the forefront of marine terminal innovation, specializing in advanced stevedoring, cargo velocity, and speed to market, while reducing our carbon ……
#4 Google Cloud Console
Domain Est. 1997
#5 Port of Galveston, TX –
Domain Est. 1998
Website: portofgalveston.com
Key Highlights: Just 45 minutes from open seas, the 840-acre port has infrastructure and assets to serve growing cruise, cargo and commercial businesses. The port is the fourth ……
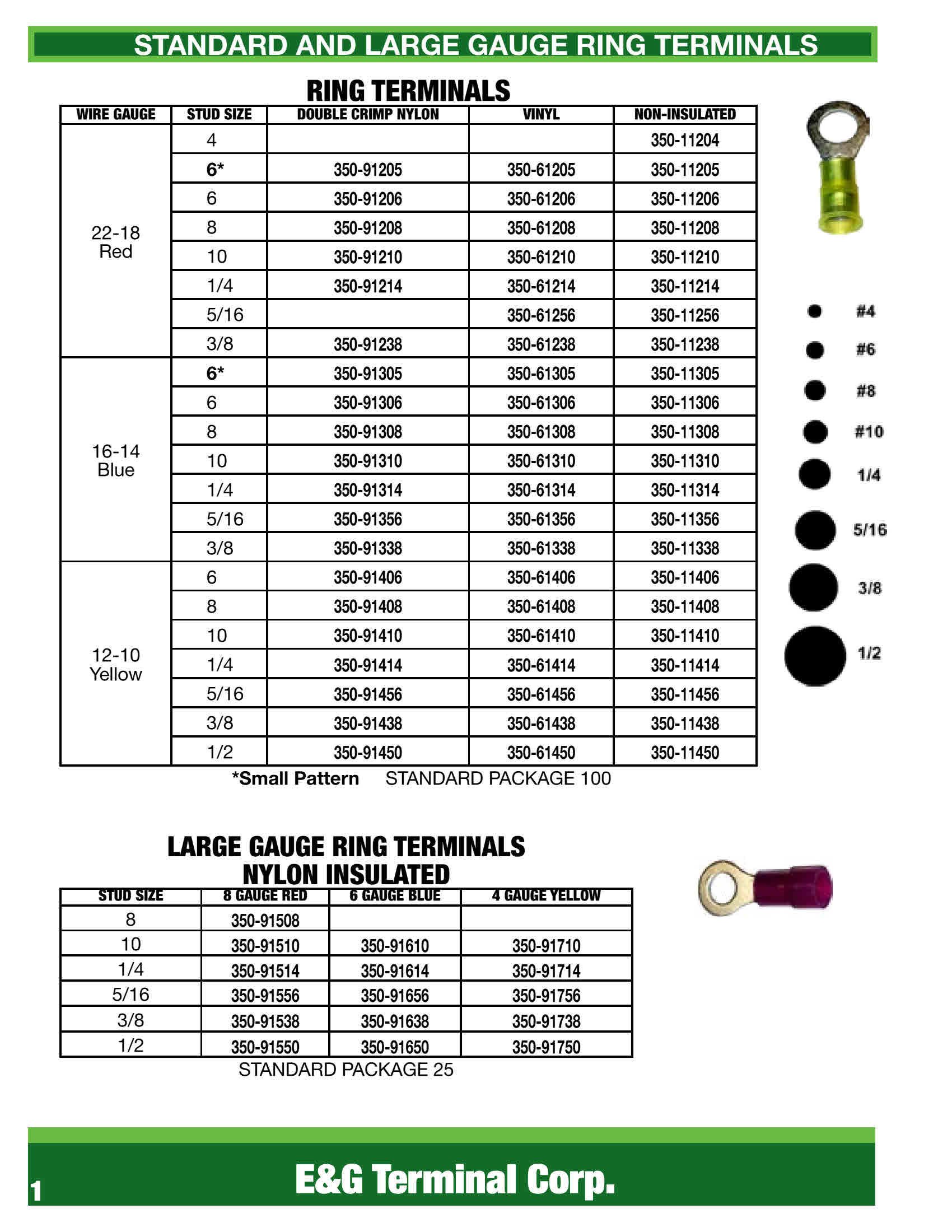
#6 E & G Terminal 303
Domain Est. 2003
Website: egterminal.com
Key Highlights: E & G Terminal 303-287-2900. Everything To Fasten Almost Anything. Menu. Home · ABRASIVES · ASSORTMENTS · BATTERY RELATED · BITS & BLADES ……
#7 Houston Airport System
Domain Est. 2005
Website: fly2houston.com
Key Highlights: Houston Airports is the City of Houston’s Department of Aviation. HAS manages and operates IAH, HobbyAirport and HouSpaceport….
#8 Ports America
Domain Est. 2007
Website: portsamerica.com
Key Highlights: This year, six Ports America terminals became Green Marine certified, which is the leading environmental certification program for North America’s maritime ……
#9 Godel Terminal
Domain Est. 2023
Website: godelterminal.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to the Godel Terminal, a professional web-based financial terminal software offering comprehensive financial and investment data….
#10 Terminal Yard Operating System
Domain Est. 2023
Website: terminal-industries.com
Key Highlights: Max throughput. Easy-to-use. Rapid ROI. Terminal Yard Operating System is the only AI-native, fully-integrated platform for the yard of the future….
Expert Sourcing Insights for G Terminal

H2: Market Trends for G Terminal in 2026
As we approach 2026, the market landscape for G Terminal—presumably a key logistics, trade, or digital infrastructure hub (such as a container terminal, port facility, or data gateway)—is being reshaped by macroeconomic forces, technological innovation, sustainability mandates, and evolving global supply chain dynamics. Below is an analysis of the major market trends expected to influence G Terminal in 2026:
1. Digitalization and Automation Acceleration
By 2026, G Terminal is expected to be deeply integrated with smart port technologies. Artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain are being leveraged to optimize cargo tracking, reduce turnaround times, and enhance security. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotic cranes, and digital twin simulations will likely be standard, improving operational efficiency and reducing labor dependency. Investment in digital infrastructure is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 12–15% through 2026, driven by competitive pressures and the need for real-time visibility in supply chains.
2. Sustainability and Decarbonization Initiatives
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) compliance is a dominant trend shaping G Terminal’s operations. In 2026, the terminal is likely to have adopted carbon-neutral or low-emission technologies such as electric or hydrogen-powered cargo handling equipment, shore power for docked vessels, and renewable energy integration (e.g., solar panels across terminal rooftops). Regulatory pressure from international bodies like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and regional carbon pricing mechanisms will compel G Terminal to report and reduce Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions.
3. Resilience and Supply Chain Reconfiguration
Post-pandemic and geopolitical disruptions (e.g., Red Sea tensions, U.S.-China trade dynamics) have led to a shift toward supply chain resilience. By 2026, G Terminal is expected to play a critical role in nearshoring and regionalization strategies, serving as a strategic node in diversified logistics networks. Increased demand for inventory buffering and multimodal connectivity (rail, road, barge) will enhance G Terminal’s value as a flexible distribution hub.
4. Expansion of E-Commerce and Fast-Track Logistics
The continued rise of e-commerce requires faster, more reliable cargo handling. G Terminal is likely to see growing volumes of high-turnover consumer goods, necessitating faster processing, last-mile integration, and cold chain capabilities. Investment in dedicated express freight zones and partnerships with logistics tech firms (e.g., autonomous delivery startups) will be evident in 2026.
5. Geopolitical and Trade Policy Influences
Trade realignments, including regional trade agreements (e.g., RCEP, AfCFTA) and sanctions-related rerouting, will impact cargo flows through G Terminal. By 2026, the terminal may experience shifts in trade lanes, with increased volumes from emerging markets in Southeast Asia, Africa, or Latin America, depending on its geographic positioning. Customs digitization and compliance automation will be essential to manage complex regulatory environments.
6. Workforce Transformation and Skills Development
As automation expands, G Terminal’s workforce will shift from manual labor toward tech oversight, data analytics, and cybersecurity roles. Upskilling programs and collaboration with vocational institutions will be critical to maintaining operational continuity. Human-machine collaboration will define the new labor model in 2026.
7. Cybersecurity and Data Governance
With the terminal’s increasing reliance on digital systems, cybersecurity threats represent a growing risk. In 2026, G Terminal will likely implement advanced threat detection systems, comply with international data protection standards (e.g., ISO 27001), and ensure secure data sharing across stakeholders in the logistics ecosystem.
Conclusion
By 2026, G Terminal is poised to emerge as a next-generation hub characterized by automation, sustainability, resilience, and digital integration. Success will depend on strategic investments in technology, agility in responding to global disruptions, and alignment with evolving environmental and regulatory standards. Stakeholders must proactively adapt to these trends to maintain competitiveness in an increasingly complex and interconnected global market.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing G Terminals (Quality, IP)
Sourcing G terminals—commonly used in electrical and industrial applications for grounding or signal connections—can present several challenges, particularly concerning quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable performance and legal compliance.
Inadequate Quality Control
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing G terminals is inconsistent or poor product quality. Low-cost suppliers, especially in competitive markets, may cut corners on materials (e.g., using substandard copper or inadequate plating), leading to increased resistance, overheating, or premature failure. Lack of proper quality certifications (such as UL, CE, or ISO) further exacerbates the risk, making it difficult to verify performance under real-world conditions.
Counterfeit or Non-Compliant Components
The market for electrical components is prone to counterfeiting. Sourcing G terminals from unauthorized distributors or gray-market suppliers increases the risk of receiving fake or re-marked parts that do not meet original specifications. These counterfeit products often fail safety and durability tests, posing serious operational and safety hazards.
Misrepresentation of IP and Compatibility
Some suppliers may offer G terminals that mimic the design of patented or proprietary products. While they may appear compatible, these clones can infringe on intellectual property rights, exposing buyers to legal risk. Additionally, slight dimensional or material differences can lead to improper fit or reduced performance, especially in high-vibration or high-current environments.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reliable sourcing requires full traceability—batch numbers, material certifications, and test reports. Many suppliers, particularly smaller or offshore vendors, fail to provide adequate documentation. This absence complicates quality audits, compliance verification, and root cause analysis in case of field failures.
Inconsistent IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
G terminals used in harsh environments must meet specific IP ratings for dust and moisture resistance. However, some suppliers exaggerate or falsify IP claims without third-party testing. Using terminals with unverified IP ratings in outdoor or industrial settings can lead to corrosion, short circuits, and system downtime.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Overreliance on a single source or region can expose procurement to supply chain disruptions. Geopolitical issues, logistics delays, or sudden changes in regulatory requirements may impact availability and quality consistency. Diversifying suppliers and conducting regular audits can mitigate these risks.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers, demanding certifications, verifying IP claims through testing, and ensuring legal compliance with IP regulations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for G Terminal
This guide outlines the essential logistics procedures and compliance requirements for operations at G Terminal. Adherence to these standards ensures efficient cargo handling, regulatory compliance, and safety.
Terminal Access & Security Protocols
All personnel and vehicles entering G Terminal must comply with the site’s access control measures. Valid identification, prior registration, and adherence to security screening procedures are mandatory. Drivers must present a valid terminal appointment (GAT) and comply with vehicle inspection requirements. Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited.
Cargo Documentation Requirements
Complete and accurate documentation is required for all inbound and outbound shipments. Mandatory documents include the Bill of Lading (B/L), Commercial Invoice, Packing List, and any applicable permits or regulatory forms. Electronic submission via the Terminal Operating System (TOS) is required 24 hours prior to arrival.
Equipment & Handling Standards
G Terminal supports standard ISO containers, including dry, reefer, and hazardous materials (HAZMAT) units. All equipment must meet ISO and CSC safety standards. Terminal-operated handling equipment (RTGs, Straddle Carriers, and Reach Stackers) are used exclusively for container movement. External equipment requires prior approval and safety inspection.
Dangerous Goods Regulations
Handling of hazardous cargo must comply with IMDG Code, local fire codes, and terminal-specific HAZMAT protocols. All dangerous goods must be declared at booking, properly labeled, and segregated according to risk class. Emergency response plans and Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) must be on file.
Customs & Regulatory Compliance
All shipments are subject to customs inspection and must meet national import/export regulations. Use of automated customs processing systems (e.g., ACE, AEO) is required. False declarations or non-compliance may result in shipment seizure, fines, or suspension of terminal access privileges.
Environmental & Sustainability Policies
G Terminal enforces strict environmental standards, including emissions controls for drayage trucks, waste management procedures, and spill prevention measures. Operators must comply with local air quality regulations and participate in the terminal’s green gate program for low-emission vehicles.
Operational Hours & Gate Procedures
The terminal operates 24/7 with designated peak and off-peak hours. Gate appointments are mandatory for all truck arrivals. Real-time gate queue status is available via the G Terminal Portal. Delays due to undocumented cargo or non-compliant vehicles may result in demurrage charges.
Incident Reporting & Emergency Response
All incidents—including equipment damage, safety violations, or hazardous spills—must be reported immediately to Terminal Control. Emergency contact numbers and response procedures are posted at all terminal entrances. Regular drills are conducted to ensure preparedness.
Compliance Monitoring & Audits
G Terminal conducts routine audits of operator compliance with logistics and regulatory standards. Non-compliant parties may face penalties, access restrictions, or termination of service agreements. Audit results are shared with relevant stakeholders upon request.
Conclusion on Sourcing G-Terminal:
Sourcing G-terminals requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. After evaluating potential suppliers, conducting technical assessments, and reviewing logistical and contractual terms, it is evident that selecting a reputable manufacturer or distributor with proven expertise in electrical connectivity solutions is critical. Factors such as material quality, certification (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS), production capacity, and after-sales support play a significant role in ensuring long-term performance and system safety.
By establishing strong supplier relationships, implementing rigorous quality control checks, and aligning procurement with project specifications, organizations can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and substandard components. In conclusion, a well-structured sourcing strategy for G-terminals not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports the integrity and reliability of the electrical systems in which they are used.