The global technical textiles market, which includes functional materials like fusible interfacing, is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand for performance-driven and durable apparel. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global technical textiles market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, with nonwoven technical textiles—key components in interfacing—playing a significant role in this expansion. Fleece manufacturers, in particular, are turning to specialized fusible interfacings to enhance fabric stability, improve shape retention, and support garment structure without compromising on the softness and flexibility inherent to fleece. As sustainability and efficiency become central to production processes, the selection of the right fusible interfacing directly impacts product quality and manufacturing yield. In this evolving landscape, six fusible interfacings have emerged as top performers—balancing adhesion strength, heat sensitivity, and compatibility with fleece’s unique thermal and mechanical properties.
Top 6 Fusible Interfacing For Fleece Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Fusible Fleece Interfacing Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2016
Website: fusibleinterfacing.com
Key Highlights: High quality fusible fleece interfacing with competitive price for wholesaler. Made by a leading fusible fleece interfacing manufacturer….
#2 Legacy Lightweight Fusible Fleece Natural
Domain Est. 1992
Website: minerva.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $200 30-day returnsLegacy 986F Fusible Fleece is a one sided fusible fleece that adds a layer of softness, body, and stability to home decorating, craft and appa…
#3 Fleece Interfacing
Domain Est. 1998
#4 Pellon 987F Fusible Fleece Polyester Interfacing
Domain Est. 2002
Website: wawak.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryPellon 987F Fusible Fleece is a one-sided fusible fleece that adds a layer of softness, body, and stability to home decorating, craft, and apparel sewing. No …
#5 Fusible Fleece 44″ Interfacing 987F White // Half Yard
Domain Est. 2023
Website: frenchfryquiltco.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.9 256 Web coated on one side for convenient application.. Iron in full lofty body to fabric. Appliques, machine quilted and padded craft projects. 100% Polyeste…
#6 Fusible interfacing for fleece
Domain Est. 2001
Website: sewing.patternreview.com
Key Highlights: I have been searching for a solution and found that fusible interfacing CAN be used on low heat setting. However, I have tried to find one that uses a low heat ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fusible Interfacing For Fleece

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Fusible Interfacing for Fleece
The global market for fusible interfacing for fleece is expected to undergo notable changes by 2026, driven by shifts in consumer preferences, advancements in textile technology, and increasing sustainability demands. Fusible interfacing—used to reinforce and stabilize fleece fabrics in garments such as jackets, hoodies, and accessories—is adapting to meet the evolving needs of both manufacturers and end consumers. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping this niche segment.
Growing Demand in Activewear and Outerwear
Fleece remains a preferred fabric in outerwear and activewear due to its warmth, softness, and moisture-wicking properties. As outdoor and athleisure fashion continues to grow, especially in North America and Europe, demand for high-performance fleece garments rises. This, in turn, increases the need for compatible fusible interfacings that maintain the stretch, drape, and comfort of fleece without compromising durability. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to prioritize interfacings with enhanced elasticity and heat-activated adhesives tailored specifically for fleece blends.
Technological Innovation in Adhesive Formulations
A major trend by 2026 is the development of low-temperature and ultra-thin adhesive coatings. These innovations prevent damage to the delicate pile structure of fleece during the fusing process. New polyamide and polyester-based adhesives offer better wash durability and flexibility, ensuring that interfaced fleece garments retain shape and performance through repeated use and laundering. Suppliers are investing in R&D to create eco-friendly, non-toxic adhesive systems that comply with global safety standards.
Sustainability and Eco-Conscious Materials
Sustainability is a driving force in the textile industry, and the fusible interfacing market is no exception. By 2026, demand for recyclable, biodegradable, and low-impact interfacing materials is projected to grow. Manufacturers are exploring bio-based adhesives and carrier fabrics made from recycled polyester or organic cotton. Certifications such as OEKO-TEX® and GOTS are becoming essential for market access, especially in Europe and North America. Brands aiming for carbon neutrality are likely to favor suppliers offering transparent, sustainable supply chains.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, remains a dominant production hub for both fleece fabrics and fusible interfacings. However, rising labor and environmental compliance costs may shift some production to Southeast Asia. In contrast, North America and Western Europe are seeing growth in localized, small-batch garment production, boosting demand for high-quality, customizable fusible interfacings. E-commerce and direct-to-consumer fashion brands are also driving demand for versatile interfacing solutions that support rapid prototyping and on-demand manufacturing.
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The fusible interfacing market is expected to witness consolidation among key players, with larger textile chemical and material companies acquiring niche innovators. Strategic partnerships between interfacing suppliers and fleece fabric manufacturers will become more common to co-develop integrated solutions. These collaborations aim to optimize compatibility, reduce production waste, and accelerate time-to-market for new garment lines.
Conclusion
By 2026, the fusible interfacing for fleece market will be shaped by a confluence of performance demands, sustainability imperatives, and technological advancement. Companies that invest in innovative, eco-friendly products and align with evolving textile manufacturing trends are poised to capture growing market share. As fleece continues to be a staple in functional and fashionable apparel, the role of high-quality, specialized interfacing will become increasingly critical in ensuring product excellence.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Fusible Interfacing for Fleece (Quality, IP)
Sourcing the right fusible interfacing for fleece garments is critical for maintaining product quality and avoiding intellectual property (IP) issues. However, several common pitfalls can compromise performance, brand reputation, and legal compliance. Being aware of these challenges helps in making informed procurement decisions.
Poor Quality Matching
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting a fusible interfacing that doesn’t align with the unique characteristics of fleece. Fleece is a stretchy, bulky, and low-melt synthetic fabric, which requires a specialized interfacing. Using standard weight or non-stretch fusibles can lead to bubbling, stiffness, or delamination after washing. Additionally, interfacing with a high melt point may damage the fleece during application, causing scorching or distortion.
Inadequate Adhesive Compatibility
Fleece is typically made from polyester, which has a relatively low melting temperature. If the fusible interfacing uses an adhesive with too aggressive a melt profile, it can penetrate through the fleece or degrade the fabric fibers. This results in poor bonding, visible adhesive bleed-through, or reduced fabric integrity. Choosing an interfacing with a low-temperature, non-migrating adhesive specifically designed for synthetic knits is essential.
Lack of Stretch Recovery
Fleece garments often require flexibility and comfort, especially in areas like collars, cuffs, and plackets. Using a non-stretch or low-recovery interfacing can restrict movement, cause puckering, or lead to premature seam failure. Sourcing interfacing without sufficient elasticity to match the fleece undermines the garment’s intended functionality and wearability.
Overlooking Heat and Pressure Sensitivity
Improper application parameters during fusing—such as excessive heat, pressure, or dwell time—can ruin both the interfacing and the fleece. Some suppliers may not provide clear technical guidelines, leading manufacturers to guess optimal settings. This increases the risk of production defects, inconsistent results, and higher rejection rates.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
A significant but often overlooked pitfall is sourcing interfacing that infringes on patented technologies. Some high-performance fusible interfacings incorporate proprietary adhesive systems, mesh structures, or application methods protected by IP rights. Sourcing from unauthorized or counterfeit suppliers may lead to legal action, shipment seizures, or costly product recalls. Always verify that the supplier is a licensed manufacturer or distributor of the interfacing product.
Insufficient Testing and Sampling
Skipping proper in-house testing before bulk ordering is a common error. Without testing the interfacing on actual fleece fabric under production conditions, brands risk discovering compatibility issues too late. This includes wash durability, bond strength, and aesthetic impact. Relying solely on supplier claims without validation can result in costly rework or customer complaints.
Choosing Based on Price Alone
Opting for the cheapest available fusible interfacing may lead to long-term quality and reputational damage. Low-cost alternatives often use inferior adhesives or inconsistent base fabrics, which compromise performance. Investing in high-quality, technically suitable interfacing reduces waste, improves efficiency, and enhances the final product’s perceived value.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in supplier selection, technical evaluation, and IP compliance—ensuring that the fusible interfacing enhances, rather than detracts from, the performance of fleece garments.
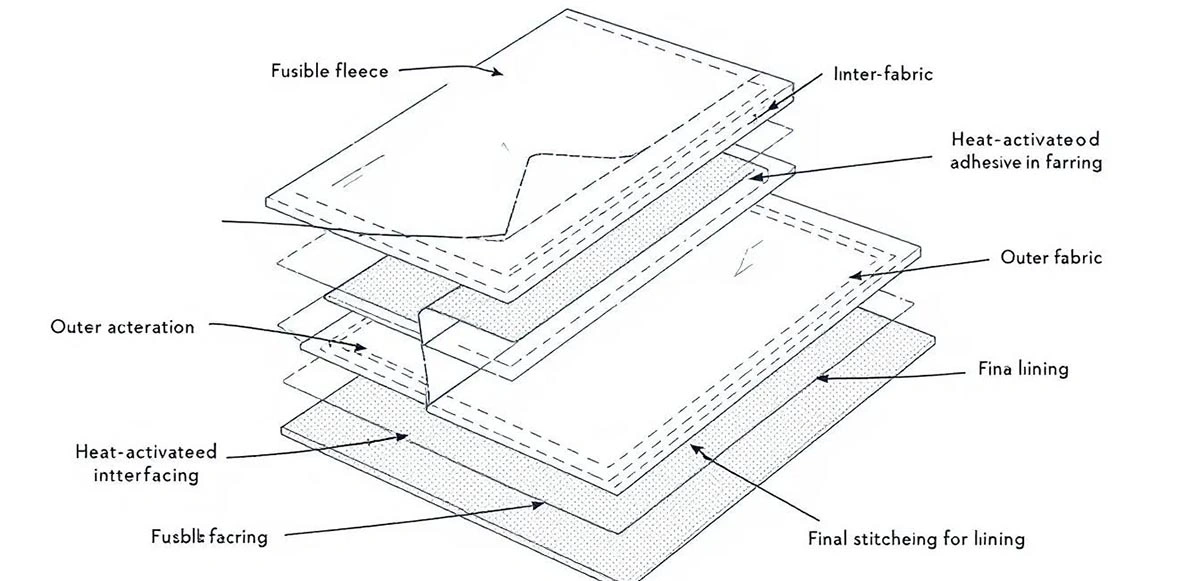
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fusible Interfacing for Fleece
Overview of Fusible Interfacing for Fleece
Fusible interfacing for fleece is a textile material designed to add structure, shape, and stability to fleece garments or accessories during manufacturing. It features a heat-activated adhesive on one side that bonds to the fabric when applied with heat and pressure. Due to the unique properties of fleece—such as its pile, stretch, and sensitivity to heat—specific handling, logistics, and compliance measures must be observed.
Storage and Handling Requirements
Temperature and Humidity Control
Store fusible interfacing rolls in a clean, dry environment with controlled temperature (15–25°C / 59–77°F) and relative humidity (40–60%). Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, moisture, or extreme temperatures, which can degrade the adhesive or cause premature activation.
Shelf Life and Rotation
Most fusible interfacings have a shelf life of 6–12 months from the manufacturing date. Practice FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation to ensure older stock is used first. Check for signs of adhesive crystallization, discoloration, or delamination before use.
Packaging Integrity
Ensure packaging remains sealed and undamaged during storage and transit. Use moisture-resistant wrapping or vacuum-sealed plastic to protect rolls from environmental exposure.
Transportation and Shipping
Domestic and International Shipping
Use sturdy, corrugated cardboard cores and outer packaging to prevent deformation during transit. For international shipments, comply with ISPM 15 regulations if wooden pallets are used. Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Do Not Stack,” “This Side Up”).
Cold and Hot Climate Considerations
Avoid shipping in extreme weather without climate-controlled transport. High temperatures may cause adhesive migration; freezing conditions can make backing brittle. In such cases, allow material to acclimatize to room temperature for at least 24 hours before use.
Regulatory and Compliance Standards
REACH and RoHS Compliance
Ensure the fusible interfacing complies with EU REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives. Suppliers must provide updated Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and compliance certificates.
CPSIA for Children’s Apparel
If the interfacing is used in children’s clothing (under age 12), verify compliance with the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA), including limits on lead, phthalates, and flammability standards.
Oeko-Tex Standard 100 Certification
For eco-conscious markets, consider sourcing interfacing certified under Oeko-Tex Standard 100, ensuring no harmful levels of toxic substances are present.
Customs and Import Documentation
HS Code Classification
Fusible interfacing for fleece typically falls under HS Code 5903.20 (Textiles impregnated or coated with plastics, with a hot-melt adhesive). Confirm the correct classification with local customs authorities to ensure accurate duty assessment.
Country of Origin Labeling
Maintain documentation of the country of origin for all shipments. This is critical for tariffs, trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP), and retail labeling requirements.
Import Permits and Duties
Check for any import restrictions, anti-dumping duties, or textile quotas in the destination country. Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin with all shipments.
Quality Control and Testing
Pre-Production Testing
Conduct adhesion, wash durability, and shrinkage tests before full-scale production. Test compatibility with different fleece types (polyester, cotton blends) and sewing processes.
In-Line Quality Checks
Monitor for uniform adhesive distribution, consistent weight, and absence of wrinkles or edge damage during cutting and fusing operations.
End-Use Performance
Validate that the fused interface does not cause stiffness, bubbling, or delamination after repeated washing or wear.
Sustainability and Disposal
Eco-Friendly Materials
Opt for fusible interfacings made from recycled or biodegradable backings (e.g., non-woven cellulose) and low-impact adhesives (e.g., EVA or PA-based).
Waste Management
Dispose of off-cuts and expired rolls according to local waste regulations. Explore recycling programs for textile waste where available.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Partner with suppliers who use sustainable manufacturing practices and offer carbon-neutral shipping options.
Conclusion
Efficient logistics and strict compliance are essential for the successful handling and use of fusible interfacing for fleece. Adhering to storage, transportation, regulatory, and sustainability guidelines ensures product integrity, legal compliance, and environmental responsibility across the supply chain. Always maintain open communication with suppliers and customs brokers to stay updated on evolving standards.
In conclusion, sourcing the right fusible interfacing for fleece requires careful consideration of weight, flexibility, and bonding strength to ensure compatibility with the fabric’s unique properties. Since fleece is a knit fabric with natural stretch and a soft, lofty texture, using a heavy or rigid interfacing can compromise its drape and comfort. Opting for a lightweight, knit-specific fusible interfacing—such as a fleece-backed or stretch fusible—helps maintain the fabric’s elasticity and warmth without adding bulk. Additionally, conducting sample tests before full production is crucial to confirm adhesion quality and performance after washing. Sourcing from reputable suppliers who specialize in technical textiles or crafting materials ensures consistency and reliability. Ultimately, selecting an appropriate fusible interfacing enhances the structure and durability of fleece garments or accessories while preserving their inherent softness and functionality.