The global microwave oven market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising consumer demand for convenience appliances and advancements in cooking technology. According to Mordor Intelligence, the microwave oven market was valued at USD 10.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. As microwave usage increases worldwide, so does the need for reliable, high-quality replacement components—particularly fuses, which are critical for safety and performance. With consistent operational stress and voltage fluctuations, fuse durability and precision have become key differentiators among component suppliers. This growing demand has positioned several manufacturers as leaders in producing microwave fuses that meet rigorous electrical and safety standards. Below are the top six manufacturers shaping the fuse-for-microwave landscape, selected based on production capacity, compliance certifications, market reach, and technological innovation.
Top 6 Fuse For Microwave Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Newark Electronics
Domain Est. 1994
Website: newark.com
Key Highlights: Newark Electronics – We’re a fast and reliable distributor of products and technology for electronic and industrial system design, maintenance, and repair….
#2 Microwave Fuses
Domain Est. 1999
Website: partselect.com
Key Highlights: This fuse, also known as a cartridge fuse, is a genuine OEM replacement part for microwaves. It has a glass cylindrical body with a metal cap on each end….
#3 Fuse 5304509451
Domain Est. 2004
Website: ereplacementparts.com
Key Highlights: This is a 120-volt/20-amp line fuse for a wide range of microwave models. Fuses are used within microwaves to protect them from overloading….
#4 Advanced Electronic Components & Solutions
Domain Est. 2021
Website: kyocera-avx.com
Key Highlights: KYOCERA AVX is a leading global manufacturer of advanced electronic components engineered to accelerate technological innovation and build a better future….
#5 replacing the fuse in the Kenmore Microwave
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ifixit.com
Key Highlights: The fuse is part #34 and the HV capacitor is part #51. Fuses rarely if ever, fail of their own accord. There is usually a contributing factor that causes them ……
#6 Fuse Specialty Appliances
Domain Est. 2019
Website: fusespecialtyappliances.com
Key Highlights: Fuse Specialty Appliances is one of South Florida’s top luxury appliance stores with competitive pricing, appliance services, and delivery on your favorite ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fuse For Microwave

H2: Market Trends for Fuse for Microwave in 2026
As the global microwave oven market evolves in 2026, demand for specialized components like fuses continues to be shaped by broader technological, regulatory, and consumer trends. The fuse for microwave segment is experiencing steady transformation, driven by increasing safety standards, energy efficiency demands, and advancements in appliance design. Here are the key market trends expected to define the landscape for microwave fuses in 2026:
1. Rising Emphasis on Enhanced Safety and Compliance
By 2026, stringent global safety regulations—such as updated IEC 60335 and UL 60730 standards—are compelling manufacturers to adopt higher-rated, more reliable fuses. Microwave ovens, particularly those with inverter technology and smart connectivity, require fuses capable of handling variable loads and surges. Thermal cutoff (TCO) fuses and time-delay (slow-blow) fuses are seeing increased adoption due to their ability to protect against overcurrent and overheating without nuisance tripping, aligning with evolving safety expectations in both residential and commercial kitchens.
2. Growth in Smart and Inverter Microwave Adoption
The proliferation of smart microwaves equipped with Wi-Fi, voice control, and sensor-based cooking is driving demand for precision-engineered fuses. These advanced models generate complex electrical environments, necessitating fuses with tighter tolerances and higher durability. Inverter microwaves, which modulate power continuously rather than cycling on/off, place unique stress on circuitry, requiring fuses designed for sustained performance under fluctuating conditions. This shift is favoring suppliers offering high-reliability, miniaturized fuse solutions.
3. Miniaturization and Space Optimization
As microwave designs become more compact and feature-rich, there is growing pressure to reduce component footprint. In 2026, manufacturers are prioritizing surface-mount (SMD) fuses and sub-miniature cartridge fuses that deliver robust protection in smaller form factors. This trend supports sleeker appliance designs and increased PCB integration, particularly in countertop and built-in models targeting urban consumers with limited kitchen space.
4. Sustainability and Longevity Focus
With heightened consumer awareness around sustainability, microwave manufacturers are focusing on product longevity and repairability. Fuses that offer longer service life, higher endurance, and easier replacement are gaining favor. Additionally, eco-design regulations in the EU and North America are encouraging the use of RoHS-compliant and lead-free fuse materials, pushing the supply chain toward greener alternatives.
5. Supply Chain Localization and Resilience
Post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have led to a strategic shift toward regional sourcing. In 2026, microwave OEMs are increasingly partnering with fuse suppliers in North America and Europe to reduce dependency on single-source Asian manufacturers. This trend supports faster delivery times, better customization, and improved compliance with local regulatory frameworks.
6. Growth in Emerging Markets
Rising disposable incomes in regions like Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa are boosting microwave ownership. Entry-level and mid-range models dominate these markets, creating strong demand for cost-effective yet reliable fuse solutions. Localized production and simplified fuse designs are enabling broader market penetration while maintaining safety benchmarks.
Conclusion
By 2026, the fuse for microwave market will be characterized by innovation in safety, miniaturization, and sustainability. Suppliers that offer high-performance, compliant, and adaptable fuse technologies—particularly those aligned with smart and inverter microwave trends—will be best positioned to capture market share. As consumer expectations and regulatory standards continue to rise, the role of the fuse as a critical safety component will only grow in importance.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Fuse for Microwave (Quality, IP)
Sourcing the correct fuse for a microwave oven involves more than just matching physical dimensions or amperage ratings. Critical issues related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to product failure, safety hazards, or legal complications. Below are common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Quality Components
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing microwave fuses is selecting low-quality components from unreliable suppliers. Microwave fuses operate under high voltage and temperature conditions, so substandard materials can lead to premature failure, fire hazards, or damage to the appliance.
- Inconsistent Ratings: Cheap fuses may be mislabeled, with actual current or voltage tolerances falling short of specifications.
- Thermal Instability: Low-quality fuses may not withstand the high internal temperatures of a microwave, leading to nuisance tripping or failure to blow when needed.
- Lack of Safety Certifications: Fuses without recognized certifications (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS) may not meet international safety standards, increasing liability risks.
Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Parts
Using counterfeit or IP-infringing fuses poses significant legal and operational risks.
- Brand Imitation: Some suppliers offer fuses that mimic well-known brands (e.g., Littelfuse, Bourns) but are unauthorized copies. These may infringe on trademarks or patented designs.
- Unauthorized Replication: Reverse-engineered fuses that copy protected specifications or housing designs can lead to intellectual property disputes, especially in regulated markets.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Sourcing from gray-market vendors increases the risk of receiving counterfeit components, which can compromise product reliability and void warranties.
Inadequate Technical Specifications
Microwave fuses require precise characteristics such as time-delay (slow-blow) functionality, high breaking capacity, and resistance to arcing.
- Incorrect Fuse Type: Using a fast-acting fuse instead of a slow-blow fuse can cause unnecessary interruptions during microwave startup surges.
- Voltage Mismatch: Fuses rated below the microwave’s operating voltage present serious safety risks.
- Poor Documentation: Suppliers may lack detailed datasheets or test reports, making it difficult to verify compatibility and compliance.
Lack of Traceability and Compliance
Reputable sourcing requires full traceability and adherence to regulatory standards.
- Missing Documentation: Without lot numbers, test reports, or compliance certificates, it’s difficult to ensure quality or respond to recalls.
- Non-Compliance with Regional Regulations: Fuses must meet local safety standards (e.g., UL 248 in the U.S., IEC 60127 internationally). Ignoring these can block market access.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, always source microwave fuses from authorized distributors or manufacturers with verifiable quality systems and clear IP compliance. Prioritize components with proper certifications, accurate specifications, and full documentation to ensure safety, reliability, and legal compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fuse for Microwave
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, and regulatory adherence of fuses used in microwave ovens. Proper management ensures product safety, regulatory conformity, and efficient supply chain operations.
Product Classification and Identification
Fuses for microwave ovens are classified as electrical safety components. They are typically categorized under:
– HS Code: 8536.10 (Circuit breakers, fuses, and other apparatus for protecting electrical circuits) – country-specific variations may apply.
– UN Number: Generally not classified as hazardous (UN3171 may apply if containing small lithium components, but most fuses are exempt).
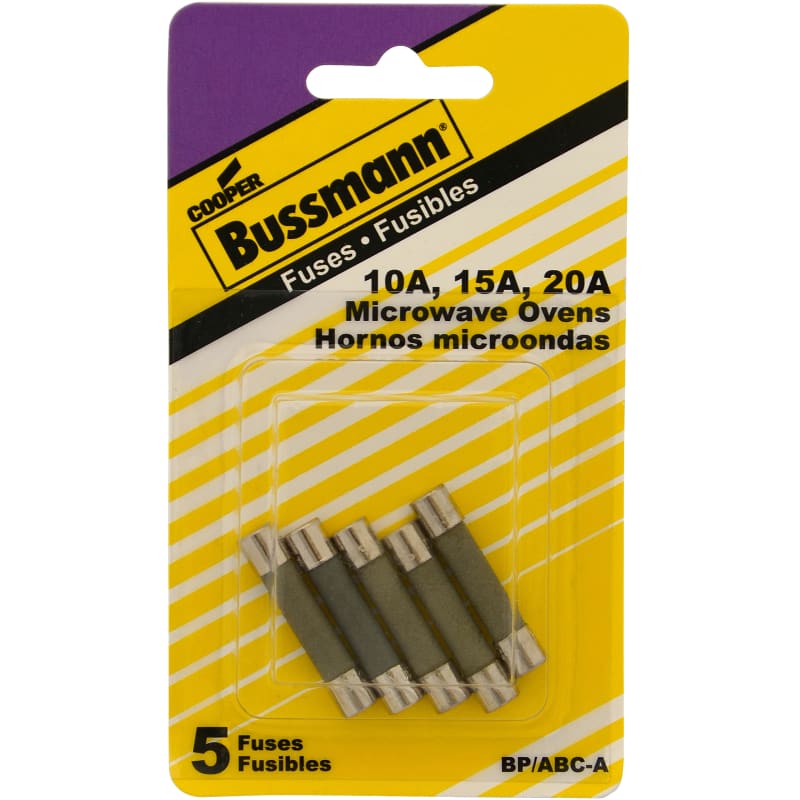
– Component Type: Overcurrent protection device; often ceramic or glass body with current ratings between 10A–20A and voltage ratings of 250V AC.
Ensure each fuse is clearly labeled with amperage, voltage, breaking capacity, and safety certifications (e.g., TUV, UL, CSA).
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Fuses used in microwave ovens must comply with international and regional safety standards to ensure reliability and user protection.
Key Certifications
- UL 248-14 (North America): Standard for fuses used in household appliances.
- IEC 60127 (International): Covers miniature fuses, including those used in microwaves.
- RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances – ensures lead, mercury, cadmium, and other restricted substances are below permissible levels.
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals – requires disclosure of SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern).
- UKCA Marking (UK): Required for products sold in Great Britain post-Brexit.
- CCC (China): Mandatory for fuses sold in the Chinese market.
Ensure all documentation (test reports, certificates of conformity, Declarations of Conformity) is current and accessible for audits.
Packaging and Labeling Standards
Proper packaging safeguards fuses during transit and ensures regulatory compliance.
Packaging Guidelines
- Use anti-static packaging if fuses are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD).
- Secure individual fuses in blister packs or tubes to prevent physical damage.
- Place packaged units in sturdy outer cartons with sufficient cushioning.
- Label each package with:
- Product name and part number
- Quantity
- Manufacturer and supplier details
- HS code and country of origin
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”)
- Compliance marks (UL, CE, etc.)
Shipping and Transportation
Fuses are generally non-hazardous and can be shipped via standard freight methods, but attention to detail is required.
Domestic and International Shipping
- Air Freight: Acceptable under IATA regulations; no special handling required unless part of a larger hazardous assembly.
- Ocean Freight: Standard container shipping; ensure moisture protection using desiccants if necessary.
- Ground Transport: Compliant with local road transport regulations; stack loads securely.
Documentation
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Certificate of Origin
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) – typically not required for simple fuses but may be requested
- Import/export licenses (if applicable)
Import and Customs Clearance
Proper documentation and classification are vital to avoid delays at customs.
Key Actions
- Confirm correct HS code with customs broker.
- Provide all required compliance certificates (UL, IEC, RoHS, etc.).
- Declare accurate value to prevent duties disputes.
- Use an experienced freight forwarder familiar with electrical components.
Note: Some countries may require additional testing or local certification (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC in South Korea).
Storage and Handling
Fuses should be stored under controlled conditions to preserve performance.
Best Practices
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (15°C–30°C, 30%–60% RH).
- Avoid exposure to dust, moisture, and corrosive atmospheres.
- Follow FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management.
- Minimize handling to reduce risk of mechanical damage.
End-of-Life and Environmental Compliance
Fuses are mostly recyclable but must be disposed of responsibly.
Disposal Guidelines
- Do not dispose of in regular electronic waste without checking local regulations.
- Partner with certified e-waste recyclers.
- Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU.
- Document recycling procedures for audit purposes.
Summary
Ensuring the compliant and efficient logistics of microwave oven fuses requires attention to classification, packaging, regulatory standards, and documentation. Adherence to international safety and environmental regulations not only mitigates risk but also supports sustainable and reliable supply chain performance. Regular audits and updates to compliance protocols are recommended to adapt to evolving regulations.
In conclusion, sourcing a fuse for a microwave requires careful attention to specifications such as voltage rating, current rating, fuse type (commonly ceramic or glass), physical size, and response time (e.g., fast-blow or slow-blow). It is essential to use a replacement fuse that matches the original manufacturer’s specifications to ensure safety, proper functionality, and compliance with electrical standards. Sourcing from reputable suppliers or OEM providers minimizes the risk of counterfeit or substandard components. Always prioritize safety by disconnecting power before replacement and, if uncertain, consult a qualified technician. Properly sourced and installed fuses help maintain the reliability and longevity of the microwave while protecting against electrical hazards.