The global furnace insulation market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for energy efficiency and thermal management across industrial sectors such as steel, petrochemicals, and ceramics. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial insulation market size was valued at USD 37.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by stringent energy conservation regulations and the rising need to reduce carbon emissions in high-temperature processing environments. As industrial operations prioritize operational efficiency and regulatory compliance, the demand for high-performance furnace insulation materials continues to rise. Against this backdrop, leading manufacturers are innovating with advanced materials like ceramic fibers, refractory bricks, and aerogel-based solutions to meet evolving industry standards. The following list highlights nine of the top furnace insulation manufacturers shaping the market through technological leadership, global reach, and comprehensive product portfolios.
Top 9 Furnace Insulation Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Insul
Domain Est. 1998
Website: insulfab.net
Key Highlights: Insul-Fab, a leading custom OEM insulation fabricator, has over 30 years of experience providing specification, fabrication, and distribution of products….
#2 OEM Insulation Products & Appliance
Domain Est. 1996
Website: owenscorning.com
Key Highlights: Choose Owens Corning’s top-tier global OEM insulation & appliance products for expert, comprehensive, energy-efficient, thermal & acoustic solutions….
#3 Products and Applications
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rockwool.com
Key Highlights: We supply an array of OEM insulation products for any type of building, system or application, increasing energy efficiency, built-in fire protection, and ……
#4 FI-FOIL® Reflective Insulation Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fifoil.com
Key Highlights: Based in Florida, FI-FOIL® is your leading source for sustainable, high-value, advanced performance reflective insulation products and systems….
#5 ISOVER
Domain Est. 1995 | Founded: 1937
Website: saint-gobain.com
Key Highlights: Since 1937, we imagine, manufacture and deliver a broad range of insulation solutions made of different materials. A MULTI-MATERIAL OFFER….
#6 Fiberglass Insulation
Domain Est. 1997
Website: jm.com
Key Highlights: Johns Manville Formaldehyde-free™ fiberglass insulation provides thermal and accoustical control for both vertical and horizontal applications….
#7 Heat treatment furnaces by SECO/WARWICK GROUP
Domain Est. 1998
Website: secowarwick.com
Key Highlights: SECO/WARWICK GROUP is the leader in technologies: atmosphere, aluminum and vacuum furnaces, controlled atmosphere brazing and vacuum melting systems….
#8 General Insulation Company
Domain Est. 2001
Website: generalinsulation.com
Key Highlights: A wholesale distributor, providing a full line of sustainable products and solutions for thermal efficiency, condensation/moisture control, and life safety….
#9 Heat treatment
Domain Est. 2006
Website: us.mersen.com
Key Highlights: Heat treatment. The unique combination of Mersen expertise in cc composite, graphite and high temperature insulation for high temperature furnace construction….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Furnace Insulation

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Furnace Insulation
The furnace insulation market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, regulatory changes, and growing demand for energy efficiency across industrial and residential sectors. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Increased Demand for Energy Efficiency
As global energy costs rise and sustainability goals intensify, industries are prioritizing high-performance furnace insulation to reduce heat loss and improve thermal efficiency. By 2026, advanced insulation materials such as ceramic fibers, aerogels, and microporous insulation are expected to gain market share due to their superior thermal resistance and longevity. -
Stringent Environmental Regulations
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions and energy efficiency standards, particularly in manufacturing, steel, cement, and petrochemical industries. These regulations are pushing companies to retrofit older furnaces with modern insulation solutions, driving demand in both developed and emerging markets. -
Growth in Industrial Automation and High-Temperature Processes
The expansion of heavy industries in regions like Asia-Pacific—especially in China, India, and Southeast Asia—is fueling demand for reliable, high-temperature insulation. Automated manufacturing and electric arc furnaces in the steel industry will require durable insulation systems capable of withstanding extreme conditions. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmental concerns are prompting manufacturers to develop bio-based or recyclable insulation materials. By 2026, there will be a noticeable shift toward low-global-warming-potential (GWP) materials and products with reduced embodied carbon, aligning with corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) targets. -
Technological Advancements and Smart Insulation
Integration of IoT sensors and smart monitoring systems within insulation layers is emerging as a trend. These “smart” insulation systems can detect hotspots, degradation, or energy leaks in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing furnace performance—a key growth area by 2026. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Regional Manufacturing
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to localize production. This trend is expected to boost regional insulation manufacturing hubs, particularly in North America and Europe, to ensure reliability and reduce import dependence. -
Rising Adoption in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Furnace insulation is increasingly being used in emerging clean energy applications, such as hydrogen production facilities and concentrated solar power (CSP) plants. These high-heat processes require advanced insulation, creating new market opportunities by 2026.
In summary, the furnace insulation market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, regulatory influence, and a strong emphasis on sustainability and performance. Companies that invest in next-generation materials and digital integration are likely to lead the market.
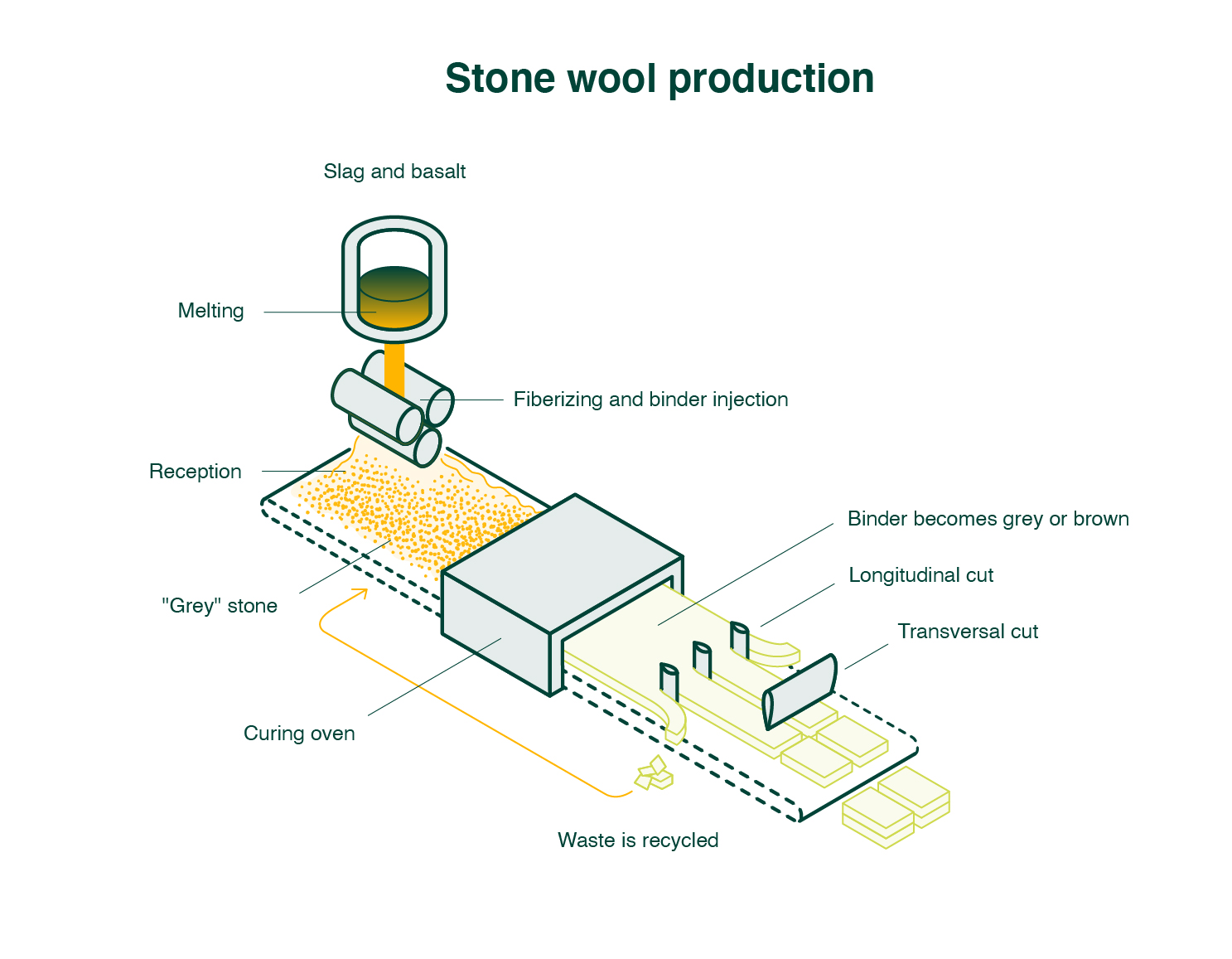
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Furnace Insulation: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing furnace insulation involves critical decisions that directly impact safety, energy efficiency, operational costs, and compliance. Overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to severe consequences. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Performance Misrepresentation
One of the most frequent issues is receiving insulation materials that fail to meet specified thermal, mechanical, or chemical performance standards. Suppliers may exaggerate temperature resistance, thermal conductivity (k-value), or durability under thermal cycling. This can result in premature insulation degradation, increased energy consumption, and even furnace failure or safety hazards. Always demand certified test reports (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and conduct independent validation when possible.
Use of Substandard or Counterfeit Materials
Unreliable suppliers may substitute high-performance materials (e.g., ceramic fiber, alumina-silicate) with lower-grade or recycled content without disclosure. This compromises insulation integrity and operational safety. Counterfeit products may bear fake certifications or mimic reputable brand packaging. Conduct supplier audits and verify material traceability through batch testing and supply chain transparency.
Inadequate Documentation and Certification
Missing or falsified documentation—such as Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), compliance certificates (e.g., REACH, RoHS), or fire safety ratings—poses regulatory and operational risks. Without proper certification, facilities may face non-compliance penalties or insurance issues. Ensure all documentation is up-to-date, verifiable, and specific to the delivered product batch.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Sourcing from manufacturers that replicate patented insulation technologies—such as proprietary fiber formulations, layering techniques, or bonding methods—exposes buyers to legal liability. Even unintentional use of IP-infringing products can lead to lawsuits, import seizures, or forced replacement costs. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s R&D origins and request IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
Lack of Traceability and Chain of Custody
Without clear traceability from raw material to finished product, it becomes difficult to investigate failures or verify compliance. This is especially critical in regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, energy). Insist on batch tracking, supplier affidavits, and documented manufacturing processes to ensure accountability.
Failure to Address Long-Term Performance and Aging
Some suppliers provide data based on short-term lab tests rather than real-world aging behavior. Furnace insulation degrades over time due to thermal stress, chemical exposure, and mechanical wear. Sourcing decisions should consider long-term performance data, including shrinkage rates and resistance to devitrification (in ceramic fibers), to avoid unplanned downtime.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable, safe, and legally compliant furnace operations while protecting their supply chain integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Furnace Insulation
Overview
Furnace insulation materials, such as ceramic fiber blankets, refractory bricks, mineral wool, and high-temperature insulation boards, are essential in industrial and manufacturing processes. Due to their thermal, physical, and sometimes hazardous properties, transporting and handling these materials requires strict adherence to logistics and regulatory standards. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure safe, efficient, and compliant logistics operations.
Material Classification and Handling
Furnace insulation products vary widely in composition and risk profile. Common types include:
- Ceramic Fiber Insulation: Often classified as hazardous due to respirable fibers (similar to synthetic mineral fibers). Requires handling precautions to avoid inhalation.
- Refractory Bricks and Castables: Heavy and abrasive; require secure packaging to prevent breakage.
- Mineral Wool and Rockwool: Generally non-hazardous but can irritate skin and respiratory systems during handling.
- Insulating Firebricks (IFBs): High-density materials requiring robust palletization.
Handling Recommendations:
– Use personal protective equipment (PPE): gloves, dust masks, and safety goggles.
– Avoid dry sweeping; use HEPA-filtered vacuums to control dust.
– Store materials indoors on elevated, dry platforms to prevent moisture absorption.
Packaging and Load Securing
Proper packaging ensures product integrity and transport safety.
- Flexible Insulation (e.g., blankets, rolls): Vacuum-packed or compressed and strapped onto wooden or plastic pallets. Cover with polyethylene to protect from moisture.
- Rigid Materials (e.g., bricks, boards): Stacked on pallets with edge protectors and stretch-wrapped or banded. Use corner boards for added stability.
- Loose Granular Insulation: Double-bagged in moisture-resistant liners, then boxed or placed in bulk bags (FIBCs) rated for the load.
Load Securing:
– Use load bars, straps, and dunnage to prevent shifting during transit.
– Ensure loads do not exceed vehicle weight limits or height restrictions.
– Follow EUMOS40509 or ISTA 3A standards for load stability testing where applicable.
Transportation Requirements
Transport regulations depend on material classification and regional jurisdiction.
- Non-Hazardous Insulation (e.g., most mineral wool): Subject to general freight regulations. Use standard dry van trailers or containers.
- Hazardous Insulation (e.g., certain ceramic fibers): May require labeling under GHS (Globally Harmonized System) and transportation under ADR (Europe), 49 CFR (USA), or TDG (Canada) if classified as harmful by inhalation.
- Documentation: Include Safety Data Sheets (SDS), packing lists, and transport declarations. For hazardous materials, provide proper shipping names, UN numbers (e.g., UN 2211 for ceramic fiber waste), and hazard class labels (typically Class 9 – Miscellaneous).
Modal Considerations:
– Road: Most common; ensure trailers are clean and dry.
– Rail: Suitable for bulk shipments; secure loads against vibration.
– Sea: Use moisture-resistant packaging; avoid condensation with vapor barriers.
– Air: Restricted for hazardous insulation types; verify IATA regulations.
Regulatory Compliance
Furnace insulation must meet multiple regulatory standards across regions.
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals. Ensure substances in insulation (e.g., binders) are registered.
- CLP Regulation (EU): Classify and label insulation materials correctly based on hazard properties.
- OSHA (USA): Comply with hazard communication (HazCom 2012) and permissible exposure limits (PELs) for airborne fibers.
- EPA Regulations: Follow NESHAP standards for emissions during manufacturing; manage waste per RCRA if applicable.
- RoHS and WEEE: May apply if insulation contains restricted substances or is part of electrical equipment.
Labeling Requirements:
– GHS-compliant labels with pictograms, signal words, and hazard statements.
– Mark packages with handling instructions: “Fragile,” “This Way Up,” “Protect from Moisture.”
Storage and Inventory Management
- Indoor Storage: Required for all insulation types. Protect from rain, humidity, and direct sunlight.
- Stacking Limits: Adhere to manufacturer guidelines to prevent collapse or compression damage.
- Segregation: Store hazardous insulation separately from food, pharmaceuticals, or reactive chemicals.
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO): Maintain rotation to prevent aging or degradation.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Used or damaged furnace insulation may be classified as industrial or hazardous waste.
- Waste Classification: Test per TCLP (USA) or Waste Acceptance Criteria (EU) to determine disposal route.
- Disposal: Use licensed facilities for hazardous insulation. Landfill or incineration must comply with local regulations.
- Recycling: Some ceramic fibers and mineral wool can be recycled; partner with certified recyclers.
Training and Documentation
- Train staff on:
- Safe handling and PPE use
- Emergency procedures (e.g., fiber exposure)
- Regulatory requirements and documentation
- Maintain records of:
- SDS for all materials
- Transport manifests and waste disposal certificates
- Training logs and compliance audits
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for furnace insulation demand attention to material properties, proper packaging, regulatory alignment, and safety protocols. By adhering to classification standards, securing loads correctly, and maintaining documentation, businesses can ensure safe delivery, avoid penalties, and support environmental responsibility. Regular audits and team training are recommended to maintain compliance across the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Furnace Insulation
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate furnace insulation is a critical decision that significantly impacts energy efficiency, operational safety, process consistency, and long-term cost savings. The selection process should involve a thorough evaluation of operating temperatures, thermal performance requirements, chemical and mechanical resistance, fire safety standards, and regulatory compliance. Key insulation materials such as ceramic fiber, refractory bricks, calcium silicate, and mineral wool each offer distinct advantages depending on the specific application.
When sourcing, it is essential to partner with reliable suppliers who provide high-quality, certified materials and technical support. Conducting a lifecycle cost analysis—rather than focusing solely on upfront costs—can lead to more sustainable and economical choices over time. Additionally, considering environmental impact and ease of installation contributes to overall operational efficiency.
Ultimately, investing in the right furnace insulation not only enhances performance and safety but also supports energy conservation and reduced emissions. A well-informed sourcing strategy ensures durability, compliance, and optimal return on investment for industrial heating systems.