The global powder manufacturing industry is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, chemicals, and additive manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global powder processing equipment market was valued at USD 28.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion underscores the increasing need for efficient, reliable material handling solutions—particularly industrial funnels designed to streamline powder transfer, minimize waste, and ensure product integrity. As manufacturers scale operations and prioritize precision and hygiene, selecting the right funnel system has become a critical factor in maintaining throughput and compliance. In this context, we examine the top nine funnel solutions tailored specifically for powder manufacturers, evaluating them based on flow efficiency, material compatibility, ease of cleaning, and integration capabilities within modern production environments.
Top 9 Funnel For Powder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
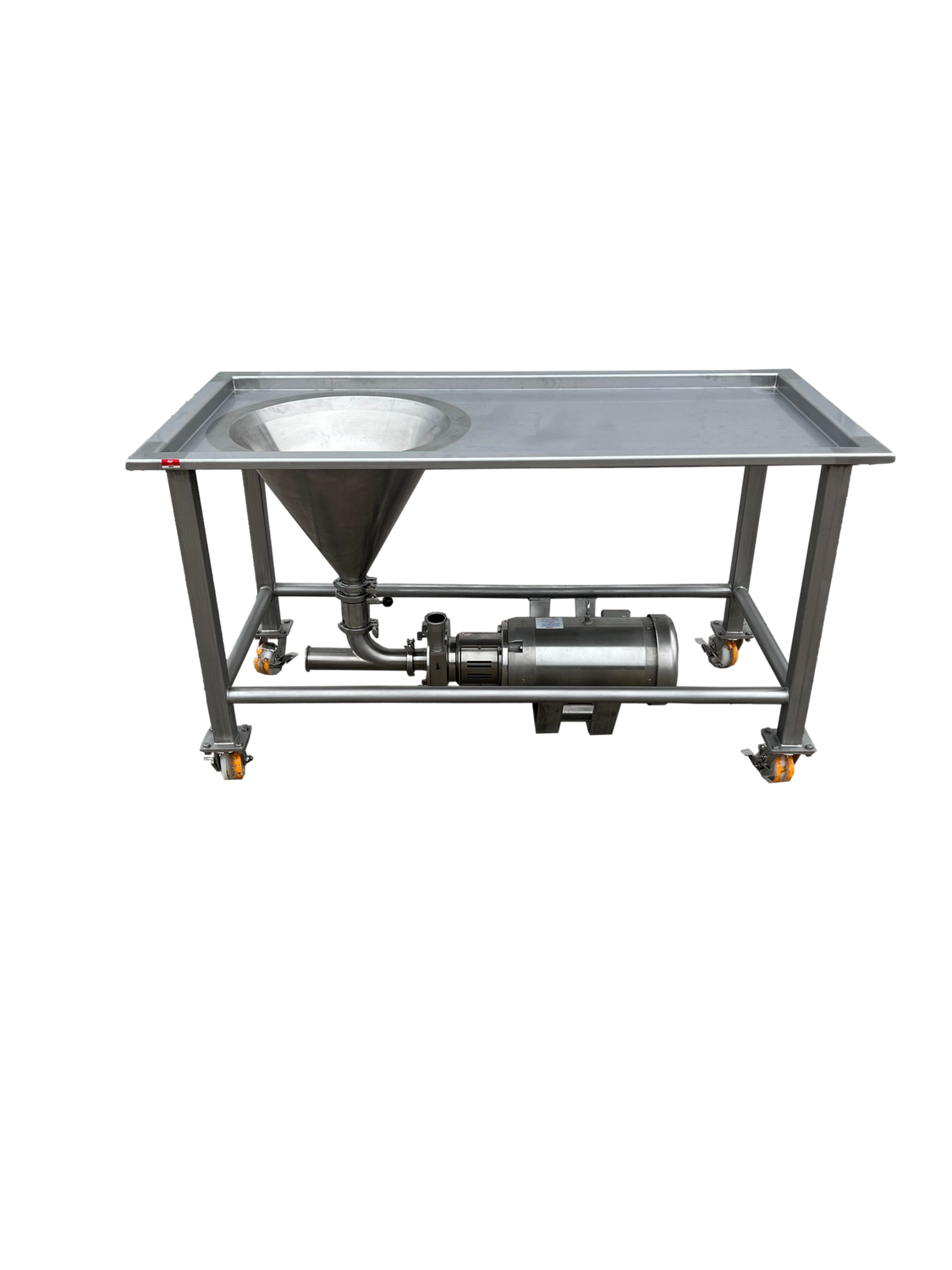
#1 Powder Funnel Tables
Domain Est. 1997
Website: kossindustrial.com
Key Highlights: Quickly add dry ingredients to fluids using a stainless steel powder funnel table from Koss. Built to order in the size you need….
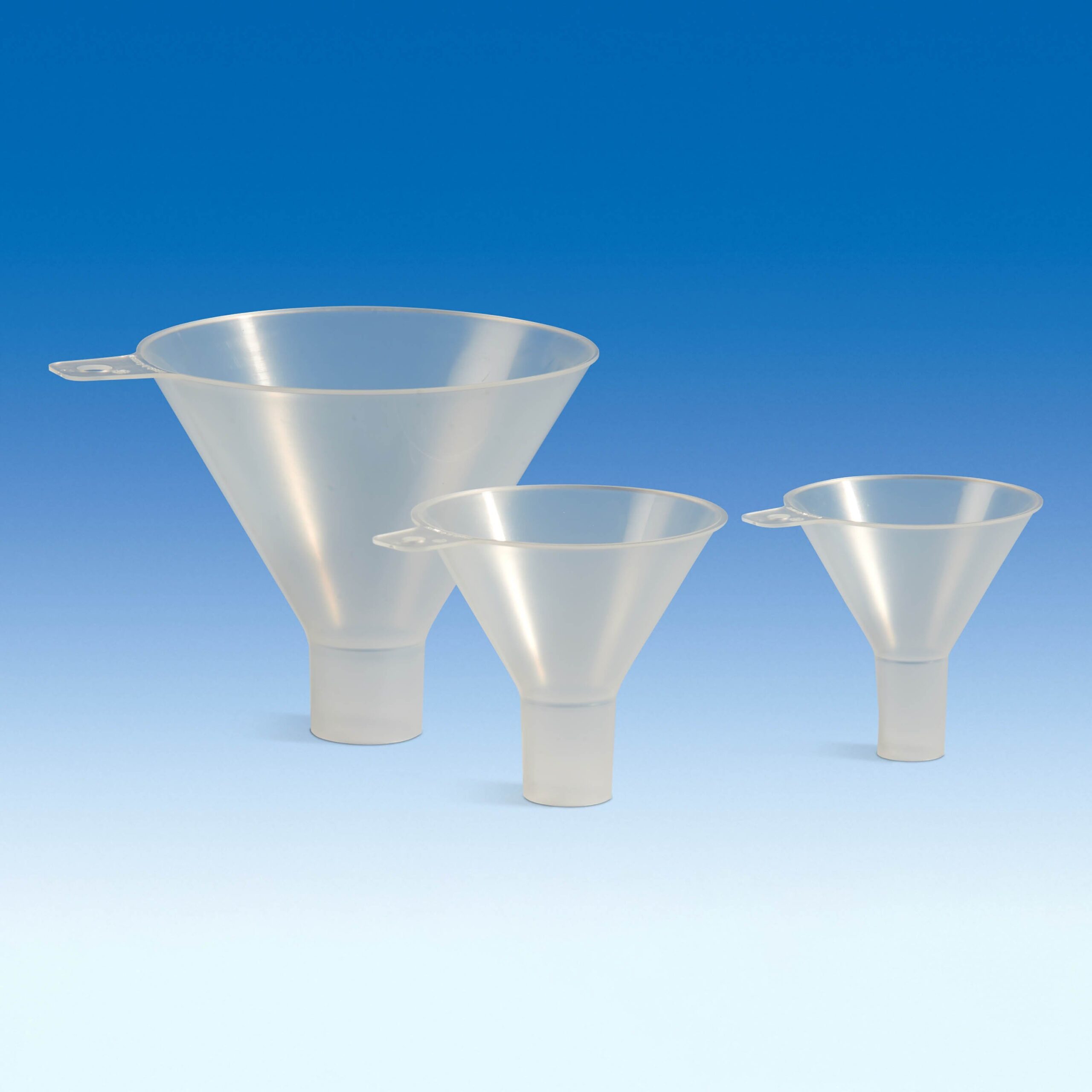
#2 BrandTech Polypropylene Powder Funnel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: universalmedicalinc.com
Key Highlights: BrandTech Transparent Polypropylene Powder Funnel features a wide spout for easy transfer. Available in a variety of sizes, and stem diameters to fit your ……
#3 Funnels
Domain Est. 1995
Website: fishersci.com
Key Highlights: Transfer powders with these powder funnels. Parallel stem minimizes bridging of powder and external ribbing prevents air locks….
#4 SP Bel
Domain Est. 1996
Website: belart.com
Key Highlights: High density polyethylene funnel is ideal for powders and general use. Extra wide 1½“ stem exit allows for extra coarse or clumping powders to easily pass…
#5 Funnel & Adapters
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hornady.com
Key Highlights: Basic Powder Funnel Item #586051 Anti-static funnel fits all calibers between 22 and 45. Squared rim design won’t roll off the table….
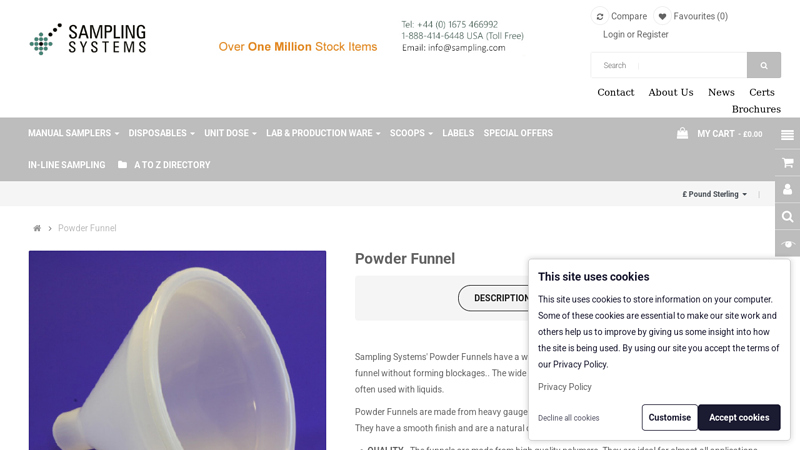
#6 Powder Funnel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sampling.com
Key Highlights: Powder Funnels are made from heavy gauge polymers and therefore have excellent corrosion resistance. They have a smooth finish and are a natural colour….
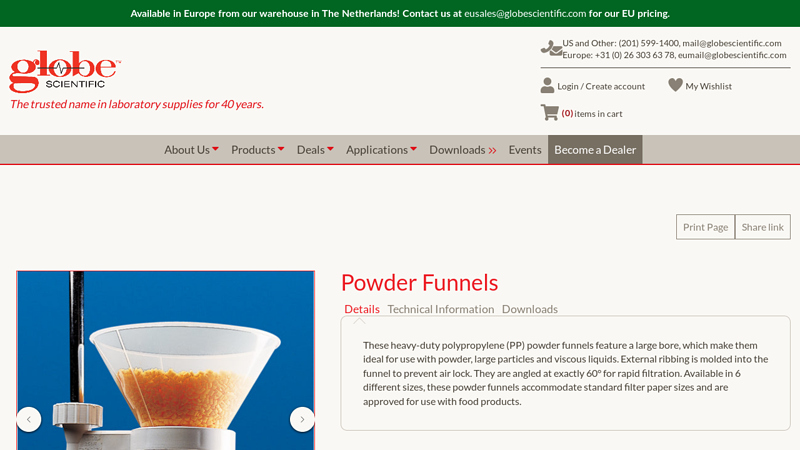
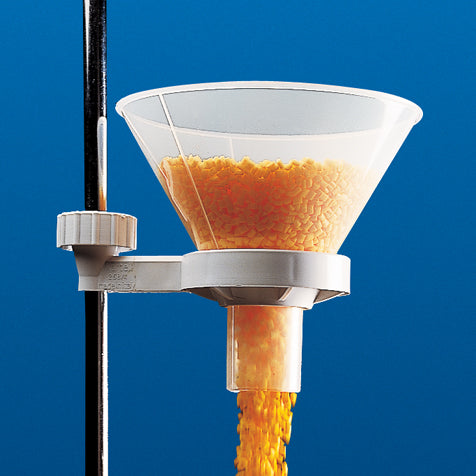
#7 Funnel, Powder, PP, 60mm
Domain Est. 1997
Website: globescientific.com
Key Highlights: These heavy-duty polypropylene (PP) powder funnels feature a large bore, which make them ideal for use with powder, large particles and viscous liquids….
#8 Globe Scientific Polypropylene Powder Funnel
Domain Est. 2004
Website: amscope.com
Key Highlights: These heavy-duty polypropylene (PP) powder funnels feature a large bore, which make them ideal for use with powder, large particles and viscous liquids….
#9 Disposable powder funnel, sterile
Domain Est. 2015
Website: burkle-inc.com
Key Highlights: The disposable powder funnel has a short, wide discharge and is suitable for transferring powdered samples and materials, granulates and suspensions as well ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Funnel For Powder

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Funnels for Powder
While “funnel for powder” may seem like a niche industrial tool, its market in 2026 will be shaped by broader industry dynamics, technological advancements, and evolving regulatory and sustainability demands. Here’s an analysis of the key trends likely to define this market:
H2: Rising Demand from Core Industries
The primary driver for powder funnels in 2026 will be sustained growth in sectors requiring precise, hygienic, or efficient powder transfer:
* Pharmaceuticals & Biotechnology: Continued expansion in solid-dose manufacturing (tablets, capsules) and the rise of complex formulations (e.g., inhalable powders, lyophilized products) will demand high-precision, contamination-free funnels. Investment in continuous manufacturing will further increase the need for reliable transfer solutions.
* Food & Beverage: Growing consumer demand for functional foods, protein powders, supplements, spices, and bakery ingredients necessitates hygienic handling. Powder funnels that meet strict food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU 1935/2004) and prevent cross-contamination will be essential.
* Chemicals & Advanced Materials: The production of specialty chemicals, pigments, catalysts, and battery materials (especially lithium compounds for EVs) relies on efficient powder handling. Funnels resistant to corrosive or reactive powders will see increased demand.
H2: Emphasis on Hygiene, Cleanability, and Material Safety
Regulatory scrutiny and quality standards will push innovation in funnel design:
* Advanced Materials: Wider adoption of higher-grade, non-porous materials like specific FDA/USP Class VI compliant plastics (e.g., PTFE, PFA, UHMW-PE) and polished 316L stainless steel for easier cleaning and reduced microbial adhesion.
* Sanitary Design: Features like crevice-free construction, quick-disconnect fittings, rounded edges, and integrated drip trays will become standard, especially in pharma and food. CIP (Clean-in-Place) compatibility will be a key selling point.
* Traceability & Compliance: Demand for funnels with material certifications (e.g., material test reports, compliance statements) will grow to meet audit requirements.
H2: Automation and Integration
As industries automate, manual tools like funnels must adapt:
* Integration with Automated Lines: Development of funnels designed as components of automated powder filling, dispensing, or blending systems, featuring standardized interfaces and sensors.
* Smart Features: Emergence of “smart” funnels with basic sensors (e.g., flow detection, level indication, RFID tags for asset tracking) for process monitoring and data collection, particularly in high-value pharma or chemical applications.
* Ergonomics for Semi-Automation: Designs optimized for use with robotic arms or collaborative robots (cobots) in semi-automated settings.
H2: Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Environmental concerns will influence material choices and functionality:
* Durability & Reusability: Shift towards durable, long-lasting funnels (e.g., high-quality stainless steel, robust engineering plastics) over single-use plastic options to reduce waste.
* Minimizing Product Loss: Designs focused on zero-drip, anti-static properties (to reduce powder clinging), and efficient transfer will help reduce valuable powder waste, a key economic and environmental driver.
* Recyclable Materials: Increased use of recyclable plastics where performance allows, and clearer end-of-life disposal instructions.
H2: Customization and Specialization
One-size-fits-all solutions will become less common:
* Application-Specific Designs: Growth in custom funnels tailored for specific powders (e.g., ultra-fine, cohesive, explosive, hygroscopic) with features like anti-static coatings, specialized angles, or integrated vibrators.
* Size & Shape Variability: Demand for a wider range of sizes and specialized geometries (e.g., double-wall for insulation, wide-mouth for clumping powders, narrow for precise dosing) to meet diverse process needs.
* Modularity: Systems allowing interchangeable tips, extensions, or adapters for greater flexibility.
H2: Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Geopolitical factors and lessons from recent disruptions will impact sourcing:
* Nearshoring/Regional Manufacturing: Increased pressure to source funnels from suppliers closer to end-user manufacturing hubs (e.g., in North America, Europe, Southeast Asia) to reduce lead times and logistics risks.
* Dual Sourcing: Companies will seek multiple qualified suppliers to mitigate supply chain vulnerabilities.
* Focus on Supplier Reliability: Proven track record in quality, consistency, and on-time delivery will become a major competitive advantage.
H2: Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market will see consolidation and innovation:
* Differentiation through Tech & Service: Leading players will differentiate via material science expertise, design software (e.g., CFD for flow optimization), testing capabilities, and value-added services (e.g., cleaning validation support).
* Consolidation: Smaller, specialized manufacturers may be acquired by larger fluid handling or industrial supply companies seeking to expand their portfolio.
* Price Pressure vs. Value: While cost remains a factor, the trend will favor suppliers offering demonstrable value through quality, durability, compliance support, and technical expertise over the lowest price.
Conclusion for 2026: The funnel for powder market in 2026 will be far from static. It will be characterized by a shift towards higher performance, enhanced hygiene, greater integration with automation, and stronger sustainability credentials. Success will depend on suppliers’ ability to innovate in materials and design, meet stringent regulatory demands, offer customization, and ensure resilient supply chains. The funnel will evolve from a simple transfer tool into a critical component of efficient, safe, and sustainable powder handling processes.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Funnel For Powder (Quality, IP)
When sourcing a funnel designed specifically for powder handling, businesses often encounter challenges related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failure, safety risks, legal disputes, or supply chain disruptions. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Compatibility
Powder properties—such as abrasiveness, hygroscopicity, or reactivity—require funnels made from compatible materials (e.g., food-grade stainless steel, anti-static polymers). Sourcing funnels made from unsuitable materials can result in contamination, degradation, or blockages.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy
Improper funnel geometry (angle, diameter, surface finish) can lead to poor powder flow, bridging, or segregation. Sourcing from suppliers without powder flow testing capabilities increases the risk of inefficient performance.
Lack of Certification and Traceability
Industries like pharmaceuticals or food processing require certified components (e.g., FDA, 3A, ATEX). Failing to verify certifications or material traceability can result in non-compliance and regulatory setbacks.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Low-cost suppliers may lack quality control systems (e.g., ISO 9001), leading to inconsistent wall thickness, weld defects, or surface imperfections that compromise hygiene and durability.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing Copycat or Infringing Designs
Some suppliers replicate patented funnel designs (e.g., specialized anti-caking features or discharge mechanisms). Purchasing such products may expose the buyer to IP infringement claims, especially in regulated markets.
Lack of Design Ownership Clarity
When customizing funnels, unclear contracts may result in ambiguity over who owns the design IP. This can limit future production options or lead to disputes if the supplier reproduces the design for competitors.
Reverse Engineering by Suppliers
Sharing detailed specifications with overseas manufacturers without proper IP protection (e.g., NDAs, patents) risks unauthorized replication or sale of your design to third parties.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier audits, including site visits and quality system reviews.
- Require material certifications, flow test reports, and compliance documentation.
- Work with legal counsel to secure IP rights and include protective clauses in procurement contracts.
- Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and consider patenting unique funnel designs prior to sourcing.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection of proprietary innovations when sourcing powder funnels.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Funnel for Powder
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal handling, storage, transportation, and use of powder transfer funnels. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and workplace safety.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all powder funnels and associated processes meet relevant national and international regulations. This includes compliance with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards for workplace safety, FDA (Food and Drug Administration) or equivalent food-grade regulations if used in food, pharmaceutical, or cosmetic applications, and any applicable REACH or RoHS directives in the EU. Materials used in the funnel (e.g., stainless steel, food-grade plastics) must be certified for their intended use and contact with specific powders.
Material Handling & Contamination Control
Powder funnels must be cleaned thoroughly between uses, especially when handling different materials or in sensitive environments such as laboratories or food production. Use validated cleaning procedures to prevent cross-contamination. Store funnels in clean, dry environments away from dust, moisture, and incompatible substances. Consider using color-coded or dedicated funnels for different materials to enhance traceability and reduce risk.
Packaging & Labeling for Shipment
When shipping powder funnels, use protective packaging to prevent damage during transit—corrugated boxes with internal padding are recommended. Clearly label packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile” or “This Side Up.” Include proper product identification, batch/lot numbers (if applicable), and compliance markings (e.g., FDA-compliant, NSF-certified). Accurate documentation, including packing slips and safety data sheets (SDS) if relevant, must accompany shipments.
Transportation Requirements
Select carriers experienced in handling industrial or laboratory equipment. For international shipments, ensure compliance with IATA, IMDG, or other applicable transport regulations—even if the funnel itself is non-hazardous, its prior use with hazardous powders may require declaration or cleaning verification. Maintain records of shipping manifests and customs documentation where required.
Storage Conditions
Store powder funnels in a controlled environment with stable temperature and low humidity to prevent corrosion (especially for metal components) or degradation of plastic parts. Keep them off the floor on shelves or racks to avoid contamination and damage. Organize storage by size, material, or application to support efficient inventory management and retrieval.
User Training & Documentation
Provide personnel with training on proper funnel use, cleaning procedures, and safety protocols. Maintain up-to-date standard operating procedures (SOPs) and training records. Document maintenance, inspections, and any incidents involving funnel use to support compliance audits and continuous improvement.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
Dispose of damaged or contaminated funnels according to local waste management regulations. Recycle materials when possible—especially metals like stainless steel. For funnels used with hazardous powders, follow hazardous waste disposal protocols and maintain disposal records to demonstrate regulatory compliance.
Conclusion: Sourcing Funnel for Powder
The sourcing funnel for powder ingredients has effectively streamlined the supplier selection and procurement process, ensuring quality, reliability, cost-efficiency, and compliance with regulatory standards. By progressing through defined stages—identifying needs, market research, supplier qualification, sampling and testing, negotiation, and final selection—the organization minimizes risks associated with supply chain disruptions, quality inconsistencies, and cost overruns.
This structured approach enables data-driven decision-making, allowing for the evaluation of suppliers based on critical criteria such as product specifications, certifications (e.g., FDA, ISO, GMP), scalability, sustainability practices, and logistical capabilities. Additionally, maintaining a diversified supplier base enhances resilience and supports business continuity.
In conclusion, implementing a robust sourcing funnel not only optimizes the acquisition of powder materials but also strengthens overall supply chain integrity. Continuous monitoring, supplier performance reviews, and market re-evaluation will ensure the funnel remains adaptive to changing demands, technological advancements, and industry standards—ultimately supporting product quality and long-term operational success.