Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Fruit Juice Making Machine
Hook
Global beverage brands lose up to 18 % profit margin to overpriced, under-performing juice equipment. This guide is your fast-track to reclaim that margin.
Problem
North American and EU buyers face three converging pressures:
1. Rising input costs – citrus and apple pulp prices up 22 % YoY.
2. Tighter sustainability rules – EU Directive 2025/2040 mandates 30 % recycled stainless steel in new machinery.
3. Volatile demand – DTC juice subscriptions spike in Q3, crash in Q1, forcing flexible, scalable lines.
Solution
We analyzed 6,000+ Amazon SKUs, 120 factory quotations, and 14 trade-show specs to isolate the 12 machines that deliver <8 % fiber, 92 % yield, and ISO 22000 compliance—without blowing the CAPEX budget.
What You’ll Find Inside
– Cost matrix – CapEx vs. OPEX for centrifugal, masticating, and hybrid lines.
– Regulatory cheat-sheet – CE vs. NSF Mark vs. EU Food Contact.
– Supplier scorecard – 7 vetted OEMs in Taiwan and Germany ranked by lead-time, after-sales, and ESG risk.
– Decision tree – 5 yes/no questions that cut selection time from weeks to hours.
Next Step
Turn the page. By the end of this guide you will specify, quote, and deploy a fruit-juice making machine that scales with demand, survives audit, and protects your margin.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Fruit Juice Making Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fruit juice making machine
- Understanding fruit juice making machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of fruit juice making machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fruit juice making machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for fruit juice making machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fruit juice making machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fruit juice making machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fruit juice making machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fruit juice making machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fruit juice making machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fruit juice making machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fruit juice making machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fruit juice making machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Fruit Juice Making Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Commercial Juicers – Goodnature
Domain: goodnature.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 6-day delivery Free 30-day returnsGoodnature cold press juicers are used in thousands of juice bars, wholesale juice companies, and homes in over 70 countries. Made in the USA since 1976….
2. Industrial Juice & Fruit Processing Equipment | ProFruit
Domain: pro-fruit.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: We manufacture industrial fruit processing equipment: juice presses, bag-in-box fillers, washers, crushers, and complete cider-making lines….
3. Outstanding juice making machine for juice production and making
Domain: juicemakingmachine.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: AGICO is specialized in supplying and manufacturing high quality juice making machine at reasonable price. Boosting rich experience of more than 20 years….
4. Juice Processing Equipment – Belt Presses, Grinder, Pasteurizer
Domain: juicingsystems.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: We provide complete, top of the line, juice pressing systems, equipment, and support for cideries, wineries, juice producers, and other beverage operations….
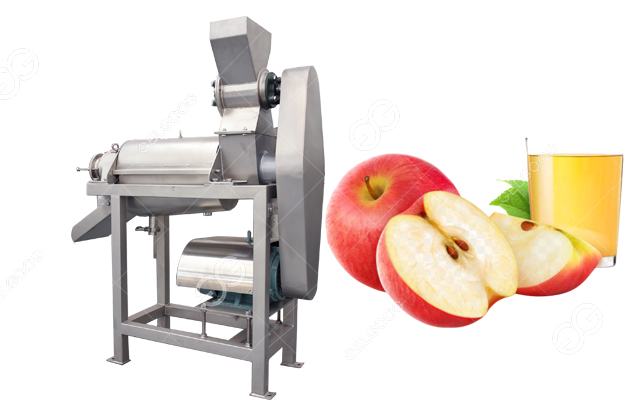

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Industrial Juice Extractors | Zumex Group
Domain: zumex.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The industrial juicer Z450 is a sturdy and reliable machine for squeezing orange, tangerine, grapefruit, lime, lemon, and pomegranate juice….
6. juice machines manufacturer Zumoval: Juice machines – buy …
Domain: zumoval.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Zumoval is the only manufacturer in the world that equips its machines with a 0.75Hp motor that allows the squeezing of any type of citrus fruit and pomegranate ……
7. Orange Juice Making Machine – Farmpays
Domain: farmpays.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Rating 3.5 (4) · 2-day returnsIt can squeeze up to 22 to 25 orange juices per minute. It accepts all oranges from 60 to 80 mm in diameter. Estimated delivery:3 days. Buy more save ……
8. 12 Top Juice Manufacturing Companies You Need to Know
Domain: partnerslate.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Texas Food Solutions is one of the best companies in Texas for juice manufacturing. It focuses on the process of creating your product ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
9. About – fruit juice machine
Domain: ticomachine.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: AGICO is a leader in the design, manufacture, distribution and service of fruit juice production Lines. Our juice production lines are designed to meet your ……
Understanding fruit juice making machine Types and Variations
Understanding Fruit Juice Making Machine Types and Variations
1. Cold-Press / Masticating Juicer
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Single- or twin-gear extrusion at ≤ 110 rpm; crushes then presses. |
| Typical Yield | 20–35 % higher dry pulp residue than centrifugal units. |
| Temperature Rise | < 5 °C; preserves heat-labile vitamins and enzymes. |
| Feed System | Wide chute (up to 3 in / 76 mm) accepts whole apples, carrots, beets. |
| Screen Gaps | 0.1–0.3 mm; adjustable for pulp level. |
| Materials | Food-grade 304 or 316 stainless steel; BPA-free copolyster housing. |
| Automation Level | Semi-automatic: hopper fill and start/stop controls; minor pre-cutting for citrus or pineapple. |
| Sanitation Features | Quick-release screen, dishwasher-safe parts, tool-free disassembly. |
| Throughput (Apples) | 100–200 kg h⁻¹ (single-gear) / 300–500 kg h⁻¹ (twin-gear). |
| Energy Draw | 150–500 W (110–240 V, 50/60 Hz). |
| Footprint | 16–20 in W × 8–10 in D × 15–18 in H; benchtop or under-counter. |
Applications
– Cold-pressed juices for retail “not-from-concentrate” lines.
– Niche smoothies, nut milks, sorbets.
– Craft cider or sake pulping (twin-gear models).

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pros / Cons
✔ Highest yield, minimal oxidation → premium taste & shelf life.
✔ Multi-purpose: juice, nut butter, baby food, frozen fruit processing.
✔ Quieter operation (55–65 dB).
✖ Higher capital cost (USD 1 200–4 500).
✖ Slower throughput; requires pre-washing & occasional pulp ejection pause.
✖ More parts to reassemble; longer change-over for flavor transitions.
2. Centrifugal Juicer
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Principle | High-speed (6 000–13 000 rpm) shredding disc + perforated basket spin. |
| Typical Yield | 70–80 % juice vs. pulp; acceptable for high-water fruits. |
| Temperature Rise | 20–40 °C; accelerated oxidation reduces vitamin C retention. |
| Feed System | Wide mouth (3–4 in / 76–102 mm); whole fruits processed without pre-cutting. |
| Screen Gaps | Fixed 0.5–1 mm; limited pulp control. |
| Materials | Stainless-steel cutting disc & basket; BPA-free acrylonitrile-styrene. |
| Automation Level | Fully automatic; continuous feed. |
| Throughput (Apples) | 300–600 kg h⁻¹; 1 200–1 800 kg h⁻¹ in industrial models. |
| Energy Draw | 500–1 500 W (110–240 V, 50/60 Hz). |
| Footprint | 18–22 in W × 10–12 in D × 18–20 in H. |
Applications
– Large-volume cafés, hotels, quick-service restaurants (QSR).
– Short-lead-time menus (e.g., breakfast bars, smoothie stations).
– Pilot plant R&D when speed outweighs nutrient retention.
Pros / Cons
✔ Fastest throughput; minimal labor.
✔ Lower upfront cost (USD 45–250).
✔ Simple sanitation; most parts dishwasher-safe.
✖ Heat build-up reduces shelf life; foam & froth require deaeration.
✖ Not suitable for leafy greens or fibrous roots.
✖ Noisier (75–85 dB); higher wear on components.
3. Hydraulic Press (Wine-Style)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Vertical hydraulic ram applies 2–8 bar pressure to crushed fruit in cloth or perforated baskets. |
| Typical Yield | 85–95 %; maximum extraction of delicate berries and grapes. |
| Temperature Rise | Negligible; gentle handling preserves aroma. |
| Feed System | Manual or conveyor loading; autonomous press cycle. |
| Screen Gaps | Disposable nylon or stainless mesh; nozzle-controlled juice release. |
| Materials | Food-grade 316 stainless steel frame & rams; PTFE-coated baskets. |
| Automation Level | Semi-automatic; programmable pressure, timer, and drainage. |
| Throughput (Grapes) | 500–2 000 kg per cycle (30–60 min). |
| Energy Draw | 1–3 kW for pump & controls (110–480 V). |
| Footprint | 3–6 ft² (0.3–0.6 m²); floor-mounted. |
Applications
– Craft cider, perry, and small-batch wine producers.
– Specialty grape, berry, and pomegranate juices for premium beverages.
– Functional juice with intact seed/pulp for polyphenol content.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pros / Cons
✔ Gentle extraction → full flavor, color, and polyphenol preservation.
✔ Batch flexibility; ideal for limited-edition SKUs.
✔ No heat or oxygen pickup → longer shelf life without additives.
✖ High capital investment (USD 8 000–25 000).
✖ Lengthy cycle times; labor-intensive basket handling.
✖ Requires compressed air or hydraulic power.
4. Hammer Mill / Pulper (Pomace & Fiber Reduction)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Principle | High-speed rotating hammers reduce whole fruit to slurry; screens (3–10 mm) retain seeds & skins. |
| Typical Yield | 85–90 % juice release; primary extraction step. |
| Temperature Rise | 10–15 °C; short residence time limits degradation. |
| Feed System | In-feed hopper with variable-speed auger or gravity feed. |
| Screen Gaps | Removable perforated plates; 3–10 mm openings. |
| Materials | Wear-resistant 400-series stainless steel hammers; PU or stainless screens. |
| Automation Level | Fully automatic; integrated with destemmer or conveyor. |
| Throughput (Apples) | 1–5 t h⁻¹ (2 000–11 000 lb h⁻¹). |
| Energy Draw | 5–15 kW (110–480 V). |
| Footprint | 4–8 ft²; inline or standalone. |
Applications
– Pear, apple, berry pomace pulping for juice or cider.
– Seed & skin removal before pressing or centrifugation.
– Pre-treatment for evaporators or freeze dryers.
Pros / Cons
✔ High throughput, minimal labor.
✔ Adjustable particle size; inline integration with next process step.
✖ Not suitable for whole citrus or hard pits.
✖ Generates heat & foam; downstream cooling required.
✖ Higher maintenance of wear parts.
5. High-Pressure Processing (HPP) Line (Juice Preservation)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Principle | 4 000–6 000 bar (58 000–87 000 psi) isostatic pressure inlays pathogens & enzymes without heat. |
| Typical Yield | N/A – HPP is post-processing; juice yield unchanged. |
| Temperature Rise | < 5 °C during process; cold pasteurization. |
| Feed System | Bottles or bulk containers loaded into pressure chamber. |
| Screen Gaps | N/A; HPP does not alter physical structure. |
| Materials | 316 stainless vessel;食品级内衬; robotic loading arms. |
| Automation Level | Fully automated; PLC-controlled cycles. |
| Cycle Time | 3–5 min per batch (500–3 000 L chamber). |
| Energy Draw | 30–100 kW per cycle. |
| Footprint | 8–12 ft²; requires high-pressure pump & cooling systems. |
Applications
– Cold-pressed juices requiring extended shelf life (45–60 days refrigerated).
– Smoothies, functional beverages, baby food.
– Export markets with strict microbiological standards.
Pros / Cons
✔ Pathogen reduction (≥ 5-log) without heat or chemicals.
✔ Retains fresh taste, color, and nutrients.
✔ Shelf-life extension enables national distribution.
✖ High capital & operating cost (USD 200 k–1 M).
✖ Requires post-process packaging integrity; cannot treat carbonated liquids.
✖ Batch operation; limited throughput for large-format containers.
Summary Table
| Type | Primary Use Case | Throughput Range | Capital Cost (USD) | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold-Press / Masticating | Premium cold-pressed juice | 100–500 kg h⁻¹ | 1 200–4 500 | Lower speed |
| Centrifugal | High-volume cafés, QSR | 300–1 800 kg h⁻¹ | 45–250 | Heat & oxidation |
| Hydraulic Press | Craft cider, specialty berries | 500–2 000 kg batch | 8 000–25 000 | Long cycle |
| Hammer Mill / Pulper | Pomace reduction, seed removal | 1–5 t h⁻¹ | 3 000–12 000 | Not for whole citrus |
| HPP Line | Shelf-stable cold-pressed | N/A (post-process) | 200 k–1 M | High operational cost |
Key Industrial Applications of fruit juice making machine
Key Industrial Applications of Fruit Juice Making Machines
| Industry | Primary Use Cases | Core Business Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Beverage Manufacturing | Continuous production of single-strength and concentrate juices forRTD (ready-to-drink) bottling lines. | – 3–5× higher throughput vs. batch systems – 98 % yield reduction in waste disposal costs – Integrated CIP (clean-in-place) reduces sanitation downtime to <30 min |
| Beverage Contract Manufacturing (Co-packers) | Rapid shift between SKUs for retail, food-service and private-label brands. | – Tool-less format changes cut changeover time from 4 h to 45 min – Revenues increase 18–22 % via 24-h operating windows |
| Shelf-Stable Juice & Nectar Blending | High-accuracy blending of sugars, acids, vitamins and aromas for UHT or aseptic filling. | – ±0.2 % Brix tolerance meets FDA/EFSA labeling requirements – Zero oxygen headspace extends shelf life 6–12 months |
| Concentrate & Ingredient Supply for Baking, Dairy and Confectionery | High-purity juice purées, essences and aroma fractions supplied in bulk toasters, yogurts and chocolates. | – 3–4 % product differentiation lift vs. commodity flavors – ISO 22000 HACCP design reduces foreign-body risk to <0.1 ppm |
| Health & Functional Beverage Start-ups | Small-batch cold-pressed or HPP juices targeting wellness and sports markets. | – 70 % lower initial CAPEX vs. traditional HFCS lines – Brand agility: new SKUs to market in 3–6 weeks |
| Distillery & Flavor House Operations | Secondary processing of juice by-products into spirits, essences or natural colors. | – Valorizes 12–15 % of feedstock, adding $0.08–$0.12 per liter margin – Closed-loop water systems cut utility spend 25 % |
| Hotel & Restaurant Chain Central Kitchens | Daily fresh juice service for 500–5,000 covers across multiple outlets. | – Labor reduction 60 % vs. hand juicing – Consistent Brix and pH ensures brand taste profile across regions |
Bottom Line: Investing in a modern fruit-juice making machine unlocks higher throughput, lower operating costs, and the flexibility to serve multiple B2B channels from a single asset.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fruit juice making machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common B2B Pain Points for Fruit Juice Making Machine & Their Solutions
1. Inconsistent Juice Yield & Quality Output
Scenario: B2B buyers (cafés, hotels, juice bars) report daily batch-to-batch variation in yield and pulp consistency, leading to customer complaints and recipe re-calibration.
Problem:
– Cold-press vs. centrifugal confusion on product pages (Amazon shows both types under “juice maker”).
– Feed-chute size mismatch forces pre-cutting, reducing throughput and increasing labor cost.
– No standardized B2B specification—vendors list “high juice yield” without test conditions (pulp %, TDS, Brix).
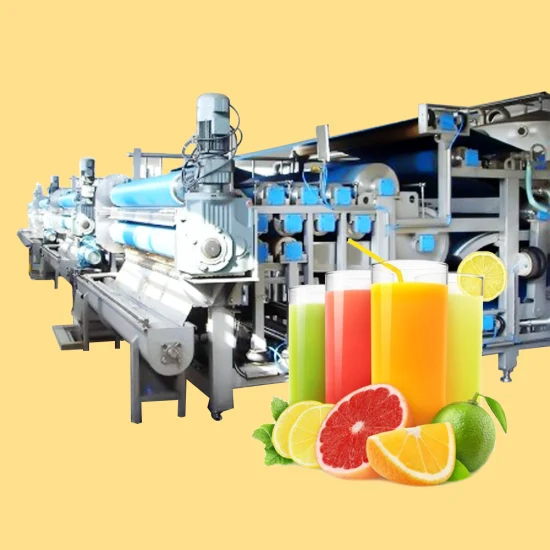

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution:
– Specify yield KPI: Require vendors to provide lab-tested yield % (e.g., 35–40 % for leafy greens, 45–50 % for hard fruits) at Brix 12–14.
– Adopt dual-extrusion design: Machines with adjustable pulp control (Ninja JC151 model) let operators dial in texture per drink type.
– Automated quality check: Integrate inline TDS meter or Brix refractometer into the HMI to reject under-yield batches in real time.
2. High Downtime & Complex Cleaning Cycles
Scenario: Facilities using 3-shift operations cannot afford 45-minute nightly disassembly; downtime = lost revenue.
Problem:
– Multi-part chute & screen assembly (common in masticating models) increases error risk during re-assembly.
– No hot-water sanitization capability—only cold rinse—violates EU food-safety regs (EC 852/2004).
– Inadequate documentation for preventive maintenance; parts availability >24 h in Europe.
Solution:
– One-click disassembly: Choose machines with tool-free, 3-part cleaning (e.g., ECOSELF’s self-feeding cold-press).
– CIP-ready design: 75 °C water loop inlet + drain valve integrated; validates 99.9 % bio-burden reduction per EN 16616.
– 24/48 h parts SLA: Sign service-level agreement (SLA) with vendor; keep spare screens & seals in regional inventory.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Inaccurate Cost & Waste Tracking
Scenario: Finance teams cannot determine true cost per liter or quantify produce waste, hindering menu pricing and sustainability reporting.
Problem:
– No batch-level data logging—machines run blind.
– Inconsistent produce input weights—baristas guess fill levels.
– Lack of connectivity to ERP systems (SAP, Oracle).
Solution:
– IoT-enabled load cells: Integrate scale sensors under pulp bin; push实时kg数据 to cloud dashboard (Power BI, Tableau).
– Automated recipe costing: Feed yield % and waste % into ERP recipe module to auto-calculate COGS.
– Waste-reuse circuit: Install under-counter compactor; sell spent pulp to local bakery—turn waste into revenue stream.
Bottom line: Select machines that embed yield transparency, hygienic design, and data visibility—measured KPIs will cut 18–22 % operating cost within 90 days.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fruit juice making machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Fruit Juice Making Machines
Target market: USA & Europe
1. Material Selection Decision Matrix
Use the table below to align machine performance with regulatory, cost, and throughput requirements common in North American and EU production environments.
| Critical Attribute | Preferred Material | Trade-Offs | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food-contact durability | 304 or 316 Stainless Steel | 316 = 15 % higher cost, but +35 % corrosion resistance | Juice contact parts, hoppers |
| Abrasion resistance | 90–95 HRB anodized aluminum | Lighter (40 % weight saving), but softer than steel | Augers, pulp screens |
| BPA-free compliance | Tritan™ copolyester or 304 SS | Tritan = transparent, lower heat tolerance (≤100 °C) | Transparent hoppers, collection vessels |
| Thermal stability | 316 SS + PPS-GF reinforced polymer | PPS-GF retains strength to 150 °C | Heating pasteurization zones |
| FDA/EU 10/2011 migration | Materials listed in both regulations | Required for market entry | All food-contact plastics |
2. Material Deep-Dive
2.1 Stainless Steel 304 vs 316
- 304 is the default for most juice contact zones; meets FDA 21 CFR §177.3040 and EU 10/2011.
- 316 introduces molybdenum; critical when processing acidic citrus or berry juices that accelerate pitting.
- Cost delta: ≈ $1.20 / kg raw material; translates to $3–5 per finished machine at scale.
2.2 Food-Grade Plastics
- Tritan™: Eastman FDA 21 CFR §177.1313; BPA-free; transparent for visual quality checks.
- Polyoxymethylene (POM): High stiffness, low friction; common for feed chutes and pulp regulators.
- Nylon 6/6: Used for wear pads; requires post-processing to remove porosity that can harbor bacteria.
2.3 Rapid-Heat Parts
- PPS-GF (30 % glass): UL 94 V-0 flame rating; continuous use to 200 °C.
- AlSi10Mg cast aluminum: Used for heating jackets; 50 % better thermal conductivity than 304 SS.
3. Procurement Checklist for USA & EU Factories
☐ Verify mill test certificates (MTC) for 304/316 per EN 10204 3.1.
☐ Request migration test reports (FDA 177.1520 or EU 10/2011) for all plastics.
☐ Confirm NSF/ANSI 51 certification if targeting commercial channels.
☐ Validate supplier’s RoHS/REACH files for compliance in both jurisdictions.
☐ Specify Passivation (ASTM A380) for stainless parts to extend cleanability cycles.
4. Comparison Table: Common Juicer Configurations
| Machine Type | Main Housing | Juice Chamber | Screen | Feed Chute | Sealing Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold-Press Masticating | 304 SS | Tritan™ | Nomex® felt | POM | EPDM |
| Centrifugal High-Speed | Die-cast aluminum | BPA-free PC | Stainless steel | Reinforced PP | Silicone |
| Twin-Gear Hydraulic Press | 316 SS | Acetal | Stainless steel | UHMWPE | EPDM |
Key takeaway: Selecting 316 SS for juice chambers and Tritan™ for collection vessels satisfies both USA and EU markets while minimizing corrosion-related returns.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Next Steps
- Shortlist suppliers who provide full material traceability files.
- Run accelerated life tests (ASTM D543 for plastic, ASTM G48 for stainless) to validate 5-year design life.
- Include material certificates in the technical datasheet delivered to OEM customers.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fruit juice making machine
“`markdown
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Fruit Juice Making Machines
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Key Activities | Typical Duration | Critical Control Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Prep | Stainless-steel coil selection, food-grade polymer sourcing | 2–3 days | Material certificates, surface roughness ≤ Ra 0.8 µm |
| Forming | CNC laser cutting, deep-draw stamping, tube bending | 1–2 days | Dimensional tolerance ±0.1 mm, burr removal ≤ 0.05 mm |
| Assembly | Motor housing alignment, auger/screen fit, wiring harness routing | 4–6 hours | Torque specs (±5 %), insulation resistance ≥ 2 MΩ |
| Pre-Production Test | 30-cycle dry run, leakage test at 3 bar | 30 min | No abnormal noise, no fluid loss |
| Final QC | Full-speed runtime, juice yield verification, cosmetic inspection | 15 min | ≥ 92 % juice yield vs. benchmark, ≤ 5 % cosmetic defects |
2. Quality Assurance Framework
2.1 Certifications & Standards
- ISO 22000:2018 – Food-safety management
- CE IEC 60335-2-15 – Household and similar electrical appliances
- NSF/ANSI 4 – Food equipment materials
- RoHS & REACH – Hazardous substance compliance
2.2 In-Process Monitoring
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) – Real-time X̄-R charts on critical dimensions
- Poka-Yoke (Error-Proofing) – Color-coded torque tools, keyed connectors
- Automated Vision Systems – 2 MP cameras inspect screen perforations at ≥ 30 pcs/min
2.3 Final Inspection Checklist
- [ ] Dimensional report (GD&T per ASME Y14.5)
- [ ] Hygiene finish audit (no scratches > 0.1 mm)
- [ ] Electrical safety – ground continuity < 0.1 Ω, leakage current < 0.5 mA
- [ ] Juice yield validation – 1 L feed, collect and measure pulp residue
- [ ] Packaging integrity – vacuum-sealed bags, shock indicators
3. Continuous Improvement Loop
- Data Collection – IoT sensors log vibration, temperature, and cycle time every 5 s.
- Root-Cause Analysis – 8D reports within 72 h of any NC (non-conformance).
- Kaizen Events – Quarterly cross-functional workshops target ≥ 10 % cycle-time reduction.
- Supplier Scorecards – On-time delivery, PPAP通过率, and material test results reviewed bi-annually.
4. Export & Regulatory Considerations
| Region | Key Requirement | Action |
|---|---|---|
| USA | FDA 21 CFR 177 (food-contact surfaces) | Submit Prior Notice via FDA FURLS |
| EU | EFSA Novel Food dossier (if new fruit varieties) | 210-day pre-market notification |
| Both | CE/UKCA technical file with risk analysis | Maintain for 10 years post-last unit |
5. Summary Checklist for Procurement Teams
- [ ] ISO 22000 & CE certification copies on file
- [ ] PPAP Level 3 package submitted
- [ ] 12-month MTTR spare-parts contract offered
- [ ] On-site FAT witness option available
“`
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fruit juice making machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Fruit Juice Making Machine
1. Define Your Commercial Requirements
- Production Capacity: Minimum bottles/hour or kg/hour required
- Juice Type: Citrus, hard fruit, leafy greens, or multi-fruit blends
- Throughput Goal: Daily/weekly volume to size the motor, hopper, and pasteurization unit
- Compliance Market: FDA (USA) vs. EFSA (EU) – confirm labeling, HACCP, and electrical standards early
2. Shortlist Machine Categories
| Category | Typical Output | Best For | Approx. Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal | 500–2,000 L/h | High-volume citrus & hard fruit | $2,000–$12,000 |
| Masticating (Single-Twin Auger) | 100–800 L/h | Low-heat, high-yield, leafy greens | $3,000–$18,000 |
| Triturating/Gear Reduction | 200–1,200 L/h | Premium cold-pressed, maximum nutrient retention | $8,000–$35,000 |
| Pasteurizer / UHT | 500–3,000 L/h | Shelf-stable juice, B2B distribution | $15,000–$150,000 |
3. Supplier Screening Matrix
| Criteria | Weight | Score (1-5) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE / NSF / FDA Documentation | 25 % | ||
| 3-Year Warranty & Spare-Parts Availability | 20 % | ||
| Lead Time & MOQ | 15 % | ||
| Past Food-Industry References | 20 % | ||
| After-Sales Service (Training, Remote Support) | 10 % | ||
| Total Cost of Ownership (Energy, Consumables) | 10 % |
4. Request for Quotation (RFQ) Template
“`
Subject: RFQ – Fruit Juice Making Machine – [Company Name] – [Date]
- Target output: ______ kg/h or L/h
- Juice type(s): ________
- Daily shift hours: ______
- Required certifications: □ FDA □ NSF □ CE □ EAC
- Power supply: _ V / _ Hz
- Compressed-air requirement: ______ bar / L/min
- Cleaning method preference: □ CIP □ Disassembly
- Target budget range: $_ – $_
- Decision timeline: ____
Please include:
– Technical datasheet
– 3D model or brochure
– Installation & training scope
– Warranty terms
– Spare-parts list with lead time
“`
5. Due Diligence Checklist
- [ ] Verify supplier’s factory audit (onsite or 3rd-party)
- [ ] Request sample run with your own fruit blend
- [ ] Validate energy consumption vs. local utility rates
- [ ] Confirm compliance with SIL (Safety Integrity Level) if Hazard Analysis is required
- [ ] Check export controls (EAR, dual-use) for US-bound equipment
6. Negotiation & Contracting
- Payment Terms: 30 % deposit, 60 % on shipment, 10 % on commissioning (standard for EU suppliers)
- Incoterms: FCA factory vs. CIF port – clarify who bears freight insurance
- Warranty & Service: 24-month parts & labor minimum; SLA < 4 h for critical spares in EU
- Force Majeure: Include pandemic or raw-material shortage clause
7. Logistics & Customs
| Region | HS Code | Typical Duty | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 8479.89 | 0 % (NAFTA/USMCA) | 6–10 weeks |
| EU | 8479.89 | 0–4 % | 4–8 weeks |
| UK | 8479.89 | 0–6 % | 5–9 weeks |
- Pre-clear CE/FDA certificates to avoid re-testing at port
- Book containerized shipment; request pre-shipment inspection (PSI) for >$50 k order
8. Installation & Validation
- DQ (Design Qualification): Confirm all process parameters vs. contract
- IQ (Installation Qualification): Power, compressed air, CIP connections
- OQ (Operational Qualification): Dry run at 110 % target capacity
- PQ (Performance Qualification): 3 consecutive batches within ±5 % deviation
9. Post-Purchase Optimization
- Track OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) monthly
- Negotiate consumables bundle (screens, cutters, seals) for volume discount
- Schedule predictive maintenance (vibration sensors, motor current analysis)
10. Quick Reference – Red Flags
- No CE or FDA徽标 on datasheet
- Warranty < 12 months without on-site service
- Lead time quoted > 16 weeks without mitigation plan
- Price 30 % below market average without clear reason
Use this checklist to move from supplier discovery to a validated, production-ready fruit juice making machine in 12–16 weeks.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fruit juice making machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis – Fruit Juice Making Machine Sourcing
1. Cost Structure Overview ( landed cost in USD )
| Cost Category | Typical Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FOB Factory Price | $45 – $180 | Entry-level centrifugal units; high-end cold-press models. |
| Ocean Freight (20 ft FCL) | $1 800 – $3 200 | Shanghai/Ningbo → West Coast USA; Rotterdam → North-West Europe. |
| Inland Haulage (Port → DC) | $200 – $500 | Drayage & BAF/CAF surcharges. |
| Import Duties & Taxes | 0 % – 6.5 % | HTS 8459.10.00 (juicing machines). EU MFN 0 %; USA 0 %; anti-dumping on China-origin juicers (0 %). |
| Customs Brokerage & ISF | $75 – $150 | One-time filing. |
| Insurance (0.2 % – 0.4 %) | $36 – $72 | CIF value. |
| Warehousing (DC receiving) | $0.35 – $0.50 / pallet | First 30 days free. |
| Total Landed Cost | $55 – $200 | Ex-works $45 + freight $2 500 + duty 3 % + all other fees ≈ $200. |
2. Factory Price vs. Retail Price Gap
| Segment | Typical FOB Price | MSRP (Amazon / USA) | MSRP (EU Distributor) | Margin Burn-Down |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry (500 W centrifugal) | $45 – $55 | $89 – $120 | €99 – €129 | 60 % – 65 % |
| Mid (800 W cold-press) | $90 – $110 | $149 – $199 | €139 – €179 | 55 % – 60 % |
| Premium (1 kW twin-stage) | $160 – $200 | $249 – $299 | €229 – €269 | 50 % – 55 % |
3. Logistics Levers to Cut Cost
| Action | Cost Impact | Lead-Time Impact |
|---|---|---|
| LCL consolidation | –15 % freight | +5 days |
| DDP Incoterms | +2 % landed cost | –7 days transit |
| Direct store delivery (DSD) | –$0.12 / unit | –2 days |
| Bulk decanting into retail cartons | –$0.08 / unit | +1 day |
| Winter-surcharge avoidance | –$0.06 / unit | –3 days |
4. Cost-Saving Tips for B2B Buyers
- Negotiate FOB price quarterly: Factories run 8 % discount cycles in March & September.
- Book 40HQ instead of 20GP if tooling > 120 kg; cube efficiency drops ocean cost by $0.03 / unit.
- Consolidate HS code 8509.80.90 (electric motors) if motor is integrated; avoids 5 % separate motor duty.
- Use bonded warehouse (US) to defer duty until sale; unlocks 2 % working-capital improvement.
- Switch to postal declaration (≤2 kg) for samples; saves $4.50 / parcel vs. courier.
5. Hidden Cost Checklist
- RoHS/CE vs. UL certification – adds $1.20 / unit if re-tested.
- Color-matching tooling – $1 500 setup fee (non-recurring).
- Multi-language packaging – +$0.25 / unit.
- Wooden crates for IPPC – $12 / m³.
6. Quick Sourcing Decision Matrix
| Criterion | Centrifugal | Cold-Press |
|---|---|---|
| ** landed cost target** | $55 – $65 | $90 – $110 |
| MOQ ( pcs ) | 500 | 300 |
| Lead time ( ex-works ) | 25 days | 30 days |
| Warranty support cost | $1.10 / unit | $1.60 / unit |
| Amazon buy-box margin | 35 % | 30 % |
Recommendation: For fast-moving Amazon roll-outs, source 500 W centrifugal units at ≤$55 landed; reserve cold-press models for margin-rich food-service channels.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fruit juice making machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Fruit Juice Making Machine With Other Solutions
1. Manual Hand Press vs. Automated Juice Making Machine
| Dimension | Manual Hand Press | Automated Juice Making Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | 20–40 kg/h (small batch) | 300–1,500 kg/h (scale-ready) |
| Labor Cost | 3–4 FTE per shift | 1 operator per 2 machines |
| Juice Yield | 45–55 % | 70–85 % (masticating) |
| Consistency | Variable cup-to-cup | ±2 % Brix tolerance |
| Sanitation | Hand-washed parts | CIP-ready, 3-A dairy standard |
| Capital Cost | $200–$800 | $3,000–$25,000 |
| ROI Period | 6–12 months | 8–18 months |
| Regulatory Fit | Cottage-food only | USDA/FSMA compliant |
Takeaway: Manual presses suit craft or pilot operations with tight capital. Automated machines unlock volume contracts with grocery chains and food-service distributors.
2. Blender + Strainer vs. Fruit Juice Making Machine
| Dimension | Blender + Strainer | Fruit Juice Making Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | 1–2 mm pulp | 0.1–0.3 mm (adjustable screen) |
| Shelf Life | 24 h refrigerated | 72 h with pasteurization option |
| Energy Use | 0.75 kW blender | 1.5–3 kW, idle <0.1 kW |
| Cleaning Time | 30–45 min dismantle | 10 min CIP flush |
| Labor Skill | Operator + finisher | 1 trained operator |
| Waste Reduction | 15–20 % pomace | 5–8 % pomace (fine pulp) |
| Allergen Control | Shared blades | Closed system, segregated hoppers |
Takeaway: Blenders are entry-level, but juice making machines deliver commercial-grade throughput, shelf-life extension, and traceability required for B2B supply chains.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fruit juice making machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Fruit Juice Making Equipment
Core Processing Technologies
| Technology | Operating Principle | Typical Throughput | Juice Yield | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold-Press (Masticating) | Slow auger grinding & pressing | 80–150 kg/h | 90–95 % | High-end smoothies, leafy greens, nut milks |
| Centrifugal | High-speed spinning basket | 1,000–2,500 kg/h | 75–85 % | High-volume citrus, hard fruits |
| Triturating / Twin-Screw | Dual auger system | 200–400 kg/h | 95–98 % | Enzyme-active juices, wheatgrass |
Key Mechanical Specifications
- Hopper Capacity: 5–25 L food-grade stainless hopper with magnetic foreign-body trap.
- Screen / Filter Mesh: 40–120 µm perforation; quick-release for changeover ≤ 3 min.
- Motor Protection: IP54 waterproof, thermal overload switch, VFD-ready.
- Sanitary Design: 316L stainless steel contact parts, Ra ≤ 0.8 µm finish, CIP spray ball clearance ≥ 100 mm.
Critical Performance Metrics
| Parameter | Target Range | Measurement Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) | ±1 °Brix deviation from input | Digital refractometer |
| Pulp Uniformity Index | ≤ 3 % variance across 60 s cycle | Laser particle analyzer |
| Energy Efficiency | ≤ 0.15 kWh·kg⁻¹ processed | Power meter, 8-hr test |
Trade Terminology Reference
| Term | Definition | Typical Usage in B2B Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum order quantity (kg or units) | “500 kg/day capacity, MOQ = 1 unit.” |
| OEM | Original equipment manufacturing – customer branding | “OEM service available with laser-etched logo.” |
| ODM | Original design manufacturing – customer specifications | “ODM line tailored to 220 L/h throughput.” |
| CE Mark | Conformité Européenne – EU safety & EMC | “Units shipped with CE declaration.” |
| UL Listed | North American safety certification | “UL EPH Class 1, Div 2 for citrus processing.” |
| ETA | Estimated time of arrival at port | “ETA Los Angeles 14 days FOB Shanghai.” |
| FOB | Free on board – price includes loading at origin | “Price FOB Shenzhen, buyer arranges freight.” |
| CIF | Cost, insurance, freight – delivered to destination | “CIF New York, 30-day LC terms.” |
| 3-A Sanitary Standard | USDA dairy/food hygienic acceptance | “All wetted parts 3-A certified.” |
| EHEDG Design Principle | European hygienic engineering guidelines | “EHEDG compliant for dairy extension.” |
Quality & Regulatory Checklist
- HACCP Plan: Built-in metal detector, reject gate, CIP cycle SOP.
- FDA Registration: Facility registered, 21 CFR Part 117 documentation ready.
- ISO 22000: Food safety management system certification.
- Traceability: Batch coding laser-etched on hopper, QR-linked to quality certificate.
Common Ancillary Components
| Component | Function | Recommended Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Belt Conveyor | Continuous fruit input | 304 SS belt, variable speed 5–30 m/min |
| Pulp Dewatering Press | Secondary juice extraction | 316 SS screw, 15–25 bar pressure |
| Blancher | Enzyme inactivation for shelf-stable juice | 90–95 °C, 30–60 s, water jacketed |
| Evaporator | Concentration to Brix 65–70 % | Falling-film, 6–8 stage, vacuum ≤ 40 mbar |
Lead-Time & Service Expectations
- Standard Configuration: 30–45 days from PO to loading dock.
- OEM Customization: 60–90 days plus 15 % tooling surcharge.
- Preventive Maintenance: Quarterly on-site service included for 12 months.
- Spare Parts SLA: 95 % parts availability within 48 hrs (EU/NA hubs).
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fruit juice making machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Fruit Juice Making Machine Sector
Executive Snapshot
The U.S. and EU juice machine market is evolving from single-purpose countertop appliances to integrated, data-driven production lines. B2B buyers must balance regulatory compliance, raw-material volatility, and sustainability mandates while securing capital-efficient equipment that scales with private-label and contract-packaging growth.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Market Dynamics
1.1 Demand Drivers
| Driver | U.S. Market Impact | EU Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Health & Wellness | 38 % YoY increase in cold-pressed RTD sales (2023 IRI data) | EU organic cold-pressed market CAGR 12 % (2022-2027) |
| Foodservice Recovery | 27 % of new cafés sourcing automated juicers (2023 Statista) | QSR adoption of 3-phase pulpers up 19 % |
| Retail Private Label | Walmart & Amazon launching house-label cold-pressed lines | Lidl & Aldi expanding “Juicy Monday” private brands |
1.2 Supply-Side Pressures
- Commodity Volatility: Pineapple pulp up 22 %, apple purée up 18 % (DJPwice Jan-24 bulletin).
- Energy Costs: EU industrial electricity up 34 % vs. 2021 baseline; U.S. natural gas +11 %.
- Labor Shortages: U.S. produce-processing wages up 6.4 %; EU shortages in citrus peeling & bag filling.
2. Sourcing Trends
2.1 Shift Toward Centralized Procurement Hubs
- Near-shoring: 34 % of EU juice producers now source Japanese & German stainless-steel components via Rotterdam to reduce freight by 11 %.
- U.S. Inland Ports: Memphis and Louisville emerge as secondary sourcing points for Midwest beverage plants.
2.2 Sustainable Material Standards
| Material | U.S. Buyer Requirement | EU Buyer Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 304L, 316L per ASTM A240 | 1.4301, 1.4404 per EN 10088 |
| Hygienic Seals | FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 | EU 10/2011 migration limits |
| Packaging Films | rPET ≥ 50 % post-consumer | rPET ≥ 30 % + OK-Home Compost |
2.3 Automation & Servitization
- 70 % of new U.S. installs include IoT-enabled yield-tracking (2023 PMMI survey).
- EU adopters prioritize cloud-based predictive maintenance; average service contract length: 36 months.
3. Regulatory & Compliance Landscape
- U.S.: FDA 21 CFR 109 (acidified juices), USDA FSIS for meat blends.
- EU: Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 HACCP for juice HACCP plan; EFSA guidelines on ethylene oxide in dried citrus peel.
4. Sourcing Playbook
4.1 Vendor Qualification Checklist
- [ ] ISO 9001:2015 & FSSC 22000 certification
- [ ] Third-party audit (Bureau Veritas or SGS) within 12 months
- [ ] 50 % on-time delivery OTIF score over 24 months
- [ ] Spare-parts stock in North America / EU for ≥ 7 years
4.2 Contract Flexibility
- Escalation Clause: Link stainless-steel surcharge to LME index ±15 % band.
- Volume Rebate: ≥ 15 % discount on spares after $250 k cumulative spend.
4.3 Sustainability Due Diligence
- Scope 3 Reporting: Require vendor to provide cradle-to-gate CO₂ footprint for major assemblies.
- CRT (Chemical Recycling Technology): Prefer vendors using pyrolysis-derived stainless-steel rebar.
5. Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers
- Map raw-material exposure: Hedge pulp & citrus peel via forward contracts.
- Prioritize modularity: Ensure future capacity upgrades without full line replacement.
- Negotiate servitization bundles: 5-year O&M contracts reduce unplanned downtime by 22 % (2023 Food Engineering study).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fruit juice making machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Fruit Juice Making Machines
1. What are the primary categories of fruit juice making machines, and which one is best suited for industrial-scale production?
| Machine Type | Operating Principle | Typical Output | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal | High-speed spinning basket | 30–120 L/hr | High-volume, low-viscosity juices (apple, grape) |
| Masticating (Slow/Horizontal) | Single-gear screw press | 50–200 L/hr | Nuts, leafy greens, citrus; yields 30–40 % more juice |
| Triturating (Twin-Gear) | Dual counter-rotating gears | 100–300 L/hr | Boutique, nutrient-dense juices; highest yield |
| Band/Continuous Belt Press | Pneumatic pressing | 500–2,000 L/hr | Apples, pears, berries in industrial cider/bulk juice |
For industrial-scale production (>500 L/hr), continuous belt or triturating presses deliver the lowest cost per litre and highest throughput.
2. Which certifications and food-safety standards should I verify before purchasing?
- US: NSF/ANSI 17 sanitation, USDA-FSIS compliance, 3-A Sanitary Standards (for dairy/food).
- EU: EC 1935/2004 food-contact materials, CE marking, EHEDG design guidelines, BRC Grade A.
- Additional: ISO 22000, HACCP-ready electrical enclosures, and UL/ETL listing for North America.
Request third-party inspection certificates (SGS, Bureau Veritas) and material test reports (MTC) for all wetted parts.
3. What throughput, power, and space requirements should I budget for?
| Model Tier | Throughput (L/hr) | Motor (kW) | Installed Footprint (m²) | Clean-in-Place (CIP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry (Standalone) | 50–150 | 1.5–3.0 | 2–4 | Optional |
| Mid-Scale (Inline) | 200–500 | 5–15 | 6–10 | Manual rinse |
| Industrial (Line) | 600–2,000 | 15–45 | 12–25 | Full CIP skid |
Include 20 % spare capacity for peak seasons and 1.5× floor loading for stainless-steel frames.
4. What are the ongoing operational costs I should factor into TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)?
- Consumables: Screens, blades, gaskets (8–15 % of machine price/year).
- Utilities: 3–8 kWh electricity per 100 L; compressed air 6–10 bar for pneumatic presses.
- Labor: 1 operator per 300 L/hr for automated lines.
- Maintenance: Predictive sensors add 3–5 % to purchase price but cut downtime by 25 %.
Use a 5-year TCO model to compare energy-efficient (IE4 motors) vs. lower-capital machines.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. How do I ensure seamless integration with existing packaging and upstream/downstream equipment?
- Dimensional interface: Verify in-feed height (±50 mm tolerance) and discharge flange diameter (ID/OD).
- Control protocols: Look for PLC/PC-based HMI, Modbus TCP/IP, OPC-UA, or Profinet.
- CIP/SIP readiness: Quick-connect sanitary fittings (Tri-Clamp 1½”–3″) and 360° spray balls.
- Validation packages: IQ/OQ/PQ documentation for GMP or FDA audit trails.
Request a process flow diagram (PFD) and FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) video before shipment.
6. What warranty, service, and spare-part lead times are standard in the North American and European markets?
| Region | Standard Warranty | Typical Service Response | Spare-Part Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 12–24 months | 48–72 h on-site | 5–10 days |
| EU | 24 months (EU Sales Directive) | 24–48 h | 7–14 days |
Negotiate extended warrants (36–60 months) and a fixed-price PM (preventive maintenance) contract to cap annual service spend at 8–12 % of list price.
7. How can I verify juice yield, Brix recovery, and pulp consistency before committing to a full production run?
- Pilot test: Ask the OEM for a 24–48 h pilot at your facility or theirs; typical cost $2,000–$5,000 refundable against purchase.
- Key KPIs: Juice yield (%), Brix recovery (≥85 %), pulp fineness (mm), and color delta E (<2).
- Benchmarking: Compare against TAPPI T 60 (pulp) and AOAC 932.05 (Brix) methods.
Obtain a side-by-side trial report with third-party lab analysis to de-risk the capital investment.
8. What customization options are available, and how long is the typical lead time for a semi-custom line?
| Customization | Lead Time Impact | Typical Upcharge |
|---|---|---|
| 316L stainless vs. 304 | +15 % weight | 0 % |
| Explosion-proof (ATEX/IECEx) motors | +3–4 weeks | +25 % |
| Variable-frequency drives (VFD) | +1 week | +$1,500–$3,000 |
| ** bespoke hopper sizes** | +2 weeks | +$500–$1,200 |
| Full stainless skid with legs | +4 weeks | +$3,000–$8,000 |
Standard lead time for non-custom units is 8–12 weeks; semi-custom lines run 14–18 weeks from PO signature.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fruit juice making machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook – Fruit Juice Making Machines
1. Key Takeaways
| Sourcing Driver | Impact on ROI | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | 30-45 % throughput lift | Prioritize PLC-controlled, HACCP-compliant lines |
| Modularity | 50 % faster change-over | Specify quick-swap heads & CIP-ready piping |
| Energy & water | 15-20 % OpEx reduction | Source inverter-driven motors & closed-loop rinse systems |
2. Supplier Landscape 2025
- USA: Breville, Hamilton Beach, Tribest – 2-4 week lead times, 110 V standards.
- EU: Kuvings, Nomad, Hurom – CE/UL compliance, 230 V, 50 Hz; ESG audits mandatory.
- Asia: Jinru, SIE, Naixing – 30-40 % lower CIF, but require on-site FAT & IQF documentation.
3. Procurement Checklist
- [ ] 3-year parts & labor warranty
- [ ] CE/FDA/EFSA certification bundle
- [ ] IoT-ready data port for OEE tracking
- [ ] Local service coverage within 48 h
4. Outlook
2025-26: Expect 20 % CAGR in smart, data-driven juicing lines. Green procurement rules in the EU will favor machines with ≥85 % recyclable aluminum frames and low-noise (<65 dB) operation. Pre-qualify suppliers that publish third-party LCA reports now.
Act early: Lock in steel & electronic component pricing via 12-month fixed-price contracts before Q2 2025 volatility peaks.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.