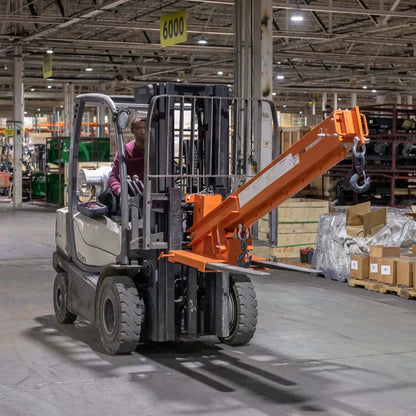
The global forklift boom market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for material handling equipment across industries such as construction, warehousing, and manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global forklift truck market was valued at USD 54.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by advancements in equipment versatility, rising automation in logistics, and growing industrialization in emerging economies. Fork lift booms—specialized attachments that enhance reach and lifting capabilities—are becoming critical components in modern material handling solutions. As demand for high-performance, adaptable machinery rises, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, reliability, and market reach. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 forklift boom manufacturers shaping the future of industrial operations.
Top 10 Fork Lift Boom Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 JLG Industries
Domain Est. 1995
Website: jlg.com
Key Highlights: JLG is a leading manufacturer of access equipment. Get up-to-date news, events, tech tips and even machine sightings. Where will you find JLG?…
#2
Domain Est. 1995
Website: genielift.com
Key Highlights: Genie® articulated boom lifts, telescopic boom lifts, scissor lifts and telehandler products are used in a wide range of industries around the world….
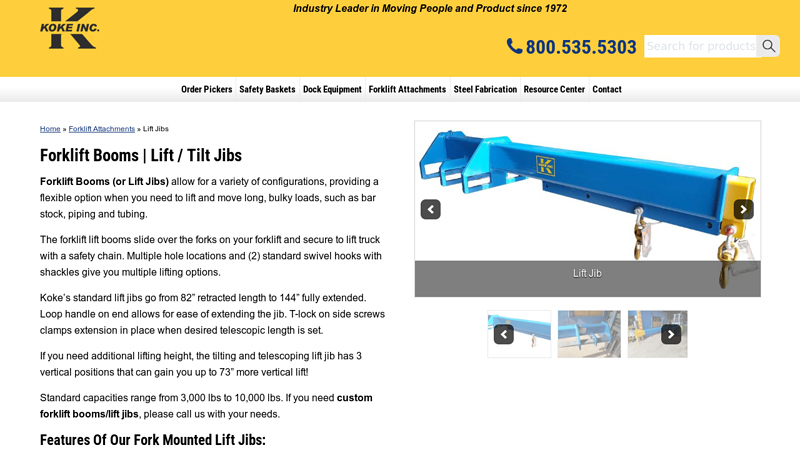
#3 Forklift Booms/Lift Tilt Jibs For Flexible Lifting Of Bulky Loads
Domain Est. 1996
Website: kokeinc.com
Key Highlights: Koke Inc Forklift Booms and Tilt Lift Jibs are flexible for lifting long, bulky loads. Our forklift boom attachments are perfect for piping and tubing….
#4 Cherry Picker, Boom Lift & Work Platforms
Domain Est. 1996
Website: niftylift.com
Key Highlights: Our compact and low weight articulating booms offer the maximum performance and reliability you need to deliver a high-quality service to your clients….
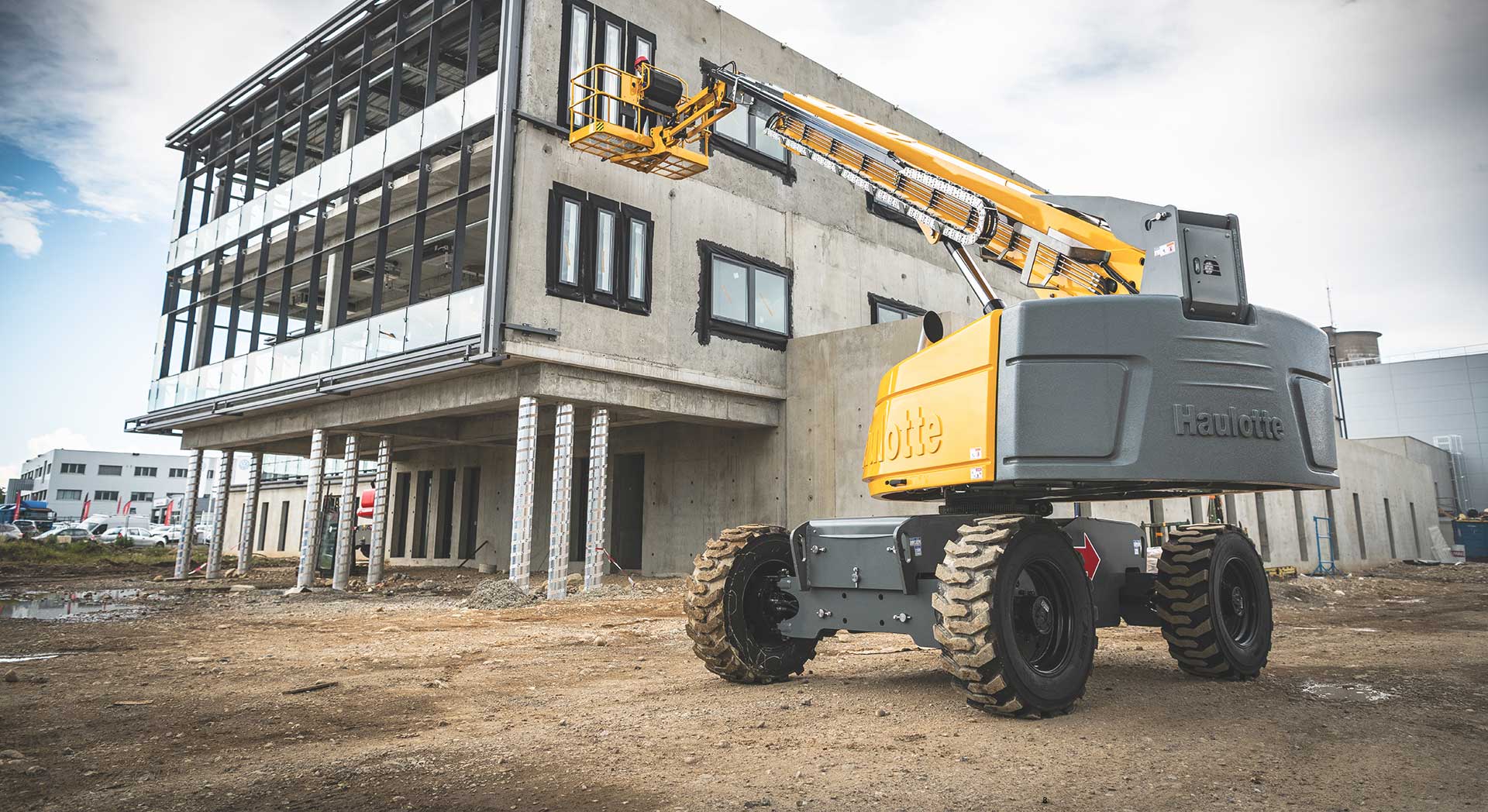
#5 Haulotte Group
Domain Est. 1997
Website: haulotte.com
Key Highlights: Haulotte is a global leader of people lifting equipment. As European leader, the group designs, manufactures and markets a wide range of aerial work platforms….
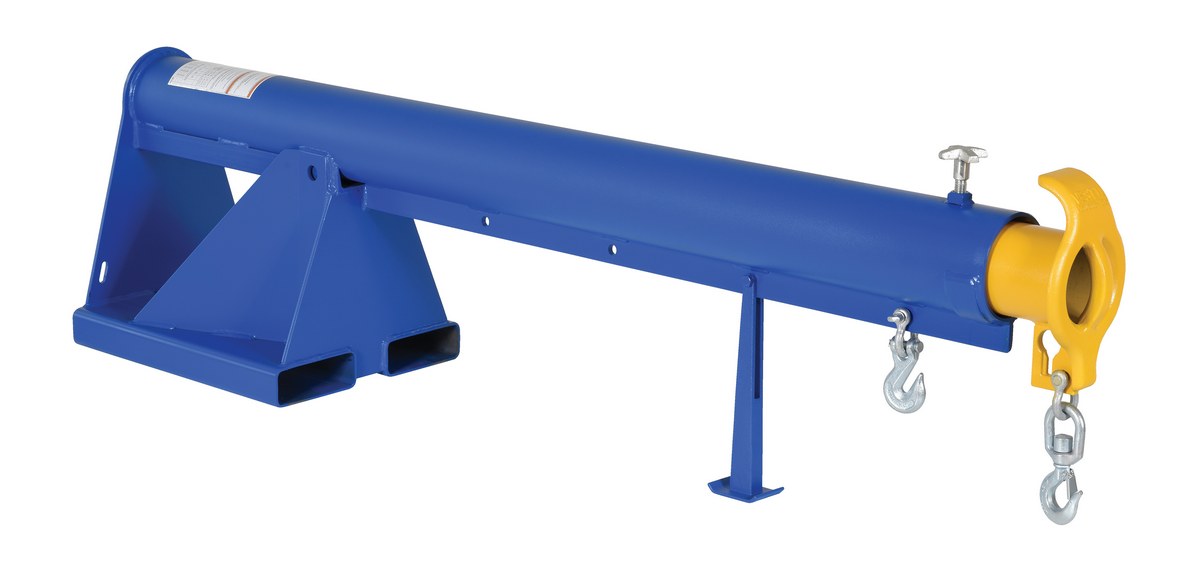
#6 Category: Lift Master Booms
Domain Est. 1998
Website: vestil.com
Key Highlights: Vestil Lift Master Booms are robust fork truck attachments designed to transform your fork truck into an overhead lifting crane, ensuring long-term service ……
#7 Attachments for Forklifts, Skid Steers, Excavators & Cranes
Domain Est. 1998
Website: starindustries.com
Key Highlights: Discover machinery attachments that last longer at Star Industries. Explore our range of quality attachments for forklift, cranes, and skid steers….
#8 Big Joe Forklifts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bigjoeforklifts.com
Key Highlights: Discover Big Joe’s innovative lithium-ion forklifts and autonomous solutions, backed by expert support and engineering, for efficient material handling ……
#9 Taylor Forklifts: Heavy
Domain Est. 2000
Website: taylorforklifts.com
Key Highlights: Explore heavy-duty forklifts and container handling equipment from Taylor. Built for tough industries, backed by expert service, parts, and dealer support….
#10 Material Handling Equipment
Domain Est. 2013
Website: arrowmhp.com
Key Highlights: Heavy Duty Skid Steer Pallet Forks & Frames · SAME DAY SHIPPING for orders made before 2PM · Upgraded Capacity – Up to 9,000 lb 2 Bolt-On Steps (Select Styles)…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fork Lift Boom

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Forklift Booms
The forklift boom market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological innovation, increasing demand for material handling automation, and a growing emphasis on workplace safety and efficiency across industrial sectors. Forklift booms—hybrid attachments that combine the lifting capabilities of forklifts with the reach and elevation of boom lifts—are gaining traction as versatile solutions in construction, warehousing, logistics, and maintenance operations.
-
Rising Demand for Multi-Functional Equipment
A key trend shaping the 2026 market is the rising preference for multi-functional machinery. Forklift booms enable a single machine to perform both vertical lifting and elevated reach tasks, reducing the need for separate forklifts and aerial work platforms. This dual functionality lowers capital and operational costs, making it especially attractive to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) seeking operational efficiency. -
Growth in Automation and Smart Attachments
By 2026, integration with automation and IoT-enabled systems is expected to become standard. Smart forklift booms equipped with sensors, load monitoring, and remote diagnostics will enhance precision and safety. These intelligent systems allow real-time data tracking, predictive maintenance, and improved operator oversight—features increasingly demanded in smart warehouses and Industry 4.0 environments. -
Expansion in E-commerce and Logistics Infrastructure
The continued expansion of e-commerce is fueling investments in modern warehousing and distribution centers. Forklift booms are well-suited for high-bay storage and order-picking operations where vertical reach and load maneuverability are crucial. As logistics networks scale up, the demand for adaptable, space-efficient equipment like forklift booms will grow significantly. -
Emphasis on Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Safety remains a top priority in industrial operations, and by 2026, stricter safety regulations are expected to influence equipment design. Forklift booms are being engineered with enhanced stability controls, anti-tip mechanisms, and operator-assist features to comply with global safety standards such as ANSI and ISO. This focus on safety will drive product innovation and adoption. -
Regional Market Growth and Industrialization
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, is anticipated to lead market growth due to rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and government initiatives promoting manufacturing. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, supported by modernization of existing facilities and a shift toward sustainable and efficient material handling solutions. -
Sustainability and Electrification Trends
With the global push toward carbon neutrality, the forklift boom market is witnessing a shift toward electric and hybrid-powered systems. By 2026, electric forklift booms are expected to capture a larger market share, especially in indoor environments where emissions and noise levels are critical concerns.
Conclusion
The 2026 forklift boom market will be defined by versatility, technological integration, and sustainability. As industries seek to optimize space, labor, and capital, forklift booms represent a strategic convergence of lifting and reaching capabilities—an innovation that aligns perfectly with the future of material handling. Manufacturers who invest in smart, safe, and eco-friendly designs will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Fork Lift Boom: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a forklift boom—especially a custom or aftermarket attachment—exposes buyers to significant risks related to both quality control and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Material Defects
One of the most prevalent risks when sourcing forklift booms, particularly from low-cost or unverified suppliers, is substandard manufacturing quality. Inferior materials, improper welding techniques, and lack of rigorous quality assurance can compromise the structural integrity of the boom. Components made from low-grade steel or with inconsistent heat treatment may fail under load, leading to equipment damage or serious safety incidents. Buyers often overlook the need for material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) or third-party inspections, assuming visual inspection is sufficient—this can be a costly mistake.
Lack of Compliance with Safety and Industry Standards
Many sourced forklift booms do not meet recognized safety standards such as ISO 10899, ASME B56.1, or local regulatory requirements. Non-compliant booms may lack proper load ratings, safety decals, or structural reinforcements required for safe operation. Using non-certified equipment can void insurance coverage and expose operators and employers to legal liability in the event of an accident. Buyers must verify that the supplier provides documentation proving compliance and, where necessary, engages accredited testing bodies.
Intellectual Property Infringement
A significant but often overlooked risk is IP infringement. Many forklift boom designs are protected by patents, trademarks, or design rights held by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Sourcing generic or “OEM-compatible” booms from unauthorized suppliers may involve copying proprietary designs, potentially violating patent rights. Even if the supplier is overseas, importing such products into jurisdictions like the U.S. or EU can trigger customs seizures, legal action, and financial penalties under IP enforcement laws. Buyers may be held liable as contributory infringers, even if unaware of the infringement.
Inadequate Design Validation and Testing
Suppliers—especially smaller or non-specialist manufacturers—may not conduct proper engineering analysis or load testing on their boom designs. Finite element analysis (FEA), stress testing, and real-world performance validation are essential to ensure reliability. Without documented testing and engineering sign-off, there is no assurance the boom will perform safely under operational conditions. Relying solely on supplier claims without requesting test reports or engineering documentation increases the risk of field failures.
Insufficient Warranty and After-Sales Support
Low-cost suppliers may offer minimal or no warranty, and lack technical support for installation, maintenance, or troubleshooting. When quality issues arise, delays in resolution can lead to extended equipment downtime. Additionally, spare parts may be unavailable, making repairs difficult or impossible. Buyers should assess the supplier’s service network and support capabilities before committing to a purchase.
Hidden Costs from Re-Work and Downtime
Initially attractive pricing can be misleading when poor quality leads to frequent breakdowns, safety incidents, or premature replacement. The total cost of ownership increases significantly when factoring in lost productivity, repair expenses, and potential regulatory fines. Investing in a properly vetted, high-quality boom from a reputable source often proves more economical in the long run.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits and request proof of certifications (ISO, CE, etc.).
– Require material test reports, engineering drawings, and load test documentation.
– Perform or commission independent inspections and quality checks.
– Consult legal counsel to assess IP risks, especially when sourcing “compatible” or replica parts.
– Prioritize suppliers with proven industry experience, strong warranties, and technical support.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure safe, compliant, and legally sound procurement of forklift booms.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fork Lift Boom
This guide outlines the essential logistics procedures and compliance requirements for the safe and efficient handling, transportation, and operation of a Fork Lift Boom attachment. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, protects personnel, and maintains equipment integrity.
Purpose and Scope
This document applies to all personnel involved in the shipping, receiving, storage, transportation, installation, use, and maintenance of Fork Lift Boom attachments. It covers regulatory standards, safety protocols, and logistical best practices.
Regulatory Compliance Overview
Fork Lift Boom attachments must comply with relevant national and international safety and transportation regulations. Key standards include:
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910.178: Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards for powered industrial trucks.
– ASME B30.22: Safety standard for below-the-hook lifting devices, including boom attachments.
– ANSI/ITSDF B56.1: Safety standards for low-lift and high-lift trucks.
– DOT Regulations (49 CFR): For transportation of heavy equipment, including securement during transit.
– Local Jurisdiction Requirements: Compliance with regional safety and environmental regulations.
Pre-Transportation Inspection
Before any movement, conduct a thorough inspection of the Fork Lift Boom:
– Check for structural damage, cracks, or deformation in the boom arm, welds, and mounting brackets.
– Verify integrity of hydraulic lines, hoses, and connections (if applicable).
– Inspect pins, bolts, and locking mechanisms for wear or looseness.
– Confirm load capacity labels are legible and correctly affixed.
– Document inspection findings using a standardized checklist.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Ensure proper protection during shipping:
– Secure all moving parts with protective covers or locking pins.
– Wrap hydraulic components and electrical connections in moisture-resistant material.
– Use skids or pallets suitable for the weight and dimensions of the boom.
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Heavy Equipment” indicators.
– Attach a compliance tag showing inspection date, load rating, and handling instructions.
Transportation Guidelines
During transit, follow these procedures:
– Use flatbed or low-boy trailers with adequate weight capacity.
– Secure the boom attachment using rated chains, straps, or load binders (minimum 4-point tie-down).
– Ensure load is centered and balanced on the transport vehicle.
– Comply with highway weight and dimension restrictions; obtain permits if required.
– Provide a transport manifest including equipment ID, weight, dimensions, and safety warnings.
Receiving and Unloading Procedures
Upon delivery:
– Inspect the shipment for damage before unloading.
– Use certified lifting equipment (e.g., forklift with appropriate capacity) and rigging.
– Employ trained personnel to guide and supervise unloading operations.
– Verify contents against packing list and inspect for transit damage.
– Report any discrepancies or damage immediately to the carrier and supplier.
Storage Recommendations
Store the Fork Lift Boom properly when not in use:
– Place on a level, dry, and well-ventilated surface.
– Elevate off the ground using wood blocks to prevent corrosion.
– Cover with a breathable tarp to protect from dust and moisture.
– Store away from high-traffic areas and corrosive substances.
– Ensure easy access for inspections and future use.
Installation and Integration
Only trained and authorized personnel may install the boom:
– Confirm compatibility with the host forklift model and lift capacity.
– Follow manufacturer’s installation manual precisely.
– Use calibrated torque tools for fastener installation.
– Verify safety interlocks and warning systems are functional.
– Conduct a post-installation inspection and load test per ASME B30.22.
Operator Training and Certification
Operators must be trained and certified before using the Fork Lift Boom:
– Training must cover equipment-specific operation, load charts, and hazard recognition.
– Include instruction on boom angle limitations, load moment, and stability.
– Refresher training required annually or after incidents.
– Maintain training records for audit and compliance purposes.
Operational Safety Protocols
During use:
– Never exceed the rated load capacity of the boom or host forklift.
– Conduct pre-shift inspections of the boom and forklift.
– Use taglines to control load swing during lifting operations.
– Operate only on stable, level surfaces; avoid slopes and soft ground.
– Prohibit personnel from standing under suspended loads.
Maintenance and Inspection Schedule
Implement a routine maintenance program:
– Perform daily visual checks by operators.
– Conduct periodic inspections (monthly/quarterly) by qualified technicians.
– Follow manufacturer’s service intervals for lubrication, hydraulic checks, and wear part replacement.
– Keep detailed maintenance logs accessible for audits.
Compliance Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain the following records:
– Equipment manuals and compliance certifications.
– Inspection and maintenance logs.
– Operator training records.
– Incident reports and corrective actions.
– Load test documentation (per ASME B30.22 requirements).
Emergency Procedures
In case of malfunction or incident:
– Immediately cease operations and secure the area.
– Follow company emergency response plan.
– Report incidents to supervisor and safety officer.
– Do not attempt repairs without proper training and authorization.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance practices are critical for the safe and legal use of Fork Lift Boom attachments. By adhering to this guide, organizations ensure operational safety, reduce liability, and extend equipment service life. Regular reviews and updates to this guide are recommended to reflect changes in regulations or equipment specifications.
Conclusion for Sourcing Forklift Boom
In conclusion, sourcing a forklift boom requires a strategic approach that balances equipment compatibility, operational needs, safety standards, and cost-effectiveness. After evaluating various suppliers, models, and customization options, it is evident that selecting a high-quality forklift boom from a reputable manufacturer enhances operational efficiency, improves load-handling capabilities, and ensures compliance with safety regulations. Factors such as lifting capacity, durability, ease of installation, and after-sales support play a crucial role in making an informed procurement decision. Additionally, conducting thorough due diligence and considering long-term maintenance and total cost of ownership will contribute to a sustainable and productive material handling solution. Ultimately, investing in the right forklift boom not only optimizes performance but also supports workplace safety and operational reliability.