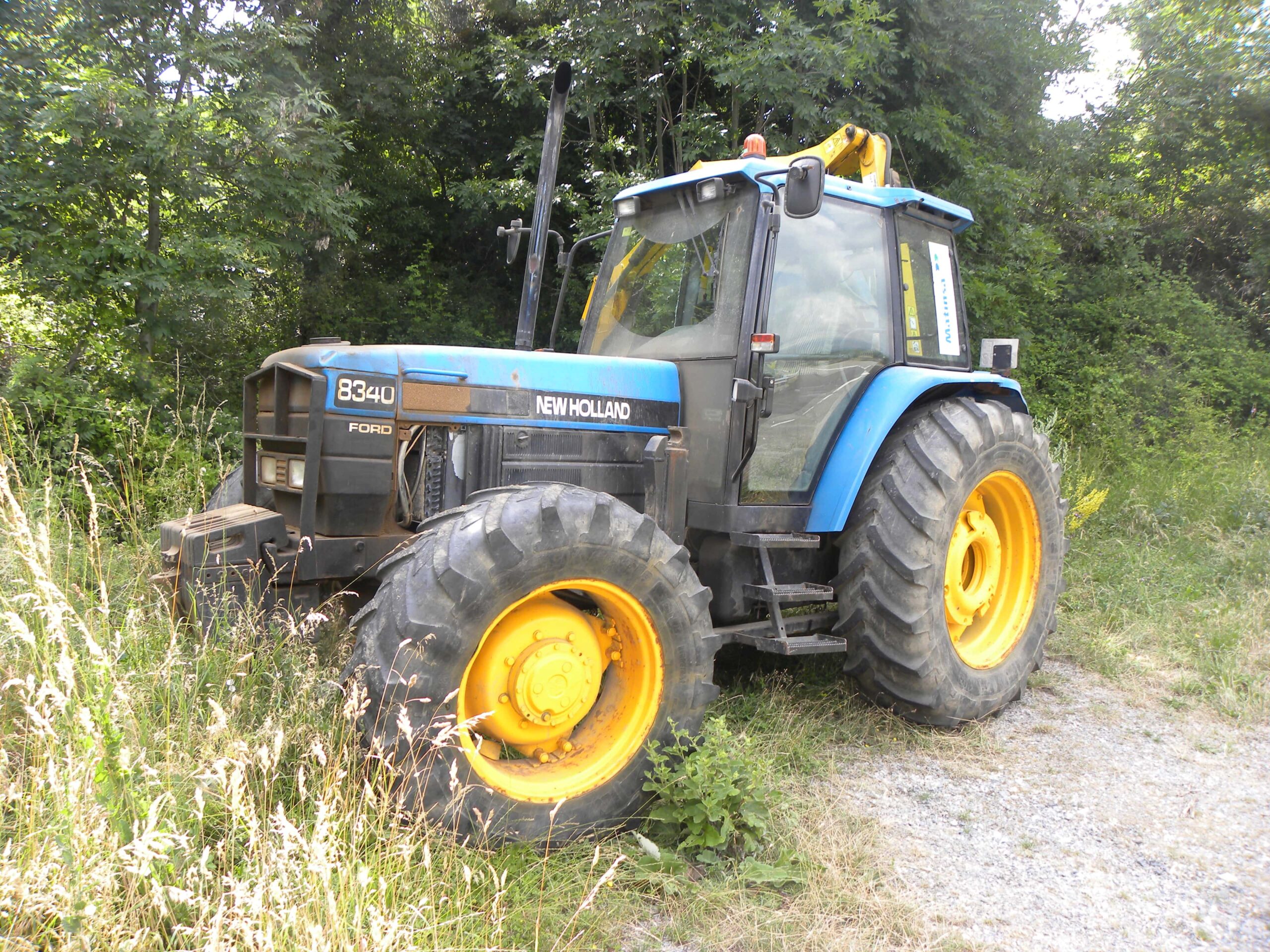
The global agricultural machinery market is undergoing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for efficient farming equipment and increasing adoption of mechanized practices. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 161.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% through 2029. As one of the leading integrated agricultural equipment manufacturers worldwide, Ford New Holland Agriculture—a key player within CNH Industrial—holds a significant share in this growing landscape. Backed by a legacy of innovation and a vast distribution network spanning over 170 countries, Ford New Holland contributes to advancements in tractors, harvesters, and precision farming technologies. This positions the brand among the top five manufacturers in the sector, alongside industry giants like John Deere, CLAAS, and AGCO. With increasing emphasis on sustainable agriculture and smart farming solutions, companies like Ford New Holland are at the forefront of shaping the future of global food production.
Top 5 Ford New Holland Agriculture Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 OEM New Holland Parts & Accessories (In
Domain Est. 2000
Website: messicks.com
Key Highlights: Messick’s has industry’s largest ready-to-ship, in-stock New Holland parts inventory with more than 250000 pieces. We ship nationwide, browse today!…
#2 New Holland Agriculture Genuine Parts
Domain Est. 2019
Website: mycnhstore.com
Key Highlights: Get Genuine OEM Parts and Replacement Parts for New Holland AG. Discover special offers and seasonal sales and events….
#3 Ford
Website: farmingsimulator.wiki.gg
Key Highlights: Ford Tractor Company (or just Ford), which also known as Ford-New Holland, is a licensed North American tractor manufacturer first featured in Farming Simulator ……
#4 to our World
Domain Est. 1997
Website: newholland.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to the World of New Holland. Choose your Industry (Agriculture or Construction), your Market and your Language, and start browsing the website….
#5 Agricultural Equipment & Farm Machinery
Domain Est. 1997
Website: agriculture.newholland.com
Key Highlights: World leader in the field of agricultural machinery including agricultural tractors, combines, grape harvesters, hay balers & much more….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ford New Holland Agriculture

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ford New Holland Agriculture
As Ford New Holland Agriculture (a brand under CNH Industrial) navigates the agricultural machinery sector toward 2026, several key market trends are expected to shape its strategic direction, product development, and market positioning. These trends reflect broader shifts in technology, sustainability, regulatory environments, and global demand dynamics.
1. Accelerated Adoption of Precision Agriculture and Digital Farming
By 2026, precision agriculture is projected to become standard practice across major agricultural regions. Ford New Holland Agriculture is expected to deepen integration of GPS-guided systems, telematics, and data analytics into its equipment lineup. The brand’s emphasis on smart farming solutions—such as real-time yield monitoring, variable rate technology (VRT), and farm management software (e.g., CLAAS CEMIS or interoperable platforms)—will allow farmers to optimize inputs, reduce waste, and increase productivity. Partnerships with agritech firms and cloud-based data platforms will enhance the value proposition of New Holland’s connected machinery.
2. Expansion of Sustainable and Low-Carbon Technologies
With increasing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for sustainable practices, Ford New Holland Agriculture is likely to accelerate its shift toward low-emission and alternative fuel solutions by 2026. The brand’s existing commitment to the “Clean Energy Leader” initiative—highlighted by methane-powered tractors like the T6 Methane—will expand further. Expect broader commercialization of biogas, electric, and hybrid-electric models tailored for mid-to-heavy-duty applications. These innovations align with EU Green Deal objectives, U.S. EPA emissions standards, and carbon credit programs, positioning New Holland as a sustainability leader in ag tech.
3. Growth in Emerging Markets and Localization Strategies
In 2026, emerging markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa will represent high-growth opportunities. New Holland is expected to strengthen localized manufacturing, distribution networks, and after-sales support to meet rising demand for mid-range, fuel-efficient, and durable machinery. Tailored product designs—such as compact tractors for smallholder farms and cost-effective harvesting solutions—will be critical. Additionally, financing solutions and government partnerships will play a key role in expanding market penetration in these regions.
4. Focus on Autonomous and Semi-Autonomous Machinery
While full autonomy may still be limited to select applications by 2026, Ford New Holland Agriculture is anticipated to roll out more advanced driver-assist systems (ADAS) and semi-autonomous features across its tractor and harvesting lines. These include automated steering, implement control, and task-specific automation (e.g., auto-guidance during plowing or planting). Such features improve operational efficiency, reduce operator fatigue, and address labor shortages—a growing concern in both developed and developing markets.
5. Circular Economy and Aftermarket Services Expansion
The agricultural sector is increasingly valuing total cost of ownership over initial purchase price. In response, New Holland is expected to enhance its circular economy initiatives—offering remanufactured parts, equipment refurbishment programs, and extended warranties. By 2026, digital platforms for predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and spare parts logistics will become standard, improving uptime and customer loyalty. This shift will strengthen the brand’s service-led revenue model.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Digital Integration
Post-pandemic and geopolitical disruptions have underscored the need for resilient supply chains. By 2026, Ford New Holland Agriculture will likely continue investing in supply chain digitization, nearshoring, and inventory optimization. Blockchain for traceability, AI-driven demand forecasting, and supplier collaboration platforms will play a growing role in ensuring equipment availability and reducing lead times.
Conclusion
By 2026, Ford New Holland Agriculture is poised to leverage technological innovation, sustainability leadership, and global market diversification to maintain competitiveness. The convergence of digital farming, clean energy transition, and customer-centric services will define its market strategy. Success will depend on agile adaptation to regional needs, strong R&D investment, and ecosystem partnerships that drive agricultural productivity in a resource-constrained world.
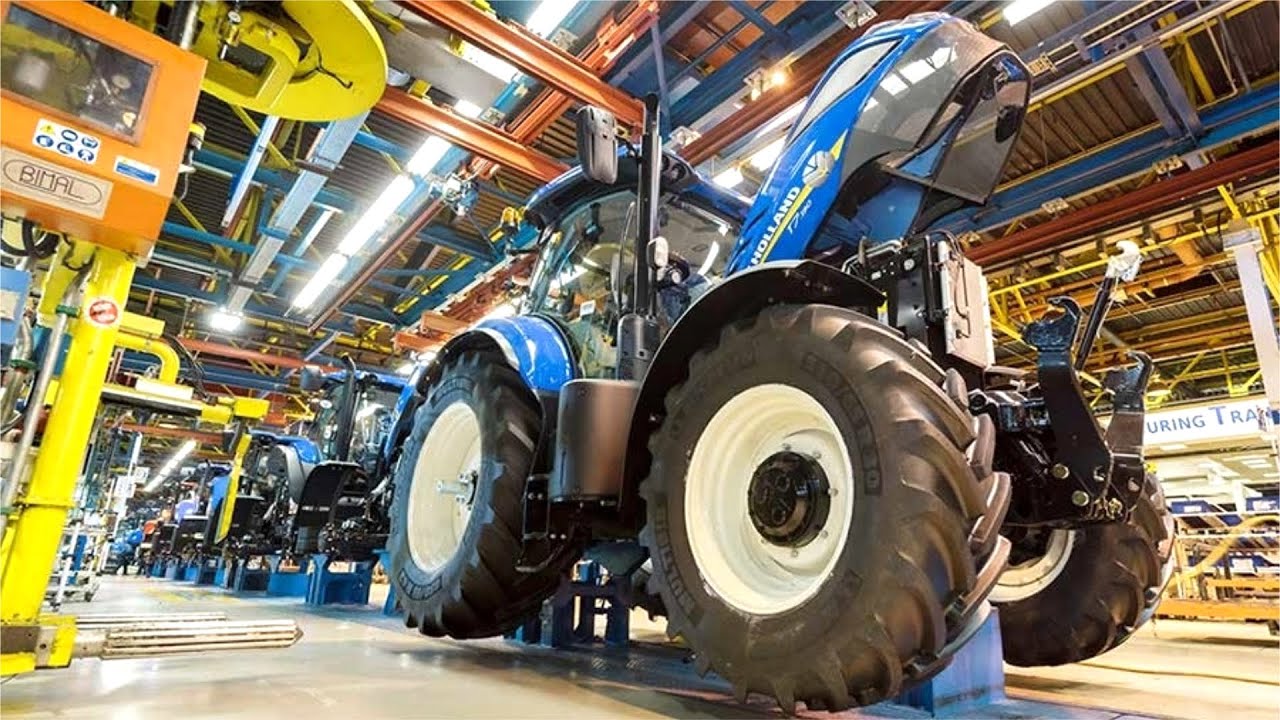

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Ford New Holland Agriculture Equipment (Quality, Intellectual Property)
Sourcing agricultural machinery and parts under the Ford New Holland Agriculture brand—either directly from the manufacturer or through third-party suppliers—can present several challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for distributors, resellers, and OEMs to maintain product integrity, comply with regulations, and protect brand value.
Quality Assurance Risks
One of the most significant concerns when sourcing Ford New Holland Agriculture equipment is maintaining consistent product quality. Unauthorized or non-certified suppliers may offer lower-cost alternatives that appear identical but fail to meet the stringent performance and durability standards set by the manufacturer.
-
Counterfeit or Substandard Parts: The market is rife with counterfeit components that mimic genuine Ford New Holland parts. These may use inferior materials or manufacturing processes, leading to premature failure, equipment downtime, and potential safety hazards.
-
Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards: Third-party manufacturers, especially in regions with less rigorous oversight, may not adhere to the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications. This can result in variations in fit, function, and longevity.
-
Lack of Traceability: Sourcing from unverified channels often means missing documentation, such as batch numbers, certification of conformance, or test reports. Without traceability, it becomes difficult to address quality issues or conduct recalls if necessary.
-
Warranty and Support Limitations: Non-genuine parts or equipment sourced through unofficial channels typically void manufacturer warranties. Customers may also be denied access to technical support, service networks, and software updates.
Intellectual Property Violations
Ford New Holland Agriculture owns extensive intellectual property, including trademarks, patents, and proprietary designs. Sourcing from unauthorized suppliers can inadvertently lead to IP infringement, exposing businesses to legal and financial risks.
-
Trademark Infringement: Using the Ford New Holland name, logo, or branding without authorization—even on compatible or imitation parts—constitutes trademark violation. This includes packaging, marketing materials, and online listings.
-
Patented Technology Use: Many components, such as hydraulic systems, transmission designs, and electronic control units, are protected by patents. Reproducing or selling parts that incorporate these technologies without licensing can result in litigation.
-
Design and Trade Dress Copying: Even if a part is not an exact replica, mimicking the unique appearance or functional design of Ford New Holland parts may breach design patents or trade dress rights.
-
Gray Market Imports: Purchasing genuine equipment or parts from international markets intended for other regions and reselling them domestically can violate distribution agreements and IP licensing terms. While the products may be authentic, unauthorized importation undermines regional IP controls and brand management strategies.
To mitigate these risks, businesses should:
– Source exclusively through authorized dealers or certified partners.
– Request and verify documentation for authenticity and compliance.
– Conduct regular supplier audits and quality inspections.
– Consult legal counsel to ensure adherence to IP laws and distribution agreements.
By proactively addressing quality and intellectual property concerns, companies can safeguard their operations, maintain customer trust, and uphold the reputation associated with Ford New Holland Agriculture products.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ford New Holland Agriculture
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for Ford New Holland Agriculture (FNHA) operations. Adherence to these standards ensures efficient supply chain management, regulatory compliance, and operational excellence across all regions.
Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management is critical to meeting customer demand and maintaining inventory accuracy. All FNHA logistics activities must align with global supply chain strategies and regional requirements.
- Maintain real-time visibility of inventory across manufacturing plants, distribution centers, and dealerships.
- Utilize FNHA-approved transportation management systems (TMS) for shipment planning and tracking.
- Coordinate with suppliers to ensure Just-in-Time (JIT) and Just-in-Sequence (JIS) delivery standards where applicable.
- Conduct regular supply chain risk assessments and implement mitigation strategies.
Transportation & Freight Operations
All freight movements must comply with FNHA policies, carrier agreements, and local regulations to ensure safety, cost efficiency, and on-time delivery.
- Engage only FNHA-qualified carriers who meet safety, insurance, and performance benchmarks.
- Adhere to standardized packaging and loading procedures to prevent product damage.
- Use approved routing guides and freight classification standards (e.g., NMFC, HS codes).
- Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as on-time delivery rate, freight cost per unit, and damage claims.
Customs & International Trade Compliance
Global shipments must conform to international trade laws and customs regulations to avoid delays, fines, or shipment seizures.
- Ensure accurate classification of goods using Harmonized System (HS) codes.
- Prepare and maintain complete export documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Comply with export control regulations (e.g., EAR, ITAR) and economic sanctions (e.g., OFAC, EU sanctions lists).
- Conduct regular training for logistics personnel on changes in trade regulations and Incoterms® (e.g., FOB, DDP).
Regulatory & Environmental Compliance
FNHA operations must meet all applicable environmental, safety, and regulatory standards in every market.
- Follow local and international hazardous materials regulations (e.g., ADR, IMDG, 49 CFR) when shipping batteries, fuels, or lubricants.
- Comply with emissions and vehicle safety standards for owned or leased transport fleets.
- Implement waste reduction and recycling programs in warehouses and distribution centers.
- Maintain records for environmental audits and certifications (e.g., ISO 14001).
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Accurate documentation is essential for traceability, audit readiness, and legal compliance.
- Retain shipping records, customs filings, and compliance certificates for a minimum of seven years.
- Use standardized FNHA forms and digital platforms for data entry and reporting.
- Ensure all documentation is available in required languages and formats per destination country regulations.
- Conduct quarterly audits of logistics records to verify completeness and accuracy.
Training & Continuous Improvement
Ongoing training and process optimization support compliance and operational excellence.
- Provide mandatory compliance training for all logistics and supply chain personnel annually.
- Encourage reporting of compliance concerns through FNHA’s confidential ethics hotline.
- Participate in continuous improvement programs (e.g., Lean, Six Sigma) to reduce waste and enhance efficiency.
- Review logistics performance metrics monthly and adjust strategies as needed.
Adherence to this Logistics & Compliance Guide ensures that Ford New Holland Agriculture maintains the highest standards in global operations, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction. All employees and partners are responsible for understanding and implementing these guidelines.
Conclusion: Sourcing Ford/New Holland Agricultural Equipment
In conclusion, sourcing agricultural machinery from Ford and New Holland—both historically significant brands in the farming industry—offers a strategic advantage for farmers and agribusinesses seeking reliable, durable, and technologically advanced equipment. While Ford exited the agricultural machinery market decades ago, its legacy lives on through the foundation it laid for modern farm equipment. New Holland, as a continuation and evolution of that heritage, has positioned itself as a global leader in agricultural innovation, offering a comprehensive range of tractors, harvesters, and precision farming technologies.
Sourcing from New Holland today ensures access to high-performance machinery backed by extensive dealer support, parts availability, and service networks worldwide. The brand’s commitment to sustainability, fuel efficiency, and smart farming solutions further enhances its value proposition. For stakeholders evaluating sourcing options, New Holland stands out as a trusted provider that combines historical expertise with forward-thinking agricultural advancements.
Therefore, while Ford’s direct involvement in agriculture is historical, sourcing through the evolved lineage via New Holland Agriculture represents a prudent, future-ready decision for modern farming operations seeking quality, reliability, and innovation.