The global foam rubber sheet market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industries such as automotive, construction, healthcare, and consumer goods. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global flexible polyurethane foam market—of which foam rubber sheets are a key component—was valued at USD 48.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing applications in cushioning, insulation, vibration dampening, and sealing solutions. Additionally, rising awareness of material performance and energy efficiency in emerging economies is accelerating adoption. As the demand for high-performance, customizable foam rubber sheets intensifies, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, combining innovation, scalability, and quality control to meet evolving global standards. Below, we highlight the top 10 foam rubber sheet manufacturers shaping the future of the industry.
Top 10 Foam Rubber Sheet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Foam Factory, Inc.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: foambymail.com
Key Highlights: We proudly offer traditional foam products like cushions, insulation, and packaging materials, as well as memory foam and latex mattresses, toppers, and even ……
#2 Custom Sponge Rubber Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: aerorubber.com
Key Highlights: Aero Rubber Company®, Inc. manufactures sponge rubber products in a variety of elastomers, densities, thicknesses and widths, in both sheets and rolls….
#3 Rubber Products Supplier & Distributor in Portland, Oregon
Domain Est. 1998
Website: rubberresource.com
Key Highlights: Rubber Resources is an industrial converter and fabricator of all types of rubbers, foams, films, and papers, as well as fabrics, adhesives, cork, hook and ……
#4 Closed Cell Foam & Rubber Sheet Stock
Domain Est. 1999
Website: manuf-rubber.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturers Rubber has specialized in closed cell foam & rubber sheet stock for over 18 years. Click to view specifications….
#5 Monmouth Rubber & Plastics
Domain Est. 1999
Website: monmouthrubber.com
Key Highlights: Monmouth Rubber & Plastics has been a U.S. Manufacturer of Durafoam™ closed cell sponge rubber and plastic foam materials for more than 54 years….
#6 Zotefoams
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zotefoams.com
Key Highlights: Zotefoams offers lightweight, high-performance AZOTE and ZOTEK foam solutions for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries….
#7 Sponge Rubber Sheet Supplier
Domain Est. 1997
Website: amfoam.com
Key Highlights: At AM Foam Products, we supply premium rubber sheets tailored to your specifications. Whether you need chemical-resistant, heat-tolerant, or weatherproof ……
#8 Fabricated Foam & Rubber
Domain Est. 1998
Website: insulfab.net
Key Highlights: Insul-Fab offers a wide range of fabricated foam products including neoprene, EPDM, polyethylene, vinyl nitrile, PVC polyurethane, and silicone. Call now!…
#9 Sponge & Foam Materials
Domain Est. 2013
Website: therubbercompany.com
Key Highlights: The Rubber Comany can supply a wide selection of rubber sponge and foam materials in a variety of grades, densities, thicknesses and formats to suit you….
#10 Viton™ Sponge Sheets
Domain Est. 2014
Website: j-flex.com
Key Highlights: We supply a vast range of quality items including rubber sheet and an array of fabrications made from premium grade elastomers including silicone and Viton™ – ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Foam Rubber Sheet
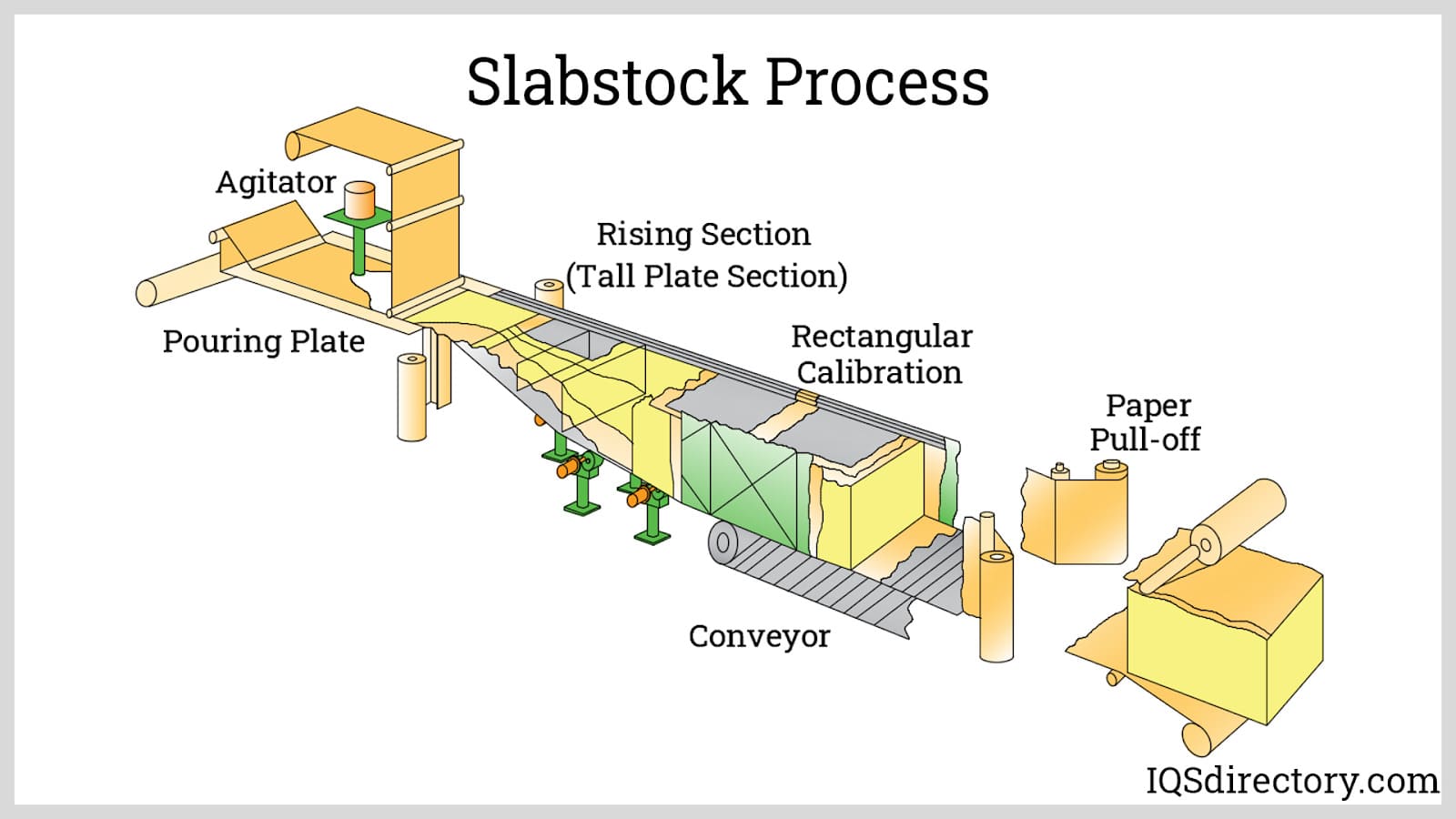
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Foam Rubber Sheet
The global foam rubber sheet market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by rising demand across diverse industrial and consumer sectors. Key trends shaping the market include technological advancements in material performance, increasing focus on sustainability, and expanding applications in automotive, construction, healthcare, and consumer goods industries.
One of the most significant trends is the shift toward eco-friendly and recyclable foam rubber materials. With growing environmental regulations and consumer awareness, manufacturers are investing in bio-based and low-emission foam rubber solutions. This includes the development of foam rubber sheets using natural rubber blends and non-toxic blowing agents, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In the automotive sector, foam rubber sheets are increasingly used for insulation, sealing, and vibration damping. As electric vehicles (EVs) gain market share, demand for lightweight, durable, and sound-absorbing materials is rising—foam rubber sheets meet these requirements effectively. The construction industry also contributes to growth, especially in emerging economies, where foam rubber is used in HVAC systems, roofing, and acoustic insulation due to its thermal and noise control properties.
Technological innovation is another driver. Enhanced formulations offering improved resistance to UV, ozone, and extreme temperatures are expanding the usability of foam rubber sheets in outdoor and industrial environments. Closed-cell foam rubber, known for its water resistance and durability, is seeing increased adoption in marine and transportation applications.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the market by 2026, fueled by rapid urbanization, industrialization, and infrastructure development in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations. North America and Europe are focusing on product differentiation and compliance with stringent environmental standards, such as REACH and RoHS.
In conclusion, the 2026 foam rubber sheet market will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and diversification of applications. Companies that prioritize R&D, environmental compliance, and strategic partnerships are likely to gain competitive advantage in this evolving landscape.
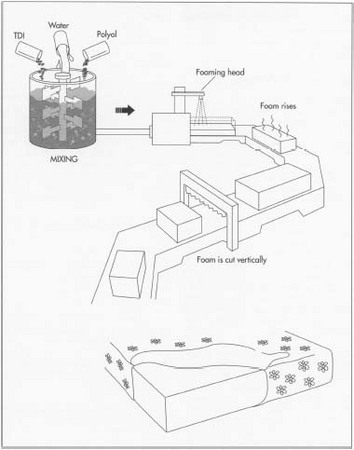
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Foam Rubber Sheet (Quality, IP)
Sourcing foam rubber sheets involves navigating several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning material quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these can lead to product failures, supply chain disruptions, legal issues, or reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Specifications
Suppliers may provide foam rubber sheets with varying densities, hardness (durometer), thickness tolerances, or cell structures. Without clear, enforceable specifications and third-party testing, inconsistencies can affect performance in critical applications such as sealing, cushioning, or insulation.
Poor Environmental and Chemical Resistance
Not all foam rubbers perform equally under exposure to UV, ozone, oils, or extreme temperatures. Sourcing without verifying resistance data for the intended application can result in premature degradation or failure, especially with low-cost or uncertified materials.
Use of Recycled or Substandard Raw Materials
Some suppliers cut costs by using high percentages of recycled content or inferior-grade polymers (e.g., reclaimed rubber, off-spec batches). This compromises physical properties like tensile strength, compression set, and long-term durability.
Inadequate Certifications and Testing Documentation
Lack of standardized testing reports (e.g., ASTM, ISO) or certifications (e.g., UL, FDA, RoHS) increases the risk of non-compliance in regulated industries. Buyers may unknowingly receive materials unsuitable for food contact, medical use, or flammable environments.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Compliance Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Formulations
Some manufacturers may reverse-engineer or illegally replicate branded foam materials (e.g., imitation EPDM or neoprene blends). Sourcing such materials exposes buyers to IP infringement claims, especially in export markets with strong IP enforcement.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Materials
Suppliers may falsely label generic foams as specialty types (e.g., calling standard polyurethane “high-performance memory foam”). This misrepresentation can mislead engineers and result in product liability issues.
Lack of Supply Chain Transparency
Opaque sourcing chains make it difficult to verify the origin of raw materials or confirm that no patented technologies are being used without license. This is especially critical when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement.
Non-Compliance with International Standards and Regulations
Using foam rubber that violates regional regulations (e.g., REACH, Prop 65, or TSCA) can lead to shipment rejections, fines, or legal action. Some suppliers may not be aware of or disregard these requirements, especially in less regulated markets.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough supplier audits, require material test reports, specify exact technical requirements, and include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Foam Rubber Sheet
Classification and HS Code
Foam rubber sheets are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) code 4008.21 or 4008.29, depending on the specific type and composition. These codes apply to unvulcanized or vulcanized rubber sheets, whether or not surface-coated or reinforced, but without backing. Accurate classification is crucial for determining import duties, taxes, and regulatory requirements in the destination country. Always verify the correct HS code with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker, as misclassification may result in delays, fines, or shipment rejection.
Regulatory Compliance
Foam rubber sheets may be subject to various international and national regulations, particularly concerning fire safety, environmental impact, and chemical content. Key compliance standards include:
- REACH (EU): Ensure the product is compliant with Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals regulations, especially regarding Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
- RoHS (EU): Applicable if the foam rubber contains electrical or electronic components; restricts hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium.
- California Proposition 65 (USA): Requires warning labels if the product contains chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm.
- CPSIA (USA): If intended for children’s products, compliance with phthalates and lead content limits may be required.
- Fire Safety Standards: Foam rubber may need to meet flammability requirements such as FMVSS 302 (automotive), BS 5852 (UK), or ASTM E84 (USA), depending on the application.
Manufacturers and importers must obtain material safety data sheets (MSDS/SDS) and ensure proper documentation is available upon request.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent physical damage, moisture exposure, and contamination during transit. Recommended practices include:
- Wrap sheets in moisture-resistant plastic or kraft paper to protect against humidity.
- Use protective corner boards or edge protectors for stacked sheets to avoid crushing.
- Securely bundle or palletize materials to prevent shifting during transport.
- Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack”, “Protect from Moisture”).
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight and extreme temperatures during storage and transport, as foam rubber can degrade under UV radiation and thermal stress.
Transportation Considerations
Foam rubber sheets are generally non-hazardous and can be shipped via air, sea, or land freight. However, due to their low density and compressibility, they may be subject to volumetric (dimensional) weight calculations, especially in air freight. Key points include:
- Optimize packaging to minimize unused space and reduce freight costs.
- Declare accurate dimensions and weight to avoid billing adjustments.
- Use appropriate incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) to clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.
- For international shipments, ensure all required export documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin) is complete and accurate.
Import and Customs Clearance
Successful customs clearance requires thorough documentation and adherence to destination country regulations. Essential documents typically include:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin (may be required for preferential tariff treatment)
- Import License (if applicable)
- Test Reports or Compliance Certificates (e.g., fire safety, REACH)
Ensure that foam rubber sheets are not restricted or prohibited in the destination market. Some countries may have specific labeling requirements (e.g., country of origin, material content) that must be met prior to entry.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Foam rubber is often derived from synthetic polymers and may not be biodegradable. Disposal must comply with local waste management laws. In many regions:
- Foam rubber is classified as non-hazardous waste but may require disposal at licensed facilities.
- Recycling options may be limited; check with local recyclers for accepted materials.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) regulations may apply in the EU and other jurisdictions, requiring producers to manage end-of-life product take-back.
Consider sustainability by sourcing foam rubber from manufacturers with environmental management systems (e.g., ISO 14001) and recyclable or low-VOC formulations.
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure smooth logistics and compliance for foam rubber sheet shipments:
- Confirm the correct HS code and regulatory requirements for the destination country.
- Maintain up-to-date compliance documentation and test reports.
- Use protective, space-efficient packaging.
- Partner with experienced freight forwarders and customs brokers.
- Monitor regulatory changes, especially in target markets.
- Implement traceability and quality control processes throughout the supply chain.
Adhering to this guide will help minimize risks, reduce delays, and support responsible trade practices for foam rubber sheet products.
In conclusion, sourcing foam rubber sheets requires a careful evaluation of material specifications, supplier reliability, cost efficiency, and intended application requirements. Factors such as foam density, thickness, temperature resistance, durability, and compliance with industry standards play a crucial role in selecting the right product. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers, considering both domestic and international options, can help ensure consistent quality and timely delivery. Additionally, balancing cost with performance and sustainability goals will contribute to a successful sourcing strategy. Ultimately, a well-informed and strategic approach to sourcing foam rubber sheets supports improved product quality, operational efficiency, and long-term cost savings.