The global flexible magnetic materials market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand across automotive, electronics, HVAC, and renewable energy sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 3.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2028. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of compact, lightweight magnetic solutions in electric vehicles and consumer electronics, where flexibility, ease of integration, and cost-efficiency are paramount. Grand View Research further supports this trajectory, noting that advancements in bonded magnet technologies—particularly those based on neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) and strontium ferrite—are enhancing performance in high-temperature and miniaturized applications. As industries prioritize energy efficiency and design versatility, flexible magnetic manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation. Below are nine leading companies shaping this dynamic landscape through scalable production, R&D investment, and strategic global outreach.
Top 9 Flexible Magnetic Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Professional Flexible Magnetic Products Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2013
Website: flexiblemagnetchina.com
Key Highlights: Flexible Magnet (China) Co., Ltd, is a professional manufacturer specialized in producing Flexible Magnetic materials and related products. When you need ……
#2 Magnum Magnetics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: magnummagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Magnum Magnetics is the largest flexible magnet manufacturer in the United States, including printable magnetic sheeting and magnetic rolls, magnetic strips, ……
#3 Top Flexible Magnet Manufacturers & Suppliers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jasdi.com
Key Highlights: Looking for trusted flexible magnet suppliers? JASDI offers high-quality flexible magnetic sheets and rolls with 40+ years of experience….
#4 Flexible Magnetic Strips
Domain Est. 1995
Website: magnetics.com
Key Highlights: In stock $2.30 deliveryFlexible magnetic strips are made of a Ferro-Magnetic powder mixed with a polymer bonding. These high energy strips resist demagnetization and will not chip,…
#5 Flexible Magnets
Domain Est. 1997
Website: adamsmagnetic.com
Key Highlights: Adams Magnetic Products provides high-quality, customizable flexible magnets that meet exacting and demanding engineering specifications….
#6 Magnets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: magnetshop.com
Key Highlights: Magnet shop is an industry leading magnets supplier for high-quality, rare-earth and permanent magnets in assorted shapes, sizes and premium grades….
#7 Flexible Magnets & Products
Domain Est. 2001
Website: arnoldmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture the highest-quality flexible magnetic sheets, strips, tape and extrusions. Ideal applications for our printable, flexible-magnet products ……
#8 Flexible magnets and materials for signage and display applications
Domain Est. 2002
Website: eclipsemagnetics.com
Key Highlights: We offer a comprehensive range of magnets and magnetic products to meet the marketing and advertising needs for Point of Sale displays, packaging products and ……
#9 MAGHOLD LLC large format PET printable magnet media
Domain Est. 2008
Website: maghold.com
Key Highlights: MAGHOLD LLC is an international supplier of magnetic products: flexible magnets, receptive, neodymium and finished magnet products….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Flexible Magnetic
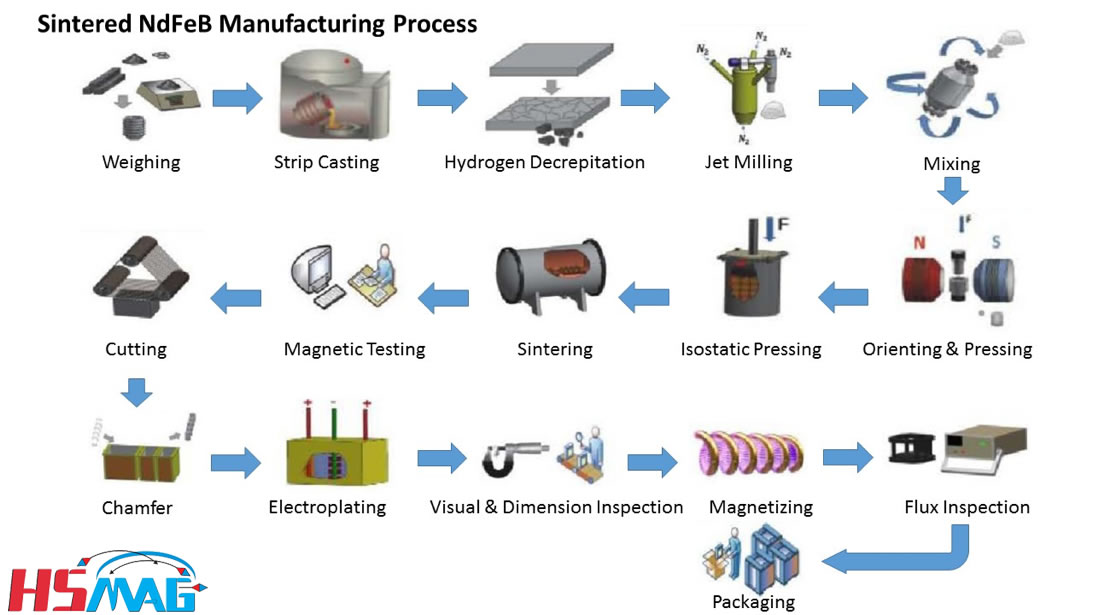
H2: Market Trends for Flexible Magnetic Materials in 2026
As we approach 2026, the global flexible magnetic materials market is undergoing significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, evolving industry demands, and increasing sustainability initiatives. Flexible magnetic materials—comprising rubber-like magnetic sheets composed of magnetic powders (typically strontium or barium ferrite) embedded in polymeric binders—are experiencing growth across diverse applications, including consumer electronics, automotive, signage, renewable energy, and smart home technologies.
1. Rising Demand in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Automotive Applications
The automotive sector remains a key growth driver. With global EV adoption accelerating due to government regulations and consumer demand for sustainable transport, flexible magnets are increasingly used in sensors, motors, gaskets, and interior trim components. Their lightweight nature, design flexibility, and electromagnetic compatibility make them ideal for modern EV systems. By 2026, the integration of flexible magnets in battery management systems and motor encoders is expected to rise significantly.
2. Expansion in Consumer Electronics and IoT Devices
Flexible magnetic materials are being adopted in compact, high-efficiency electronic devices such as wearables, foldable smartphones, and smart home sensors. Their ability to conform to curved surfaces and resist mechanical stress supports miniaturization trends. In H2 2026, increased deployment in magnetic latches, wireless charging alignment systems, and reed switches for IoT applications is anticipated, particularly in North America and Asia-Pacific markets.
3. Growth in Renewable Energy and Smart Infrastructure
Flexible magnets are finding new uses in solar inverters, wind turbine sensors, and smart grid components. As renewable energy infrastructure expands globally, demand for cost-effective, corrosion-resistant magnetic solutions will grow. Additionally, smart building technologies—such as magnetic door/window sensors and automated HVAC systems—are integrating flexible magnets for improved reliability and ease of installation.
4. Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to develop lead-free, recyclable, and bio-based flexible magnetic composites. By H2 2026, companies are expected to commercialize eco-friendly formulations using recycled ferrite powders and biodegradable polymer matrices. This shift aligns with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals and is particularly strong in Europe and Japan.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific continues to dominate production and consumption, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, due to robust electronics and automotive manufacturing. However, North America is witnessing rapid growth due to reshoring of electronic production and EV investments under policies like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act. Meanwhile, Europe’s demand is fueled by green technology incentives and smart city developments.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Sourcing
Concerns over rare earth supply volatility are leading to increased R&D in ferrite-based flexible magnets as cost-effective alternatives to rare-earth magnets. By H2 2026, diversification of raw material sourcing and localized manufacturing are expected to enhance supply chain resilience, particularly in response to geopolitical risks.
Conclusion
By the second half of 2026, the flexible magnetic materials market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6.5–7.5% since 2023. Innovation in material science, coupled with expanding applications in high-tech and green industries, will position flexible magnets as critical enablers of next-generation technologies. Companies investing in scalable, sustainable, and application-specific solutions are likely to capture significant market share in this evolving landscape.
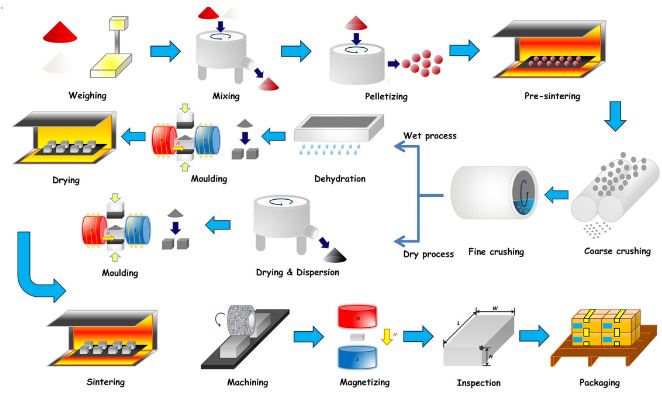
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Flexible Magnetic Material (Quality, IP)
Sourcing flexible magnetic material—commonly used in signage, displays, gaskets, and industrial applications—can be riddled with challenges, particularly when it comes to ensuring consistent quality and protecting intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to product failures, legal disputes, and increased costs. Below are key areas to watch:
Quality Inconsistencies
Flexible magnetic sheets and rolls are manufactured using a mixture of magnetic particles (typically barium or strontium ferrite) in a polymer binder (often PVC or rubber). Variability in raw materials, manufacturing processes, and supplier standards often results in inconsistent product quality.
- Inconsistent Magnetic Strength: Suppliers may use different loadings of magnetic particles, resulting in variable pull force and performance. Low-quality batches may lose magnetism over time or fail to adhere reliably.
- Dimensional Tolerances: Thickness, width, and flatness can vary significantly between batches, affecting fit and function in precision applications.
- Surface Finish and Printability: Poor surface coating leads to ink adhesion issues during printing, causing smudging or peeling in graphic applications.
- Durability Issues: Inferior materials may degrade under UV exposure, heat, or mechanical stress, leading to cracking, warping, or demagnetization.
- Lack of Testing and Certification: Many suppliers do not provide verifiable test data (e.g., Gauss readings, peel strength, thermal stability), making it difficult to ensure compliance with technical specifications.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
When sourcing custom magnetic components or formulations, especially from overseas suppliers, protecting proprietary designs, formulations, or applications is critical.
- Design and Tooling Theft: Suppliers may replicate custom dies, molds, or product designs and sell them to competitors without authorization.
- Reverse Engineering: Flexible magnetic products with unique performance characteristics (e.g., high-coercivity compounds) can be reverse-engineered if not properly protected.
- Weak Contractual Protections: Inadequate or unenforceable non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and intellectual property clauses in supply contracts can leave your innovations exposed.
- Lack of IP Enforcement in Jurisdictions: Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of unauthorized production and distribution of your product.
- Unlicensed Use of Patented Technologies: Some suppliers may use patented magnetic compounds or manufacturing methods without proper licensing, potentially exposing your company to infringement claims.
Mitigation Strategies
- Qualify Suppliers Rigorously: Audit manufacturing facilities, request material test reports, and conduct sample performance testing.
- Specify Clear Technical Requirements: Define magnetic strength (Gauss, pull force), thickness tolerances, environmental resistance, and compliance standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH).
- Secure Strong Legal Agreements: Use comprehensive NDAs, IP ownership clauses, and contracts with clear remedies for breaches.
- Limit Access to Sensitive Information: Share only essential technical details and consider modular designs to protect core innovations.
- Monitor Supply Chain Continuously: Conduct periodic quality audits and maintain alternative supplier options to reduce dependency.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, technical clarity, and proactive IP management throughout the sourcing process.
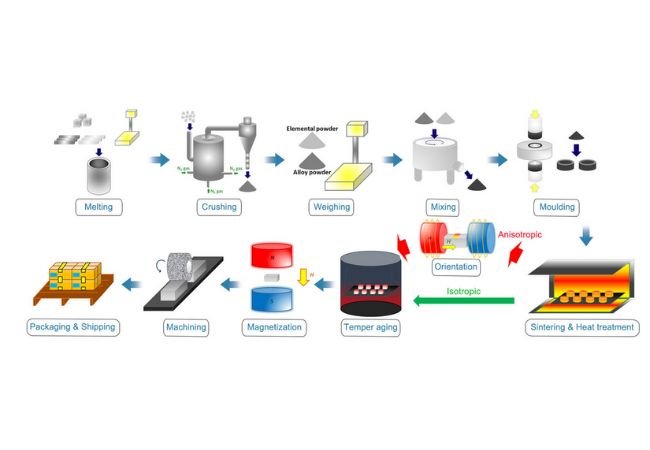
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Flexible Magnetic Materials
Flexible magnetic materials, commonly used in signage, displays, gaskets, and industrial applications, require specific handling, shipping, and regulatory considerations due to their unique physical and magnetic properties. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance protocols to ensure safe, legal, and efficient transportation and storage.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Flexible magnetic products are typically classified under international and national regulations based on composition and magnetic strength. Accurate classification ensures proper handling and customs clearance.
- HS Code Identification: Confirm the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code for flexible magnetic sheeting or rolls (e.g., 8505.20 for permanent magnets in semi-finished form). This ensures correct customs duties and import/export compliance.
- REACH and RoHS Compliance: Verify that magnetic materials comply with EU REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives, particularly regarding phthalates, lead, or other restricted substances.
- TSCA Compliance (U.S.): Ensure compliance with the U.S. Toxic Substances Control Act, especially when importing into North America.
- SDS Availability: Maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheets (SDS) detailing composition, handling precautions, and environmental impact, even if the material is generally non-hazardous.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents damage, demagnetization, and safety risks during transit.
- Roll Protection: Store and ship flexible magnetic rolls on durable cores (typically 3″ or 6″) and cap both ends to prevent edge damage and core collapse.
- Flattening for Sheets: When shipping cut sheets, interleave with kraft paper or low-tack film and stack flat within rigid containers to avoid curling and creasing.
- Magnetic Shielding: Avoid direct contact with sensitive electronic devices, credit cards, or pacemakers. Use non-magnetic packaging materials (e.g., cardboard, plastic) and avoid ferrous metals in packaging.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages as “Flexible Magnetic Material,” “Keep Flat,” and “Avoid High Heat” to guide handling.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Flexible magnetic materials are generally non-hazardous but may be subject to special handling due to their physical properties.
- Non-DG Classification: Most flexible magnetic products are not classified as Dangerous Goods (DG) under IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations, provided magnetic field strength is below regulatory thresholds (e.g., 0.159 A/m at 2.1 meters for air transport).
- Magnetic Field Testing: For large shipments or rolls with strong magnetic properties, conduct a magnetic field test per IATA Packing Instruction 953 to confirm non-regulated status.
- Temperature Control: Avoid exposure to temperatures above 80°C (176°F), which may cause demagnetization or delamination. Ship in climate-controlled environments when necessary.
- Stacking and Loading: Do not stack heavy items on magnetic rolls or sheets. Use edge protectors and ensure secure strapping on pallets to prevent shifting.
Import/Export Compliance
Cross-border shipments require adherence to country-specific regulations.
- Customs Declarations: Provide accurate product descriptions, weight, dimensions, and value. Include certification of origin if claiming preferential tariffs.
- Country-Specific Restrictions: Check for import restrictions in destination countries (e.g., China, India) regarding magnetic or plastic-based materials.
- Labeling in Local Language: For consumer-facing products, ensure compliance with local labeling laws, including language, safety warnings, and recycling symbols.
Storage Best Practices
Proper storage maintains product integrity and operational safety.
- Environment: Store in a dry, cool area (15–25°C / 59–77°F) away from direct sunlight and sources of heat.
- Orientation: Keep rolls stored vertically on end caps to prevent deformation. Store sheets flat on racks.
- Separation: Keep away from strong magnetic fields, electronic equipment, and ferromagnetic materials to prevent unintended attraction or interference.
- Shelf Life: Most flexible magnetic materials have a shelf life of 3–5 years; rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices.
Sustainability and Disposal
Environmental responsibility is increasingly important in logistics operations.
- Recyclability: Confirm whether the magnetic material (typically PVC or rubber-based with ferrite powder) is recyclable in local waste streams. Provide disposal guidance to customers.
- Waste Handling: Follow local regulations for industrial waste disposal. Avoid incineration if materials contain halogens or heavy metals.
- Eco-Friendly Options: Consider sourcing RoHS-compliant or bio-based magnetic alternatives to meet sustainability goals.
Summary
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures the safe, efficient, and legal handling of flexible magnetic materials across the supply chain. Key focus areas include regulatory alignment, proper packaging, non-hazardous shipping protocols, and responsible end-of-life management. Regular review of international regulations and customer requirements is recommended to maintain compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Flexible Magnetic Material
Sourcing flexible magnetic material requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, lead times, and supplier reliability. These materials, commonly used in signage, displays, gaskets, and various industrial applications, offer versatility due to their lightweight, easy-to-cut nature and ability to adhere magnetically to steel surfaces. When sourcing, it is essential to clearly define technical requirements such as magnetic strength (gauss rating), thickness, adhesive backing, temperature resistance, and environmental durability.
The global supply landscape offers numerous options, including manufacturers in Asia, North America, and Europe, each with varying price points and quality standards. Establishing long-term partnerships with certified suppliers who adhere to industry standards ensures consistent product performance and supply chain resilience. Additionally, factors like customization capabilities, minimum order quantities, and logistics should be evaluated to meet specific project demands efficiently.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of flexible magnetic material hinges on thorough supplier evaluation, clear specifications, and ongoing quality assurance. By focusing on these elements, businesses can secure reliable, cost-effective, and high-performing magnetic solutions that support their operational and strategic goals.