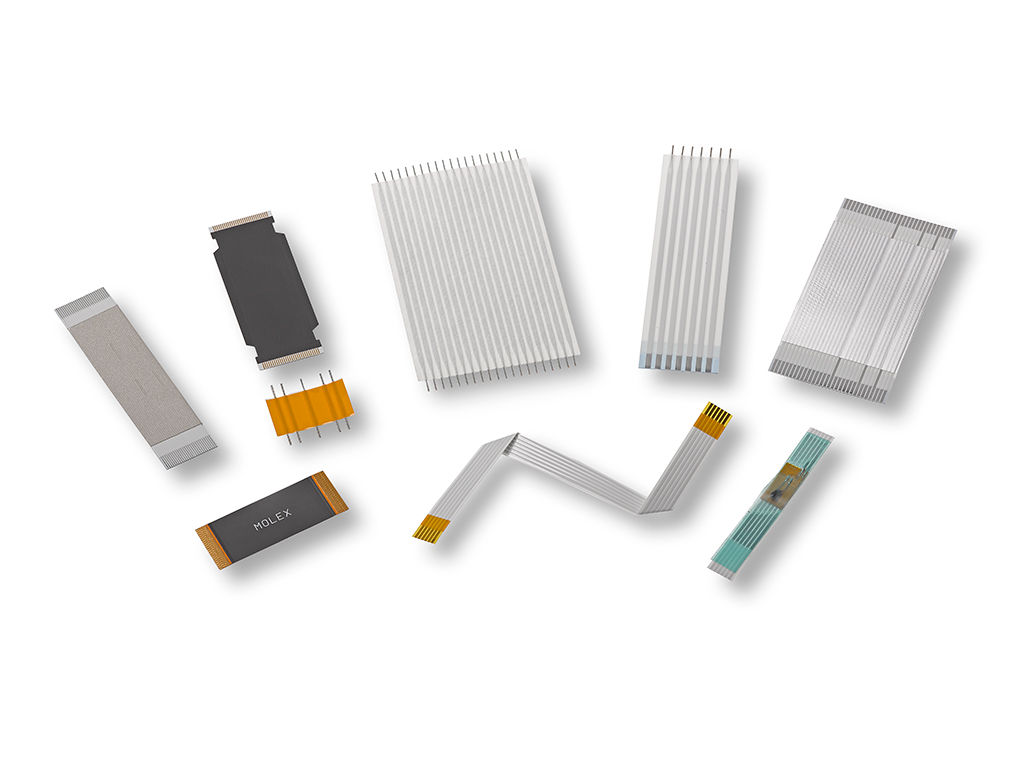
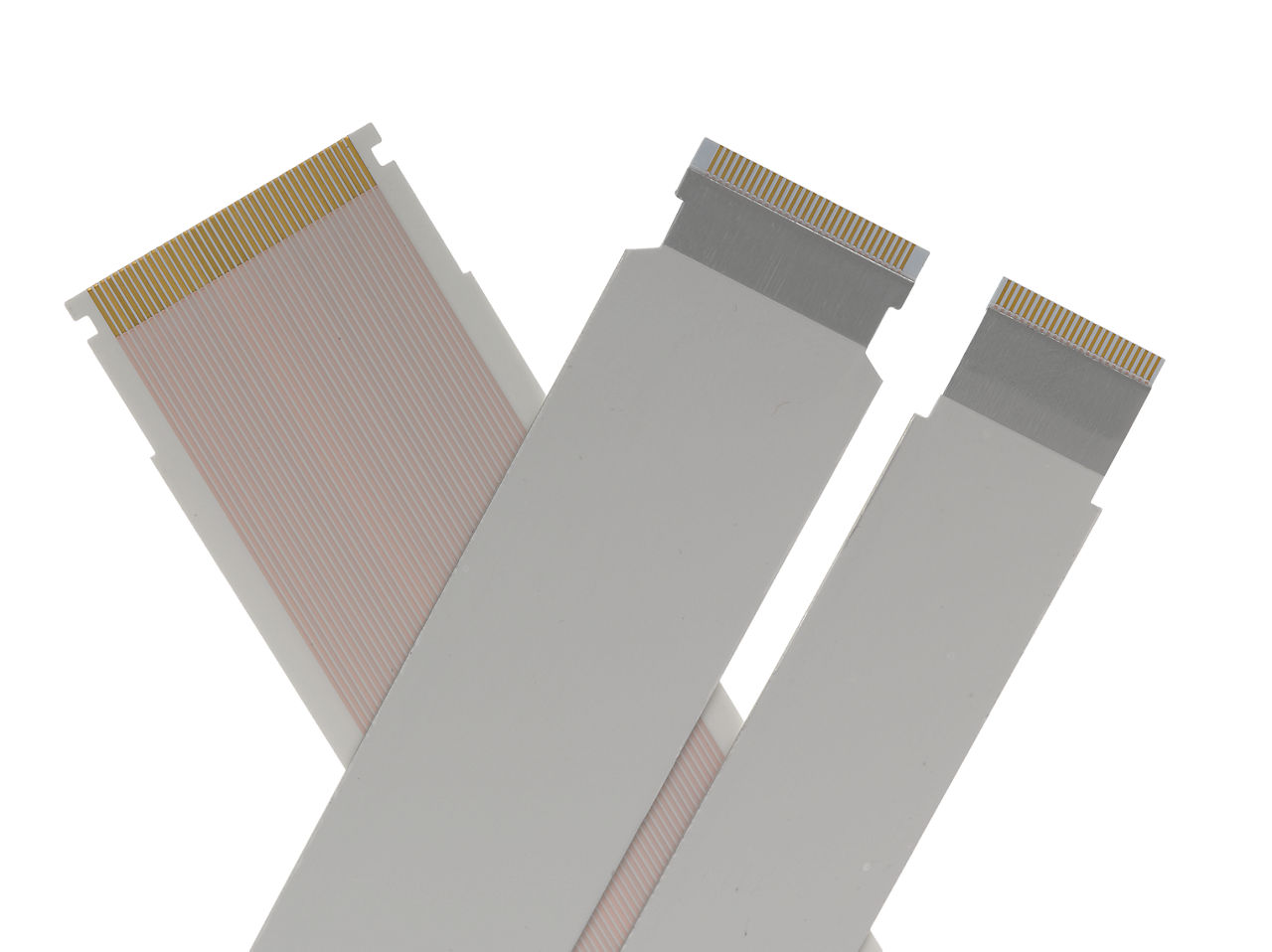
The global Flexible Flat Cable (FFC) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for compact, lightweight, and high-performance interconnection solutions across consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, and industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the global flexible printed circuit (FPC) and FFC market was valued at USD 14.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 6.5% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, fueled by the proliferation of wearable devices, foldable smartphones, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) in vehicles. As manufacturers strive to meet the evolving requirements for space-saving and durable cable solutions, a select group of suppliers have emerged as leaders in innovation, quality, and global reach. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 9 FFC manufacturers shaping the future of flexible interconnect technology.
Top 9 Flexible Flat Cable Ffc Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FFC Flexible
Domain Est. 1998
Website: tw.hamburg.com.tw
Key Highlights: HAMBURG Flexible Flat Cable is a high-quality FFC with compact, lightweight and thin properties. HAMBURG Flexible Flat Cable is soft and ……
#2 What is Flat Flexible Cable?
Website: wavelinkcable.com
Key Highlights: Wavelink FFC is a laminated cable consisting of 1 or more flat conductors laid parallel on a specified pitch and laminated between two layers of dielectric….
#3 Premo
Domain Est. 1994
Website: molex.com
Key Highlights: 5-day returnsPremo-Flex FFC/FPCs offer reliable, durable and flexible board-to-board and board-to-display connections that reduce assembly weight and size requirements….
#4 Flat Flexible Cable Systems, ZIF Connectors and Jumpers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: samtec.com
Key Highlights: Flat Flexible Cable systems and jumpers featuring 0.50 mm (.0197″) and 1.00 mm (.0394″) pitch systems with standard and zero insertion force (ZIF) connectors….
#5 Flat Flexible Cable (FFC)
Domain Est. 1996
Website: johnsonelectric.com
Key Highlights: Parlex has years of expertise with a wide range of laminated flexible flat cable to provide superior reliability solutions in dynamic flex and service loop ……
#6 Bulk flexible flat cables
Domain Est. 1996
Website: axon-cable.com
Key Highlights: Axon’ Flat flexible cables are designed for board-to-board connections in electronic systems. From 0.30 mm to 1.25 mm pitch, Axon’ Flat Flexible Cables (FFC) ……
#7 FFC cables
Domain Est. 1997
Website: configurator.nicomatic.com
Key Highlights: FFC cables are made with conductive copper laminated between 2 layers of polyester, with thermic adhesive increasing life expectancy….
#8 Flat Flexible Cable – FFC
Domain Est. 2010
Website: gct.co
Key Highlights: Click to view GCT’s Flat Flexible Cable (FFC) range, offering 0.5mm and 1.00mm pitches in a variety of styles, including special options such as shielded….
#9 Flat Flexible Cables (FFC)
Domain Est. 2015
Website: picamfg.com
Key Highlights: PICA designs and manufactures Flat Flex Cables (FFCs) for compact, high-speed, and space-sensitive applications. Built with precision flat ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Flexible Flat Cable Ffc
2026 Market Trends for Flexible Flat Cable (FFC)
The Flexible Flat Cable (FFC) market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving technological demands, miniaturization across industries, and the proliferation of connected devices. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
Increasing Demand in Consumer Electronics and Wearables
By 2026, the consumer electronics sector will remain the dominant driver of FFC demand. The relentless push for slimmer, lighter, and more compact devices—such as foldable smartphones, ultra-thin laptops, and advanced wearables—will necessitate high-density, ultra-thin FFCs capable of reliable signal transmission in tight spaces. Innovations in flexible circuitry will enable curved and dynamic designs, supporting the growing adoption of flexible displays and ergonomic wearable devices like smart rings and health-monitoring patches.
Growth in Automotive Electronics and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The automotive industry is undergoing a digital and electric revolution, positioning FFCs as critical components in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment systems, digital instrument clusters, and in-cabin sensing technologies. With the surge in EV production, FFCs are increasingly used in battery management systems (BMS) due to their lightweight nature and efficient space utilization. By 2026, the demand for high-reliability, temperature-resistant FFCs capable of withstanding harsh automotive environments will rise significantly.
Advancements in Miniaturization and High-Speed Data Transmission
As data rates increase with 5G integration and high-resolution imaging, FFCs will need to support higher bandwidths and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). By 2026, manufacturers will focus on developing shielded FFCs and impedance-controlled designs to meet these requirements. The trend toward finer pitch and multi-layer FFCs will accelerate, enabling more connections in smaller footprints—essential for applications in medical devices, robotics, and industrial automation.
Expansion in Industrial Automation and Robotics
The Industry 4.0 transformation will boost FFC adoption in automated manufacturing, collaborative robots (cobots), and smart sensors. FFCs offer superior flexibility and durability in moving parts and robotic joints compared to traditional wiring. By 2026, demand will grow for ruggedized, high-flex-life FFCs that can endure continuous motion and challenging industrial conditions.
Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will drive innovation in eco-friendly FFC materials. By 2026, expect increased use of halogen-free, recyclable, and low-outgassing materials, particularly in automotive and medical applications. Additionally, research into biodegradable substrates and lead-free solder-compatible designs will gain momentum.
Regional Manufacturing Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions will prompt a reevaluation of FFC production locations. By 2026, there will be a notable shift toward regionalization, with increased manufacturing capacity in Southeast Asia, India, and Eastern Europe to reduce dependency on single sources. Investments in automation and smart factories will enhance production efficiency and quality control.
Rising Adoption in Medical and Healthcare Devices
Miniaturized and portable medical equipment—such as wearable diagnostics, endoscopic devices, and hearing aids—will drive FFC demand due to their space-saving design and reliability. By 2026, biocompatible and sterilizable FFC variants will see growing adoption, supported by stringent regulatory compliance and advances in medical electronics.
In summary, the 2026 FFC market will be characterized by technological innovation, diversification across high-growth industries, and a strong emphasis on performance, reliability, and sustainability. Companies that invest in R&D, adapt to evolving application needs, and ensure supply chain agility will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Flexible Flat Cables (FFC) – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Flexible Flat Cable (FFC)
Overview of Flexible Flat Cable (FFC)
Flexible Flat Cables (FFCs) are thin, flat electrical cables commonly used in compact electronic devices such as laptops, printers, smartphones, and medical equipment. Their lightweight and space-saving design make them ideal for high-density interconnects. However, due to their delicate construction and use in regulated industries, proper logistics handling and compliance adherence are essential for safe and legal distribution.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
FFCs are sensitive to mechanical stress, moisture, and electrostatic discharge (ESD). Proper packaging ensures product integrity during transit. Use anti-static bags and moisture barrier packaging (MBB) when necessary, especially for humid environments. Coiled FFCs should be shipped on reels or in rigid containers to prevent kinking or creasing. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “Do Not Bend,” and “ESD Sensitive” to guide handlers. Avoid stacking heavy items on FFC shipments.
Storage Conditions
Store FFCs in a controlled environment with temperatures between 15°C and 30°C and relative humidity below 60%. Keep coils flat or vertically mounted on racks to prevent deformation. Protect from direct sunlight, dust, and corrosive chemicals. Shelf life varies by manufacturer; adhere to first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory practices and monitor expiration dates for moisture-sensitive components.
Transportation Guidelines
Use climate-controlled vehicles for long-distance or international shipments to prevent thermal and humidity damage. Secure packages to avoid movement during transit. For air freight, comply with IATA regulations—ensure packaging meets drop and vibration test standards. Ground transport should minimize sharp turns and sudden stops. Partner with carriers experienced in handling electronic components.
Regulatory Compliance
FFCs must comply with regional and industry-specific regulations. Key standards include:
– RoHS (EU): Restricts hazardous substances like lead, cadmium, and mercury.
– REACH (EU): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
– IPC-620: Specifies acceptability criteria for cable and wire harness assemblies.
– UL/CSA: Safety certification for use in North American markets.
– China RoHS: Similar to EU RoHS but with different labeling requirements.
Ensure suppliers provide compliance documentation such as Declarations of Conformity (DoC), material content sheets, and test reports.
Export and Import Regulations
When shipping FFCs internationally, verify tariff classifications under the Harmonized System (HS Code). Common codes include 8544.42 (flat cables) or 8544.30 (insulated wiring). Complete accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Some countries require additional permits for electronic components. Use Incoterms (e.g., EXW, FOB, DDP) to clarify responsibility for logistics and customs clearance.
Environmental and Safety Standards
FFCs may contain halogen-free materials, especially for applications in confined spaces like public transport or healthcare. Confirm compliance with standards such as IEC 60754 (halogen acid gas emission) and IEC 61249-2-21 (halogen-free printed wiring boards). Properly dispose of defective or excess FFCs according to local e-waste regulations (e.g., WEEE Directive in Europe).
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Maintain full traceability of FFC batches using serial or lot numbers. Implement quality checks upon receipt and before distribution. Audit suppliers regularly for adherence to IPC, ISO 9001, and environmental standards. Keep records of inspections, test results, and non-conformance reports for at least five years.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for Flexible Flat Cables ensures product reliability, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. By following proper packaging, storage, transportation, and documentation practices—and staying updated on international regulations—businesses can minimize risk and support seamless integration of FFCs into electronic systems worldwide.
Conclusion for Sourcing Flexible Flat Cables (FFC):
Sourcing Flexible Flat Cables (FFCs) requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, lead times, and supplier reliability. As critical components in electronics requiring space-saving, reliable interconnections—such as in laptops, mobile devices, medical equipment, and automotive systems—choosing the right FFC supplier is essential for product performance and durability.
Key considerations when sourcing FFCs include verifying the manufacturer’s capabilities in terms of custom design (pitch, length, conductor count), material quality, and adherence to industry standards (e.g., UL, RoHS). Working with suppliers that offer prototyping support and volume production scalability ensures flexibility during product development and launch phases.
Additionally, evaluating lead times, geographic location (for logistics efficiency), and communication responsiveness helps mitigate supply chain risks. Establishing long-term partnerships with qualified suppliers not only enhances consistency in quality but also supports innovation through collaborative engineering support.
In summary, successful FFC sourcing hinges on thorough due diligence, clear technical specifications, and building relationships with trustworthy, technically proficient manufacturers. By focusing on these factors, businesses can secure reliable, high-performance FFCs that meet both technical requirements and production demands.