The global flexible shaft market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision tools across industries such as automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and consumer electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global flexible shaft market size was valued at USD 2.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in material science, rising automation, and the growing need for compact, high-performance power transmission solutions. As industries prioritize durability, versatility, and efficiency, flexible drill shafts have become critical components in both conventional and specialized tooling applications. With this backdrop, selecting the right manufacturer has become more important than ever. Based on production capabilities, innovation, global reach, and industry reputation, we’ve identified the top 10 flexible drill shaft manufacturers shaping the future of industrial tooling.
Top 10 Flexible Drill Shaft Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 GI Industries Custom Flexible Shafts Available up to 200ft or 60 mtrs.
Domain Est. 2001
Website: giind.com
Key Highlights: GI Industries Inc. has a decade of experience in the flexible shaft market with its own custom shop. Call us if you have a unique or difficult application….
#2 Flex
Domain Est. 2007
Website: avaligntech.com
Key Highlights: Flex-Shaft Technology is bi-directional with minimal “wind-up” effect, especially when compared to wound-wire versions. Easily adapted to screwdrivers, taps and ……
#3 Flexible Shaft Drill, Hang
Domain Est. 1996
Website: stoeltingco.com
Key Highlights: A Lab Standard™ drill for over 20 years. The powerful motor and flexible shaft offer very low vibration and noise for long-term, reliable performance….
#4 What are the parts of a flex shaft?
Domain Est. 1997
Website: elliottmfg.com
Key Highlights: Generally, a flex shaft is made up of the following: Core: Wire wound in layers in opposing directions around a center wire….
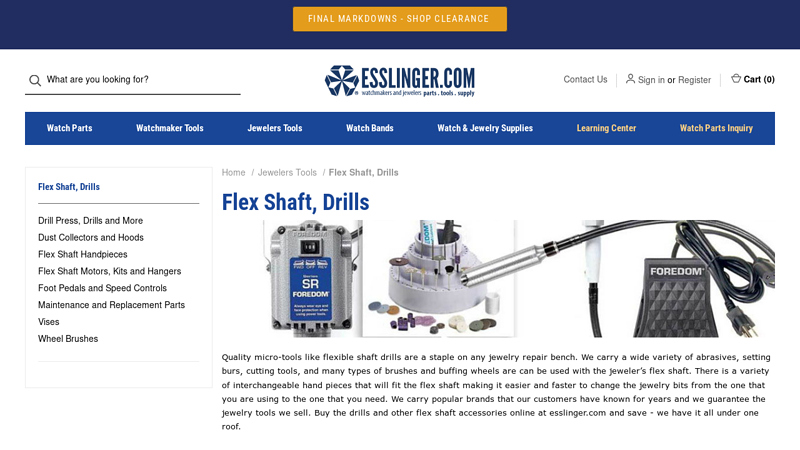
#5 Flex Shaft Drills
Domain Est. 1997
Website: esslinger.com
Key Highlights: 3–5 day delivery · 30-day returnsFind foredom flex shafts and watch drills for your watchmaker’s tool set. These drill bits and dremel-type motor drills make watches and jewelry p…
#6 Minnich Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1998
Website: minnich-mfg.com
Key Highlights: Minnich Manufacturing is an industry leader in the production of Dowel Pin Drills, Concrete Paving Vibrators and Vibrator Monitoring Systems….
#7 Power tools for professional craftsmen
Domain Est. 1999
Website: flex-tools.com
Key Highlights: FLEX power tools ✚ accessories for professional craftsmen. System solutions for: Renovation, refurbishment & modernising, metalworking, automotive, ……
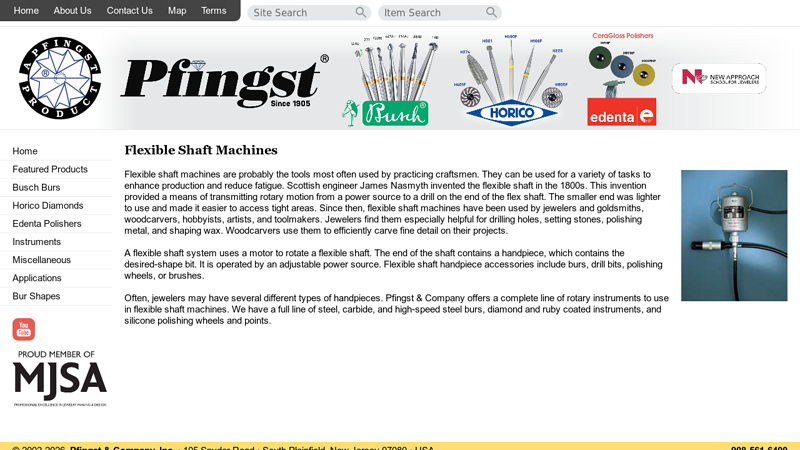
#8 Flexible Shaft Machines
Domain Est. 2001
Website: pfingstco.com
Key Highlights: Pfingst Flexible Shaft Machines and Handpieces are manufactured and serviced at the Company’s 15000 square foot facility in South Plainfield, New Jersey….
#9 Foredom Flexible Shaft Tools
Domain Est. 2008
Website: foredom.net
Key Highlights: A complete Foredom flexible shaft machine has a motor that rotates a flexible shaft connected to a precision handpiece. It also requires a speed control….
#10 Flexible Shaft Angle Drills
Domain Est. 2011
Website: zephyrtoolgroup.com
Key Highlights: Zephyr’s flexible shaft angle drills are built with a durable, oil-resistant shaft for flexibility and reliable performance in aerospace applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Flexible Drill Shaft

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Flexible Drill Shaft
The global Flexible Drill Shaft market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing demand across various industrial and commercial applications. Key trends shaping the market include technological advancements, rising automation, and expanding use in precision-driven sectors.
-
Growing Demand in Industrial Automation
As industries adopt more automated systems, the need for precision motion transfer components like flexible drill shafts is increasing. These shafts are critical in robotic arms, CNC machinery, and automated assembly lines due to their ability to transmit torque efficiently in non-linear configurations. The shift toward smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 is expected to further boost demand. -
Expansion in Medical and Dental Equipment
Flexible drill shafts are increasingly used in medical devices, particularly in dental handpieces and surgical tools where precision and reliability are paramount. With rising healthcare investments and advancements in minimally invasive procedures, this sector is set to be a key growth driver by 2026. -
Advancements in Material Technology
Innovations in materials—such as high-strength alloys, composite materials, and coated surfaces—are improving the durability, flexibility, and corrosion resistance of flexible drill shafts. These enhancements allow for longer service life and performance in extreme environments, expanding their applicability in aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors. -
Increased Adoption in Automotive and Aerospace
In automotive manufacturing, flexible shafts are used in drive systems, throttle controls, and specialized tools. Similarly, the aerospace industry relies on them for maintenance tools and in-flight systems requiring high precision. As electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced aircraft production grow, so will the need for specialized flexible shaft solutions. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Japan, is expected to dominate market growth due to rapid industrialization and expanding manufacturing bases. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, supported by high-tech industries and stringent quality standards. -
Sustainability and Customization Trends
Manufacturers are focusing on sustainable production practices and offering customized shaft solutions to meet specific application needs. Modular designs and quick-connect features are gaining traction, allowing for easier integration and maintenance.
In conclusion, the Flexible Drill Shaft market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, diversification, and integration into high-tech applications. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainability, and application-specific solutions are likely to lead the market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Flexible Drill Shafts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing flexible drill shafts requires careful evaluation to avoid performance issues, premature failure, or non-compliance. Below are key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) that buyers should be aware of:
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Manufacturing
Using substandard materials such as low-grade stainless steel or inadequate spring steel can lead to reduced torque transmission, increased flex fatigue, and shortened service life. Inconsistent heat treatment or winding processes result in shafts with uneven flexibility, torsional weakness, or susceptibility to kinking—especially critical in precision or high-cycle applications.
Inadequate Tolerance Control
Flexible drill shafts often operate in tight spaces with strict alignment requirements. Poor dimensional control—such as variations in outer diameter, pitch, or straightness—can cause binding, excessive wear, or failure to integrate with couplings and drive systems. Suppliers lacking precision manufacturing capabilities may not meet required tolerances, especially for miniaturized or medical-grade shafts.
Misrepresentation of Performance Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate torque capacity, maximum RPM, or bend radius capabilities. Without independent validation or test data, these inflated claims can lead to system failures. Always verify performance metrics through technical documentation, testing, or third-party certifications.
Lack of Environmental and IP Protection (IP Ratings)
Many applications—especially in medical, automotive, or industrial automation—require drill shafts with specific ingress protection (IP) ratings to resist dust, moisture, or chemicals. Sourcing shafts without proper sealing or protective coatings, or falsely claiming IP67/IP68 compliance, can result in corrosion, electrical failure, or non-compliance with industry standards.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Using or sourcing flexible shaft designs that mimic patented configurations (e.g., proprietary winding patterns, coupling interfaces, or composite layers) without licensing can expose your company to legal action. This is common when sourcing from manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement. Always verify the originality of design and request documentation confirming freedom to operate.
Insufficient Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide full material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH, ISO 9001), batch traceability, and test reports. Lack of documentation makes it difficult to ensure consistent quality or meet regulatory requirements—particularly in aerospace, medical, or defense sectors.
Overlooking Application-Specific Needs
Flexible drill shafts vary widely based on use case (e.g., dental handpieces vs. industrial drilling). Sourcing generic or off-the-shelf shafts without considering torque profiles, sterilization needs, or vibration resistance leads to poor performance. Customization should be balanced with proven design expertise.
Choosing Suppliers Without Technical Support
Flexible shaft integration often requires engineering collaboration. Suppliers who lack technical support or application know-how may deliver products that look correct but fail under real-world conditions. Engage partners who offer design validation and testing support.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vet suppliers thoroughly, request samples and test data, confirm compliance with standards, and protect your IP when developing custom solutions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Flexible Drill Shaft
Product Classification & Regulatory Overview
The Flexible Drill Shaft is typically classified under industrial mechanical components. Accurate classification is critical for compliance with international trade regulations. Most countries categorize such items under Harmonized System (HS) Code 8466.30, which covers interchangeable tools for hand tools, including drill components. Confirm the applicable HS code with local customs authorities, as minor variations may exist by region. Ensure the product meets relevant machinery safety standards such as ISO 14122 (safety of machinery) and ISO 8686 (crane design), if applicable to the end-use application.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Flexible Drill Shafts must be packaged to prevent mechanical damage, corrosion, and deformation during transit. Use anti-static, moisture-resistant wrapping (e.g., VCI paper or shrink-wrapped plastic) and secure shafts in rigid cardboard or wooden crates with internal foam or molded inserts to minimize movement. Clearly label packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “Do Not Bend,” and “This Side Up.” For bulk shipments, ensure proper segregation to avoid cross-contamination with corrosive or sharp materials. Include product identification tags with part number, batch/lot number, and manufacturing date.
Transportation & Shipping Considerations
Flexible Drill Shafts can be shipped via air, sea, or ground freight depending on urgency and destination. For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if packaging includes lithium batteries (e.g., for integrated tools). Most shafts are non-hazardous and can be shipped as general cargo. Use climate-controlled containers if transporting through extreme environments to prevent material degradation. Provide detailed shipping documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading, with accurate weight, dimensions, and declared value. Mark export shipments with country of origin and compliance statements.
Import/Export Documentation & Compliance
Ensure all export documentation complies with destination country regulations. Required documents typically include:
– Commercial Invoice (with value, quantity, and HS code)
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– Export Declaration (as required by exporting country, e.g., AES filing for U.S. exports)
Some countries may require additional certifications, such as a conformity assessment (e.g., CE marking in the EU, or KC certification in South Korea). Verify if the Flexible Drill Shaft is subject to export controls under regimes like the Wassenaar Arrangement, particularly if designed for high-precision or aerospace applications.
Customs Clearance & Duties
Partner with licensed customs brokers in the destination country to facilitate clearance. Provide complete product specifications (material composition, dimensions, intended use) to avoid classification disputes. Be prepared to pay applicable import duties and VAT, which vary by country. Maintain records of all compliance documentation for a minimum of five years for audit purposes. Monitor changes in trade agreements or tariff schedules that may impact duty rates (e.g., USMCA, RCEP).
Environmental & Safety Compliance
Flexible Drill Shafts made from steel or composite materials must comply with environmental regulations such as REACH (EU) and RoHS if containing restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium). Provide a Declaration of Conformity or SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) statement when requested. Waste from production or end-of-life disposal should be managed in accordance with local environmental laws. For workplace safety, ensure user instructions include proper handling and installation procedures to prevent injury.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
Maintain a traceability system that tracks each Flexible Drill Shaft from manufacturing to delivery. Include batch numbers, inspection records, and test results (e.g., torsion strength, flexibility tests) in the quality documentation. Comply with ISO 9001 standards for quality management if certified. Conduct periodic audits of logistics providers to ensure packaging and handling standards are consistently applied.
Risk Mitigation & Contingency Planning
Identify potential supply chain risks such as port delays, customs inspections, or material shortages. Diversify logistics providers and maintain safety stock where feasible. Implement a recall procedure in case of non-compliance or safety issues, including communication protocols with distributors and regulatory bodies. Use tracking systems (e.g., GPS or RFID) for high-value shipments to monitor location and conditions in real time.
Conclusion for Sourcing Flexible Drill Shaft
After a thorough evaluation of available suppliers, material options, manufacturing capabilities, and cost considerations, sourcing a flexible drill shaft requires a balanced approach that prioritizes quality, durability, and performance in alignment with the intended application. Flexible drill shafts must exhibit high torsional strength, resistance to fatigue, and consistent performance under varying loads and operating conditions.
Key factors in successful sourcing include selecting the appropriate material—such as stainless steel or high-grade alloys—ensuring precise manufacturing tolerances, and partnering with reliable suppliers with proven industry experience and quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001). Additionally, considering customization options, lead times, and long-term availability is essential for maintaining supply chain stability.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing strategy that combines technical requirements with supplier reliability will ensure the acquisition of a high-performance flexible drill shaft, contributing to improved efficiency, reduced maintenance, and enhanced operational longevity in end-use applications. Regular supplier assessment and performance monitoring should be maintained to support continuous improvement and supply resilience.