The global fipronil pesticide market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4.3% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence, driven by rising agricultural demand for broad-spectrum insect control and increasing challenges from pest resistance to conventional chemistries. As one of the most effective phenylpyrazole insecticides, fipronil is widely used across crops, livestock, and urban pest management due to its non-systemic mode of action and efficacy against resistant insect populations. With the global push for higher crop yields and intensified focus on vector-borne disease control, key players in the fipronil space are scaling production, investing in formulation innovation, and expanding geographic reach. This data-backed environment underscores the strategic importance of identifying the leading manufacturers shaping supply, quality, and innovation in the fipronil market. Based on production capacity, global footprint, and market influence, here are the top 9 fipronil pesticide manufacturers driving industry growth.
Top 9 Fipronil Pesticide Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Fipronil Pesticide Manufacturers and Suppliers, Factory
Domain Est. 2019
Website: bigpesticides.com
Key Highlights: Fipronil Pesticide Manufacturers, Factory, Suppliers From China, We welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business ……
#2 Fipronil 0.3% GR
Domain Est. 2016
Website: peptechbio.com
Key Highlights: Peptech biosciences is leading manufacturer and supplier of fipronil 0.3% gr. Best quality product. 100% results. Get best market price….
#3 Fipronil Technical Manufacturer & Bulk chemical Supplier in USA
Domain Est. 2019
Website: scimplify.com
Key Highlights: Fipronil Technical is a high-purity, broad-spectrum insecticide belonging to the phenylpyrazole class, widely recognized for its potent and long-lasting ……
#4 Fipronil
Domain Est. 1996
Website: goldbio.com
Key Highlights: Fipronil is a phenylpyrazole derivative that is used as an insecticide in agriculture for its neurotoxic effects. It is researched for environmental impact ……
#5 Gharda Fipronil Technical
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ghardausa.com
Key Highlights: FIPRONIL is a broad-spectrum, moderately systemic insecticide acts by contact and ingestion. It belongs to the new class of phenylpyrazole insecticides….
#6 Fipronil
Domain Est. 2012
Website: adooq.com
Key Highlights: Fipronil is a broad-spectrum insecticide that belongs to the phenylpyrazole chemical family. Fipronil disrupts the insect central nervous system by blocking ……
#7 Insecticide Fipronil80%WDG, 200 g/l SC
Domain Est. 2012
Website: agrogreat.com
Key Highlights: Uses Control of multiple species of thrips on a broad range of crops by foliar, soil or seed treatment. Control of corn rootworm, wireworms and termites by soil ……
#8 Fipronil
Domain Est. 2020
Website: veseris.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free delivery over $500Fipronil-Plus-C Insecticide ; 16 oz bottle · Fipronil · Liquid Concentrate · Asian Lady Beetles, Boxelder Bugs, Flies , Pillbugs, Cockroaches, Crick…
#9 Fipronil
Domain Est. 2023
Website: uplcorp.com
Key Highlights: Fipronil is a broad-spectrum insecticide with different mode of action, effective against wide range of insect pests….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fipronil Pesticide

H2: Market Trends for Fipronil Pesticide in 2026
As the global agricultural sector continues to evolve in response to environmental regulations, food security demands, and technological advancements, the market for fipronil—a broad-spectrum insecticide—faces a complex and shifting landscape leading into 2026. Fipronil, widely used to control pests in crops, livestock, and urban pest management, is experiencing both challenges and opportunities due to regulatory scrutiny, resistance development, and shifting consumer preferences.
One of the primary drivers shaping the fipronil market in 2026 is tightening regulatory oversight, particularly in Europe and North America. The European Union has maintained a near-total ban on fipronil in agricultural applications due to its harmful effects on non-target species, especially bees. This regulatory stance is expected to persist through 2026, limiting market growth in Western Europe. However, in regions such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa, where regulatory frameworks are less stringent and pest pressure remains high, fipronil continues to see demand—particularly in rice, cotton, and maize production.
Another significant trend is the growing resistance among pest populations to fipronil and other phenylpyrazole insecticides. By 2026, resistance in key pests such as the diamondback moth and certain termite species is expected to reduce fipronil’s efficacy, pushing farmers and agrochemical companies toward integrated pest management (IPM) strategies and alternative chemistries. This shift may slow growth in fipronil sales or lead to its use in rotation with other modes of action to preserve effectiveness.
Despite these challenges, fipronil maintains a strong foothold in non-agricultural markets. Its use in veterinary applications—particularly for flea and tick control in pets—and in termite control for urban infrastructure remains robust. These sectors are projected to sustain demand, especially in developing economies where urbanization and pet ownership are on the rise.
Furthermore, technological enhancements such as microencapsulation and seed treatment formulations are improving fipronil’s targeted delivery and environmental profile, helping to mitigate ecological concerns. These innovations may support a more sustainable use pattern, potentially easing regulatory pressure in certain markets.
In summary, the 2026 fipronil pesticide market is characterized by regional divergence: declining in highly regulated areas due to environmental concerns and resistance issues, but holding steady or growing in emerging markets and non-agricultural applications. Strategic formulation improvements and integration into broader pest control systems will be key to maintaining relevance in an increasingly sustainability-focused agricultural landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Fipronil Pesticide (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Fipronil, a potent broad-spectrum insecticide, involves navigating significant challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Failure to address these pitfalls can lead to operational disruptions, legal liabilities, financial losses, and reputational damage. Key risks include:
Substandard or Counterfeit Products
A primary concern when sourcing Fipronil is receiving products that fail to meet purity, efficacy, or safety standards. Unscrupulous suppliers may offer formulations with incorrect active ingredient concentrations, harmful impurities, or entirely falsified labels. These substandard or counterfeit products not only reduce pest control effectiveness but can also pose environmental and health risks. Buyers must verify supplier credentials, demand third-party analytical testing (e.g., HPLC for assay), and inspect Certificates of Analysis (CoA) to ensure compliance with international standards such as FAO specifications.
Lack of Regulatory Compliance
Fipronil is a restricted-use pesticide in many countries due to its toxicity and environmental persistence. Sourcing from suppliers who do not comply with local or international regulations (e.g., EPA in the U.S., EU MRLs, or China’s pesticide registration requirements) can result in shipment seizures, fines, or import bans. Buyers must confirm that the Fipronil product is registered for use in the destination country and that the supplier adheres to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and proper labeling requirements.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Fipronil is a patented molecule originally developed by BASF. While the core compound patent has expired in most jurisdictions, related formulation patents, trademarks (e.g., “Regent”), and process patents may still be enforceable. Sourcing generic Fipronil from manufacturers who use protected formulations or branding without authorization exposes buyers to IP litigation. It is critical to conduct due diligence on suppliers’ IP status, obtain legal assurances of freedom to operate, and avoid products that mimic branded packaging or use protected trade names.
Inadequate Supply Chain Transparency
Opaque supply chains increase the risk of unknowingly procuring Fipronil from unauthorized or unethical sources. Lack of traceability makes it difficult to verify origin, manufacturing practices, and adherence to ethical labor and environmental standards. Buyers should require full supply chain disclosure, conduct supplier audits, and consider third-party certification (e.g., ISO, ECOCERT) to ensure responsible sourcing.
Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Quality
Even with legitimate suppliers, variability in manufacturing processes can lead to inconsistencies in Fipronil concentration, particle size, or formulation stability. Such inconsistencies affect application performance and crop safety. Implementing strict quality control protocols, including pre-shipment sampling and batch-specific testing, is essential to maintain product reliability.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires a proactive sourcing strategy that emphasizes supplier vetting, legal compliance, quality assurance, and IP due diligence. Engaging with reputable, transparent suppliers and leveraging third-party verification can mitigate risks and ensure a safe, lawful, and effective Fipronil supply.
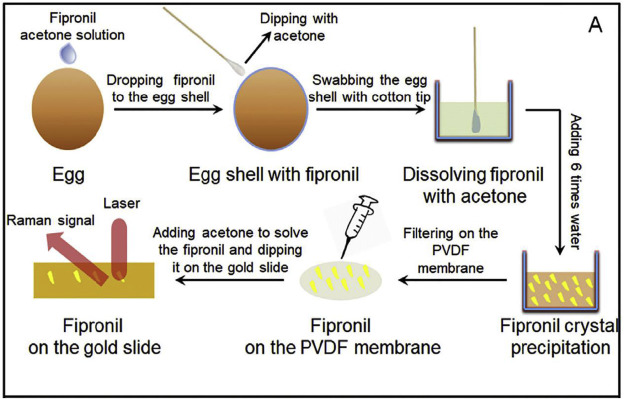
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fipronil Pesticide
Overview of Fipronil
Fipronil is a broad-spectrum insecticide used in agriculture, veterinary products, and urban pest control. It works by disrupting the insect central nervous system, leading to paralysis and death. Due to its high toxicity to non-target species—especially bees and aquatic organisms—its use, transport, storage, and disposal are strictly regulated globally.
Regulatory Classification
Global Regulatory Status
Fipronil is classified under various regulatory frameworks:
– WHO: Class II (Moderately hazardous)
– EPA (USA): Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP)
– EU: Approved under Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 with strict usage limitations; banned for use on crops attractive to bees
– Rotterdam Convention: Fipronil is listed in Annex III, requiring Prior Informed Consent (PIC) for international trade
Hazard Classification (GHS)
- Acute Toxicity (Oral): Category 2
- Acute Toxicity (Dermal): Category 3
- Acute Toxicity (Inhalation): Category 2
- Hazardous to Aquatic Life: Category Acute 1, Chronic 1
- Hazardous to Bees: Yes, highly toxic
Always verify the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the specific formulation, as classifications may vary.
Transport and Logistics
Packaging Requirements
- Must be packaged in UN-certified containers compliant with UN 3077 (Environmentally hazardous substance, solid, not otherwise specified)
- Packaging must be leak-proof, tamper-resistant, and labeled with:
- Proper shipping name: “ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. (Fipronil)”
- UN Number: 3077
- GHS pictograms (Skull & Crossbones, Environment)
- Handling instructions and hazard statements
Transport Regulations (IMDG, IATA, ADR)
- Road (ADR): Class 9 – Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods; requires placarding for loads >1,000 kg gross weight
- Air (IATA): Class 9, UN 3077; permitted only with special arrangements and quantity limits
- Sea (IMDG): Class 9, Marine Pollutant (marked with “Marine Pollutant” symbol)
Special documentation (Dangerous Goods Declaration) and trained personnel (DGSA) required.
Storage Guidelines
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight
- Keep in original, labeled containers; never mix with other chemicals
- Segregate from food, feed, fertilizers, and flammable materials
- Use secondary containment (e.g., spill trays) to prevent environmental contamination
- Access restricted to trained personnel; maintain inventory logs
Use and Application Compliance
Approved Uses
- Crop protection (specific approved crops only)
- Seed treatment (restricted)
- Veterinary products (e.g., flea control on pets)
- Termite and ant baits (indoor/outdoor)
Prohibited Uses
- Application on flowering crops where bees are foraging
- Use in residential areas without adequate buffer zones
- Unregistered formulations or off-label applications
Always follow label instructions and local pesticide regulations.
Environmental and Health Safety
Environmental Precautions
- Avoid drift to non-target areas
- Do not apply near water bodies (buffer zones required)
- Prevent runoff into drains or soil contamination
- Do not dispose of wash water into sewage or waterways
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and face shield
- Respirator (if dust or aerosol is generated)
- Protective clothing (coveralls)
- Wash hands and exposed skin after handling
First Aid Measures
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical attention
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water; remove contaminated clothing
- Eye Contact: Rinse thoroughly with water for 15 minutes
- Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting; seek immediate medical help
Disposal and Spill Management
Spill Response
- Evacuate area and restrict access
- Contain spill with absorbent materials (e.g., sand, vermiculite)
- Collect waste in labeled, sealed containers
- Decontaminate surfaces with appropriate agents
- Report spills per local environmental regulations
Waste Disposal
- Fipronil waste is hazardous and must be disposed of at licensed facilities
- Never pour down drains or dispose of in regular trash
- Follow local, national, and international (Basel Convention) hazardous waste protocols
Recordkeeping and Documentation
- Maintain logs of:
- Purchases and inventory
- Application dates, rates, and locations
- Personnel training records
- Spill incidents and disposal activities
- Retain records for a minimum of 3–5 years (as required by jurisdiction)
International Trade Compliance
- Export/import requires Prior Informed Consent (PIC) under the Rotterdam Convention
- Verify importing country’s authorization status
- Include SDS and proper labeling in all shipments
- Notify national authorities in advance for cross-border movements
Training and Certification
- Personnel handling fipronil must be certified under national pesticide applicator programs (e.g., EPA in USA, NRO in EU)
- Regular training on safe handling, emergency response, and regulatory updates is mandatory
Conclusion
Fipronil is a highly effective but strictly regulated pesticide. Compliance with logistics, safety, and environmental regulations is essential to prevent harm to human health and ecosystems. Always consult local regulatory authorities and use up-to-date SDS and labeling to ensure full compliance.
Conclusion on Sourcing Fipronil Pesticide:
Sourcing fipronil pesticide requires strict adherence to regulatory, safety, and environmental standards due to its classification as a hazardous substance. Fipronil is a broad-spectrum insecticide effective against a variety of pests, but it poses significant risks to human health, non-target organisms—including pollinators like bees—and the environment if misused or improperly handled.
Therefore, sourcing fipronil should only be conducted through authorized, reputable suppliers who comply with national and international regulations such as those set by the EPA, EU pesticide directives, or equivalent local authorities. Importers and users must ensure proper licensing, documentation, and end-use compliance, particularly since misuse—especially in food-producing animals—has led to major food safety incidents in the past.
In addition, alternatives with lower ecotoxicological impact should be considered where feasible. When fipronil is necessary, responsible sourcing involves due diligence in supply chain transparency, adherence to safety data sheets (SDS), and implementation of integrated pest management (IPM) practices.
In conclusion, while fipronil remains a valuable tool in specific pest control applications, its sourcing must be approached with caution, accountability, and full compliance with legal and environmental safeguards to prevent public health risks and ecological damage.