The global laser marking and engraving equipment market has experienced robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision surface finishing across industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser marking market size was valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.9% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in manufacturing, and the need for permanent, high-contrast markings on metal, plastic, and composite materials. As industries prioritize efficiency, traceability, and aesthetic quality, finish-removing lasers—used for cleaning, texturing, and surface preparation—have become critical in high-precision production environments. With a competitive landscape shaped by innovation and regional manufacturing expansion, identifying the top players in finish-removing laser manufacturing requires an analysis of technological capability, market reach, and customer adoption. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers leading this specialized segment based on product performance, market presence, and industry reputation.
Top 10 Finish Removing Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#2 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#3 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: Our laser systems are primarily in operation with mold and tool cleaning, paint stripping and decoating as well as cleaning and modification of metallic ……
#4 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning removes paint, contaminants, rust, and residues with a high-energy laser beam which leaves the substrate untouched. Our Laser Ablation is the ……
#5 Laser Rust Removal
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Efficiently remove rust with KEYENCE America’s advanced laser rust removal machine. Discover the precision and power of laser technology for effective rust ……
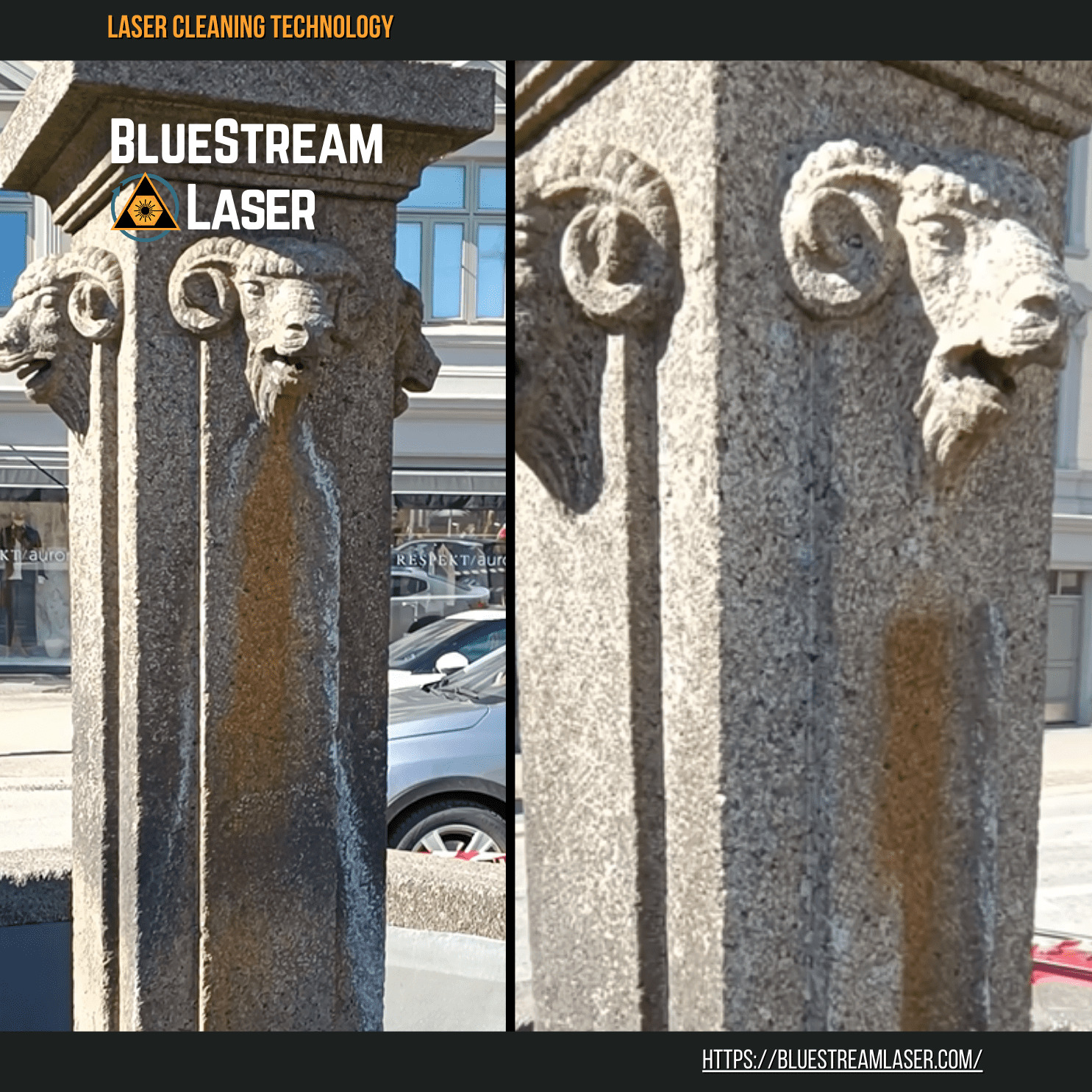
#6 Bluestream Laser Cleaning, restoration of monuments, industrial …
Website: bluestreamlaser.com
Key Highlights: We are specialists in laser cleaning for the restoration and maintenance of cultural heritage, surface treatment, and technical cleaning….
#7 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#8 to Sciton Medical & Aesthetic Laser Technologies
Website: sciton.com
Key Highlights: A leader in energy-based medical aesthetics. Sciton was founded to build exceptional lasers and light sources to improve people’s lives….
#9 Laser Cleaning vs. Dustless Blasting
Website: dustlessblasting.com
Key Highlights: While laser cleaning excels in precision for delicate surfaces, Dustless Blasting is superior for tough jobs like removing coatings and profiling surfaces….
#10 Laser Rust Removal Guide
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: A practical guide for professionals and entrepreneurs using PULSAR Laser systems to remove rust safely, efficiently and without abrasives….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Finish Removing Laser

H2: Market Trends for Finish-Removing Lasers in 2026
The global market for finish-removing lasers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in laser technology, increasing demand for precision manufacturing, and the growing emphasis on automation and sustainability across industries. As a specialized application within laser surface treatment, finish-removing lasers—used to strip coatings, paints, oxides, and surface contaminants without damaging the underlying substrate—are gaining traction in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and heritage restoration.
1. Technological Advancements Driving Adoption
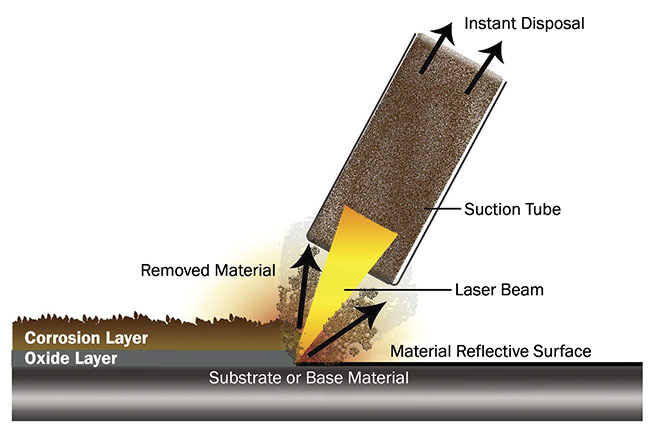
By 2026, fiber and ultrafast (picosecond and femtosecond) laser systems are expected to dominate the finish-removing segment due to their precision, minimal heat-affected zones, and compatibility with a wide range of materials. Innovations in beam delivery, real-time monitoring, and AI-integrated control systems will enhance process efficiency and repeatability. These systems enable selective material ablation, making them ideal for delicate applications such as removing paint from aircraft skins or cleaning historical artifacts.
2. Growth in Industrial Automation and Industry 4.0 Integration
The integration of finish-removing lasers into automated production lines is accelerating. Robotics combined with laser ablation systems allow for consistent, high-throughput surface preparation. In 2026, smart factories will increasingly deploy laser cleaning cells with IoT connectivity, enabling predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and data-driven process optimization—key features of Industry 4.0.
3. Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Stringent environmental regulations limiting chemical-based stripping methods (e.g., methylene chloride bans) are pushing industries toward eco-friendly alternatives. Laser-based removal produces no secondary waste, requires no solvents, and reduces worker exposure to hazardous materials. This regulatory tailwind is expected to boost market adoption, especially in Europe and North America.
4. Expansion in Aerospace and Automotive Applications
The aerospace industry will remain a key adopter, using lasers for paint stripping from composite and aluminum airframes, adhesive removal, and surface preparation prior to repainting or bonding. Similarly, electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers are exploring laser cleaning for battery component preparation and weld zone cleaning, contributing to market growth.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, is projected to witness the fastest growth due to expanding manufacturing bases and government support for advanced manufacturing technologies. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will maintain strong market shares, supported by defense, aerospace, and high-end industrial applications.
6. Cost Reduction and Wider Accessibility
As laser source costs decline and system reliability improves, mid-sized and even small enterprises will gain access to finish-removing laser technology. Plug-and-play systems with simplified user interfaces will lower the barrier to entry, broadening adoption beyond large OEMs.
7. Challenges and Limitations
Despite positive trends, challenges remain—high initial investment, limited throughput for large-area applications, and the need for skilled operators. However, ongoing R&D focused on higher-power lasers and multi-beam scanning techniques aims to address throughput issues by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the finish-removing laser market will be shaped by technological innovation, regulatory support, and industrial digitization. With growing emphasis on precision, sustainability, and automation, laser-based surface finishing is set to replace traditional methods across multiple high-value industries, positioning it as a critical enabling technology in modern manufacturing.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Finish Removing Lasers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Finish Removing Lasers—high-precision tools used in industrial applications to strip coatings, oxides, or surface layers—requires careful evaluation. Overlooking critical factors can lead to performance issues, safety risks, and costly downtime. Two major areas where pitfalls frequently arise are quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) concerns.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inadequate Laser Specifications Matching
A common mistake is selecting a laser based on nominal power alone without verifying actual beam quality (M² factor), pulse stability, and wavelength suitability for the target material. Poor beam quality leads to uneven finish removal, thermal damage, or incomplete processing. -
Substandard Component Sourcing
Some suppliers use lower-grade optics, diodes, or cooling systems to cut costs. These components degrade quickly under industrial use, resulting in frequent maintenance, reduced uptime, and inconsistent output over time. -
Lack of Environmental and Operational Testing
Lasers not tested under real-world conditions (e.g., temperature fluctuations, dust, continuous operation) may fail prematurely in production environments. Absence of robust IP-rated enclosures exacerbates this risk. -
Insufficient Calibration and Traceability
Reputable manufacturers provide calibration certificates and traceable quality control. Sourcing from vendors without documented QC processes increases the risk of receiving units that perform below specification.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Use of Counterfeit or Cloned Technology
Some low-cost suppliers replicate patented laser designs or control software without licensing. Purchasing such equipment exposes the buyer to legal liability, especially in regulated industries or export-controlled markets. -
Unclear or Missing IP Documentation
Failing to obtain proof of IP ownership, licensing agreements, or freedom-to-operate assurances can jeopardize product compliance and lead to infringement claims, particularly in international supply chains. -
Proprietary Software and Firmware Risks
Hidden use of unlicensed firmware or software libraries in laser control systems can result in security vulnerabilities, lack of updates, or legal disputes. Buyers should verify software provenance and licensing terms. -
Inadequate Support for IP Compliance in End Products
If the laser is integrated into a larger system, unresolved IP issues in the source component can compromise the entire product’s marketability and regulatory approval.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers for technical certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), requesting full technical documentation, verifying IP ownership, and conducting on-site or third-party audits when possible.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Finish Removing Laser
Overview and Purpose
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal transport, installation, operation, and maintenance of a Finish Removing Laser system. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and personnel safety across jurisdictions.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Finish Removing Lasers are subject to strict national and international regulations due to their use of high-powered laser technology. Key compliance areas include:
– Laser Safety Standards: Compliance with IEC 60825-1 (international) or ANSI Z136.1 (U.S.) for laser classification, labeling, and safety controls.
– Electrical Safety: Conformity with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC 60364 in Europe).
– Machine Safety: Adherence to ISO 13849 for control system safety and risk assessment.
– EMC Regulations: Compliance with FCC Part 15 (U.S.) or CE EMC Directive (EU) to minimize electromagnetic interference.
– Environmental Compliance: Proper disposal of waste materials (e.g., ablated coatings, filters) in accordance with EPA or local environmental regulations.
Packaging and Transportation
Proper packaging and transport protocols are critical to prevent damage and ensure safety:
– Crating and Shock Protection: Use custom-engineered, shock-absorbent crates with internal bracing to secure optical components and laser head.
– Environmental Controls: Protect against moisture, dust, and temperature extremes during transit; use desiccants and climate-controlled shipping if necessary.
– Labeling: Clearly mark packaging with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” laser warning labels (Class 4), and handling instructions.
– Hazardous Materials: Declare any included batteries or cooling agents per IATA/IMDG regulations if shipping internationally.
Import and Export Documentation
Cross-border movement of laser systems requires careful documentation:
– Export Licenses: Obtain required licenses from national authorities (e.g., U.S. Department of Commerce for EAR-controlled items).
– Customs Declarations: Provide accurate HS codes (e.g., 8515.21 for laser machinery), commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
– Laser Product Reports: Submit FDA compliance forms (e.g., FDA-2877) for U.S. imports of laser products.
– CE or UKCA Marking: Ensure equipment bears appropriate conformity marks for European or UK markets.
Installation and Site Preparation
Proper site setup is essential for compliance and operational readiness:
– Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Install certified fume extraction systems with HEPA filtration to capture particulates from laser ablation.
– Electrical Requirements: Provide stable power supply with correct voltage, grounding, and surge protection; isolate from sensitive equipment.
– Laser Controlled Area: Designate and mark a Class 1 or interlocked Class 4 laser area with safety interlocks, warning signs, and restricted access.
– Floor Load and Space: Ensure adequate floor loading capacity and clearance for operation, maintenance, and emergency access.
Operational Safety and Training
User safety and regulatory adherence during operation are mandatory:
– Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint a trained LSO to oversee laser safety program and compliance.
– Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Require laser safety eyewear (wavelength-specific), protective clothing, and respiratory protection as needed.
– Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and enforce SOPs covering startup, operation, emergency shutdown, and maintenance.
– Training Certification: Ensure all operators complete laser safety training and are certified per ANSI or equivalent standards.
Maintenance and Servicing Logistics
Scheduled maintenance must follow compliance and safety protocols:
– Service Access: Plan for technician access, spare parts storage, and calibration tools on-site.
– Laser Alignment and Calibration: Perform by qualified personnel only; document all adjustments for audit purposes.
– Waste Handling: Collect and dispose of contaminated filters, lenses, and debris as hazardous waste if applicable.
– Service Records: Maintain logs of maintenance, repairs, and safety inspections for regulatory audits.
End-of-Life and Disposal Compliance
Decommissioning and disposal must follow environmental and safety laws:
– Laser Decommissioning: Disable and remove laser source under supervision of qualified technician.
– Hazardous Components: Identify and manage batteries, capacitors, and electronic waste per WEEE (EU) or RCRA (U.S.) regulations.
– Recycling and Disposal: Use certified e-waste recyclers for metal, electronics, and optics; retain disposal certificates.
Audit and Documentation Retention
Maintain comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance:
– Retention Period: Store safety certifications, training records, maintenance logs, and regulatory filings for a minimum of 5–7 years.
– Internal Audits: Conduct annual reviews of laser safety program and compliance status.
– Readiness for Inspection: Ensure all documentation is accessible for OSHA, FDA, or other regulatory inspections.
Adhering to this guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient handling of Finish Removing Laser systems throughout their lifecycle.
Conclusion: Sourcing Finish and Removing Laser
After a thorough evaluation of suppliers, technologies, and operational requirements, sourcing a finishing and laser removal solution demonstrates significant potential to enhance manufacturing precision, improve surface quality, and streamline post-processing workflows. The integration of advanced laser ablation systems offers a non-contact, highly accurate method for removing coatings, oxides, or imperfections, particularly in applications demanding tight tolerances and material integrity.
Key considerations in the sourcing decision include laser type (e.g., fiber, pulsed, or CO₂), power requirements, compatibility with existing production lines, maintenance needs, and total cost of ownership. Partnering with reputable suppliers offering proven track records, technical support, and scalability ensures long-term reliability and process consistency.
Ultimately, investing in a well-sourced laser-based finishing and removal system represents a strategic step toward automation, improved product quality, and increased operational efficiency. With proper implementation and supplier collaboration, this technology supports continuous improvement and competitive advantage in advanced manufacturing environments.