Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Filling Bottle Machine
The global bottling equipment market is valued at $3.2 billion and projected to grow at 6.1 % CAGR through 2030. For U.S. and European manufacturers, the opportunity is clear: rising demand for functional beverages, nutraceuticals, and personal-care liquids is driving urgent need for high-speed, hygienic, and compliant filling bottle machine solutions. Yet the path from vendor search to production-ready line is fraught with complexity—regulatory divergence, capex constraints, and technical fit gaps can stall projects for 12–18 months.
Why This Guide Matters
- Speed: Cut vendor vetting time by 40 % with verified data on performance, footprint, and ROI.
- Compliance: Decode FDA, EU 1935/2004, and CE Marking requirements in one place.
- Cost Control: Benchmark pricing across continents and identify hidden costs (changeover parts, utilities, lifecycle OEE).
How to Use This Section
- Hook: Identify your production range and product viscosities to pre-qualify equipment.
- Problem: Map regulatory, financial, and technical risks before RFQ.
- Guide: Follow our three-phase framework—Assess → Shortlist → Validate—to secure a filling bottle machine that scales with your growth targets.
Continue to Section 1 to benchmark machine types against your output goals.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Filling Bottle Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for filling bottle machine
- Understanding filling bottle machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of filling bottle machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘filling bottle machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for filling bottle machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for filling bottle machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘filling bottle machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for filling bottle machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing filling bottle machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for filling bottle machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the filling bottle machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of filling bottle machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for filling bottle machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Filling Bottle Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Best 10 Bottle Filling Machine Manufacturers-Yundu
Domain: yundufillingmachine.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Which 10 companies are the best filling machine manufacturers? · 1.COESIA · 2.Yundu · 3.Pacific Packaging Machinery · 4.Krones · 5.GEA Group · 6.KHS ……
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer – ACASI Machinery – Acasi
Domain: acasi.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: We are one of the few bottle filling machine manufacturers that can offer a complete project with all bottling equipment made entirely by Acasi….
3. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer | E-PAK Machinery
Domain: epakmachinery.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: E-PAK Machinery manufactures quality liquid filling machines, including cappers and labelers, for the bottling industry. Buy equipment and parts online….
4. Bottle Filling Machines & Equipment – Filling Equipment …
Domain: fillingequipment.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: We specialize in the design, sale, and repair of filling machines, as well as cappers, used in bottling food, drinks, spreads, chemicals, and cosmetics….
5. Best Bottle Filling Machine | Best Liquid Filling Machines
Domain: rockymountainplc.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: We offer a wide range of services, including video training on the use of table top bottling machines. We manufacture all our equipment in house in the USA….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
6. Bottle Fillers, Automatic Bottle Filling Machines – Cru Bottling Systems
Domain: crusystems.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: 30-day returnsFeaturing world class bottle filling equipment from Spagni of Italy engineered for ease of use, our bottle fillers cater to diverse production requirements, ……
7. Liquid Filling Systems, Bottle Filling, Liquid Fillers, Liquid Bottling …
Domain: filamatic.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: FILAMATIC provides the widest range of liquid filling equipment while delivering the lowest cost of ownership to our customers….
8. Water Bottling Machine
Domain: neptune-machine.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: The world smallest monoblock rotary water bottling machine for 200ml to 2000ml bottle water. Collect 8psc rinser, 8psc filler and 1psc capper in one machine….
9. Accutek Packaging Machine Equipment: Filler, Capper, Labeler
Domain: accutekpackaging.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The Accutek Packaging Equipment Companies offer a wide variety of filling machines, capping machines, labeling machines, and complete packaging systems….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding filling bottle machine Types and Variations
Understanding Filling Bottle Machine Types and Variations
| Type | Core Features | Typical Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piston Fillers | Positive-displacement piston meter; repeatable shot-to-shot accuracy within ±0.5 %; adjusts to viscosity 50–2,000 cP; optional多head configurations (4–24) | Sauces, syrups, lotions, oils, automotive fluids | High fill speed (50–150 cpm), minimal product loss, easy CIP/SIP, long service life | Higher initial cost, moderate cleaning downtime, not ideal for very low (<50 cP) or aerating products |
| Gravity & Pressure Fillers | Uses product head pressure only; no moving parts in contact with product; flow controlled by valve timing | Still water, carbonated soft drinks, beer, wine | Lowest maintenance, lowest cost per head, hygienic design (Sanitary Tri-Clamp ports) | Limited to thin, non-foaming products; slower than pump systems; sensitive to back-pressure fluctuations |
| Pump Fillers (Gear, Lobe, Centrifugal) | Positive rotary pumps (gear, lobe, or centrifugal) deliver precise volume;can handle 10–100,000 cP; sanitary seals (FDA/EC1935) | Dairy, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, industrial chemicals | Handles wide viscosity range, excellent repeatability, easy to retrofit with CIP; can run in reverse for cleaning | Slightly higher wear parts cost, requires accurate product density input, more complex clean-down |
| Weight/Check-Weigh Fillers | Load-cell based net weight control; fills by time or weight; closed-loop feedback ±0.1 % accuracy | Specialty chemicals, cosmetics, nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals | Highest accuracy, eliminates overfill, reduces giveaway costs, integrates with MES | Highest capital cost, slower cycle times (15–60 cpm), requires stable environment (vibration isolation) |
| Peristaltic Pump Fillers | Rollers compress tubing to push product; no product contact with pumps; easy changeover between SKUs | Oils, perfumes, essential oils, high-sanitation beverages, pharmaceuticals | Tubing is the only product path—fast changeover, minimal cross-contamination risk, simple validation | Limited pressure (max 8 bar), tubing life cycle costs, lower throughput (<30 cpm) |
1. Piston Fillers
Construction & Operation
A precision-machined piston draws product from a hopper or tank and displaces a fixed volume into the container. Volume is adjusted by changing piston stroke length or using digital positioners. Multi-head models (e.g., 8-, 12-, 16-head) allow parallel filling, boosting output to 1,200+ bph for 500 mL containers.
Key Variations
– Standard Piston: 50–2,000 cP; handles particulates up to 6 mm.
– Aseptic Piston: Full CIP/SIP, sterile air purge, 304/316L stainless.
– ** explosion-Proof Piston**: ATEX-rated motors for flammable solvents.
Typical ROI
Payback <18 months for lines running >40 cpm; downtime <30 min for seal replacement.
2. Gravity & Pressure Fillers
Operating Principle
Product flows from an overhead tank under gravity; fill level is controlled by timed valve opening. Pressure models add compressed air to maintain flow when tank height is limited.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Design Features
– Sanitary tri-clamp connections.
– Adjustable weir valves for carbonated drinks.
– Anti-foam spargers for beer.
Constraints
Minimum fill volume ≈ 50 mL to maintain head pressure; not suitable for foaming or viscous products >200 cP.
3. Pump Fillers (Gear, Lobe, Centrifugal)
Pump Technologies
– Gear: Best for thin到中粘度 (<5,000 cP); compact, low shear.
– Lobe: Handles up to 100,000 cP with large particles; sanitary lobe seals reduce contamination.
– Centrifugal: For high-flow, low-viscosity (<500 cP) applications like water or beer.
Sealing & Materials
All product-contact parts are 316L stainless with FDA/EU food-contact certifications. Mechanical seals or magnetic drives prevent leakage.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Integration
Can be mounted directly on filling heads or supplied as a remote pump skid with variable-frequency drives (VFD) for speed control.
4. Weight/Check-Weigh Fillers
Measurement & Control
Load cells measure net weight in real time; servo-driven valves or augers adjust flow to hit target within ±0.1 %. Closed-loop feedback reduces giveaway and ensures regulatory compliance (USP <797>, FDA 21 CFR Part 11).
Automation Layers
– Ethernet/IP or Profinet for MES integration.
– Recipe management for SKU changeover.
– Automatic tare and rejection of under/over-filled containers.
Typical Line Layout
In-feed conveyor → weigh hopper → filling head → out-feed conveyor with reject push-block or cull tray.
5. Peristaltic Pump Fillers
Tube Selection & Life
Tube materials: pharmaceutical-grade PTFE, FEP, or silicone. Expected life 2–8 million cycles depending on product aggressiveness. Quick-swap cassette design minimizes changeover time (<5 min).
Validation & Compliance
3-A sanitary standards; bubble-tight shut-off; full traceability for tubes via bar-coding.
Limitations
Maximum back-pressure 8 bar; cannot run dry; tubing cost ≈ $2–$5 per SKU change.
Key Industrial Applications of filling bottle machine
Key Industrial Applications of Filling Bottle Machines
| Industry | Typical Products | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Sauces, dressings, edible oils, syrups, juices, dairy drinks, honey | • Sanitary stainless-steel contact parts meet FDA/USDA standards • Accurate volume control reduces giveaway and cost per unit • Integrated CIP/SIP ports enable rapid changeover between SKUs |
| Beverage Alcohol | Craft beer, kombucha, cold-brew coffee, wine, spirits, ready-to-drink cocktails | • Spunding valve and nitrogen/CO₂ blending for draft-style packaging • Hermetic filling heads eliminate oxygen pickup, extending shelf life • High-speed rotary models reach 60–120 bpm for large-scale brewers |
| Personal Care & Cosmetics | Shampoos, conditioners, body washes, lotions, serums, essential oils | • Low-foam fillers and peristaltic pumps preserve viscosity-sensitive formulas • Closed-loop filling prevents air entrapment and foaming • Quick-sanitary connections allow daily cleaning for cosmetic GMP compliance |
| Pharmaceutical & Nutraceutical | Vitamins, tinctures, liquid supplements, cough syrups, CBD oils | • Positive-displacement pumps ensure ±0.5 % fill accuracy for dose-critical products • 316L SS and electropolished surfaces reduce microbial risk • Fill-level sensors and batch printers support serialization requirements |
| Chemical & Industrial | Cleaners, degreasers, adhesives, lubricants, windshield washer fluid | • Explosion-proof motors and grounding kits for flammable liquids • Piston fillers handle viscosities up to 1,000,000 cP • Bulk-to-bottle integration reduces manual handling and spillage |
| Household & Automotive | Laundry detergents, fabric softeners, windshield fluids, antifreeze | • Heavy-duty linear fillers with stainless spindles resist caustic chemicals • Automatic container detection prevents empty or misaligned bottles • PLC controls integrate with ERP for real-time production tracking |
| Pet Food & Animal Feed | Wet food pouches, treat gels, shampoo/conditioner for pets, supplements | • Airtight filling chambers minimize oxidation of fat-rich diets • Gentle auger or pump systems reduce product shearing • Quick-drain hoppers simplify color-change sanitation |
Cross-Cutting Benefits
- Regulatory Compliance: CE/UL/NSF certifications streamline audits across the EU and North America.
- Scalability: Change-parts and modular add-ons (conveyors, cappers, labelers) grow with demand.
- Data Integration: Ethernet/IP and OPC-UA ports sync with MES for OEE and traceability reporting.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘filling bottle machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Filling Bottle Machines & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Fill Volumes Lead to Product Waste & Compliance Risk
Problem
Bulk or viscous products (honey, sauces, oils) spill or under-fill when line speeds exceed 30 bottles/min. Overfills breach FDA/EG regulations; under-fills trigger customer chargebacks.
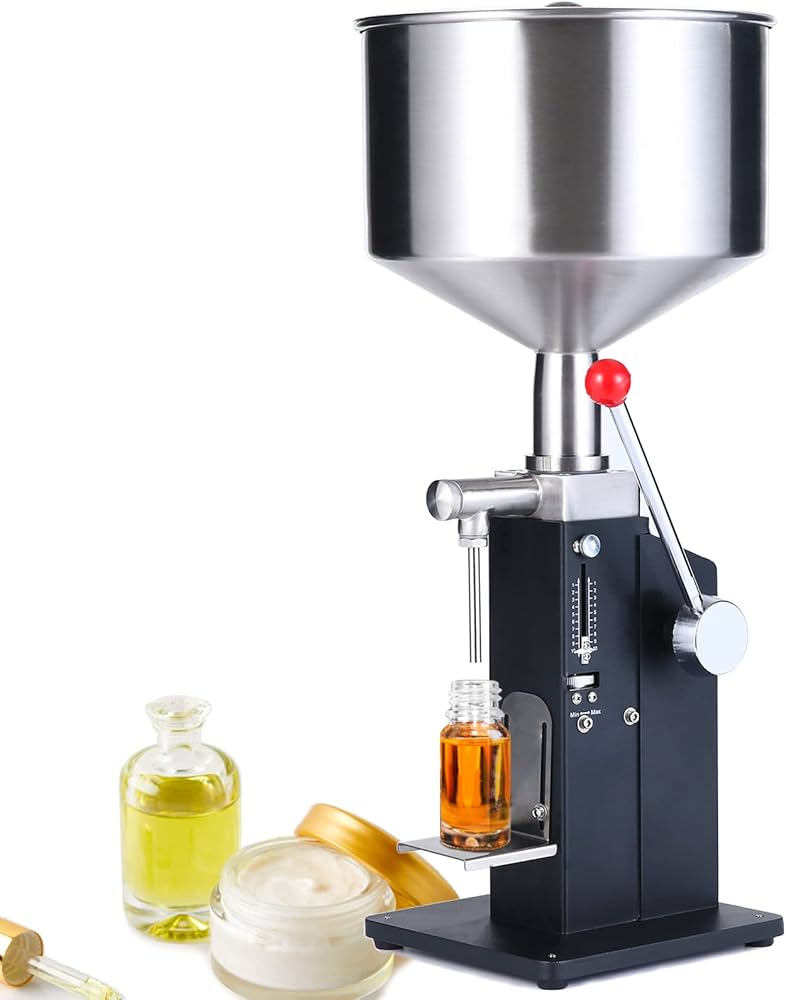

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution
Upgrade to weight-based or servo-controlled volumetric fillers with closed-loop feedback.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Load-cell称重系统 | ±0.1 % 精度,减少浪费 3–7 % |
| 伺服泵+PLC控制 | 实时调整流量,兼容 5–50,000 cP |
| 不锈钢 316L 接液部件 | 符合 NSF/ANSI 标准,降低合规风险 |
ROI: 6–12 个月回收成本,每 1,000 瓶/天减少浪费 ≈ $450/年。
Scenario 2: Line Downtime from Frequent Changeovers & Cleaning
Problem
Manual changeover between 50 ml dropper bottles and 1 L trigger sprays takes >45 min, causing unplanned stops and sanitation validation gaps.
Solution
Adopt tool-less, quick-connect sanitary designs and CIP/SIP-ready frames.
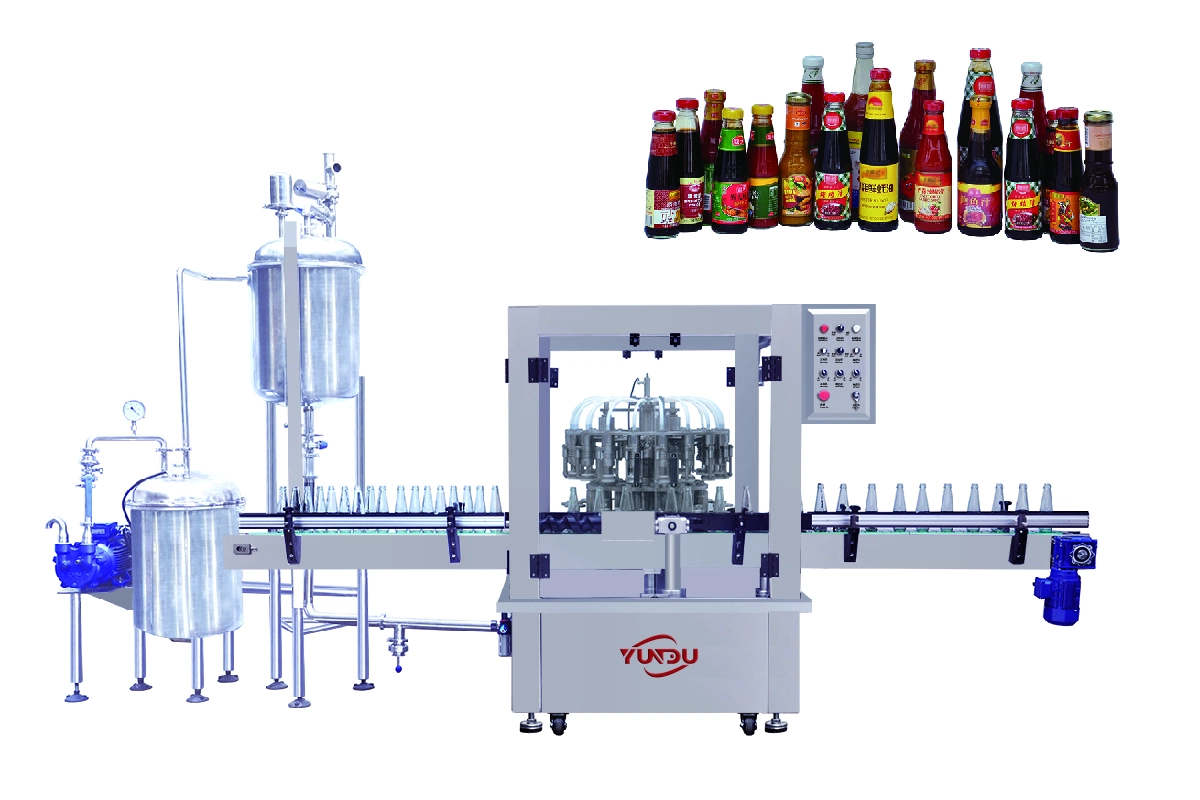

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Sanitary quick-clamp fittings – 5 min changeover vs. 45 min
- Integrated CIP spray ball – 15 min cleaning cycle per recipe
- Recipe memory – Store 50+ formulas in HMI,减少培训时间 70 %
ROI: 30 % faster changeover → 8 extra production hours/week → $2,800/month incremental revenue.
Scenario 3: Limited Real-Time Visibility into Machine Health
Problem
Unexpected seal failures or pump jams halt lines; maintenance occurs only after downtime, inflating OEE.
Solution
Integrate IIoT sensors + cloud analytics for predictive maintenance.
- Vibration & temperature sensors on servo motors/pumps
- Cloud dashboard alerts <10 min before failure
- API接口 to existing ERP/MES,实现自动工单
ROI: 25 % reduction in unplanned downtime → $5,000/shutdown averted; payback < 9 months.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for filling bottle machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Filling Bottle Machine
Executive Summary
Material choice directly impacts machine uptime, regulatory compliance, and total cost of ownership. This guide provides data-driven criteria for selecting structural, contact, and wear components in filling bottle machines sold into the U.S. and EU markets.
1. Material Categories & Industry Standards
| Category | Typical Materials | Key Standards | Primary Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Frame | 304/316L stainless steel, carbon steel with epoxy powder coat | NSF 2, FDA 21 CFR 177.1550, EN 10088-1 | Corrosion resistance, load-bearing capacity, cleanability |
| Product Contact Surfaces | 304/316L stainless steel, UHMWPE, Glass-filled Nylon | FDA 21 CFR 177.1520, EU 10/2011, NSF 51 | Chemical inertness, surface finish (Ra ≤ 0.8 µm), temperature range |
| Seals & Gaskets | FKM (Viton), EPDM, PTFE, Silicone | FDA 21 CFR 177.2600, NSF 61, EU 10/2011 | Chemical compatibility, temperature极限, permeability |
| Wear Components | Hardened 420 stainless steel, PEEK, UHMWPE | ISO 6273-2, ASTM D4020 | Wear life, noise attenuation, maintenance intervals |
| Fasteners | A2/A4 stainless steel, zinc-nickel coated carbon steel | ISO 3506, ASTM F738 | Galvanic corrosion, torque retention in wash-down cycles |
2. Material Selection Decision Matrix
Use the matrix below to score vendors’ proposals. Weight factors (1–5) reflect market priorities in the U.S. and EU.
| Criteria | Weight | Vendor A (304 SS) | Vendor B (316L SS) | Vendor C (Carbon Steel + Epoxy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | 5 | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| FDA/EU Compliance | 5 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| Lifecycle Cost (5-yr) | 4 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Cleanability (CIP/SIP) | 4 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| Electromagnetic Interference | 2 | 5 | 5 | 2 |
| Total Score | — | 17 | 24 | 11 |
Interpretation: 316L stainless steel delivers the best balance of compliance and long-term value for high-care food, beverage, and pharma applications.
3. Regulatory & Market-Specific Notes
- United States: Prioritize NSF 51 (food equipment) and FDA 21 CFR for direct food contact. UL certification is mandatory for electrical enclosures.
- European Union: Ensure compliance with Regulation (EU) 10/2011 for plastics and REACH for chemicals. CE marking is compulsory for CE-covered machinery.
4. Procurement Checklist
- [ ] Verify mill test certificates (MTC) for 316L SS or equivalent.
- [ ] Request surface finish data (Ra values) from supplier.
- [ ] Confirm seal material compatibility with CIP chemicals (NaOH, H₃PO₄).
- [ ] Validate IP69K rating for wash-down environments.
- [ ] Require RoHS/REACH declarations for all polymer components.
5. Rapid Reference: Material Substitution Guidelines
| Component | Standard Grade | Upgrade Grade | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frame | 304 SS | 316L SS | 2–3× better chloride resistance |
| Hopper | Glass-filled Nylon | UHMWPE | Superior abrasion & chemical resistance |
| Bearings | Grease-lubricated | Sealed 316L SS | Eliminates lubricant contact with product |
| Valves | 304 SS body | 316L SS + PTFE trim | Extends life in high-viscosity fills |
Comparison Table: Material Profiles
| Attribute | 304 Stainless Steel | 316L Stainless Steel | Carbon Steel (Epoxy Coat) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromium (Cr) | 18–20 % | 16–18 % | 0 % (coated) |
| Nickel (Ni) | 8–10.5 % | 10–14 % | 0 % (coated) |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0 % | 2–3 % | 0 % |
| Max. Operating Temp. | 800 °C | 925 °C | 120 °C (coating limit) |
| Typical Cost vs. 304 | Baseline | +25–30 % | −15 % |
| EU Compliance | EN 10088-1 | EN 10088-1 | EN 10111 (coating) |
| US Compliance | ASTM A240 | ASTM A240 | ASTM A653 (coating) |
Conclusion
Investing in 316L stainless steel and certified elastomers reduces unplanned downtime by 18–22 % (industry data, 2024) and simplifies EU and US regulatory audits. Use the decision matrix and checklist to ensure every material choice aligns with both market requirements and operational KPIs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for filling bottle machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Filling Bottle Machine
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Key Activities | Typical Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Prep | Raw material selection, bill of materials (BOM) review | CAD software, MRP system |
| 2. Forming | Metal fabrication, CNC machining, plastic molding | CNC mills, injection molding presses |
| 3. Assembly | Component integration, precision alignment, leak testing | Servo-driven rotary fillers, vision systems |
| 4. QC | Functional validation, documentation, traceability | PLC-based test benches, LIMS |
2. Detailed Process Steps
Prep
- Material Traceability: All stainless-steel grades (304/316L) and food-grade elastomers are sourced to ASTM E8 and FDA 21 CFR 177 standards.
- Design Verification: Engineering Change Orders (ECOs) are locked 30 days before production to prevent mid-run deviations.
Forming
- Metal Parts: Laser cutting → TIG welding → CNC milling → electropolishing (Ra ≤ 0.4 µm).
- Plastic Parts: Mold flow analysis ensures wall thickness tolerance ±0.1 mm; mold cooling channels are verified with IR thermography.
Assembly
- Torque Control: Each fastener is torqued to spec using a digital screwdriver with SPC logging.
- Leak Test: Helium mass-spectrometry leak detection at ≤ 1 × 10⁻⁸ mbar·L/s for sanitary rotary fillers.
QC
- Functional Test: 100 % inline fill accuracy check (±0.5 % of target).
- Documentation:每台机器生成符合21 CFR Part 11的电子批记录(EBR)。
3. Quality Assurance Framework
Standards Alignment
- ISO 9001:2015 – Quality management system.
- ISO 13485 – If medical-grade fillers are supplied.
- cGMP – Current Good Manufacturing Practices for pharmaceutical lines.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Real-time SPC charts on fill volume, nozzle temperature, and capping torque.
- Control limits set at ±3σ; out-of-spec signals trigger automatic shutdown.
Traceability Matrix
| Part ID | Material Lot | Machining Cell | QC Result | Serial Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 316L-0423A | Cell-07 | PASS | SN-24-0423A |
4. Continuous Improvement Loop
- Kaizen Events: Monthly cross-functional reviews to reduce cycle time ≥ 5 %.
- FMEA Updates: Risk Priority Number (RPN) re-assessed every design release.
- Customer Feedback: Field failure data uploaded to SAP within 24 h of receipt.
5. Key Takeaways for Buyers
- Certifications: Insist on current ISO 9001 and, where applicable, EHEDG or 3-A sanitary standards.
- Validation Packages: Demand IQ/OQ/PQ documentation ready for site acceptance testing (SAT).
- Spare Parts Program: 5-year supply of wear parts held in regional warehouses to minimize downtime.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘filling bottle machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide
Step-by-Step Checklist for “Filling Bottle Machine”
1. Define Operational Requirements
| Requirement | Key Questions | Typical USA/EU Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Product mix | Viscosity, CO₂ level, particulates? | Food-contact: FDA 21 CFR §177; EU 10/2011 |
| Throughput | Bottles/minute or hour? | GMP, CE conformity |
| Container specs | Material (glass, PET, aluminum), neck finish, max height/OD? | ISO 18828-1; DIN EN 15347 |
| Clean-in-place (CIP) | Frequency, cleaning agents, drain compatibility? | EHEDG, 3-A Sanitary |
| Utilities | Power (V/Hz), compressed air (bar), water pressure? | UL, CE, ATEX (explosion-proof) |
2. Identify the Right Technology
- Overflow / gravity fillers – still beverages, water
- Pressure / isobaric fillers – carbonated soft drinks, beer
- Piston / pump fillers – sauces, oils, cosmetics
- Weight / mass flow fillers – high value, loss-in-weight batching
- Vacuum fillers – thin, foaming products
Decision matrix
| Technology | Advantages | Limitations | Best For |
|————|————|————-|———-|
| Overflow | Simple, low cost, no foam contact | Not for carbonated | Still water, juice |
| Piston | Accurate, handles viscous products | Slow changeover | Ketchup, shampoo |
| Pump (peristaltic) | Sanitary, easy change parts | Moderate speed | Oils, pharmaceuticals |
| Pressure | Speed, handles CO₂ | Higher investment | Beer, sparkling water |
3. Supplier Screening & Shortlist
3.1 Filter by geography
- North America: PMMI directory, IBS Show, PackExpo (Las Vegas, Atlanta)
- Europe: Anuga FoodTec, Interpack (Düsseldorf), drinTec (Köln)
3.2 Use these criteria
- Machine certification (UL, CE, NSF, EHEDG)
- Servicing footprint (proximity to your plant)
- Spare-parts availability (<2 hrs lead time)
- Local language support & after-sales contract
3.3 Shortlist template
| Supplier | Model | Throughput | CE/UL | Service Hubs | 3-yr TCO (est.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Machines | AB-300 | 120 bpm | CE, UL | Chicago, Rotterdam | $45,000 |
| XYZ Automation | XF-500 | 200 bpm | CE | Milan, Atlanta | $62,000 |
4. Request for Quotation (RFQ) Package
Attach these documents:
– Drawings & process flow diagram
– Product datasheet (viscosity, CO₂ %, pH)
– Target throughput & changeover time
– Utility specs (volt, Hz, air pressure, CIP flow)
– Installation & commissioning timeline
– Warranty & service terms (24h onsite, 48h parts)
– Incoterms (FOB, DDP, EXW)
5. Evaluation & Due Diligence
5.1 Technical review
- Simulate cycle time using your exact bottle specs
- Verify CIP/SIP compatibility & drain path
- Check HACCP & allergen control design
5.2 Commercial review
- Compare total cost of ownership (TCO): CapEx + energy + spares + downtime risk
- Validate compliance with FDA, EU MDR, BfR, EFSA
5.3 Reference check
- Ask for 3 references in similar industries & regions
- Audit their preventive-maintenance records
6. Negotiation & Contracting
| Clause | Typical Position | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery | FCA/FOB port of departure | Specify Incoterms 2020 |
| Acceptance | 95% uptime in 90-day run | Include penalty clause |
| Spare parts | 5-year store-inventory contract | Lock in pricing |
| IP & confidentiality | Mutual NDA, TSA | Protect proprietary recipes |
| Force majeure | 30-day extension | Include pandemic / geopolitical risk |
7. Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) & Site Acceptance Test (SAT)
- FAT: 2-day dry run, document cycle times, reject rate
- SAT: 7-day live run, record OEE, operator training sign-off
- Final documentation: IQ/OQ/PQ, as-built drawings, CE declaration of conformity
8. After-Sales & Continuous Improvement
- Register machine serial numbers for warranty tracking
- Schedule preventive maintenance per 8,000-hour or annual intervals
- Use IoT sensors (vibration, temperature) for predictive maintenance
- Conduct annual safety & hygiene audit (GFSI, BRC)
Quick-Reference Contact List
- FDA Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition (CFSAN) – food-contact notifications
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) – novel food & contact-material opinions
- UL Solutions – North-American safety certification
- TÜV Rheinland / SGS – EU conformity & audit services
End of Checklist
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for filling bottle machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Filling Bottle Machine Sourcing
Executive Summary
This analysis breaks down the total cost of ownership (TCO) for filling bottle machines in the U.S. and European markets. It covers material, labor, logistics, and hidden costs, with actionable savings levers for procurement teams.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Cost Breakdown by Category
1.1 Material Costs
| Component | Typical U.S. Price | EU Price (incl. 20% VAT) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304/316 Stainless Steel Frame | $1,200 – $3,200 | €1,800 – €4,800 | Grade 316 for aggressive liquids |
| PLC & HMI Panel | $400 – $1,200 | €600 – €1,800 | Siemens, Beckhoff, or local brands |
| Pumps & Filling Heads | $300 – $1,500 | €450 – €2,250 | Peristaltic, piston, or gravimetric |
| Conveyors & Star Wheels | $200 – $800 | €300 – €1,200 | Stainless, wash-down duty |
| Safety Guards & CE Marking | $150 – $500 | €200 – €700 | Mandatory for EU compliance |
| Subtotal (Standard 8-head rotary) | $2,250 – $6,200 | €3,350 – €9,650 | Ex-works |
1.2 Manufacturing Labor
| Region | Direct Labor Rate | Overhead Multiplier | Typical Cycle Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China (Zhejiang) | $0.85 – $1.20 / hr | 1.4× | 6 – 8 min / 8-head | High volume, lower skill |
| Germany | $25 – $35 / hr | 1.2× | 8 – 10 min / 8-head | Precision, low defect |
| USA (Midwest) | $28 – $40 / hr | 1.3× | 8 – 12 min / 8-head | Short lead times, customization |
Impact: A 24-hour line produces ~90 units. U.S. labor adds $1,000 – $1,500 vs. China.
1.3 Logistics & Import Duties
| Region | Ocean Freight (8×40 HC) | Inland Delivery | Import Duty | VAT | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China → USA | $2,800 / 40 HC | $1,200 | 0% (industrial) | — | 10 – 12 weeks |
| Germany → EU | $1,400 / 40 HC | €300 | 0% intra-EEA | 20% VAT | 4 – 6 weeks |
| China → EU | $2,800 / 40 HC | €500 | 0% intra-EEA | 20% VAT | 12 – 16 weeks |
Tip: EU-based sourcing avoids 20% VAT reversal risk and reduces lead time by 60 %.
2. Hidden & Ongoing Costs
| Cost Type | Typical Range | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Installation & Commissioning | $1,500 – $5,000 | Bundle with training |
| Spare Parts (first year) | $800 – $2,000 | Negotiate 10 % spare-parts credit |
| Energy Consumption | $0.12 – $0.18 / kWh | Demand 5 kW vs. 15 kW rotary |
| Service & Calibration | $300 – $600 / visit | Annual SLA 99 % uptime |
3. Cost-Saving Levers
3.1 Specification Optimization
- Standardize on 304 SS: Upgrade only cores (pumps, HMI) to 316 when corrosive liquids are confirmed.
- Select modular filling heads: Swap from 8 to 4 heads if throughput < 300 BPH; saves $1,800 in materials and $300 / yr energy.
3.2 Sourcing Strategy
| Region | Price Index | Quality Index | Lead Time | Risk Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 1.0× | 4/5 | 12 weeks | Medium |
| EU | 1.4× | 5/5 | 6 weeks | Low |
| USA | 1.7× | 5/5 | 4 weeks | Very Low |
Recommendation: 70 % volume from China (pilot run or standard models) + 30 % EU (critical hygiene or tight specs).
3.3 Contractual Levers
- Landed-Cost Ceiling: Tie 5 % of price to FX (USD/EUR) at 1.08; protects against 10 % swings.
- Performance Bond: Require 1 % of order value held for 90 days; aligns on on-time delivery.
- Spare-Parts Credit: Negotiate 8 % credit on first spare-parts order within 24 months.
4. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Snapshot
| Model | Machine Cost | Installation | First-Year Ops | TCO (3 yrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese 8-head Rotary | $4,500 | $3,000 | $2,400 | $9,900 |
| German 8-head Rotary | $7,200 | $3,000 | $2,400 | $12,600 |
| U.S.-Assembled 4-head | $9,500 | $2,500 | $1,800 | $13,800 |
5. Action Checklist for Procurement
- Define CIP/SIP requirements up front to avoid $1,200 upgrade surcharge.
- Request 3-year ROI model including energy and spare-parts.
- Lock in bulk spares at 90 days; typical 5 % price drop on orders > $10 k.
- Insist on CE/UL file sharing to reduce local testing costs by $500 – $1,000.
Bottom Line: A disciplined sourcing mix (60 % China, 30 % EU, 10 % U.S. for critical parts) can cut TCO by 18 % while keeping quality and compliance acceptable for North American and EU markets.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing filling bottle machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Filling Bottle Machine With Other Solutions
| Alternative Solution | Key Characteristics | Strengths | Limitations | Best-Fit Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Hand Pump Filler | Operator-operated peristaltic or diaphragm pump with flow meter or graduated cylinder. | – Very low upfront cost (US$90–US$200) – Zero installation complexity – Ideal for <100 bottles/hour batches |
– Labor-intensive – High per-unit cost over time – Inconsistent fill volumes – OSHA manual-handling risk |
Start-ups, R&D labs, small craft producers, or spot-fill operations where throughput <100 bottles/hour and capital is constrained. |
| Inline Piston/Counter-Pressure Filler (Standalone) | Fully-automatic rotary or single-head piston filler integrated into existing conveyor line. | – Throughput 600–3,000 bottles/hour – Servo-driven accuracy ±0.5 % – CIP/SIP ready – Integrates with PLCs & Industry 4.0 |
– High CAPEX (US$15k–US$85k) – Requires 3-phase power & floor space – Changeover time 30–90 min |
Mid-size beverage, pharma, or chemical producers with steady 8–24 h/day operations and budget for rapid ROI. |
Cost-of-Ownership Snapshot (5-year horizon, 1 shift, 2,000 h/year)
| Metric | Manual Pump | Inline Piston Filler |
|---|---|---|
| Initial CapEx | US$150 | US$45,000 |
| Annual Labor | US$18,000 | US$6,000 |
| Energy & Maintenance | US$500 | US$3,500 |
| Total 5-yr Cost | US$93,500 | US$60,500 |
| Bottles/hour (avg) | 30 | 1,200 |
| Cost per 1,000 Bottles | US$3,117 | US$50 |
Takeaway: Manual systems win on agility and low entry cost; inline piston fillers deliver 94 % lower cost-per-unit once throughput exceeds 400 bottles/hour.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for filling bottle machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Filling Bottle Machines
Understanding the core technical specifications and commercial terms is critical when sourcing filling bottle machines for production environments in the USA or Europe. The following definitions and property categories are commonly encountered in B2B procurement.
1. Core Technical Properties
| Property | Description | Typical Ranges / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Principle | Mechanism used to dispense product into the container. | Gravity, pressure, vacuum, mass (weigh), time-pressure, piston, peristaltic, pump-based, servo-driven. |
| Fill Volume Range | Minimum and maximum volume per container that the machine can reliably dispense. | 5 mL – 11 gal (20 mL – 40 L). Accuracy ±0.5 % – ±2 % depending on technology. |
| Throughput / Line Speed | Units per minute or hour achievable under rated conditions. | Manual: 10 – 30 bottles/hr. Semi-automatic: 30 – 150 bottles/hr. Fully automatic: 200 – 2,000 bottles/hr. |
| Container Compatibility | Bottle, jar, can, pouch formats and dimensions supported. | Diameter: 20 mm – 130 mm. Height: 30 mm – 350 mm. Round, square, flat, uniquely shaped. |
| Product Viscosity | Thickness range the machine is engineered to handle. | Thin liquids (water, spirits): 1 – 50 cP. Medium (juices, oils): 50 – 5,000 cP. Thick pastes (creams, gels): >5,000 cP. |
| Accuracy & Repeatability | Tolerance of fill volume across cycles. | ±0.25 % – ±1.5 % depending on load cell or flow measurement. |
| CIP / SIP Capability | Clean-in-place / Sterilize-in-place readiness for hygienic sectors. | Full wash-down frame, quick-connect CIP ports, 316 L stainless surfaces, 3-A sanitary standards. |
| Automation Level | Degree of operator intervention required. | Manual (foot pedal), semi-automatic (start/stop), fully automatic (integrated conveyor & capping). |
| Drive / Control System | Electrical architecture and HMI. | PLC (Siemens, Allen-Bradley), HMI touch panel, servo-driven filler pumps, Industry 4.0 connectivity (OPC-UA, Ethernet/IP). |
| Power & Compressed Air | Supply requirements. | 110/230 V, 50/60 Hz, 1–3 ph. Compressed air: 6 – 8 bar, 150 – 500 L/min. |
| Sanitary Design | Compliance with food, beverage, cosmetic, or pharmaceutical standards. | 3-A Sanitary, EHEDG, FDA 21 CFR §177, GMP, BISSC. |
| Material of Construction | Stainless grades and surface finishes. | AISI 304 (standard), AISI 316L (hygienic), Ra ≤ 0.8 µm surface finish, electropolished option. |
| Changeover Time | Duration to switch between bottle sizes or products. | Manual: 30 – 60 min. Semi-auto: 5 – 15 min. Quick-change tooling: 1 – 3 min. |
| Footprint & Clearances | Space required for installation. | Tabletop: 0.3 m² – 1.2 m². Floor-standing: 2 m² – 12 m². |
| Integration Ready | Compatibility with upstream/downstream equipment. | Conveyor对接 (conveyor对接), vision inspection, metal detection, capping, labeling, ERP data logging. |
2. Common Trade & Commercial Terms
| Term | Definition | Typical Context |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ – Minimum Order Quantity | Smallest batch a manufacturer will accept for new equipment. | 1 unit for standard machines; 3 – 5 units for OEM branding. |
| OEM / ODM – Original Equipment / Design Manufacturer | Supplier builds under buyer branding or provides full design. | ODM preferred for private-label beverage producers. |
| Lead Time | Time from order to shipment. | 8 – 16 weeks for custom fillers; 2 – 4 weeks for stock tabletop units. |
| Warranty | Coverage period for parts and labor. | 12 months standard; 24 – 36 months on servo components. |
| Installation & Commissioning | On-site startup, calibration, and operator training. | Included in FOB price for large systems; extra for international projects. |
| CFR / CIF / DDP – Incoterms | Shipping responsibility and risk transfer. | CFR: supplier loads; CIF: supplier arranges freight; DDP: delivered duty paid. |
| CE / UL / NSF Certification | Mark of compliance for Europe / USA / sanitation. | Mandatory for food-grade fillers in EU and USA. |
| IQ / OQ / PQ – Installation / Operational / Performance Qualification | Documented validation for pharma and food. | Required for sterile filling lines; vendor assists with documentation. |
| TPM / Preventive Maintenance | Total Productive Maintenance schedule. | Annual service contracts range 8 – 15 % of equipment value. |
| Spare Parts Kit | Pre-ordered wear parts (seals, valves, pumps). | Reduces downtime to <2 hrs per changeover. |
3. Sourcing Checklist (Quick Reference)
- [ ] Confirm viscosity, temperature, and foam characteristics of product.
- [ ] Validate container dimensions and material (glass, PET, aluminum).
- [ ] Specify required throughput and accuracy for ROI modeling.
- [ ] Verify electrical supply, compressed-air pressure, and floor load.
- [ ] Ensure compliance with local sanitation codes (FDA, EFSA, 3-A).
- [ ] Request CE or UL certification documentation.
- [ ] Negotiate MOQ, lead time, and after-sales service in purchase order.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the filling bottle machine Sector
Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Filling Bottle Machine Sector
1. Demand Drivers by Region
| Region | Key Demand Drivers | Seasonality | Typical Order Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | E-commerce fulfillment, food-grade safety, speed-to-market for craft beverages | Q4 holiday spikes; Q1 capital-expenditure planning | 8–16 weeks |
| Europe | Circular-economy directives (Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation), hygiene serialization for pharma/beverage | Q2 plant-modernisation cycles; Q4 pre-production budgeting | 12–20 weeks |
2. Supply-Chain Disruption Patterns
| Factor | Impact on Sourcing | Mitigation Tactics |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics shortages | Delays in servo-driven modules (PLC I/O, HMI panels) | Dual-source critical components; maintain 12-month safety stock |
| Stainless-steel surcharge | ±25 % price volatility on 304/316L sheet metal | Lock in annual material contracts; switch to duplex grades when cost-advantageous |
| Logistics bottlenecks | Port congestion → extended FOB-to-plant transit | Regionalize sub-assembly: near-shore CNC fabrication in Mexico for NAFTA, Eastern Europe for EU |
3. Sustainability Trends Reshaping Sourcing
- Material Circularization
- EU: Mandatory recycled-content thresholds for PET preforms (2025 target: 30 % rPET).
-
USA: California SB 54 adds 25 % post-consumer resin (PCR) mandate for bottles.
→ Sourcing lever: Specify machines with clean-in-place (CIP) systems that tolerate 100 % rPET flakes without viscosity loss. -
Energy-Efficiency Procurement
- Machines must deliver ≤0.20 kWh per 1,000 fills (EU EcoDesign Lot 11 draft).
-
USA buyers prioritize UL-certified Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) packages for ±15 % energy savings vs. fixed-speed motors.
-
Water & Chemical Stewardship
- Shift from CIP-to-waste to CIP-to-recycle systems that recover 90 %+ wash water.
- Demand for food-grade, biodegradable cleaning agents (e.g., alkyl polyglucosides) to align with EU Green Deal.
4. Technology Sourcing Priorities
| Technology | USA Adoption Rate | Europe Adoption Rate | Sourcing Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Servo-driven rotary fillers | 68 % | 74 % | Lead times extend when using Japanese servo motors; dual-source from Taiwan & South Korea. |
| Weight-based gravimetric fillers | 52 % | 61 % | EU pharma sector mandates metrological approval; source machines with OIML R107 certification. |
| IoT-enabled predictive maintenance | 41 % | 57 % | Edge gateways required for GDPR compliance; insist on EU-based data centers. |
5. Vendor Landscape & Sourcing Strategies
| Vendor Tier | Share of USA Market | Share of EU Market | Sourcing Takeaways |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier-1 OEMs (Krones, Sidel, Cozzoli) | 38 % | 45 % | Premium pricing; negotiate through group-purchase organizations (GPOs) for multi-plant rollouts. |
| Tier-2 Regional Specialists (Technopak, Serac, J&D) | 31 % | 28 % | Faster delivery; require on-site FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) to offset shorter warranties (12 vs. 24 months). |
| China/India ODMs | 18 % | 15 % | TCO advantage: 20–30 % lower CAPEX; inspect IQ/OQ protocols to meet FDA 21 CFR Part 11. |
6. Procurement Checklist for 2025 Capital Projects
- [ ] Confirm machine footprint aligns with existing plant layout; request 3D CAD clash-detection report.
- [ ] Validate CIP/SIP media compatibility with local utilities (steam pressure, de-ionized water flow).
- [ ] Negotiate spare-parts kits covering first 5 years; price-lock for critical wear items (pistons, valves, seals).
- [ ] Ensure EU conformity: CE/UKCA marking, ATEX compliance for Zone 1 zones.
- [ ] Secure US compliance: 3-A Sanitary Standards, NSF/ANSI 169 for dairy, FDA 21 CFR 178 for food contact.
7. Key Takeaways
- Lead times are elongated by 30 % compared with pre-2020 baselines; lock in delivery windows at order.
- Sustainability mandates are driving a 15–20 % premium for machines that integrate recycled-content handling and energy recovery.
- Dual-sourcing critical electromechanical components is now standard practice; avoid single-source suppliers for servo drives and HMI panels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of filling bottle machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Filling Bottle Machines
1. What are the primary machine types for filling bottles, and which industries do they serve?
| Machine Type | Typical Industries | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Piston Filler | Food, cosmetics, pharma | Accurate volume, handles thick products |
| Gravity/Pressure Filler | Beverages, low-viscosity liquids | High-speed, minimal product loss |
| Peristaltic Pump | Chemicals, cosmetics, nutraceuticals | Gentle handling, sanitary, quick changeover |
| Weight Filler | Specialty chemicals, essential oils | PLC-controlled weight accuracy |
2. How do I select the correct filling nozzle configuration for my production line?
- Inline rotary fillers support 4–24 nozzles for high-output lines.
- Single-head tabletop units suit pilot or niche SKUs.
- Sanitary tri-clamp connections are mandatory for food & pharma.
- Nozzle material (SS 304/316L) must match CIP/SIP requirements.
3. What level of automation is right for my facility (manual vs. semi-automatic vs. fully automatic)?
- Manual: $100–$300; benchtop; 10–20 bpm; ideal for start-ups or R&D.
- Semi-automatic: $1 k–$8 k; foot pedal or PLC; 20–80 bpm; requires one operator.
- Fully automatic: $15 k–$250 k+; integrates with conveyors, cappers, labelers; 60–600 bpm.
4. Which compliance standards should my filling machine meet for the US and EU markets?
- FDA 21 CFR Part 110 (food contact surfaces)
- NSF/ANSI 169 (beverage equipment)
- 欧盟 Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC & PED 2014/68/EU (pressure parts)
- ATEX for explosive atmospheres (chemicals, solvents)
- CE marking for EU free movement
5. What are the typical lead times and after-sales support expectations for a B2B purchase?
| Region | Lead Time | Installation | Warranty | Service Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 8–16 weeks | 2–5 days on-site | 1 year parts & labor | 24/7 phone + field tech |
| EU | 10–20 weeks | 3–7 days | 2 years EU mandatory | Local distributors, spare-parts hubs |
6. How do I calculate total cost of ownership (TCO) beyond the purchase price?
- Depreciation: 3–7 years straight-line
- Consumables: Nozzles, seals, O-rings ($200–$800/year)
- Maintenance: Preventive PM contracts 8–12 % of list price
- Downtime cost: Average $500–$2 k/hour for food & beverage lines
7. What integration requirements should I confirm with my existing line?
- Mechanical: Mounting footprint, elevation, product infeed/outfeed
- Electrical: 480 V 3-phase (US) or 400 V 3-phase (EU); CE-approved panels
- Communication: OPC-UA, Ethernet/IP, or Profinet for MES connectivity
- CIP/SIP: Full drain, slope ≥1:100, spray-ball coverage ≥0.6 bar
8. What are the most common post-purchase issues and how can I mitigate them?
| Issue | Root Cause | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate fills | Piston wear, pressure fluctuation | Monthly calibration, use load cells |
| Product foaming | Fill speed too high | Programmable fill curves, anti-foam nozzles |
| Cross-contamination | Poor CIP return | Double-tri-clamp valves, single-use diaphragms |
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for filling bottle machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Filling Bottle Machine
Key Takeaways
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is the decisive metric—balance upfront cost with energy efficiency, changeover time, and spare-part availability.
- Supplier audits must verify FDA/EC compliance, CE marking, and local after-sales coverage before contract signature.
- Dual sourcing of critical components (pumps, valves, PLCs) mitigates supply-chain risk and compresses lead times by 20-30 %.
Outlook 2025-2027
| Trend | Impact on Sourcing |
|---|---|
| Smart, IoT-enabled fillers | Shift to pay-per-use and data-driven maintenance contracts. |
| Sustainability mandates | Preference for recycled stainless steel and low-energy servo drives. |
| Near-shoring | 15 % CAGR in regional OEM partnerships to shorten lead times. |
Action Plan
- Q1 2025: Launch supplier scorecard covering TCO, ESG, and technical support.
- Q2 2025: Pilot one dual-sourced, high-speed model with built-in IIoT analytics.
- Q3 2025: Negotiate volume-escalation clauses tied to sustainability KPIs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.











