The global fiber optic solar lighting market is witnessing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient illumination solutions. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global daylight harvesting systems market, which includes fiber optic solar lighting, was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by rising adoption in commercial and residential sectors, stringent energy efficiency regulations, and technological advancements in solar light transmission. As sustainability becomes a priority across industries, fiber optic solar lighting stands out for its ability to deliver natural sunlight indoors without heat or UV transmission. With innovation and investment accelerating worldwide, we spotlight the top 9 fiber optic solar lighting manufacturers leading this transformative space.
Top 9 Fiber Optic Solar Lighting Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
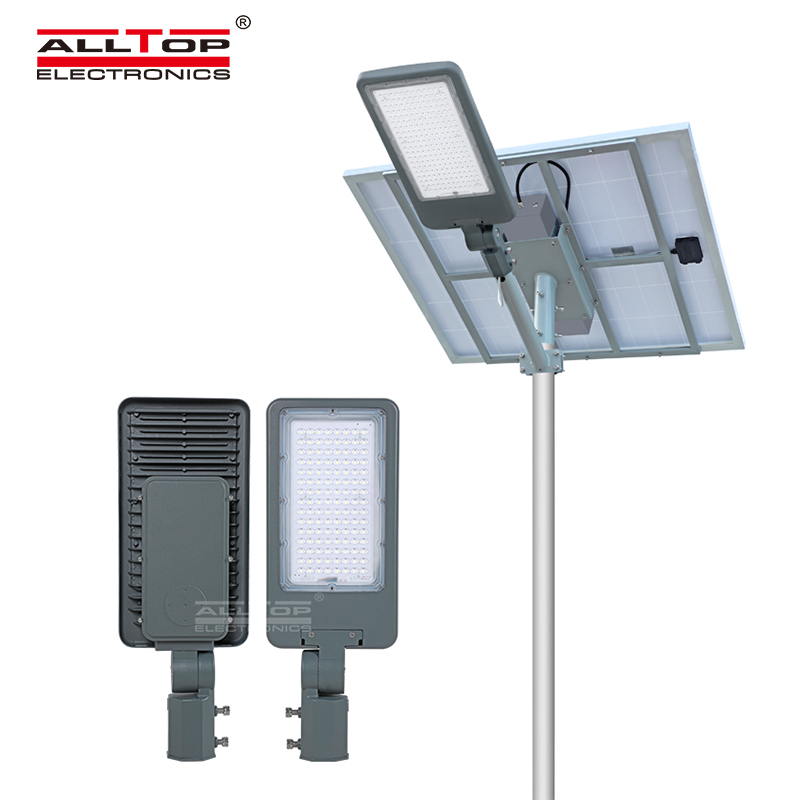
#1 Wholesale Fiber Optic Solar Tube from China Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2023
Website: alltopsolarlight.com
Key Highlights: Introducing the Fiber Optic Solar Tube, the perfect solution for illuminating your space while utilizing solar energy. The technology behind this innovative ……
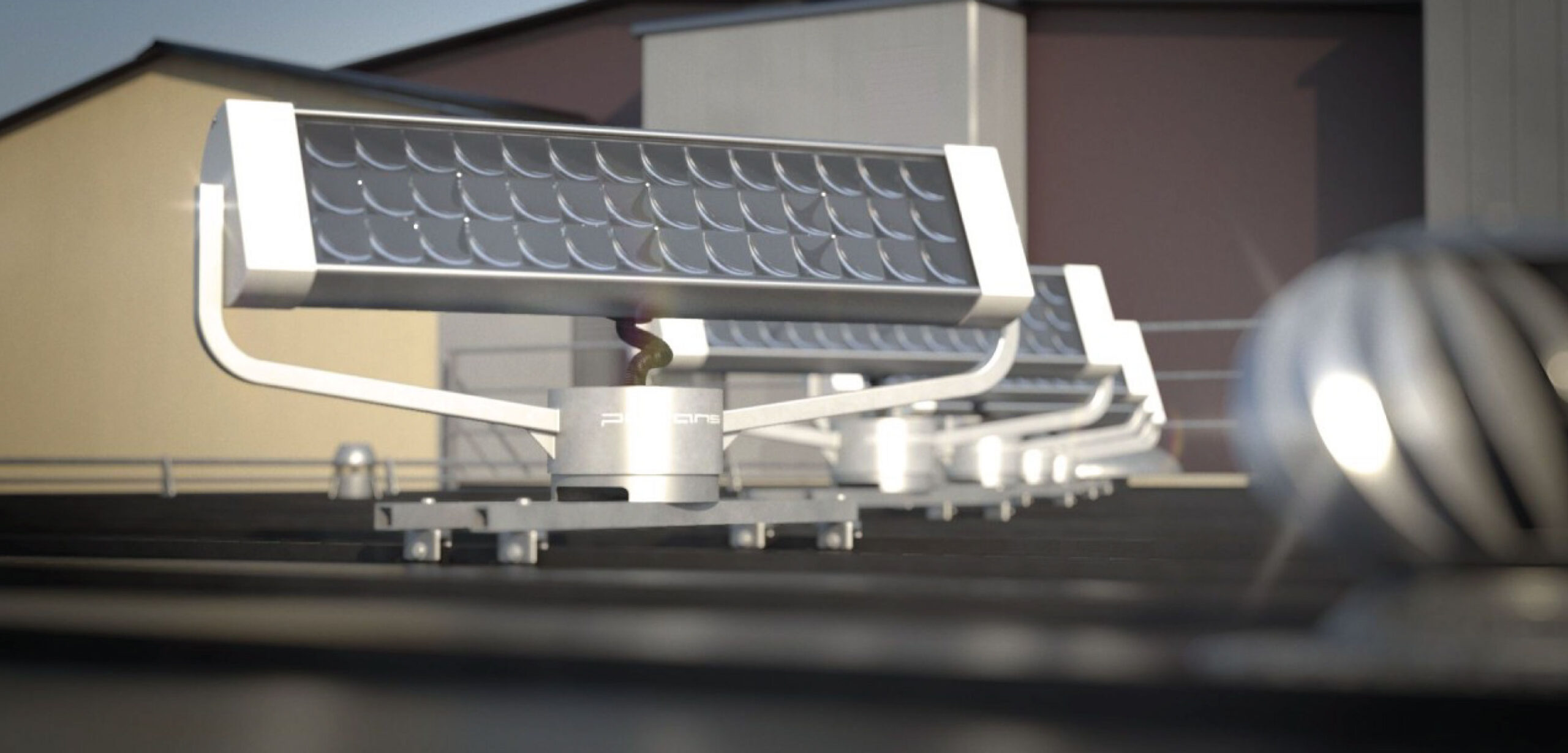
#2 Parans Sunlight System
Domain Est. 2021
Website: paranslight.com
Key Highlights: Parans solar lighting system brings zero-carbon natural light indoors with innovative fiber optic technology for sustainable spaces….
#3 FOA
Domain Est. 1999
Website: thefoa.org
Key Highlights: Fiber optic lighting uses optical fiber as a “light pipe,” transmitting light from a source through the fiber to a remote location….
#4 UFO Lighting: Fibre Optic Lighting
Domain Est. 2002
Website: fibreopticlighting.com
Key Highlights: Class leading LED, fibre optic and bespoke lighting solutions. All designed and manufactured in-house in our UK premises….
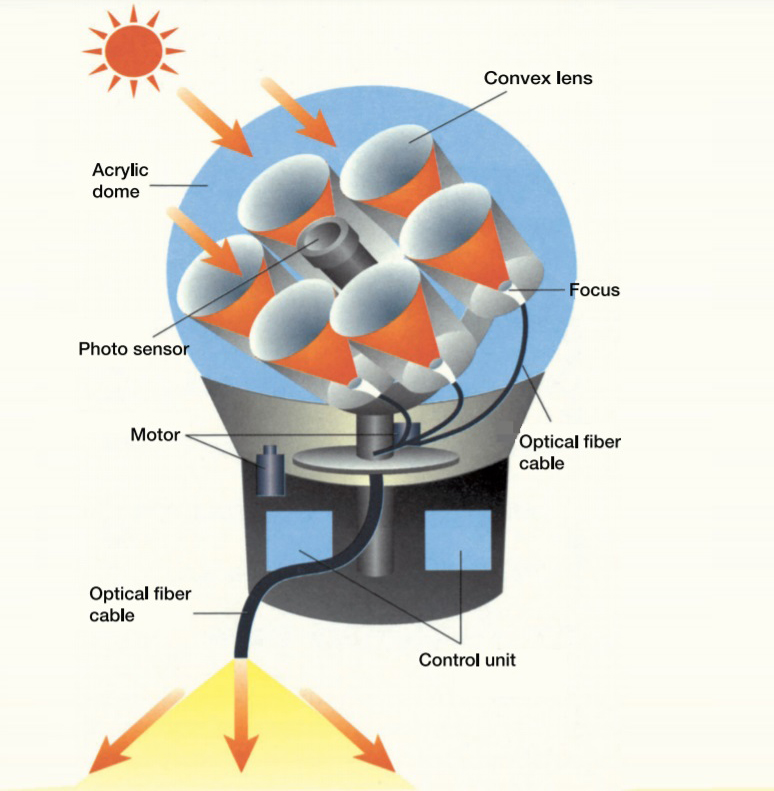
#5 Himawari Fiber Optical System
Domain Est. 2006
Website: signet.co.in
Key Highlights: Research and development, manufacture, and distribution of optical fiber lighting. Engineering of various kinds of solar energy utilization systems. Our ……
#6 Cobb Fibre Ottiche
Domain Est. 2007
Website: fibre-ottiche.it
Key Highlights: Welcome in COBB FIBER OPTICS · We specialize in the production and design of fiber optic lighting systems and LED lighting in every field of application….
#7 Fibrepros
Domain Est. 2019
Website: fibrepros.co
Key Highlights: Fibrepros is one of the leading Suppliers & Installers for Fibre Optic Lighting components, in the Middle-East. From the world’s largest Star-Field Ceiling ……
#8 How it works
Domain Est. 2021
Website: himawarisolar.com
Key Highlights: Himawari system consists of a sunlight collector and optical fiber devices. Its outdoor sunlight collector collects sunlight passes through quartz glass ……
#9 Lightforce Corporation
Domain Est. 2022
Website: lightforcecorp.com
Key Highlights: Lightforce Corporation is a leading lighting supplier that specializes in providing high-quality, reliable lighting solutions for a variety of industries….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fiber Optic Solar Lighting

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Fiber Optic Solar Lighting
As the global push toward sustainable and energy-efficient technologies accelerates, fiber optic solar lighting is poised to experience significant growth and innovation by 2026. This hybrid technology—combining solar energy collection with fiber optic light transmission—offers a unique solution for natural daylight harvesting and energy-free illumination. Several key market trends are expected to shape the industry landscape in 2026:
1. Increased Adoption in Green Building and Smart Infrastructure
With the rise of green building certifications such as LEED, BREEAM, and WELL, architects and developers are integrating energy-saving technologies into new constructions. Fiber optic solar lighting systems, which require no electricity to transmit daylight indoors, are increasingly being adopted in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and underground spaces. By 2026, integration with smart building systems—such as automated daylight dimming and IoT-enabled monitoring—is expected to enhance efficiency and user control.
2. Advancements in Optical Efficiency and Material Science
Ongoing R&D in fiber optic materials—particularly in high-purity polymer optical fibers (POF) and hybrid glass-polymer systems—is improving light transmission efficiency and durability. Innovations in solar concentrators and light-tracking mechanisms are also boosting the amount of daylight captured and delivered. By 2026, next-generation systems are expected to deliver brighter, more consistent illumination over longer distances, expanding their usability in larger architectural projects.
3. Expansion into Residential and Off-Grid Applications
While historically limited to niche commercial or institutional applications due to high initial costs, fiber optic solar lighting is becoming more accessible. Decreasing solar panel costs and modular system designs are enabling residential adoption, particularly in remote or off-grid areas with abundant sunlight. By 2026, compact, plug-and-play solutions are expected to enter the consumer market, offering natural lighting for homes, basements, and sunrooms without electrical wiring.
4. Regional Growth in Sun-Rich and Energy-Scarce Markets
Markets in the Middle East, North Africa, South Asia, and Australia are emerging as key adopters due to high solar irradiance and growing energy demands. Governments in these regions are increasingly supporting renewable lighting initiatives as part of broader sustainability goals. In contrast, European and North American markets are focusing on retrofitting existing buildings with daylighting solutions to meet strict energy efficiency regulations.
5. Integration with Renewable Energy Ecosystems
By 2026, fiber optic solar lighting systems are expected to be more frequently bundled with photovoltaic (PV) solar systems, offering dual functionality: one system for electricity generation and another for daylight harvesting. This synergy enhances the return on investment for solar installations and supports holistic energy management in smart homes and commercial complexes.
6. Regulatory Support and Incentives
Government incentives, tax rebates, and energy efficiency mandates are expected to play a crucial role in market expansion. Countries with aggressive carbon neutrality targets—such as those in the EU under the Green Deal—are likely to include daylighting technologies in building codes, further driving adoption of fiber optic solar solutions.
7. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market is witnessing increased participation from both specialized startups and established lighting/energy companies. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are anticipated by 2026 as larger firms seek to enhance their sustainable technology portfolios. This consolidation is expected to accelerate innovation and reduce product costs.
In summary, the 2026 market for fiber optic solar lighting is set to benefit from technological advancements, regulatory support, and rising demand for sustainable infrastructure. As the technology becomes more efficient, affordable, and versatile, it is expected to move from a niche innovation to a mainstream component of energy-conscious design across multiple sectors.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Fiber Optic Solar Lighting (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Fiber Optic Solar Lighting (FOSL) systems offers sustainable illumination solutions, but buyers often encounter significant challenges related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to subpar performance, safety risks, and legal complications. Below are key issues to watch for:
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
Many budget FOSL systems use low-grade optical fibers with high attenuation, resulting in weak light transmission and reduced brightness over short distances. Inferior solar panels may have low conversion efficiency and poor durability, especially under UV exposure or extreme weather. Plastic connectors and housings degrade quickly, leading to system failure. Always verify material specifications and request performance test reports.
Inaccurate or Missing IP Protection Claims
Suppliers may falsely claim proprietary technology or patent ownership to appear innovative. Always verify IP status through official patent databases. Beware of designs that closely mimic patented systems from reputable brands, as sourcing such products could expose your business to infringement lawsuits. Request documentation of IP rights and ensure freedom to operate.
Misleading IP Ratings (Ingress Protection)
A major concern is inflated or unverified IP ratings. Some suppliers claim high dust and water resistance (e.g., IP67 or IP68) without third-party certification. In reality, poorly sealed connections between solar units, fiber bundles, and emitters can allow moisture ingress, leading to mold, corrosion, and system failure. Demand certified test reports from accredited labs for any IP claims.
Lack of Compliance and Certification
Many low-cost FOSL systems lack essential certifications (e.g., CE, RoHS, IEC standards), indicating non-compliance with safety and environmental regulations. This is particularly risky for outdoor or commercial installations. Always confirm compliance documentation and check for independent testing.
Inadequate Long-Term Performance Data
FOSL systems are expected to last 10+ years, but few suppliers provide long-term reliability data. Without accelerated aging tests or field performance reports, it’s difficult to assess lifespan. Request case studies or pilot project results to evaluate real-world durability.
Hidden Costs from Poor Quality
Initial cost savings from low-quality suppliers can be offset by high maintenance, frequent replacements, and installation callbacks. Poorly engineered systems may require custom fittings or additional labor, eroding ROI. Factor in total cost of ownership, not just unit price.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence: audit suppliers, request product samples, verify certifications, and consult legal experts on IP matters before finalizing procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fiber Optic Solar Lighting
Overview
Fiber Optic Solar Lighting (FOSL) systems represent an innovative approach to sustainable illumination, harnessing natural sunlight through optical fibers to light interior spaces without electricity. While environmentally beneficial, deploying these systems involves complex logistics and strict compliance requirements across international markets. This guide outlines key considerations in transportation, import/export regulations, safety standards, certifications, and environmental compliance to ensure smooth deployment and legal operation.
Shipping and Transportation Logistics
Fiber optic solar lighting systems comprise delicate components such as solar collectors, optical fiber cables, distribution fixtures, and tracking mechanisms. Proper handling, packaging, and transportation are critical to avoid damage.
- Packaging Requirements: Use shock-resistant, anti-static, and moisture-proof packaging. Optical fibers are sensitive to bending and crushing; reels must be secured and labeled with orientation indicators.
- Transport Modes: Air freight is suitable for urgent, high-value components but increases costs. Sea freight is cost-effective for bulk shipments but requires longer lead times and careful moisture control.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Avoid extreme temperatures during transit. Optical fibers and electronic controllers can degrade if exposed to high heat or condensation.
- Labeling and Documentation: Clearly label fragile, sensitive, and orientation-specific items. Include packing lists, commercial invoices, and bill of lading with accurate product descriptions to prevent customs delays.
Import/Export Regulations
FOSL systems may be subject to import/export controls depending on their components and destination country.
- Harmonized System (HS) Codes: Correct classification is essential. Common codes include:
- 9006.59 (optical appliances and apparatus)
- 8543.70 (electronic control units)
- 7020.00 (glass components, if applicable)
Consult local customs authorities for precise categorization. - Export Controls: Systems with advanced tracking or energy management software may be subject to dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation, U.S. EAR). Verify if any encryption or surveillance features trigger export licensing.
- Import Duties and Taxes: Duties vary by country. Some nations offer reduced tariffs for green technology. Investigate eligibility for environmental product incentives.
- Restricted Materials: Ensure no conflict minerals (e.g., tantalum, tungsten) or hazardous substances are present in electronic components.
Safety and Performance Standards
Compliance with regional safety and performance standards is mandatory for market access.
- Electrical Safety:
- IEC 60598 (Luminaires): Applies to indoor distribution fixtures.
- IEC 62109 (Power Conversion Equipment): For integrated controllers or inverters.
- Optical Safety:
- IEC 62471 (Photobiological Safety of Lamps): Ensures emitted light does not pose UV, blue light, or thermal hazards.
- Mechanical and Environmental Durability:
- IP Ratings: Outdoor collectors must meet at least IP65 for dust and water resistance.
- Wind and Load Testing: Rooftop collectors should comply with local structural codes (e.g., ASCE 7 in the U.S.).
Regulatory Certifications
Mandatory certifications vary by region and application.
- European Union (EU):
- CE Marking: Required under the Low Voltage Directive (LVD), Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive, and RoHS.
- EN 12464-1: Lighting of indoor work places—verify light output meets standards.
- United States:
- FCC Part 15: For any electronic controllers emitting radio frequency energy.
- UL Certification: Recommended for safety acceptance; UL 1598 covers luminaires.
- Canada:
- CSA Certification: Required for electrical safety (CSA C22.2 No. 250.0).
- ISED Certification: For radiofrequency devices.
- Other Regions:
- UKCA Marking: For the UK market post-Brexit.
- PSE Mark: Required in Japan for electrical appliances.
- CCC Mark: Mandatory for electrical components in China.
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
FOSL systems promote sustainability but must still comply with environmental regulations.
- RoHS (EU) and similar laws (e.g., China RoHS): Restrict hazardous substances (lead, mercury, cadmium) in electrical and electronic components.
- REACH (EU): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) in products.
- WEEE Directive (EU): Producers must register and provide end-of-life take-back for electronic parts.
- Energy Efficiency Programs: Systems may qualify for LEED, BREEAM, or ENERGY STAR credits based on energy savings.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Deployment must adhere to local building and electrical codes.
- Structural Integration: Rooftop installations require engineering approval to ensure load safety.
- Electrical Wiring: Even if the system is solar-powered, auxiliary power or controls may need licensed electricians and permit approvals.
- Fire Safety: Fiber optic cables are typically non-conductive and non-flammable, but junction boxes and controllers must meet fire rating requirements (e.g., UL 94 for plastics).
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for audits and compliance verification:
- Technical files (design, testing reports)
- Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
- Test reports from accredited laboratories
- Supply chain due diligence (material sourcing, conflict minerals)
- Certificates of origin and free trade eligibility (if applicable)
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the logistics and compliance landscape for Fiber Optic Solar Lighting systems requires proactive planning and adherence to international standards. By addressing packaging, regulatory certifications, environmental regulations, and local installation codes early in the supply chain, manufacturers and installers can ensure safe, legal, and sustainable deployment of this innovative lighting technology.
Conclusion for Sourcing Fiber Optic Solar Lighting
Sourcing fiber optic solar lighting presents a sustainable, energy-efficient, and innovative solution for both residential and commercial lighting needs. By harnessing natural sunlight and transmitting it through optical fibers, this technology reduces reliance on electricity, lowers energy costs, and minimizes carbon emissions. Advances in materials and design have improved the efficiency and feasibility of these systems, making them increasingly viable for a range of applications—from indoor lighting in windowless spaces to architectural accents and off-grid installations.
When sourcing fiber optic solar lighting, it is essential to consider factors such as system efficiency, durability, ease of installation, and compatibility with existing structures. Partnering with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who offer reliable technology and after-sales support is crucial for long-term performance. Additionally, evaluating cost-benefit ratios and potential incentives for renewable energy adoption can further justify the investment.
In conclusion, fiber optic solar lighting represents a forward-thinking approach to sustainable illumination. As technology continues to evolve and global demand for green energy grows, integrating this solution into building designs and infrastructure will play a key role in creating energy-resilient and environmentally responsible spaces.