The global fiber optic laser welder market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision welding solutions in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and aerospace. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 3.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is attributed to the rising adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies and the growing need for automation to ensure weld consistency and quality. Fiber optic laser welders, in particular, are gaining traction due to their superior beam quality, energy efficiency, and integration capabilities with robotic systems. As manufacturers seek reliable, high-performance equipment, a select group of industry leaders has emerged, shaping innovation and setting benchmarks in laser welding technology. The following analysis identifies the top 9 fiber optic laser welder manufacturers leading this transformation.
Top 9 Fiber Optic Laser Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: The fiber optic laser oscillator marker has advantage of high beam quality and high reliability. It is suitable for processing fields that need high marking ……
#2 Wuhan Raycus Fiber Laser Technologies Co., Ltd.
Website: en.raycuslaser.com
Key Highlights: High efficiency of electro-optic conversion · Resistance to high resistance · Efficient sheet cutting · Output fiber length can be customized · Maintenance free ……
#3 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#4 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA….
#5 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
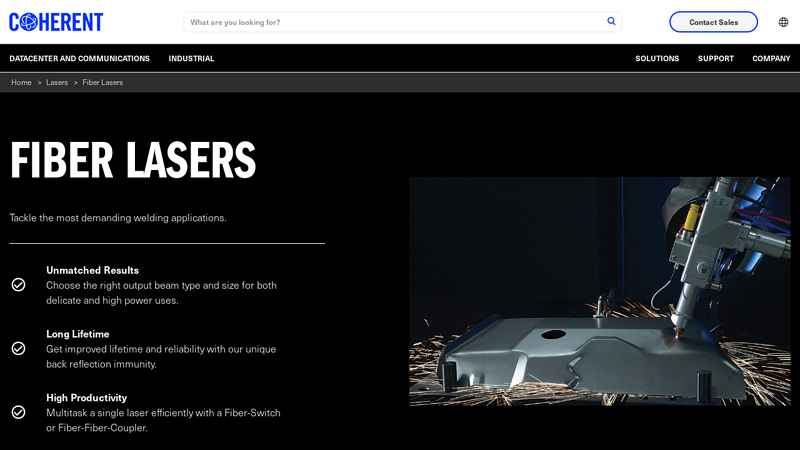
#6 Fiber Lasers
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Choose Coherent fiber lasers for exceptional capabilities and performance on challenging materials like copper, high-strength steel, aluminum, and foils….
#7 Fiber Laser Welding Machine
Website: fiberlaserwelding.com
Key Highlights: Fiber Laser Welder LLC provides top-quality fiber laser welding machines for precision, speed, and durability. Get the best solutions for your welding needs ……
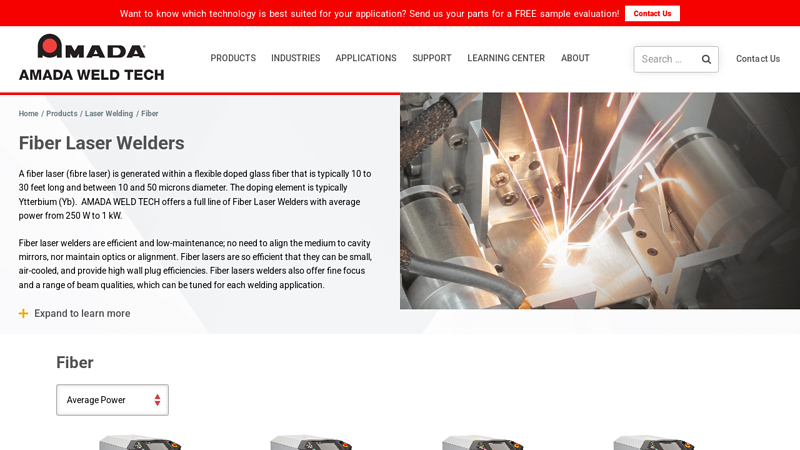
#8 Fiber Laser Welders
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: AMADA WELD TECH offers a full line of Fiber Laser Welders with average power from 250 W to 1 kW. Fiber laser welders are efficient and low-maintenance….
#9 JPT Laser
Website: en.jptoe.com
Key Highlights: JPT is a leading high-tech enterprise specializing in lasers, fiber optic devices, core laser modules, and intelligent equipment….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fiber Optic Laser Welder

H2: Market Trends Shaping the Fiber Optic Laser Welder Industry in 2026
By 2026, the global fiber optic laser welder market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, expanding industrial automation, and growing demand across high-precision manufacturing sectors. This analysis explores the key trends expected to shape the market landscape over the next few years.
-
Increased Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The rapid expansion of the electric vehicle industry is a primary driver for fiber optic laser welders. These systems offer high precision, speed, and repeatability—critical for welding battery packs, power electronics, and lightweight vehicle components. By 2026, rising EV production targets in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific will accelerate demand for advanced laser welding solutions, with fiber optic systems favored for their reliability and energy efficiency. -
Growth in Miniaturization and Precision Engineering
Industries such as medical devices, consumer electronics, and aerospace are demanding smaller, more complex components. Fiber optic laser welders, with their fine beam control and minimal heat-affected zones, are ideal for micro-welding applications. As product designs continue to shrink, especially in wearable tech and implantable medical devices, manufacturers are investing in high-precision fiber laser systems, boosting market growth. -
Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
By 2026, fiber optic laser welders are increasingly integrated into smart factory ecosystems. Enhanced connectivity through IoT, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven process optimization allow for predictive maintenance, quality assurance, and adaptive welding parameters. This shift toward intelligent laser systems improves throughput and reduces scrap rates, making fiber laser welding a cornerstone of digital manufacturing strategies. -
Advancements in Multi-Kilowatt Fiber Lasers
Ongoing improvements in fiber laser technology are enabling higher power outputs—now exceeding 20 kW in some industrial models—while maintaining beam quality and efficiency. These high-power systems are being adopted in heavy industries like shipbuilding and large-scale metal fabrication, broadening the application scope of fiber optic laser welding beyond traditional sectors. -
Regional Market Expansion and Localization
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the largest market due to strong manufacturing bases and government support for advanced industrial technologies. However, North America and Europe are witnessing renewed investment in reshoring and nearshoring manufacturing, which is increasing domestic demand for high-performance laser welding systems. This trend is encouraging regional suppliers to localize production and support services. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
As global industries prioritize carbon reduction, fiber optic laser welders are gaining favor over traditional welding methods due to their lower energy consumption and reduced material waste. Their compatibility with renewable-powered factories aligns with corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals, making them a sustainable choice for forward-thinking manufacturers. -
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with key players such as IPG Photonics, TRUMPF, Han’s Laser, and Coherent investing heavily in R&D. Innovations such as hybrid welding (laser + arc), beam oscillation techniques, and modular system designs are enhancing performance and versatility. By 2026, differentiation through software integration, ease of use, and service ecosystems will be critical for market leadership.
In conclusion, the 2026 fiber optic laser welder market will be defined by technological sophistication, sector-specific customization, and integration into next-generation manufacturing. Companies that align with automation trends, sustainability goals, and evolving customer needs will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Fiber Optic Laser Welder: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a fiber optic laser welder, especially from international suppliers or lesser-known manufacturers, involves significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is critical to ensuring a successful procurement and safeguarding your business interests.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Under-Specification and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most common issues is receiving equipment that does not meet the advertised technical specifications. Some suppliers may exaggerate laser power output, beam quality (M² factor), or welding speed. Units may also exhibit inconsistent performance over time due to poor thermal management, substandard optical components, or inadequate manufacturing controls. This leads to unreliable weld quality, increased scrap rates, and unplanned downtime.
Use of Low-Grade Components
To reduce costs, some manufacturers use inferior optical fibers, diodes, cooling systems, or control electronics. These components degrade faster, reducing the system’s lifespan and increasing maintenance costs. For example, low-quality pump diodes may fail prematurely, while poorly coated fibers can lead to power loss and beam instability.
Lack of Robust Quality Assurance and Certification
Many budget suppliers lack ISO 9001 certification or fail to provide comprehensive testing reports (e.g., power stability tests, beam profiling). Without proper QA processes, each unit may vary significantly in performance, making process validation difficult and jeopardizing product consistency in production environments.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if the initial unit functions well, poor technical support and limited access to spare parts can render the system unusable after a minor failure. Some suppliers disappear or refuse service after the warranty period, leaving users stranded with expensive, non-functional equipment.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Counterfeit or Cloned Technology
Some manufacturers reverse-engineer or outright copy patented designs from established brands. Purchasing such systems may expose your company to IP infringement claims, particularly if the equipment is used commercially. Using cloned technology can result in legal liability, product recalls, or reputational damage.
Embedded Proprietary Software Without Licensing
Fiber laser systems often include proprietary control software. Unethical suppliers may embed unlicensed or pirated software, which can lead to compliance violations, security vulnerabilities, and lack of software updates. In regulated industries, this poses audit and certification risks.
Lack of IP Ownership Clarity in Custom Solutions
When commissioning customized welders, agreements may not clearly define who owns the design improvements or process-specific configurations. This can lead to disputes if the supplier reuses your innovations for other clients or refuses to transfer design files.
Export Compliance and Technology Transfer Risks
High-power laser systems may be subject to export controls (e.g., ITAR, EAR). Sourcing from unauthorized suppliers may inadvertently violate international regulations, especially if the technology includes restricted components or software. This can lead to customs seizures or legal penalties.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence:
– Request third-party test reports and conduct on-site performance validation.
– Verify supplier certifications and audit their manufacturing facilities if possible.
– Use legally reviewed contracts that explicitly address IP ownership, software licensing, and warranty terms.
– Source from reputable manufacturers with established track records and transparent supply chains.
– Consult legal and technical experts before purchasing, especially for custom or high-power systems.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, companies can minimize risks and ensure reliable, compliant laser welding operations.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fiber Optic Laser Welder
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe and legal transport, handling, and operation of a Fiber Optic Laser Welder. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, personnel safety, and equipment integrity.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure strict adherence to all applicable local, national, and international regulations governing the import/export, transport, installation, and operation of industrial laser equipment.
Laser Safety Standards
Comply with international and regional laser safety standards, including but not limited to:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements
– ANSI Z136.1: Safe Use of Lasers (U.S.)
– EN 60825-1: European standard for laser product safety
Verify the laser welder’s classification (typically Class 4) and ensure all safety interlocks, warning labels, and protective housings are intact and functional.
Electrical Safety Compliance
Confirm the equipment meets electrical safety standards such as:
– IEC 61010-1: Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
– UL/CSA/CE Marking: Depending on the region of operation
Ensure proper grounding, voltage compatibility, and use of appropriate power cables and connectors.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Verify the laser welder complies with EMC directives to prevent interference with other electronic devices:
– IEC 61326: EMC requirements for electrical equipment
– FCC Part 15 (U.S.) or EMC Directive 2014/30/EU (EU)
Import/Export Regulations
- Obtain necessary export licenses if shipping outside your home country, especially for dual-use technologies.
- Check International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) and Export Administration Regulations (EAR) applicability.
- Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 8515 for welding machines) for customs clearance.
- Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging and handling are critical to prevent damage during transit and ensure safe on-site deployment.
Packaging Requirements
- Use manufacturer-recommended packaging with shock-absorbing materials and rigid outer casing.
- Secure all optical components, motion stages, and laser source to prevent internal movement.
- Seal all openings to prevent moisture or dust ingress.
- Include desiccants if transporting over long distances or humid environments.
Handling Instructions
- Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
- Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts, pallet jacks) and never lift by cables or connectors.
- Avoid tilting beyond manufacturer-specified angles, especially for systems with integrated optics or cooling units.
Transportation
Follow best practices for domestic and international shipping to ensure safe delivery.
Mode of Transport
- Air Freight: Requires compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if batteries (e.g., backup or UPS) are included. Most fiber laser welders are non-hazardous but verify.
- Sea Freight: Use moisture-resistant packaging and consider climate-controlled containers for long voyages.
- Ground Transport: Secure the unit to prevent shifting; avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or vibration.
Environmental Conditions
- Maintain transport temperatures within the manufacturer’s specified range (typically 0°C to 40°C).
- Avoid exposure to rain, snow, or high humidity.
- Minimize exposure to dust, dirt, and corrosive atmospheres.
Installation & Site Preparation
Prepare the installation site to meet technical and safety requirements before equipment arrival.
Facility Requirements
- Power Supply: Ensure stable, clean power with correct voltage (e.g., 208–480V, 3-phase), frequency, and grounding.
- Cooling System: Verify availability of chiller or facility cooling water (flow rate, pressure, temperature per specs).
- Compressed Air: Confirm clean, dry air supply if required for pneumatic components or lens protection.
- Ventilation & Fume Extraction: Install local exhaust ventilation to capture welding fumes (comply with OSHA or equivalent standards).
Safety Infrastructure
- Designate a Laser Controlled Area with restricted access.
- Install Laser Warning Signs at entrances (e.g., “Laser Radiation – Avoid Eye or Skin Exposure”).
- Provide Emergency Stop Buttons within easy reach.
- Equip area with appropriate Laser Safety Eyewear (OD rating matched to laser wavelength and power).
Operational Compliance
Maintain compliance during daily use to protect personnel and ensure regulatory adherence.
Training & Certification
- Ensure all operators complete certified laser safety training (e.g., LSO – Laser Safety Officer program).
- Maintain training records and update annually or per organizational policy.
Maintenance & Documentation
- Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules.
- Keep logs for laser performance, safety system checks, and repairs.
- Retain all compliance certificates (CE, UL, etc.) and user manuals on-site.
Workplace Safety
- Conduct routine audits of safety systems and protective measures.
- Report and investigate any incidents involving laser exposure or equipment malfunction.
- Update risk assessments and safety procedures as needed.
Disposal & End-of-Life
Manage decommissioning and disposal in an environmentally responsible and compliant manner.
Battery & Electronic Waste
- Dispose of backup batteries (if present) according to local WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) regulations.
- Recycle electronic components through certified e-waste handlers.
Laser Components
- Fiber laser modules may contain rare earth elements and must be disposed of following hazardous waste guidelines where applicable.
- Contact the manufacturer or authorized service provider for take-back or recycling programs.
Documentation
- Maintain records of equipment disposal, including certificates of recycling or destruction.
Note: Always consult the manufacturer’s technical documentation and local regulatory authorities for specific requirements applicable to your region and application.
Conclusion:
After a thorough evaluation of suppliers and technical specifications, sourcing a fiber optic laser welder presents a strategic investment in enhancing manufacturing precision, efficiency, and product quality. Key factors such as beam quality, power stability, automation compatibility, and post-sales support have guided the selection process. Top-tier suppliers offering reliable technology, proven industry performance, and comprehensive service networks have emerged as preferred partners. Opting for a high-quality fiber optic laser welding system not only ensures long-term cost savings through reduced maintenance and higher throughput but also positions the organization at the forefront of advanced manufacturing capabilities. Final supplier selection will balance performance, cost, and scalability to support current and future production demands.