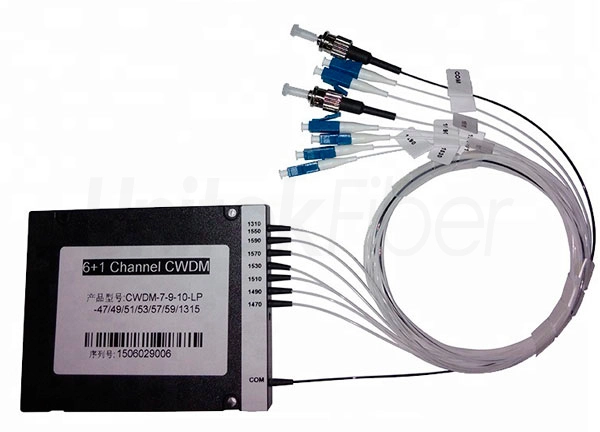
The global fiber optic multiplexer market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by surging demand for high-speed data transmission, the proliferation of 5G networks, and increasing investments in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) infrastructure. According to Grand View Research, the global fiber optic components market—encompassing multiplexers—was valued at USD 12.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.6% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts the fiber optic equipment market to register a CAGR of over 8.5% during the same period, citing escalating bandwidth requirements across enterprise, telecom, and data center applications. Within this growing ecosystem, fiber multiplexers—critical for maximizing fiber capacity through wavelength division multiplexing (WDM)—have become indispensable. As network operators seek scalable, efficient solutions to manage traffic, leading manufacturers are innovating with compact, low-power, and software-defined platforms. This report highlights the top nine fiber multiplexer manufacturers shaping the industry through technological leadership, global deployment, and strategic R&D investments.
Top 9 Fiber Multiplexer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Multiplexers & Media Converters
Domain Est. 1990
Website: moog.com
Key Highlights: Moog multiplexers are designed to provide reliable fiber optic transmission of video and data signals in the demanding subsea applications….
#2 Fiber optic multiplexers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cwic.curtisswright.com
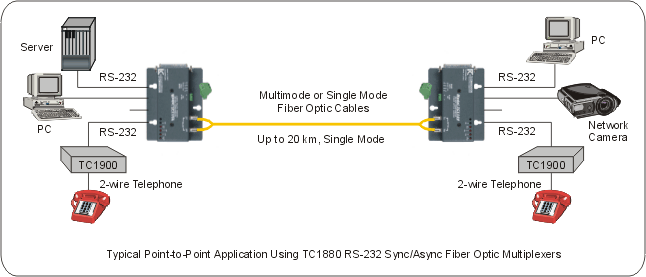
Key Highlights: Curtiss-Wright Round Rock’s industrial networking components are used to create a node necessary to transition between copper cable and fiber optic cable….
#3 Fiber Multiplexer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ctcu.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of Fiber Optical & Voice Data Multiplexer. The E1/T1 Fiber Optical Multiplexer products multiplex up to sixteen independent E1/T1 circuits and ……
#4 Fiberwdm.com
Domain Est. 2015
Website: fiberwdm.com
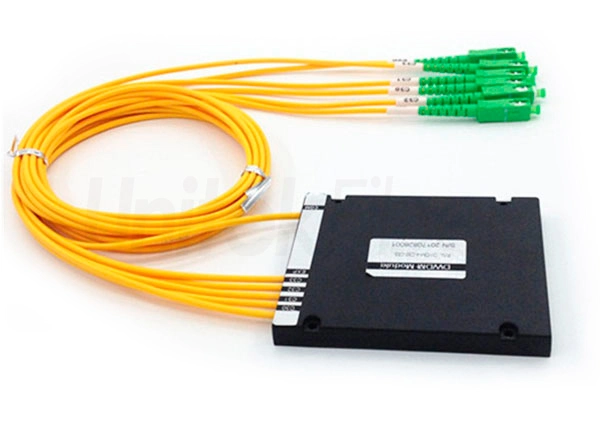
Key Highlights: FiberWDM is a fiber optic product manufacturer and integrated solution provider.Products include WDM Mux Demux,fiber optical ……
#5 MultiDyne
Domain Est. 1996
Website: multidyne.com
Key Highlights: Discover broadcast fiber optic systems for seamless signal transmission. Request a quote today for high-performance solutions….
#6 Fiber Optic Multiplexer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: oceanoptics.com
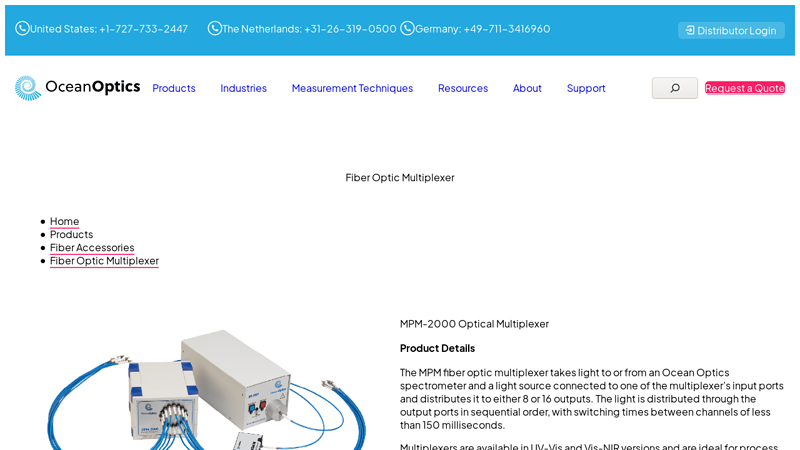
Key Highlights: The MPM fiber optic multiplexer takes light to or from an Ocean Optics spectrometer and a light source connected to one of the multiplexer’s input ports….
#7 Fiber Optic Multiplexers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: dimo.com
Key Highlights: Multiplexers are designed to provide reliable fiber optic transmission of video and data signals in the demanding subsea applications….
#8 Wave Division Multiplexers
Domain Est. 2000
Website: fiberonellc.com
Key Highlights: FIBERONE® offers a complete line of wavelength division multiplexers that enable networks to mux or demux multiple wavelengths through the same fiber….
#9 Multimode WDM for custom wavelengths
Domain Est. 2010
Website: sedi-ati.com
Key Highlights: SEDI-ATI manufactures multiplexers with different multimode waves. Contact us for a quote!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Fiber Multiplexer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Fiber Multiplexers
By 2026, the fiber multiplexer market is poised for significant transformation, driven by escalating global data demands, the rollout of next-generation networks, and advancements in optical technologies. Here are the key trends shaping the landscape:
1. Surge in High-Capacity DWDM Deployment:
Demand for higher bandwidth will accelerate the adoption of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) systems. As 5G networks mature and cloud services expand, service providers will increasingly deploy advanced DWDM multiplexers capable of supporting terabit-per-second transmission. Coherent optics, integrated with multiplexers, will become standard to maximize spectral efficiency and reach, especially in long-haul and metro networks.
2. Growth in Open and Disaggregated Architectures:
Telecom operators are shifting toward open, interoperable network designs to reduce vendor lock-in and lower costs. This trend will drive demand for open line systems (OLS) and white-box fiber multiplexers compatible with multi-vendor transceivers and controllers. By 2026, platforms supporting OpenROADM and OpenZR+ standards will gain traction, particularly in data center interconnects (DCI) and edge networks.
3. Expansion in Edge and Metro Networks:
With the proliferation of IoT devices, edge computing, and distributed cloud infrastructure, fiber multiplexers are becoming critical in metro and access networks. Compact, low-power multiplexers—especially Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and compact DWDM solutions—will see strong growth. These enable cost-effective aggregation and transport of data from edge locations to core networks.
4. Integration with Software-Defined Networking (SDN):
SDN and network function virtualization (NFV) will increasingly influence fiber multiplexer design. By 2026, intelligent multiplexers with embedded SDN control planes will allow for dynamic bandwidth allocation, automated provisioning, and real-time monitoring. This programmability enhances network agility and supports on-demand service delivery.
5. Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability:
As data traffic grows, so does the environmental footprint of network infrastructure. Equipment vendors will prioritize energy-efficient designs, leveraging advanced semiconductor processes and AI-driven power management. Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals will make low-power, high-density multiplexers a key differentiator.
6. Rising Demand in Enterprise and Private Networks:
Enterprises in finance, healthcare, and manufacturing are building private fiber networks for secure, low-latency connectivity. This will broaden the fiber multiplexer market beyond traditional telecom customers. Plug-and-play, easy-to-manage multiplexers tailored for enterprise IT teams will emerge as a niche but growing segment.
7. Regional Growth in Emerging Markets:
Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa will see accelerated fiber deployment driven by government broadband initiatives and digital transformation. This will create new opportunities for cost-optimized fiber multiplexers, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
In summary, the 2026 fiber multiplexer market will be defined by higher capacity, greater flexibility, and smarter integration—responding to the relentless demand for faster, more reliable, and scalable optical connectivity across diverse applications.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Fiber Multiplexers: Quality and IP Concerns
Sourcing fiber multiplexers—especially for mission-critical or high-bandwidth applications—requires careful due diligence. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to performance issues, compliance risks, and long-term costs. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Build Quality and Component Sourcing
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing fiber multiplexers is the use of substandard materials and components. Low-cost manufacturers may cut corners by using inferior optical transceivers, power supplies, or circuit boards. This results in reduced signal integrity, higher bit error rates (BER), and shorter equipment lifespan. Always verify component quality through third-party testing or certifications (e.g., Telcordia GR-468, CE, RoHS).
Lack of Vendor Transparency on IP Ownership
Many fiber multiplexer suppliers—particularly OEMs or white-label providers—do not clearly disclose the origin of their technology. A major pitfall is sourcing equipment that incorporates third-party IP without proper licensing. This can expose your organization to legal risks, especially in regulated industries or international deployments where IP infringement claims may halt operations or lead to costly litigation.
Inadequate Firmware and Software Security
Fiber multiplexers often run proprietary firmware that manages signal routing, diagnostics, and network integration. Sourcing from vendors with weak software development practices can introduce vulnerabilities such as unpatched security flaws, backdoors, or weak encryption. Ensure the vendor provides regular firmware updates, has a clear security roadmap, and demonstrates secure development lifecycle practices.
Non-Compliance with Industry Standards
Some multiplexers fail to meet essential telecom or datacom standards such as ITU-T G.709 (OTN), IEEE 802.3, or MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) for optical modules. This can lead to interoperability issues with existing network infrastructure. Always confirm compliance with relevant standards and request test reports or conformance certificates.
Hidden Licensing and IP Royalty Fees
Certain advanced features in fiber multiplexers—such as forward error correction (FEC), dynamic bandwidth allocation, or encryption—may be protected by patents. Vendors might not disclose ongoing royalty obligations, leading to unexpected costs after deployment. Clarify licensing terms upfront and ensure you have the right to use, maintain, and scale the technology without additional IP-related fees.
Insufficient Long-Term Support and Documentation
Low-cost or obscure suppliers may lack the resources to provide detailed technical documentation, SDKs, or long-term technical support. This becomes a critical issue when troubleshooting, integrating with management systems, or planning upgrades. Verify that the vendor offers comprehensive documentation and a clear support structure.
Counterfeit or Refurbished Equipment Misrepresented as New
In some supply chains, especially through third-party distributors, there is a risk of receiving counterfeit or refurbished fiber multiplexers labeled as new. These units may have degraded performance or hidden defects. Source only from authorized distributors and request serial number traceability and warranty validation.
By addressing these common pitfalls during the procurement process—through rigorous vendor evaluation, contractual safeguards, and technical validation—you can ensure reliable performance and protect your organization from legal and operational risks associated with fiber multiplexer sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Fiber Multiplexer
Overview
This guide provides essential information for the safe and compliant logistics handling, transportation, customs clearance, and regulatory compliance of Fiber Multiplexer equipment. Adherence to these guidelines ensures timely delivery, regulatory compliance, and product integrity.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Fiber Multiplexers are sensitive electronic devices and must be handled with care during all logistics stages.
– Use original manufacturer packaging with anti-static materials and shock-absorbing foam.
– Ensure all fiber optic ports are capped and secured to prevent contamination or damage.
– Label packages clearly with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
– Avoid stacking heavy items on top of multiplexer packages.
Transportation Guidelines
- Transport in climate-controlled vehicles when possible to avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or humidity.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or freezing conditions during transit.
- Use carriers experienced in handling high-value telecommunications equipment.
- For international shipments, ensure compliance with IATA, IMDG (if applicable), and local transport regulations.
Import/Export Compliance
Fiber Multiplexers may be subject to international trade controls due to their telecommunications functionality.
– HS Code Classification: Typically classified under HS Code 8517.62 (Transmission apparatus for telecommunications, including multiplexing equipment). Confirm exact code with local customs authority.
– Export Controls: Check compliance with export regulations such as:
– U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) – may require a license depending on destination and technical specifications.
– EU Dual-Use Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2021/821) – apply if equipment meets technical thresholds for controlled telecommunications items.
– Maintain accurate technical documentation (e.g., datasheets, block diagrams) for customs and licensing purposes.
Regulatory Certifications
Ensure the Fiber Multiplexer meets required regulatory standards in the destination country.
– FCC (USA): Certified for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and radio frequency (RF) emissions under Part 15.
– CE (Europe): Compliant with EMC Directive 2014/30/EU and RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU.
– ISED (Canada): Certified under RSS-Gen and relevant technical standards.
– Other Regions: Verify local requirements (e.g., KC mark for South Korea, NCC for Taiwan, TELEC for Japan).
Documentation Requirements
Prepare the following documents for smooth customs clearance:
– Commercial Invoice (with full product description, value, and HS code)
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (if required for preferential tariffs)
– Regulatory Compliance Certificates (FCC, CE, etc.)
– Export License (if applicable)
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive in the EU for end-of-life handling.
- Follow local e-waste regulations for proper disposal or recycling.
- Do not dispose of in regular trash; use certified electronics recyclers.
Special Considerations
- Batteries: If the multiplexer includes backup batteries, ensure compliance with UN38.3 testing for lithium batteries (if applicable).
- Software: Embedded software may be subject to encryption controls—verify if classification under ECCN 5A002 (U.S.) or Category 5, Part 2 (EU) is required.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for Fiber Multiplexers minimizes delays, avoids penalties, and ensures operational readiness upon deployment. Always consult with qualified logistics providers and regulatory experts when shipping to new or restricted markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Fiber Multiplexer
In conclusion, sourcing a fiber multiplexer requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, network requirements, vendor reliability, and total cost of ownership. Selecting the right fiber multiplexer—whether CWDM, DWDM, or TDM-based—depends on the desired bandwidth capacity, transmission distance, scalability needs, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Key factors such as channel capacity, data rate support, management interface, redundancy, and power efficiency must align with both current and future network demands.
Furthermore, partnering with reputable suppliers offering proven product quality, strong technical support, and service warranties ensures long-term performance and minimizes downtime. Conducting thorough due diligence, including product testing and reference checks, mitigates risks and supports a successful deployment.
Ultimately, a well-informed procurement decision will enhance network efficiency, support growing data demands, and deliver a scalable, cost-effective solution for optical communication needs.