The global lifting and rigging equipment market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising infrastructure development, industrial automation, and stringent safety regulations across construction, oil & gas, and manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global rigging hardware market size was valued at USD 7.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth trajectory underscores the increasing demand for high-performance lifting components, including eyebolts—critical elements in safe and efficient load suspension systems. With load capacities, material durability, and compliance standards becoming paramount, selecting the right manufacturer is essential for operational safety and reliability. In this context, the following list highlights the top eight eyebolts for lifting manufacturers who lead in innovation, quality certifications, and global market reach.
Top 8 Eyebolts For Lifting Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Your One-Stop Shop for High-Quality Eye Bolts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lifting.com
Key Highlights: 2–3 day deliveryAt Lifting.com, we provide a full selection of industrial-strength eye bolts designed for lifting, anchoring, and rigging in various ……
#2 Eye Bolts (Lifting)
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mscdirect.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryMade in USA · Fixed Lifting Eye Bolt: With Shoulder, 2,400 lb Capacity, 1/2-13 Thread, Grade 1030 Steel · Fully Threaded, 1-1/2″ Shank, 1-1/2″ Thread Length….
#3 U
Domain Est. 1999
Website: uboltit.com
Key Highlights: At U-Bolt-It, we custom manufacture bolts and fasteners made to meet all your requirements and in all materials from stainless steel and exotic materials….
#4 DIN 580 Lifting Eye Bolts Steel
Domain Est. 1997
#5 Eye Bolts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: lift-it.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $499Chicago Hardware’s shoulder pattern machinery eye bolts are made in the USA from drop forged steel that is heat treated for strength and ductility….
#6 DIN 580
Domain Est. 1999
Website: elesa-ganter.com
Key Highlights: These components are corrosion-resistant, precise-fitting, environmentally friendly, and designed for long-term use….
#7 Eyebolts & Screw Type Lifting Points
Domain Est. 2018
Website: liftingequipmentstore.us
Key Highlights: $26.50 deliveryWe offer a comprehensive range of high-quality eyebolts and screw-type lifting points, engineered to deliver exceptional strength, durability, and safety….
#8 Eyebolts and Eyenuts
Domain Est. 2020
Website: ulslifting.com
Key Highlights: 28-day returnsShop certified Lifting Eye Bolts & Eye Nuts, including Swivel, Non-Swivel, and Grade 8 high capacity fittings. All CE marked and supplied with WLL ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Eyebolts For Lifting

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Eyebolts for Lifting
The global market for eyebolts for lifting is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by expanding industrialization, infrastructure development, and increased safety regulations across key sectors. Key trends shaping the market include technological advancements, material innovations, regional demand shifts, and growing emphasis on load safety and compliance.
-
Increased Demand from Construction and Manufacturing Sectors
By 2026, the construction, manufacturing, and heavy engineering industries are expected to remain primary end-users of lifting eyebolts. Ongoing infrastructure projects in emerging economies—particularly in Asia-Pacific and Africa—are driving demand for reliable lifting hardware. As modular construction and prefabrication techniques gain popularity, the need for reusable and high-capacity eyebolts is expected to rise. -
Adoption of High-Strength and Corrosion-Resistant Materials
Market trends indicate a shift toward eyebolts made from alloy steel, stainless steel, and other corrosion-resistant materials. With industries operating in harsh environments—such as offshore, marine, and chemical processing—there is growing demand for durable and long-lasting lifting components. Manufacturers are responding by offering eyebolts with enhanced tensile strength and protective coatings. -
Focus on Safety Standards and Certification
Regulatory bodies such as OSHA (USA), CE (Europe), and ISO are enforcing stricter safety standards for lifting equipment. By 2026, certified eyebolts that meet international load testing and safety protocols (e.g., WLL – Working Load Limit labeling) will dominate the market. End-users are increasingly prioritizing products with traceability, third-party testing, and compliance documentation. -
Rise of Smart and Integrated Lifting Solutions
While still in early stages, the integration of smart sensors and IoT-enabled load monitoring systems with traditional lifting hardware is an emerging trend. Some manufacturers are exploring eyebolts with embedded strain gauges or RFID tags to provide real-time data on load conditions and usage history—improving safety and predictive maintenance. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to lead global demand due to rapid urbanization and government investments in transportation and energy infrastructure. China, India, and Southeast Asian nations are key growth markets. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see steady growth driven by industrial modernization and replacement cycles in aging infrastructure. -
Sustainability and Supply Chain Optimization
Manufacturers are focusing on sustainable production practices, including energy-efficient forging processes and recyclable materials. Additionally, supply chain resilience—especially post-pandemic—will push companies to localize production or diversify sourcing to mitigate disruptions.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for eyebolts for lifting will be defined by innovation, regulatory compliance, and regional expansion. Companies that invest in high-quality, certified products and adapt to evolving industry needs will be best positioned to capture market share in this essential segment of lifting equipment.
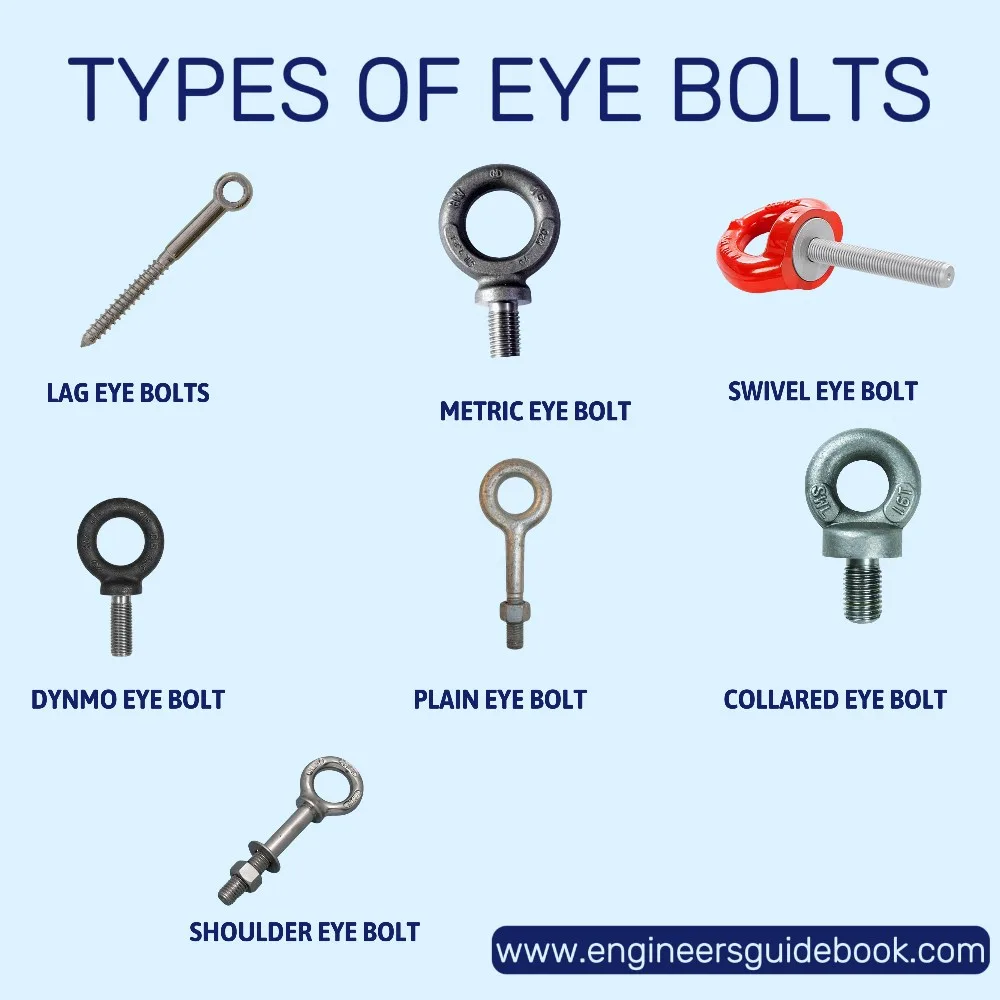
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Eyebolts for Lifting (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing eyebolts for lifting applications involves critical safety and compliance considerations. Overlooking key factors related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to serious consequences, including equipment failure, workplace injuries, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Inadequate Material and Manufacturing Standards
One of the most frequent quality pitfalls is sourcing eyebolts that do not meet recognized industry standards such as ASME B30.26, ISO 3269, or DIN 580. Suppliers may offer products that appear similar but are made from substandard materials (e.g., low-grade carbon steel instead of forged alloy steel), compromising load capacity and fatigue resistance. Always verify that eyebolts are certified to relevant standards and come with material test reports (MTRs).
Lack of Proper Forging and Heat Treatment
High-quality lifting eyebolts must be hot forged and properly heat treated to ensure grain structure integrity and mechanical strength. Sourcing from manufacturers that use cold forming or skip heat treatment results in brittle, unreliable components. Confirm the manufacturing process and request documentation showing compliance with heat treatment specifications.
Missing or Falsified Certification and Traceability
Reputable suppliers provide full traceability, including lot numbers, heat numbers, and third-party test certifications (e.g., from TÜV or SGS). A common pitfall is accepting eyebolts without valid certification or encountering falsified documents. Insist on certified mill test reports and consider independent verification for high-risk applications.
Misrepresentation of Load Ratings and Safe Working Load (SWL)
Some suppliers exaggerate load ratings or fail to specify conditions under which the SWL is valid (e.g., angular loading, reeving). Eyebolts rated for straight pull may fail under angular loads if not designed for such use. Always ensure the SWL is clearly defined, includes angular load derating charts, and is backed by certified testing.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) and Brand Imitations
Counterfeit or cloned eyebolts that mimic well-known brands (e.g., Crosby, Sling-Plow) are a growing IP concern. These products often replicate logos and packaging but lack the engineering and quality control of the original. Sourcing from unauthorized distributors or gray-market suppliers increases the risk of IP infringement and unsafe products. Purchase only from authorized channels and verify supplier legitimacy.
Inadequate Surface Protection and Corrosion Resistance
For outdoor or corrosive environments, eyebolts require proper surface treatments like hot-dip galvanizing or stainless steel construction. A common oversight is sourcing inadequately coated products that degrade quickly, leading to premature failure. Confirm coating type, thickness, and compliance with standards such as ASTM A153 or ISO 1461.
Poor Thread Quality and Engagement
Improperly cut threads or insufficient thread engagement reduce strength and increase the risk of bolt failure under load. Low-cost eyebolts may have rolled threads instead of cut threads or lack full thread engagement in the shank. Inspect thread quality and ensure compatibility with mating hardware.
Failure to Consider Application-Specific Design
Not all eyebolts are suitable for every lifting scenario. Using general-purpose eyebolts in high-cycle or dynamic lifting applications can lead to fatigue failure. Avoid the pitfall of one-size-fits-all sourcing by ensuring the eyebolt is designed for the specific use case—e.g., swivel eyebolts for angular loads, shoulder-type for perpendicular pulls.
Overlooking Supplier Audits and Factory Qualification
Relying solely on product samples without auditing the manufacturer’s facility can hide systemic quality issues. Unannounced factory audits help verify actual production practices, quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), and IP compliance. Never skip due diligence on new or offshore suppliers.
Assuming Compliance Based on Appearance
Eyebolts can look identical but vary drastically in internal quality. Visual inspection alone is insufficient. Demand test data, non-destructive testing (NDT) reports, and, when possible, destructive testing samples to validate performance claims.
By recognizing and addressing these common pitfalls—particularly those tied to quality assurance and intellectual property rights—purchasers can ensure they source safe, reliable, and legally compliant lifting eyebolts.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Eyebolts for Lifting
Eyebolts used for lifting applications are critical components in material handling and rigging operations. Proper logistics management and strict adherence to compliance standards are essential to ensure safety, regulatory conformity, and operational efficiency. This guide outlines key considerations for handling, transporting, storing, and using lifting eyebolts in compliance with industry regulations.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Eyebolts for lifting must comply with recognized international and national standards to ensure structural integrity and safe load handling. Key standards include:
- ASME B30.26: Covers design, manufacture, marking, testing, and inspection requirements for below-the-hook lifting devices, including eyebolts.
- ISO 3266:2012: Specifies mechanical properties and performance requirements for forged steel lifting eyebolts.
- EN 1677-1: European standard for chain slings and components, applicable to load-lifting attachments.
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.184: U.S. regulation covering safe practices for slings, including use of rigging hardware such as eyebolts.
Ensure all eyebolts are certified, clearly marked with load rating, manufacturer, and material grade, and accompanied by a certificate of conformity.
Material Handling and Transportation
Proper handling and transportation prevent damage that could compromise performance:
- Packaging: Eyebolts should be shipped in protective packaging (e.g., sealed plastic wrap, wooden crates, or bulk bins) to prevent corrosion, thread damage, and contamination.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with lifting capacity, part number, material type, and “FOR LIFTING – DO NOT DROP” warnings.
- Loading and Unloading: Use appropriate lifting gear during cargo transfer. Avoid dropping or impacting eyebolts, as shock loading can cause microfractures.
- Segregation: Store and transport lifting eyebolts separately from chemicals, sharp objects, or abrasive materials to avoid contamination or damage.
Storage Requirements
Improper storage can lead to degradation, increasing the risk of failure during use:
- Environment: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled indoor facility to prevent rust and corrosion. Avoid exposure to moisture, salt spray, or corrosive atmospheres.
- Orientation: Keep eyebolts in upright or horizontal positions to prevent thread deformation. Use racks or bins to avoid overcrowding.
- Inventory Management: Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system. Regularly inspect stored stock for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
Inspection and Maintenance Protocols
Routine inspection is mandatory for compliance and safety:
- Pre-Use Inspection: Check for cracks, thread damage, distortion, or wear before each use. Discard any eyebolt showing defects.
- Periodic Inspections: Conduct detailed inspections at regular intervals (e.g., monthly or quarterly), documented in a maintenance log.
- Load Testing: Perform proof-load testing during initial certification and after repairs or modifications, as required by ASME B30.26.
- Maintenance: Clean threads and apply anti-seize compound if specified. Never weld, heat, or modify eyebolts, as this voids certification.
Training and Documentation
Personnel involved in the use of lifting eyebolts must be trained and operations documented:
- Operator Training: Ensure riggers and crane operators are trained in proper selection, installation, and use of eyebolts, including angular load derating.
- Compliance Records: Maintain records of certifications, inspection logs, maintenance activities, and training completion.
- Usage Guidelines: Provide clear instructions on correct threading depth, alignment, and load angles. Never exceed the rated capacity, especially under angular loads.
Compliance and Audit Readiness
Organizations must be prepared for regulatory audits:
- Traceability: Implement a tracking system (e.g., barcodes or RFID) to trace eyebolts from supplier to point of use.
- Safety Audits: Conduct internal audits to verify adherence to handling, storage, and usage procedures.
- Regulatory Updates: Monitor changes in standards (e.g., OSHA, ASME, ISO) and update policies accordingly.
Conclusion
Safe and compliant logistics for lifting eyebolts depend on adherence to recognized standards, proper handling, storage, inspection, and documentation. By following this guide, organizations can minimize risk, ensure operational safety, and maintain full regulatory compliance in lifting operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Eyebolts for Lifting:
When sourcing eyebolts for lifting applications, safety, compliance, and reliability must be the top priorities. It is essential to select eyebolts that are certified to recognized industry standards (such as ASME B30.26, DIN 580, or ISO 3269), appropriately rated for the intended load, and compatible with the lifting angle and environmental conditions. Proper material selection—such as forged steel or stainless steel—should be based on strength requirements and corrosion resistance. Additionally, suppliers must be reputable, providing traceability, certificates of conformance, and compliance documentation. Investing time in sourcing high-quality, correctly specified eyebolts mitigates the risk of equipment failure, ensures operator safety, and supports regulatory compliance. Ultimately, a diligent sourcing process directly contributes to safe and efficient lifting operations.