The global expanded metal mesh market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across construction, industrial, and architectural sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the Expanded Metal Mesh Market was valued at USD 3.87 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 5.03 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.3% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by increased infrastructure development, especially in emerging economies, and the material’s versatility in applications ranging from safety guards and filtration systems to façade cladding and noise barriers. As demand for precision-engineered expanded metal products rises, manufacturers specializing in accurate measurement and customization are becoming key players in the supply chain. With stringent quality standards and evolving technical requirements, the ability to deliver consistent dimensional accuracy and repeatable performance is setting industry leaders apart. Based on market presence, technological capability, and product precision, here are the top 9 expanded metal measurement manufacturers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 9 Expanded Metal Measurements Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Expanded Metal Manufacturers Association (EMMA)
Domain Est. 1995
Website: naamm.org
Key Highlights: EMMA is comprised of manufacturers of expanded metal products for a variety of applications, including enclosure, protection, support, decoration and ……
#2 Metals Supplier & Service Center
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sss-steel.com
Key Highlights: Expanded Metal & Grating · Bar Grating · Expanded Metal · Perforated Metal · Fabrication Accessories · Metal Building Components · Value-Added Services….
#3 Steel Expanded Metal
Domain Est. 2001
Website: madar.com
Key Highlights: Steel Expanded Metal is a strong and lightweight mesh used in industrial flooring, security fencing, and construction reinforcements with corrosion resistance….
#4 Expanded Metals Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2008
Website: expanded-metals.org
Key Highlights: Find expanded metal manufacturers. Many of these companies are ISO certified, and offer free quotes on their metals of all materials and thicknesses….
#5 Standard Expanded Metal
Domain Est. 2014
Website: amicoglobal.com
Key Highlights: AMICO Standard Expanded Metal, also known as raised expanded metal, is a versatile material created by slitting and stretching a sheet of metal, …Missing: measurements manufactu…
#6 Expanded Metal Mesh
Domain Est. 1997
Website: metlx.com
Key Highlights: Expanded metal is an extremely versatile material. It is available in a wide variety of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, as well as a wide range of mesh sizes….
#7 Ryerson: Online Metals Supplier
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ryerson.com
Key Highlights: Ryerson is an online metal supplier, metal processor and distributor, offering more than 65000 varieties of stainless, aluminum, carbon and alloys in all ……
#8 Expanded Metal Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: directmetals.com
Key Highlights: As a supplier of metal sheets, Direct Metals offers expanded metal in many materials, such as aluminum, carbon steel, galvanized steel, or stainless steel….
#9 Expanded Metal
Domain Est. 2011
Website: kloecknermetals.com
Key Highlights: Kloeckner offers both standard expanded metal and flattened expanded metal, each designed to serve distinct functional and aesthetic applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Expanded Metal Measurements
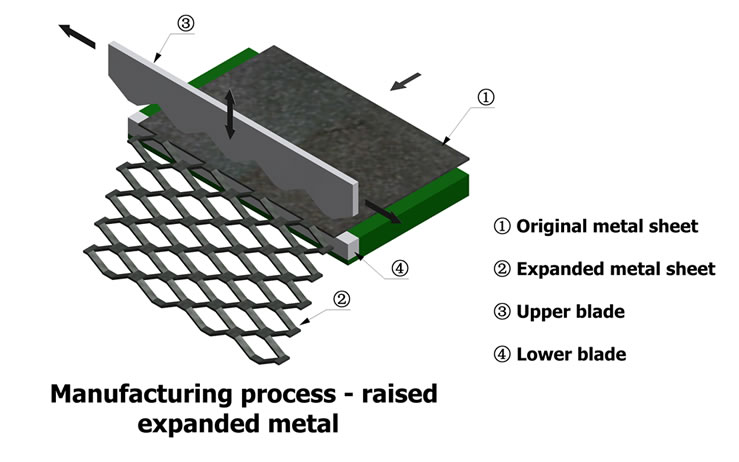
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Expanded Metal Measurements
As the global manufacturing and construction sectors continue to evolve, the market for expanded metal—characterized by its unique pattern of diamond-shaped openings created by slitting and stretching metal sheets—will experience significant shifts in demand, applications, and measurement standards by 2026. Key trends in expanded metal measurements will be driven by technological advancements, industry-specific requirements, and sustainability initiatives.
-
Standardization and Customization in Measurements
By 2026, there will be a dual trend toward both increased standardization and greater customization in expanded metal measurements. International standards (such as ASTM E566 and ISO 9022) will see broader adoption to ensure compatibility across industries like construction, aerospace, and automotive. At the same time, demand for bespoke mesh sizes, strand widths, and thicknesses will grow, particularly in architectural design and filtration systems, where precise flow, strength, and aesthetic requirements dictate non-standard dimensions. -
Precision in Digital Manufacturing and CAD Integration
Advancements in digital fabrication, including computer-aided design (CAD) and automated cutting systems, will elevate the importance of exact expanded metal measurements. Manufacturers will increasingly rely on digital twins and BIM (Building Information Modeling) platforms, requiring expanded metal products to conform to highly accurate dimensional specifications. This shift will reduce waste and improve integration in complex assemblies. -
Rise in Lightweight and High-Strength Applications
The trend toward lightweight materials in transportation and renewable energy sectors will influence expanded metal measurements. By 2026, thinner gauges with optimized strand spacing will be in demand to maintain structural integrity while reducing overall weight. Measurements such as weight per square meter, open area percentage, and tensile strength will become critical performance indicators in product selection. -
Focus on Open Area and Flow Efficiency
Industries such as HVAC, filtration, and acoustic engineering will prioritize expanded metal products with precisely controlled open area ratios. By 2026, product specifications will increasingly highlight open area percentage (typically ranging from 20% to 70%) as a key metric, with tighter tolerances demanded to ensure consistent airflow, light transmission, or sound attenuation. -
Sustainability-Driven Material Efficiency
Sustainability goals will impact how expanded metal is measured and specified. Metrics like material yield (i.e., how much usable product is generated per raw sheet) and recyclability will gain importance. Efficient patterns that maximize open area while minimizing material use—without compromising strength—will be preferred, particularly in green building projects seeking LEED or BREEAM certification. -
Regional Measurement Preferences and Compliance
Regional markets will continue to influence measurement conventions. While North America predominantly uses imperial units (inches for thickness and strand width), Europe and Asia will favor metric measurements. By 2026, global suppliers will need to offer dual-unit specifications and ensure compliance with regional regulations, such as the EU Construction Products Regulation (CPR), which may include dimensional performance requirements. -
Smart Materials and Embedded Sensors
Emerging applications in smart infrastructure may lead to expanded metal with embedded sensors or conductive tracings. This will necessitate new measurement protocols for electrical conductivity, thermal expansion, and integration tolerances, pushing the industry to adopt more sophisticated metrology tools.
Conclusion
By 2026, expanded metal measurements will serve not only as basic dimensional data but as critical indicators of performance, efficiency, and compliance. The convergence of digital manufacturing, sustainability mandates, and specialized applications will require manufacturers and buyers to adopt a more nuanced understanding of expanded metal specifications, with greater emphasis on precision, adaptability, and lifecycle impact.
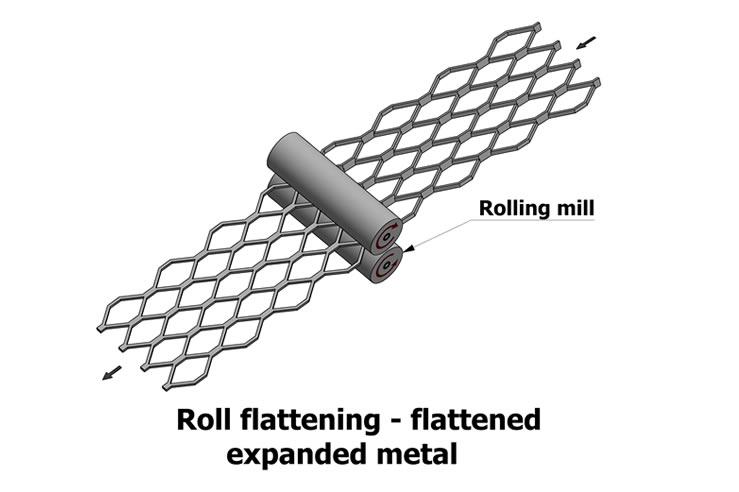
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Expanded Metal: Quality and IP Considerations
Sourcing expanded metal requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects, especially in specialized or patented applications. Overlooking these factors can lead to project delays, compliance issues, or substandard performance. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is receiving expanded metal that does not meet specified standards for thickness, strand width, or opening size. Suppliers may provide material that visually appears correct but fails under load or in precision applications due to deviations in tolerances. Always request certified mill test reports and verify conformance to standards such as ASTM E646 or ISO 9472.
2. Poor Surface Finish and Corrosion Resistance
Expanded metal is often used in architectural or outdoor environments where appearance and durability matter. Sourcing from suppliers who do not properly control surface treatments (e.g., galvanization, powder coating, or anodizing) can result in premature corrosion or aesthetic flaws. Confirm coating thickness and adhesion standards during procurement.
3. Inadequate Testing and Certification
Some suppliers provide material without proper mechanical or chemical testing. This is particularly risky in structural or safety-critical applications. Ensure that the supplier conducts and documents tensile strength, elongation, and chemical composition tests as part of quality assurance.
4. Misunderstanding Pattern and Orientation
Expanded metal has directional strength due to its diamond pattern. Sourcing without specifying grain direction can result in material that underperforms under load. Clearly communicate the required orientation (longitudinal vs. transverse strength) in technical drawings and purchase orders.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Using Patented Patterns or Processes Without Authorization
Certain expanded metal patterns, finishes, or manufacturing processes are protected by patents. Sourcing these materials from unauthorized suppliers or using them in restricted applications can lead to IP infringement claims. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s rights to produce and sell the specific product.
2. Copying Branded or Proprietary Designs
Some manufacturers develop unique expanded metal products with registered designs or trademarks (e.g., specific architectural mesh patterns). Replicating these without permission—even if sourced from a third-party supplier—can expose your organization to legal liability. Always verify the legitimacy of “equivalent” products.
3. Lack of Licensing Agreements in Contracts
When sourcing expanded metal for resale or integration into proprietary products, ensure that licensing terms are included in supply agreements. Without clear IP rights transfer or usage permissions, you may face restrictions on distribution or modification.
4. Overlooking Regional IP Laws
Intellectual property protections vary by country. A pattern that is public domain in one region may still be patented elsewhere. If sourcing internationally, consult legal experts to avoid unintentional violations in export or import markets.
Conclusion
To mitigate risks, work with reputable suppliers who provide full traceability, compliance documentation, and transparent IP disclosures. Include detailed specifications and quality assurance clauses in procurement contracts, and conduct regular audits of supplied materials. Proper due diligence ensures both performance reliability and legal compliance in expanded metal sourcing.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Expanded Metal Measurements
Understanding and accurately specifying expanded metal measurements is essential for ensuring product quality, meeting regulatory requirements, and streamlining logistics across the supply chain. This guide outlines key measurement parameters, industry standards, and compliance considerations to support efficient procurement, transportation, and application of expanded metal products.
Key Measurement Parameters
Accurate communication of expanded metal specifications begins with understanding the core measurement terms:
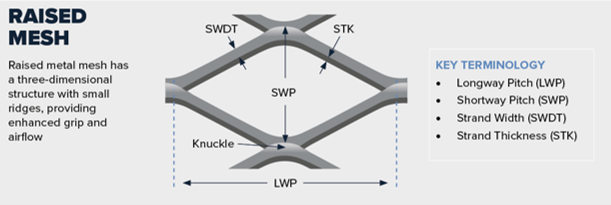
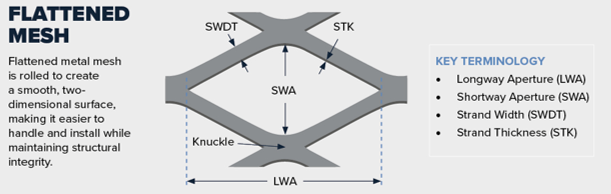
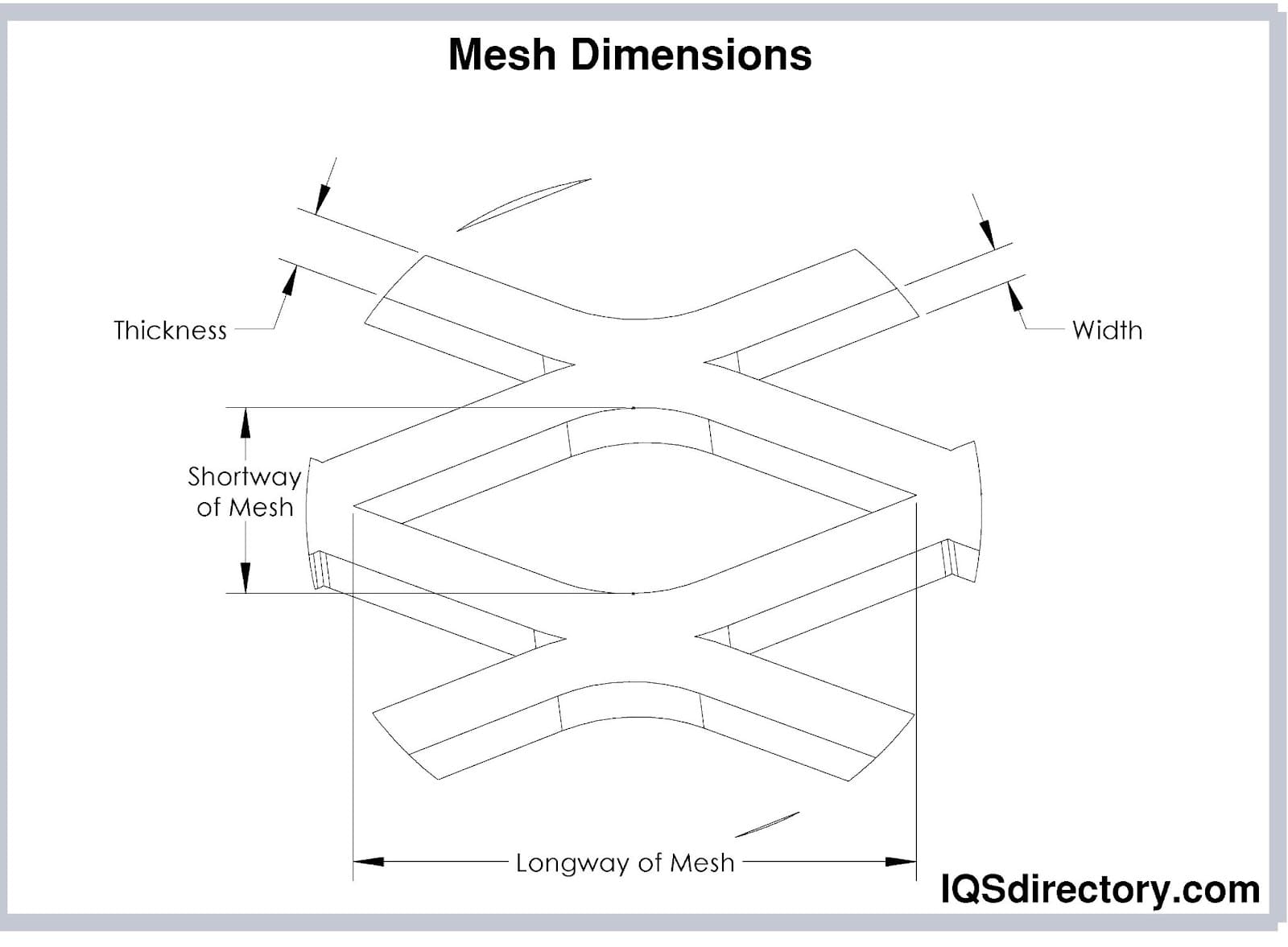
- Strand Width (SW): The width of the individual metal strands formed during the expanding process. Measured in inches or millimeters, this affects strength and open area.
- Mesh Size (Pitch): The distance from the center of one strand to the center of the next parallel strand. This determines the size of the openings.
- Opening Size (Length and Width): The actual dimensions of the diamond-shaped or other patterned openings. Critical for filtration, visibility, and airflow applications.
- Sheet Dimensions: Overall length and width of the expanded metal sheet or roll. Standard sizes vary by region and manufacturer; custom cuts may incur additional costs.
- Thickness (Gauge): The original material thickness before expansion. Often specified in gauge (e.g., 16 GA) or millimeters. Affects weight, strength, and handling.
- Expanded Width: The width of the sheet after expansion, which may differ from the raw material width due to lateral stretching.
- Weight per Unit Area: Typically expressed in pounds per square foot (psf) or kilograms per square meter (kg/m²). Vital for shipping calculations and structural load considerations.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Adherence to recognized standards ensures consistency, safety, and regulatory compliance:
- ASTM Standards: ASTM E2517 governs standard specifications for expanded metal for fencing applications. Other ASTM standards may apply based on material type (e.g., ASTM A36 for carbon steel).
- ISO Standards: ISO 1461 for hot-dip galvanized coatings may apply when corrosion resistance is required. ISO 9001 compliance indicates quality management systems in production.
- Local Building Codes: In construction applications, expanded metal must meet local codes for load-bearing capacity, fire resistance, and safety (e.g., fall protection, slip resistance).
- Material Certifications: Mill test reports (MTRs) or certificates of conformance (CoC) may be required to verify material composition and mechanical properties, especially in regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, food processing).
- Environmental and Safety Regulations: Compliance with REACH, RoHS, or OSHA standards may be necessary depending on the region and end-use application.
Logistics Considerations
Proper measurement specifications directly impact logistics efficiency:
- Packaging and Handling: Specify sheet size and weight to ensure appropriate packaging (e.g., bundles, pallets, crates) and safe handling procedures. Overly large or heavy sheets may require special lifting equipment.
- Transportation Constraints: Confirm that sheet dimensions comply with standard shipping container or truck dimensions to avoid oversized freight charges.
- Inventory Management: Standardized measurements simplify storage and reduce waste. Clearly labeled products based on precise specs improve warehouse accuracy.
- Custom vs. Standard Sizes: Custom measurements may lead to longer lead times and higher costs. Where possible, use standard sizes to improve supply chain responsiveness.
Best Practices for Specification
To ensure compliance and logistical efficiency:
- Use Consistent Units: Specify all measurements using the same unit system (imperial or metric) throughout documentation.
- Include Tolerances: Define acceptable tolerances for critical dimensions (e.g., ±1/16” for sheet size) to avoid disputes and ensure fit.
- Provide Detailed Drawings: Accompany specifications with technical drawings showing pattern type, orientation (long or short throw), and all relevant dimensions.
- Verify Supplier Capabilities: Confirm that suppliers can consistently produce to specified measurements and provide required certifications.
- Document Change Control: Maintain records of any specification changes to support traceability and audit requirements.
By standardizing expanded metal measurements and aligning with compliance and logistics best practices, organizations can reduce errors, enhance supply chain reliability, and ensure product performance in the field.
Conclusion on Sourcing Expanded Metal Measurements:
Accurately sourcing expanded metal measurements is essential to ensuring material compatibility, structural integrity, and cost-efficiency in any project. Key parameters such as strand width, mesh size, ligament length, thickness, and expansion pattern must be precisely specified to meet design and performance requirements. When sourcing, it is crucial to consult manufacturer datasheets, adhere to industry standards (such as ASTM or ISO), and verify tolerances to avoid discrepancies in fit and function. Additionally, clear communication with suppliers and the use of detailed technical drawings can minimize errors and support consistency across production batches. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of expanded metal specifications enables informed decision-making, optimizes material selection, and contributes to the overall success of engineering, architectural, and industrial applications.