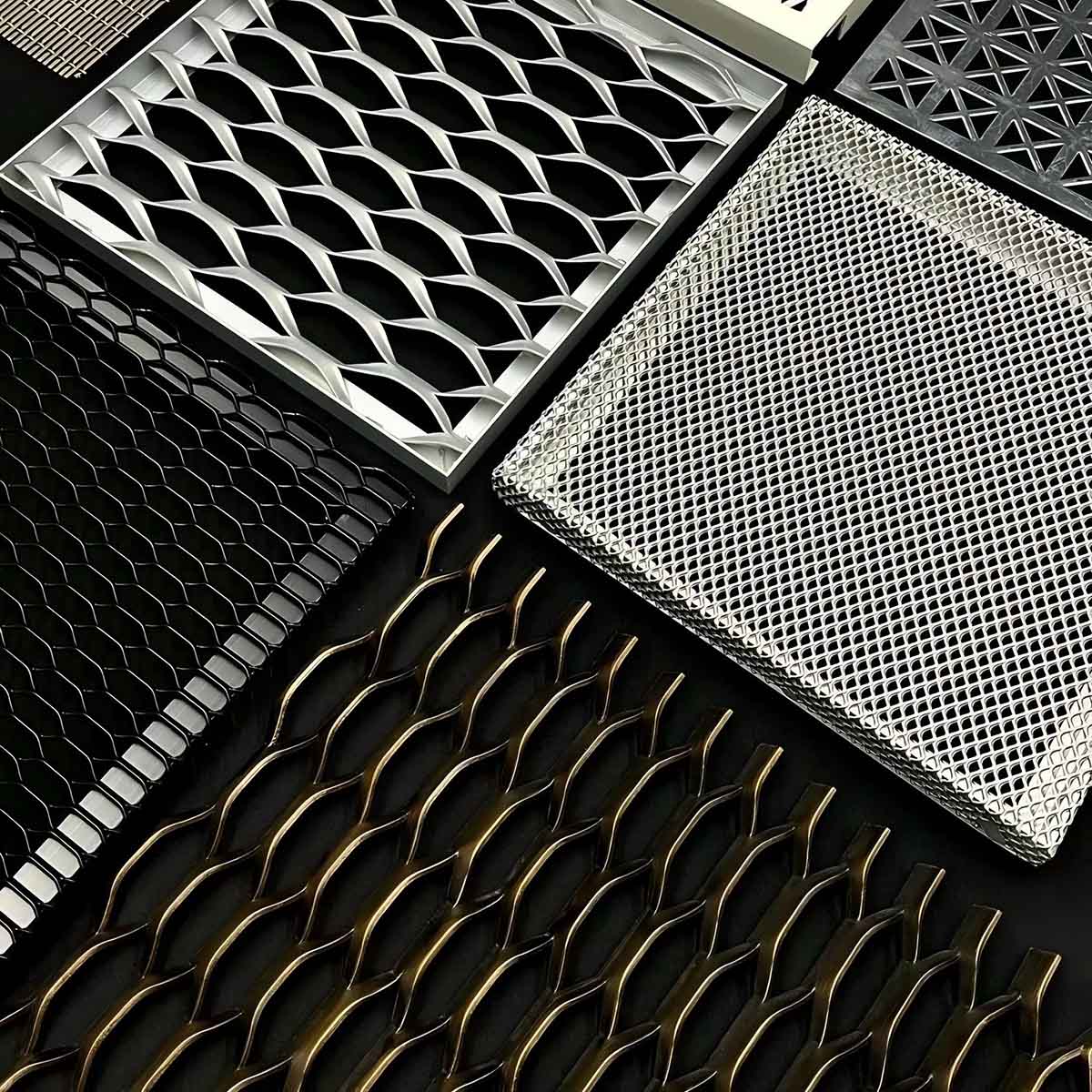
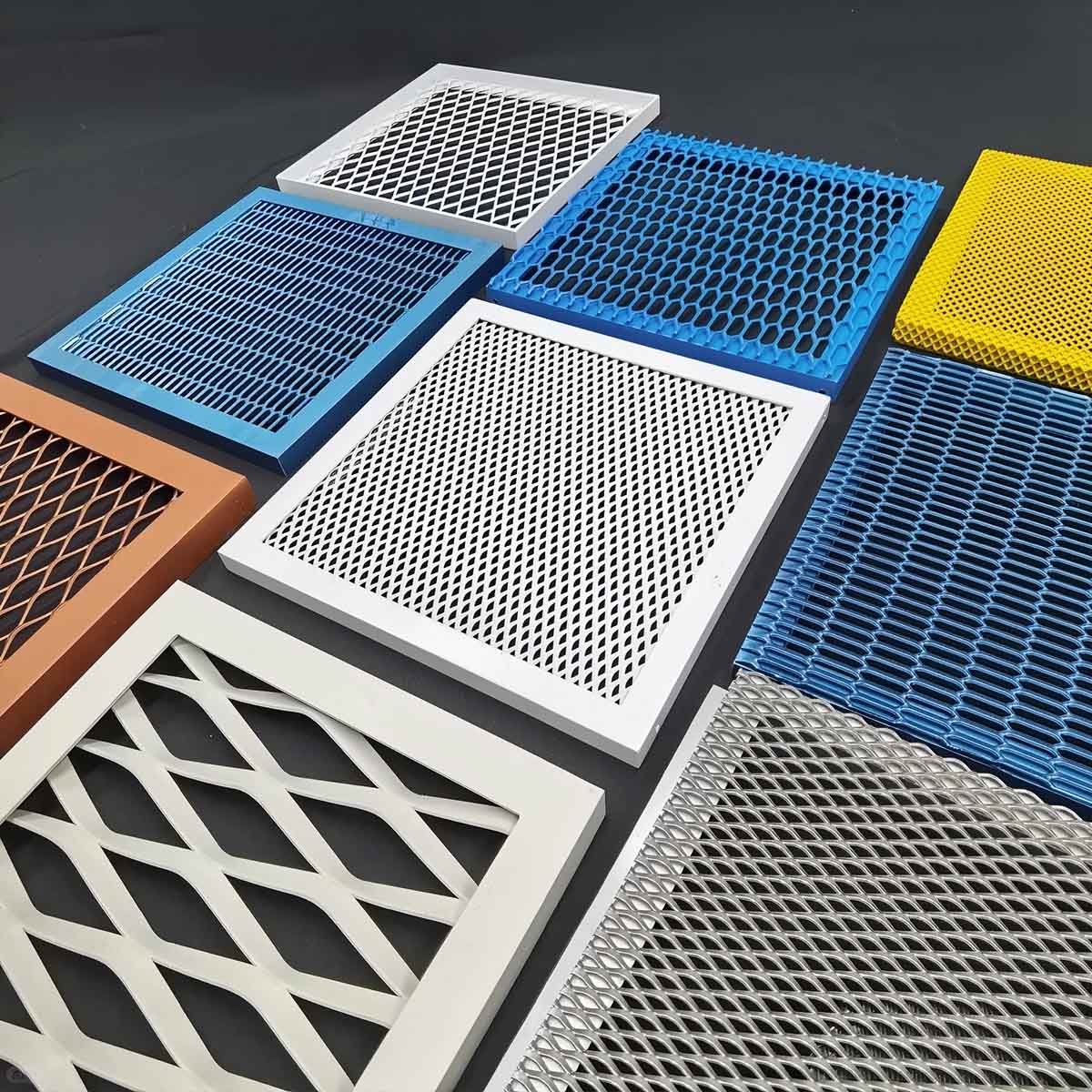
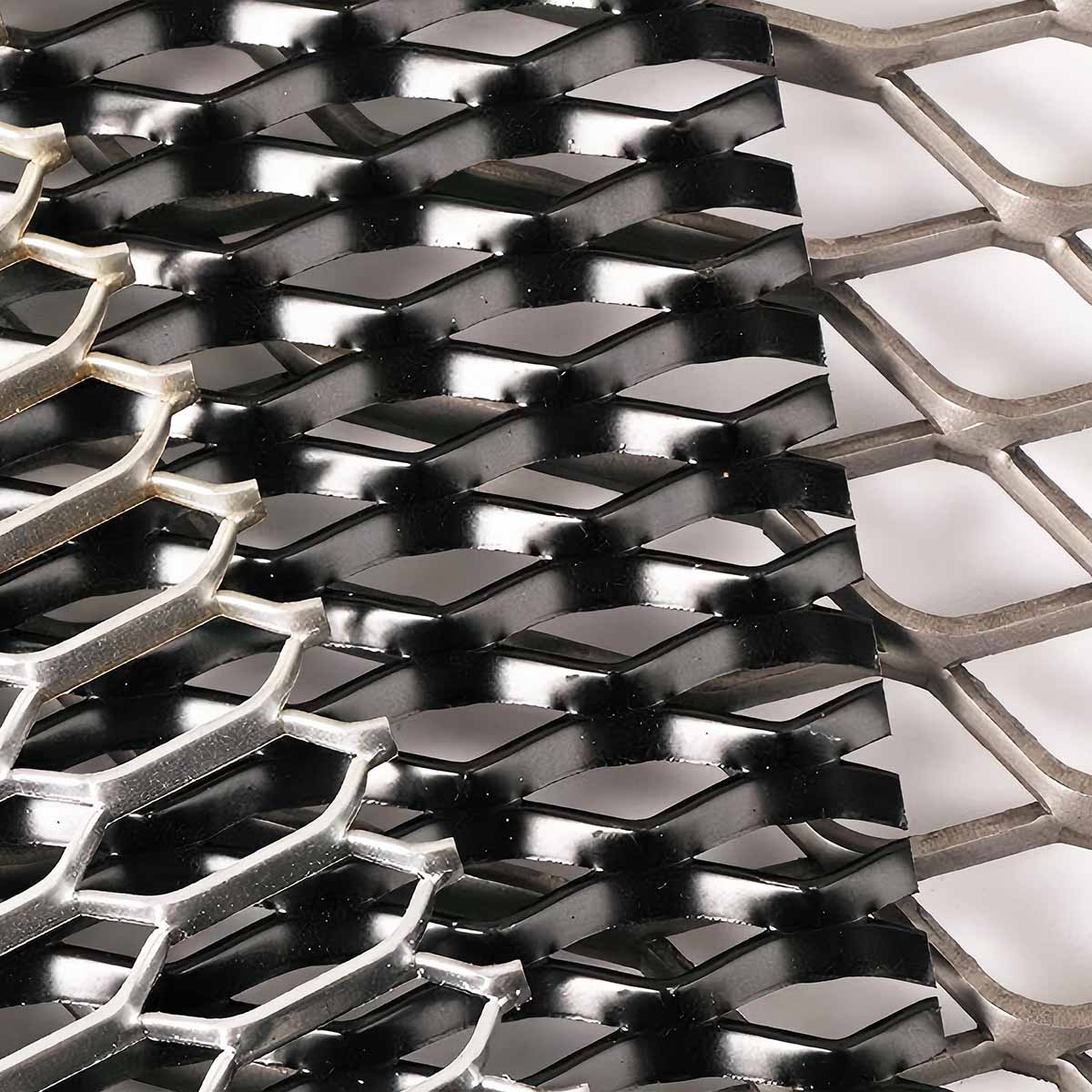
The global expanded aluminum sheet market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global aluminum mesh market—of which expanded aluminum sheets are a key segment—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research valued the global aluminum foam and expanded aluminum market at USD 1.5 billion in 2022, with expectations for continued expansion due to increased applications in lightweight structural materials and acoustic insulation. As sustainability and material efficiency become strategic priorities, manufacturers are innovating to deliver high-strength, corrosion-resistant, and recyclable expanded aluminum solutions. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in production capability, product diversity, and technological advancement. Here are the top 9 expanded aluminum sheet manufacturers shaping the future of the industry.
Top 9 Expanded Aluminum Sheet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Leading Expanded Aluminum Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2008
Website: expanded-metals.org
Key Highlights: Quickly find expanded aluminum manufacturers on this site. They are OEM distributors of their lightweight, high quality aluminum products….
#2 Common Alloy Expanded Aluminum Sheet
Domain Est. 1999
#3 The Expanded Metal Company
Domain Est. 2014
Website: expandedmetalcompany.com
Key Highlights: The Expanded Metal Company is a world-renowned manufacturer of expanded metal mesh solutions – including metal mesh sheets, mesh panels and bespoke products….
#4 Aluminum Expanded Metal Mesh Sheets
Domain Est. 2021
Website: tbkmetal.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum expanded metal mesh by TBK Metal can provide easy weight support and long life in architectural, industrial, and filtration applications….
#5 Aluminum Expanded Metal & Flooring
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ryerson.com
Key Highlights: We supply a full line of aluminum expanded metal flooring in both sheet and mesh options. Ryerson serves diverse industries with various grades, ……
#6 Niles Expanded Metals
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nilesexpandedmetals.com
Key Highlights: Niles can customize expanded metal to meet your specific needs. We specialize in expanded metal, micromesh, ExPerf, & more. Request a quote today!…
#7 Aluminum Expanded Metal
Domain Est. 2008
Website: expandedmetalsheet.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum Expanded Metal. Aluminum expanded metal is made of high quality aluminum sheet/coil after being expanded on the automatic expanded machines….
#8 Aluminum Expanded Metal Sheet for Decorative Applications
Domain Est. 2015
Website: expandedmetalsheets.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum expanded metal with light weight, various colors and solid structure is widely used in the decorative and protective applications….
#9 3003 H14 Raised Expanded Aluminum
Domain Est. 2018
Expert Sourcing Insights for Expanded Aluminum Sheet
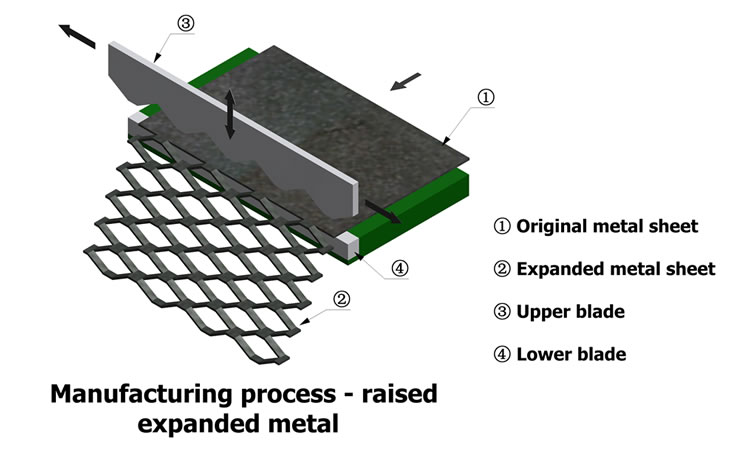
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Expanded Aluminum Sheet
The global expanded aluminum sheet market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by shifting industrial demands, sustainability imperatives, and technological advancements. As lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and recyclable materials gain prominence across key sectors, expanded aluminum sheet—a versatile metal mesh formed by cutting and stretching aluminum—continues to expand its footprint. The following H2-level analysis outlines the dominant trends expected to shape the market in 2026.
1. Rising Demand in Green Building and Architectural Applications
The construction industry is increasingly adopting expanded aluminum sheets for façades, sunscreens, and interior design due to their aesthetic appeal, durability, and energy efficiency. With global green building standards (such as LEED and BREEAM) gaining traction, manufacturers are favoring materials that enhance natural lighting and thermal regulation. By 2026, architectural use is projected to account for over 35% of market demand, particularly in urban infrastructure projects across Asia-Pacific and North America.
2. Expansion in Renewable Energy and EV Sectors
The accelerated transition to renewable energy and electric vehicles (EVs) is creating new applications for expanded aluminum. In solar panel frames and battery enclosures, the material offers optimal strength-to-weight ratios and superior thermal conductivity. Additionally, its use in EV battery trays and motor components supports weight reduction and improved efficiency. As global EV production surpasses 40 million units annually by 2026, demand for lightweight structural components—including expanded aluminum sheet—is expected to rise steadily.
3. Technological Advancements in Manufacturing
Innovations in roll forming, precision expansion, and coating technologies are enhancing the performance and customization capabilities of expanded aluminum sheets. Manufacturers are investing in automated production lines to achieve tighter tolerances and complex patterns, catering to niche applications in aerospace, acoustics, and filtration. Furthermore, the integration of digital twin and AI-driven quality control systems is improving yield rates and reducing waste, thereby lowering production costs.
4. Sustainability and Circular Economy Drivers
Aluminum’s high recyclability (up to 75% of all aluminum ever produced is still in use) positions expanded aluminum as a preferred material in circular economy models. Regulatory pressures and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are pushing industries to adopt recyclable materials. By 2026, over 60% of expanded aluminum production is expected to utilize recycled content, supported by advancements in closed-loop recycling systems and lower-carbon smelting technologies.
5. Regional Market Diversification
While North America and Europe remain key markets due to stringent building codes and mature industrial sectors, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region. China, India, and Southeast Asian countries are witnessing rapid infrastructure development and industrialization, fueling demand. Localized production hubs and government incentives for green manufacturing are expected to attract major players to establish regional supply chains by 2026.
6. Price Volatility and Supply Chain Resilience
Despite strong demand, the market may face challenges from fluctuating aluminum prices influenced by energy costs, geopolitical tensions, and trade policies. To mitigate risks, companies are diversifying raw material sources and investing in vertical integration. Digital supply chain platforms and nearshoring strategies are gaining adoption to enhance responsiveness and reduce lead times.
Conclusion
By 2026, the expanded aluminum sheet market will be shaped by a confluence of sustainability mandates, technological innovation, and sectoral growth in construction, transportation, and energy. Companies that prioritize product differentiation, environmental compliance, and agile supply chains will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this dynamic landscape.
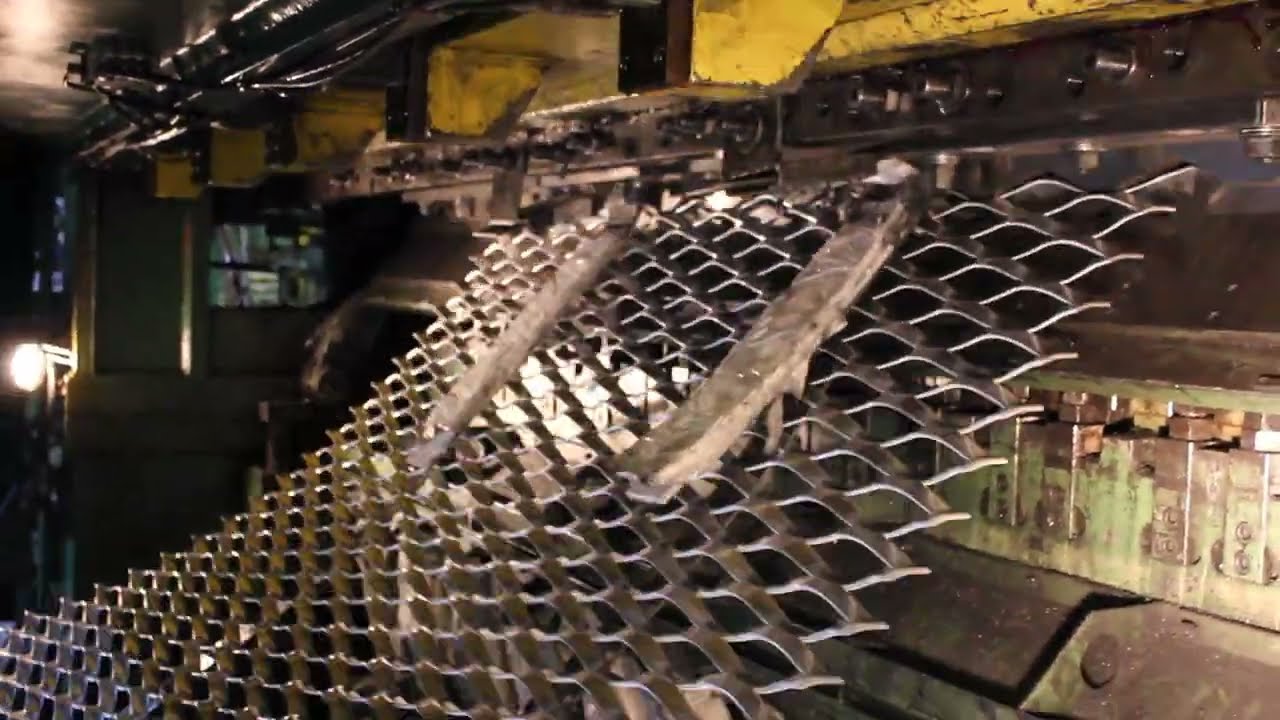

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Expanded Aluminum Sheet (Quality, IP)
Sourcing expanded aluminum sheet involves several potential pitfalls related to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Overlooking these can lead to performance issues, supply chain disruptions, legal risks, and increased costs.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is receiving material that deviates from specified dimensions, such as strand width, mesh size, or thickness. Variations can affect structural integrity, airflow, or aesthetic consistency, especially in architectural or filtration applications. Always request and verify material test reports (MTRs) and conduct incoming inspections.
Poor Surface Finish and Corrosion Resistance
Expanded aluminum is often used in outdoor or high-moisture environments. Sourcing from suppliers who cut corners on alloy selection (e.g., using non-marine-grade aluminum like 1100 instead of 5052 or 6063) or skipping proper surface treatments (anodizing, powder coating) can lead to premature corrosion and reduced lifespan.
Inadequate Tolerance Control
Expanded metal sheets with inconsistent expansion patterns or poor edge quality can impair fit and performance in precision applications. Suppliers lacking rigorous quality control may deliver sheets with warped edges, uneven openings, or dimensional inaccuracies, leading to rework or rejection.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Failure to obtain proper documentation—such as mill certifications, compliance with ASTM standards (e.g., ASTM B209), or RoHS/REACH compliance—can pose risks in regulated industries. Without traceability, it’s difficult to validate quality or address defects retroactively.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Use of Patented Patterns or Designs
Some expanded metal patterns, especially those with unique structural or aesthetic properties, may be protected by design or utility patents. Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate patented designs without licensing can expose your company to IP infringement claims, particularly in markets with strong IP enforcement.
Counterfeit or Grey Market Materials
Dealing with unauthorized distributors or third-party suppliers may result in receiving counterfeit products falsely branded as coming from reputable mills. These materials often lack proper certification and may not meet technical specifications, creating liability and performance risks.
Failure to Verify Supplier IP Compliance
Many buyers overlook the need to audit suppliers for IP due diligence. Ensure suppliers can demonstrate legal rights to produce and sell the expanded patterns you’re sourcing. Request documentation such as IP licenses or design freedom-to-operate opinions, especially for custom or proprietary designs.
Custom Tooling and Design Ownership Ambiguity
When commissioning custom tooling for unique expanded patterns, unclear contracts may lead to disputes over ownership of the tooling or design. Always define IP ownership, usage rights, and tooling custody in supplier agreements to prevent future conflicts or loss of competitive advantage.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, buyers can ensure reliable supply, maintain product integrity, and reduce legal and operational risks when sourcing expanded aluminum sheet.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Expanded Aluminum Sheet
Overview of Expanded Aluminum Sheet
Expanded aluminum sheet is a lightweight, durable metal product created by slitting and stretching aluminum coils into a mesh or diamond-patterned structure. It is widely used in architectural cladding, filtration, machine guarding, and decorative applications. Due to its unique physical characteristics—such as low density, high strength-to-weight ratio, and open surface area—specific logistics and compliance considerations apply during handling, transportation, and import/export.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit. Expanded aluminum sheets are typically bundled and secured on wooden pallets or skids using steel or plastic strapping. Edge protectors should be used to avoid deformation of the flanged edges. Sheets must be stored in a dry, covered environment to prevent corrosion from moisture. When handling, use lifting equipment with wide slings or vacuum lifters to avoid point loading and distortion. Manual handling should be minimized to reduce the risk of cuts from sharp edges.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Due to the large surface area and lightweight nature of expanded aluminum, transportation is often volume-constrained rather than weight-constrained. Secure stacking and bracing are critical to prevent shifting during transit. When shipping by container, ensure adequate lashing to walls and floor to avoid movement. For overland transport, tarps should be used to protect against weather, but ventilation must be maintained to reduce condensation. International shipments should comply with IMDG (International Maritime Dangerous Goods) Code if applicable, though expanded aluminum is generally non-hazardous.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Expanded aluminum sheets must comply with regional and international material standards. In the U.S., relevant standards include ASTM B209 (Standard Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy Sheet and Plate), which governs chemical composition and mechanical properties. For fire safety in building applications, compliance with ASTM E84 (Surface Burning Characteristics) may be required. In the EU, compliance with CE marking directives—such as the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) EN 1090 for structural use—may apply depending on the application.
Import and Export Documentation
Global trade of expanded aluminum sheet requires accurate documentation to ensure customs clearance. Key documents include commercial invoices, packing lists, bills of lading, and certificates of origin. Harmonized System (HS) codes are essential for tariff classification; a common code for expanded aluminum is 7314.19 (though aluminum-specific codes such as 7610.90 may apply depending on form and use). Exporters must verify destination country regulations, including anti-dumping duties or trade restrictions that may apply to aluminum products.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Expanded aluminum is recyclable and generally considered environmentally benign. However, manufacturing residues and packaging materials must be managed according to local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA rules in the U.S. or REACH in the EU). Workplace safety standards such as OSHA (U.S.) or the EU’s Machinery Directive apply during handling and processing due to sharp edges and potential for cuts or punctures. Safety data sheets (SDS) are typically not required for raw expanded aluminum, but may be needed if coatings or treatments are applied.
Certification and Traceability
For critical applications—especially in construction or aerospace—material traceability and mill test certificates (MTCs) are often required. These documents verify alloy type, temper, and compliance with specified standards. Suppliers should provide batch-level traceability and, when requested, third-party inspection reports from agencies such as SGS or Bureau Veritas. Proper labeling of packages with product specifications, heat numbers, and handling instructions supports compliance and quality assurance.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of expanded aluminum sheet requires attention to packaging, transportation efficiency, regulatory standards, and documentation. Adhering to industry specifications and regional regulations ensures product integrity, safety, and smooth customs processing. Proactive planning and supplier collaboration are key to minimizing delays and avoiding compliance risks in global supply chains.
In conclusion, sourcing expanded aluminum sheet requires careful consideration of several key factors including material specifications, quality standards, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and logistical capabilities. Expanded aluminum offers significant advantages such as lightweight strength, durability, ventilation, and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for applications in construction, filtration, machinery, and decorative design. By partnering with reputable suppliers who adhere to industry standards and can provide consistent quality and timely delivery, businesses can ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in their projects. Conducting thorough market research, evaluating samples, and establishing long-term supplier relationships further enhance sourcing success. Ultimately, a strategic and informed approach to sourcing expanded aluminum sheet will support project efficiency, product integrity, and overall operational goals.