The global exoskeleton market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industrial, medical, and defense sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the exoskeleton market was valued at USD 937.4 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 36.5% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 5.3 billion by the end of the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by rising workplace safety regulations, advancements in wearable robotics, and growing adoption in rehabilitation therapies. With leading economies investing heavily in human augmentation technologies, the competitive landscape is rapidly evolving. In this dynamic environment, innovation, scalability, and technological integration are key differentiators. Below are the top 9 exo-suit manufacturers shaping the future of human performance enhancement across critical industries.
Top 9 Exo-Suit Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Skelex
Domain Est. 2017
Website: skelex.com
Key Highlights: The Ultimate Exoskeleton for Industrial Work. Skelex powers the worker of the future with industrial upper body, back & gripping exoskeletons….
#2 Verve Motion: The Future of Industrial Wearables
Domain Est. 2019
Website: vervemotion.com
Key Highlights: Verve Motion’s SafeLift™ exosuit is a wearable robot helps prevent injuries for workers engaged in repetitive lifting to support a safe and productive ……
#3 Wearable Robotics
Domain Est. 1995
Website: comau.com
Key Highlights: Our innovative exoskeleton suits provide consistent and advanced movement assistance during repetitive and daily tasks. There are distinct solutions that ……
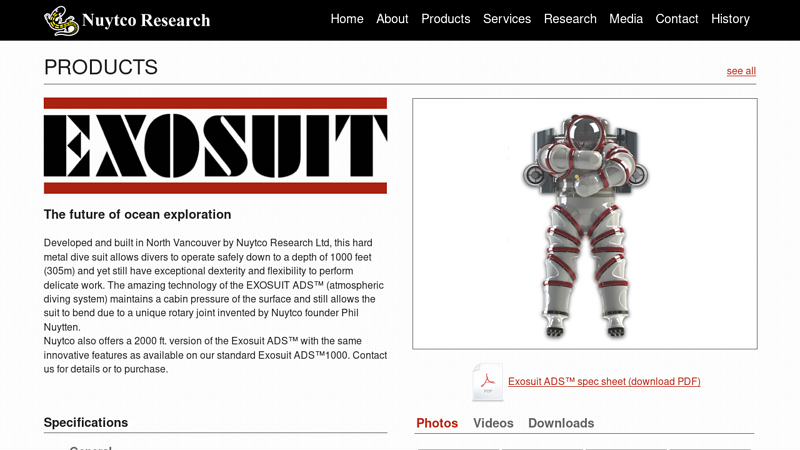
#4 Exosuit ADS™
Domain Est. 1998
Website: nuytco.com
Key Highlights: This hard metal dive suit allows divers to operate safely down to a depth of 1000 feet (305m) and yet still have exceptional dexterity and flexibility….
#5 Lifeward
Domain Est. 2007
Website: golifeward.com
Key Highlights: Lifeward is a medical device company that designs and develops powered solutions that provide gait training and mobility for lower limb disabilities….
#6 Revolutionize Mobility
Domain Est. 2011
Website: eksobionics.com
Key Highlights: Helping thousands of individuals take millions of Ekso-aided steps. At Ekso Bionics, we develop disruptive wearable robotics to take on loss of mobility….
#7 Pioneers in Smart Exoskeleton Tech
Domain Est. 2016
Website: germanbionic.com
Key Highlights: German Bionic is a European robotics firm specializing in smart power suits and wearable technologies. We were the first company to deliver connected ……
#8 Laevo Exoskeletons
Domain Est. 2018
Website: laevo-exoskeletons.com
Key Highlights: Since its founding in 2013, Laevo has been a pioneer in the exoskeleton market and is one of the oldest and most experienced exoskeleton companies in the world….
#9
Domain Est. 2020
Website: skeletonics-us.com
Key Highlights: Skeletonics is a 9-foot tall robot suit that offers an extraordinary experience. By wearing Skeletonics, you’ll be able to feel what it’s like to be a giant….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Exo-Suit
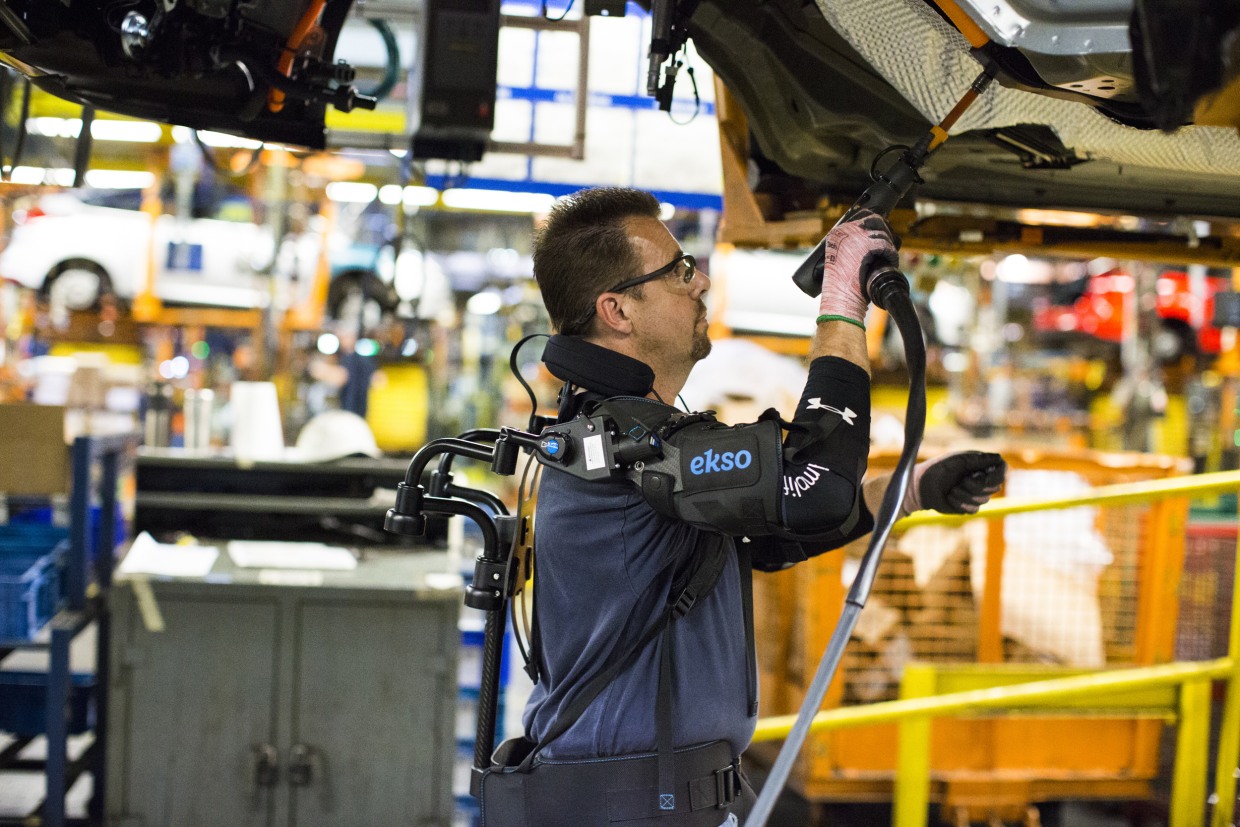

H2 2026 Market Trends for Exo-Suits
The exo-suit market in H2 2026 is poised for accelerated growth and transformation, driven by technological convergence, expanding applications, and evolving economic and regulatory landscapes. Building on advancements from earlier in the year, key trends will solidify the industry’s shift from niche applications toward broader commercialization and integration across multiple sectors.
1. Industrial Adoption Accelerates in Logistics and Manufacturing
By H2 2026, exo-suits are becoming standard equipment in high-labor environments. Warehouse automation leaders and major manufacturing firms are deploying powered upper-body exo-suits (e.g., back and shoulder supports) at scale to combat worker fatigue, reduce musculoskeletal injuries, and improve productivity. Companies like Amazon, DHL, and automotive OEMs are reporting measurable ROI through lower workers’ compensation claims and increased throughput. The integration of exo-suits with IoT sensors and predictive maintenance systems enables real-time ergonomic monitoring and data-driven workforce optimization.
2. Healthcare and Rehabilitation Transitions to Mainstream Use
H2 2026 sees the continued expansion of exo-suits in clinical and home-care settings. FDA-cleared and CE-marked lower-limb exo-suits for stroke and spinal cord injury rehabilitation are now more affordable and user-friendly, with improved battery life and intuitive control interfaces (e.g., EMG or brain-computer integration). Insurance reimbursement models are beginning to catch up, driving wider adoption in physical therapy clinics. Additionally, lightweight, soft exo-suits for elderly mobility support are gaining traction in aging societies like Japan and Germany, supported by government aging-in-place initiatives.
3. Military and First Responder Integration Reaches New Maturity
Defense departments, particularly in the U.S., EU, and allied nations, are field-testing next-generation load-bearing exo-suits designed for extended missions and rugged terrain. Powered exo-suits capable of carrying 50+ kg loads with minimal user fatigue are undergoing real-world evaluations. Simultaneously, fire and rescue units are adopting passive and hybrid exo-suits to enhance strength during search-and-rescue operations. Interoperability with communication and situational awareness systems is a key focus, turning exo-suits into integrated components of next-gen tactical gear.
4. Technological Advancements: AI, Materials, and Energy Efficiency
Exo-suit designs in H2 2026 are increasingly intelligent and adaptive. AI-driven motion prediction algorithms enable smoother, more natural movement by anticipating user intent. Advances in soft robotics, using lightweight composite materials and fluidic actuators, improve comfort and reduce bulk. Battery technology sees incremental gains, with solid-state batteries beginning to enter prototypes, offering higher energy density and faster charging. These improvements collectively enhance user acceptance and operational duration.
5. Regulatory and Ethical Frameworks Begin to Take Shape
As exo-suit use grows, regulatory bodies are drafting clearer guidelines for safety, liability, and data privacy—especially concerning biometric data collected by on-board sensors. The EU’s Machinery Regulation and U.S. OSHA are expected to release updated standards for wearable robotics in industrial settings by Q4 2026. Concurrently, ethical discussions around worker surveillance, job displacement, and equitable access are gaining attention, prompting industry groups to develop best practice frameworks.
6. Market Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The competitive landscape is shifting toward consolidation. Smaller innovators are being acquired by larger industrial automation or medical device companies (e.g., Sarcos, Ekso Bionics, or German Bionic), while strategic alliances between robotics firms and cloud/AI providers (e.g., partnerships with Microsoft Azure or AWS) are accelerating platform development. This trend enhances scalability and interoperability, paving the way for integrated exo-suit ecosystems.
Conclusion
H2 2026 marks a pivotal phase for the exo-suit market: it is transitioning from proof-of-concept and pilot deployments to scalable, economically viable solutions across industrial, medical, and defense sectors. Success will depend on continued innovation in usability and affordability, supportive regulation, and responsible integration into the human workforce. With momentum building, the exo-suit industry is on track to become a multi-billion-dollar market by the end of the decade.
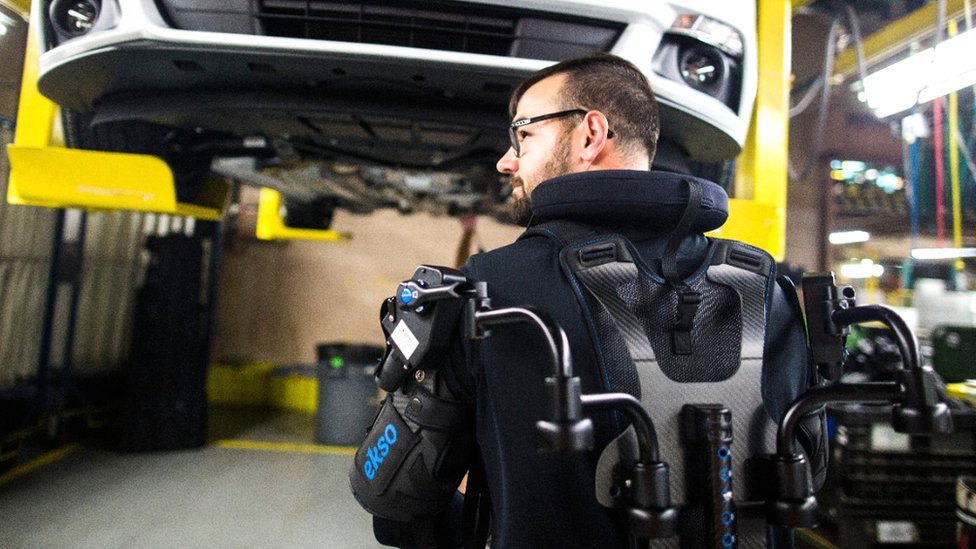

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Exo-Suits: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing exo-suits—especially for industrial, medical, or defense applications—presents significant challenges beyond typical procurement. Two critical areas where organizations often encounter problems are quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to safety hazards, project delays, legal disputes, and financial loss.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inadequate Performance Validation
Many suppliers offer exo-suits based on theoretical or lab-tested performance. A common mistake is assuming real-world durability and functionality without rigorous field testing. Sourcing without validating performance under actual operating conditions—such as variable load, environmental exposure, or user fatigue—can result in equipment failure or injury. -
Lack of Standardized Certifications
The exo-suit industry lacks universal safety and performance standards. Relying on suppliers without recognized certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, or industry-specific compliance) increases the risk of acquiring substandard or unsafe devices. Buyers must verify testing protocols and ensure traceable quality control processes. -
Poor Ergonomics and User Compatibility
Exo-suits must align with human biomechanics to prevent strain or injury. Sourcing without user trials or adjustable designs can lead to discomfort, reduced adoption, and potential long-term health issues—undermining the intended benefits. -
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Exo-suits are complex electromechanical systems requiring regular maintenance, software updates, and spare parts. Vendors with weak service networks or poor documentation can leave buyers stranded when repairs or upgrades are needed.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
-
Unclear IP Ownership
Customizing or co-developing exo-suits with suppliers can lead to disputes over IP ownership. Without explicit contractual terms, the buyer may lose rights to modifications, software algorithms, or design enhancements—limiting future innovation or competitive advantage. -
Use of Third-Party or Infringing Technology
Some suppliers integrate patented components (e.g., actuators, control systems) without proper licensing. Buyers risk legal liability if the sourced exo-suit infringes on third-party IP, potentially leading to product recalls or lawsuits. -
Inadequate Protection of Proprietary Requirements
When sharing custom specifications or integration needs with potential vendors, companies may inadvertently disclose trade secrets. Failing to use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or data security measures exposes sensitive operational or strategic information. -
Open-Source or Unlicensed Software Risks
Many exo-suits rely on embedded software that may include open-source components with restrictive licenses (e.g., GPL). Sourcing without auditing the software stack can result in unintended obligations to disclose proprietary code or pay licensing fees.
To mitigate these pitfalls, organizations should conduct thorough due diligence, demand transparency in design and testing, secure clear IP agreements, and work with reputable suppliers who provide verifiable quality controls and legal compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Exo-Suit
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the handling, transportation, use, and maintenance of exoskeleton suits (exosuits) in industrial, medical, or commercial applications.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to local, national, and international regulations governing wearable robotics. This includes compliance with occupational safety standards (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., HSE in the UK), medical device regulations (e.g., FDA, EU MDR) if applicable, and electrical safety standards (e.g., IEC 60601, UL 61010). Documentation must include CE marking, FCC certification, and RoHS compliance where required.
Import and Export Controls
Exosuits may be subject to export control regulations due to advanced sensors, software, or dual-use technologies. Verify classification under export control lists (e.g., EAR, ITAR). Obtain necessary licenses for international shipment and ensure end-user documentation to prevent unauthorized transfers.
Transportation and Shipping
Package exosuits in protective, shock-resistant containers with internal bracing to prevent damage during transit. Clearly label units with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”). Use certified carriers experienced in shipping sensitive electronic and mechanical equipment. Lithium-ion batteries must comply with IATA/IMDG regulations for air and sea transport.
Inventory and Tracking
Maintain a centralized asset management system to track each exosuit’s location, maintenance history, and usage logs. Utilize serialized identifiers (e.g., QR codes, RFID tags) for real-time monitoring. Conduct regular audits to ensure inventory accuracy and regulatory traceability.
User Training and Certification
Only trained and certified personnel should operate exosuits. Provide comprehensive training programs covering safe operation, emergency shutdown procedures, and ergonomic best practices. Maintain records of training completion for compliance audits.
Maintenance and Servicing
Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules. All servicing must be performed by authorized technicians using genuine parts. Keep detailed service logs and retain them for the equipment lifecycle. Promptly report and address any malfunctions or safety concerns.
Data Security and Privacy
Exosuits may collect biometric or operational data. Ensure compliance with data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). Implement encryption, access controls, and secure data storage protocols. Obtain user consent where personal data is collected.
End-of-Life Disposal
Dispose of exosuits and components in accordance with environmental regulations (e.g., WEEE Directive). Use certified e-waste recyclers to handle batteries, electronics, and composite materials. Document disposal procedures for audit purposes.
Site-Specific Risk Assessments
Conduct risk assessments prior to deployment at each worksite. Evaluate environmental conditions, user health factors, and operational workflows. Update safety protocols based on assessment findings and incident reporting.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Exo-suit:
Sourcing an exo-suit requires a strategic and comprehensive approach that balances technological capability, cost-effectiveness, reliability, and alignment with specific operational needs—whether for industrial, medical, military, or logistics applications. After evaluating available options, key factors such as ergonomic design, power efficiency, ease of integration, safety certifications, and vendor support emerge as critical decision-making criteria.
Investing in exo-suit technology offers significant potential to enhance human performance, reduce workplace injuries, and improve productivity. However, successful sourcing depends on thorough due diligence, pilot testing, and ongoing assessment of evolving technologies. Organizations should prioritize partnerships with reputable manufacturers, consider scalability, and plan for training and maintenance to ensure long-term success. Ultimately, a well-sourced exo-suit solution can deliver sustainable value by empowering the workforce and driving operational excellence.