The global exhaust manifold and catalytic converter market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasingly stringent emission regulations and rising demand for cleaner internal combustion engines. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the catalytic converter market was valued at USD 28.67 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 42.14 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 6.7% during the forecast period. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights that the broader automotive emission control systems market—including exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters—is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by regulatory mandates in regions like North America, Europe, and China. As automakers prioritize compliance with Euro 7, BS6, and Tier 3 standards, the role of advanced emission control components has become critical. This growth trajectory underscores the importance of innovation and scalability among manufacturers. Below, we profile the top 8 exhaust manifold and catalytic converter manufacturers leading this transformation through technological expertise, global supply chain integration, and strategic R&D investments.
Top 8 Exhaust Manifold And Catalytic Converter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
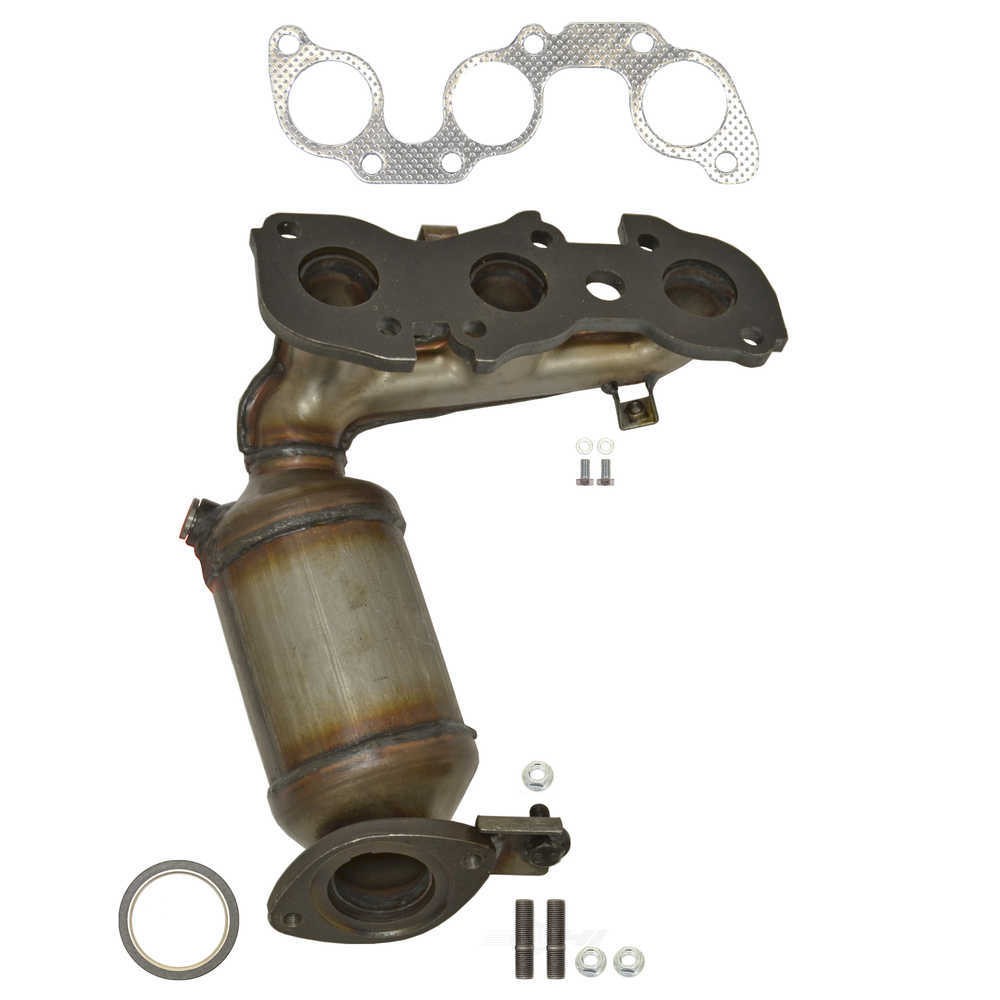
#1 Catalytic Converter With Integrated Exhaust Manifold
Domain Est. 2001
Website: parts.nissanusa.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsOrder Your OEM Catalytic Converter With Integrated Exhaust Manifold (140e26lw0c) For Your 2021-2024 Nissan Sentra Today From The Official Nissan Parts Store….
#2 Exhaust And Catalytic Converter Manifold
Domain Est. 2013
Website: moparfactoryparts.com
Key Highlights: 4–8 day delivery 30-day returnsYour Exhaust And Catalytic Converter Manifold will specifically fit your 2023-2026 Chrysler Pacifica vehicle. Affordable, reliable and built to last,…
#3 Catalytic Converter with Integrated Exhaust Manifold
Domain Est. 2023
Website: toyotaparts.ourismantoyotaofrichmond.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 1 Catalytic Converter with Integrated Exhaust Manifold – Toyota (25052-20190) … We are one of the largest online retailers for factory Toyota parts on the w…
#4 Manifold Catalytic Converters
Domain Est. 1996
Website: magnaflow.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $25 · 45-day returnsShop all MagnaFlow Manifold Catalytic Converters online. Buy a Catalytic Converter replacement for a manifold engine exhaust. Search by year…
#5 Aftermarket Catalytic Converter Database
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ww2.arb.ca.gov
Key Highlights: A database to store and retrieve information on aftermarket catalytic converters that have been approved for use in California….
#6 Walker Exhaust Systems
Domain Est. 1999
Website: walkerexhaust.com
Key Highlights: Providing performance-grade mufflers and exhaust kits for a wide variety of makes and models, Walker is the name to trust in OE-quality exhaust parts….
#7 Catalytic Converter with Integrated Exhaust Manifold
Domain Est. 2001
Website: dormanproducts.com
Key Highlights: Direct replacement – this manifold converter is designed to match the fit and performance of the original equipment on specific vehicles · Convenient kit – ……
#8 CATCO®
Domain Est. 2006
Website: apemissions.com
Key Highlights: Professional technicians count on CATCO for high quality, easy to install products and on-time delivery to reduce come-backs and increase productivity….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Exhaust Manifold And Catalytic Converter

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Exhaust Manifold and Catalytic Converter
Overview of the Exhaust Manifold and Catalytic Converter Market
The global market for exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by tightening emissions regulations, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), and advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies. While the internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle market remains substantial—especially in emerging economies—industry stakeholders must adapt to structural shifts to remain competitive.
Key Market Drivers
1. Stricter Emission Regulations
Governments worldwide are enforcing more stringent emissions standards, such as Euro 7 in Europe, China 6b, and updated EPA Tier 4 regulations in the U.S. These standards demand lower NOx, CO, and particulate matter emissions, compelling automakers to adopt high-efficiency catalytic converters and optimized exhaust manifolds. By 2026, manufacturers will increasingly integrate close-coupled catalytic converters and dual-substrate designs to meet cold-start emission requirements.
2. Growth in Hybrid Vehicle Production
As fully electric vehicles gain traction, hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs and PHEVs) are expected to serve as a transitional technology. These vehicles still rely on ICE systems, maintaining demand for exhaust components. By 2026, hybrid vehicle production is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 10%, supporting continued demand for advanced catalytic converters and lightweight exhaust manifolds.
3. Material Innovation and Lightweighting
To improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, manufacturers are investing in lightweight, heat-resistant materials such as stainless steel alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and ceramic matrix composites. 3D printing and advanced casting techniques are enabling more complex manifold designs that enhance exhaust gas flow and thermal management. By 2026, adoption of such technologies is expected to increase, particularly among premium and performance vehicle segments.
Challenges and Disruptive Forces
1. Decline in ICE Vehicle Production
The long-term outlook for exhaust components is tempered by the global shift toward electrification. Major markets like the EU and California plan to phase out new ICE vehicle sales by 2035, which will gradually erode demand. By 2026, however, the transition will still be in progress, with ICE and hybrid vehicles accounting for the majority of global auto production, particularly in regions like India, Southeast Asia, and Africa.
2. Aftermarket and Recycling Opportunities
With millions of ICE vehicles expected to remain on the road through 2030 and beyond, the aftermarket for exhaust components will remain robust. Catalytic converters, in particular, contain valuable precious metals (platinum, palladium, rhodium), driving a growing recycling industry. By 2026, the secondary market for remanufactured and recycled catalytic converters is projected to expand, especially in cost-sensitive regions.
3. Supply Chain and Raw Material Volatility
The catalytic converter industry remains vulnerable to fluctuations in precious metal prices. Geopolitical tensions, mining constraints, and increased demand from other sectors (e.g., hydrogen fuel cells) could impact supply. Automakers and suppliers are mitigating risks through long-term contracts and research into alternative catalyst materials, such as perovskite-based coatings, which may begin commercial deployment by 2026.
Regional Market Outlook
- Europe: Leading in emissions regulation, Europe will drive innovation in high-efficiency exhaust systems. Demand will be sustained by hybrid models and a large existing ICE fleet.
- North America: Steady demand from light-duty trucks and SUVs will support the market, especially in the U.S., where ICE vehicles remain popular.
- Asia-Pacific: China and India will be key growth markets due to rising vehicle ownership and lagging EV adoption rates compared to the West. Local manufacturers are investing in domestic exhaust component production.
- Rest of World: Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa will continue to rely on ICE vehicles, ensuring stable demand for exhaust systems through 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the exhaust manifold and catalytic converter market will exist at a pivotal juncture—balancing innovation and efficiency improvements against the backdrop of automotive electrification. While long-term demand faces structural decline, near-term growth will be sustained by regulatory pressures, hybrid vehicle expansion, and emerging market dynamics. Companies that invest in lightweight materials, advanced catalyst formulations, and circular economy solutions (recycling, remanufacturing) will be best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Exhaust Manifold and Catalytic Converter (Quality, IP)
Sourcing critical emissions components like exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters involves significant risks, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to costly failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Here are the key challenges to avoid:
1. Compromised Material and Manufacturing Quality
Many suppliers, especially in low-cost regions, may use substandard materials or inadequate manufacturing processes to reduce costs. For example, exhaust manifolds require heat-resistant alloys (e.g., stainless steel or nickel-based superalloys); using inferior grades can lead to cracking or premature failure. Similarly, catalytic converters depend on precise washcoat formulations and precious metal loading (platinum, palladium, rhodium). Inconsistent coating thickness or incorrect catalyst formulations reduce conversion efficiency and may cause non-compliance with emissions standards.
Best Practice: Implement rigorous supplier qualification audits, demand material certifications (e.g., mill test reports), and conduct third-party lab testing of samples for chemical composition and performance.
2. Inadequate Performance Validation and Testing
Some suppliers provide components that meet basic dimensional specs but fail under real operating conditions. Without proper thermal cycling, backpressure, and emissions testing (e.g., FTP-75 cycle), converters may degrade quickly, and manifolds may warp or leak.
Best Practice: Require suppliers to perform and document durability and emissions performance testing according to OEM or regulatory standards. Include performance warranties in procurement contracts.
3. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risk
Catalytic converter designs, substrate geometries, and proprietary washcoat formulations are often protected by patents. Sourcing from unauthorized or copycat manufacturers can expose buyers to IP litigation. Furthermore, reverse-engineered exhaust manifolds may infringe on design patents or violate OEM-specific engineering IP.
Best Practice: Conduct IP due diligence on suppliers. Require legal assurances (indemnification clauses) that components do not infringe on third-party IP. Avoid suppliers known for producing “pattern” or knockoff parts.
4. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Poor documentation—such as missing batch numbers, material traceability, or test reports—hampers quality control and regulatory compliance. In the event of a recall or non-compliance issue, untraceable components can delay root cause analysis and increase liability.
Best Practice: Enforce strict documentation requirements, including lot tracking, material data sheets, and test certifications. Use digital supply chain tools to maintain an auditable record.
5. Supply Chain Transparency and Counterfeit Components
The high value of precious metals in catalytic converters makes them a target for counterfeiting. Fake or recycled cores with diluted catalyst content are common in unregulated markets. Similarly, exhaust manifolds may be misrepresented in terms of alloy quality or manufacturing method (e.g., cast vs. fabricated).
Best Practice: Source from reputable, certified suppliers with transparent supply chains. Use secure procurement channels and conduct periodic on-site audits. Employ technologies like blockchain or serialization to verify authenticity.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, companies can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection against legal and operational risks when sourcing exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Exhaust Manifold and Catalytic Converter
Overview
Exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters are critical components in automotive emissions control systems. Due to their environmental impact, material composition (including precious metals), and regulatory significance, shipping and handling these parts involve strict logistics and compliance requirements across international, national, and regional jurisdictions. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, legal, and efficient transportation and compliance management.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
Emissions and Environmental Regulations
- EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency):
Catalytic converters are regulated under the Clean Air Act. Replacement or installation must comply with EPA standards. Tampering with or selling non-compliant converters (e.g., “test pipes” or non-OEM units) is illegal. - CARB (California Air Resources Board):
Stricter than federal EPA rules. Aftermarket catalytic converters sold in California must be CARB Executive Order (EO) certified. Verify EO number before shipping to California. - EU Emissions Standards (Euro 6/7):
Catalytic converters must meet EU type-approval requirements. Importers must ensure conformity with Regulation (EU) 2018/858 and applicable emission standards. - Other Regions:
Countries like Canada (Transport Canada), Australia (ADR), and Japan (MLIT) have similar certification and approval systems. Confirm local requirements prior to export.
Anti-Tampering Laws
- It is illegal in most jurisdictions to sell or install catalytic converters that bypass or disable emissions controls.
- Documentation must confirm that parts are for repair/replacement only and not for defeating emissions systems.
Precious Metals Reporting (Catalytic Converters)
- Catalytic converters contain platinum, palladium, and rhodium—regulated due to theft and recycling concerns.
- U.S.: Some states (e.g., California, Texas, Florida) require scrap yards and recyclers to report transactions involving catalytic converters. Maintain records of serial numbers, seller information, and transaction dates.
- EU: Follow Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) and End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) directives for recycling and tracking.
- International Transport: Declare contents accurately; misdeclaration may trigger customs or law enforcement scrutiny.
H2: Shipping and Logistics
Packaging Requirements
- Secure Packaging: Use sturdy, crush-resistant boxes with internal padding to prevent damage during transit. Exhaust manifolds are heavy and can shift; secure with void fill and banding.
- Moisture Protection: Use moisture barriers or desiccants, especially for long ocean shipments, to prevent rust.
- Labeling: Clearly label contents as “Automotive Exhaust Components” with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”). Include part numbers, model compatibility, and compliance markings (e.g., “CARB Certified”).
Transportation Modes
- Air Freight: Suitable for urgent or high-value shipments. Be aware of IATA regulations—no hazardous materials, but declare contents accurately.
- Ocean Freight: Cost-effective for bulk shipments. Use palletized loads with stretch wrap and corner boards. Include proper container desiccants.
- Ground Transport: Common for domestic distribution. Ensure proper vehicle securing and temperature control in extreme climates.
Customs Documentation
- Harmonized System (HS) Codes:
- Exhaust Manifold: Typically 8708.29.50 (Other parts of engines for vehicles)
- Catalytic Converter: Usually 8708.29.50 or 8708.29.60 (Emissions control devices)
- Confirm exact codes with local customs authority; misclassification can lead to delays or penalties.
- Required Documents:
- Commercial Invoice (with value, quantity, and detailed description)
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- CARB EO Number (if applicable)
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), if requested
Import/Export Controls
- Export Restrictions: Some countries restrict export of used catalytic converters due to precious metal content or environmental concerns.
- Import Permits: Certain destinations may require pre-approval for emissions-related components.
- Used vs. New Parts: Used or recycled converters may face stricter scrutiny. Clearly declare condition and intended use.
H2: Handling and Storage
Safety Precautions
- Exhaust components may retain contaminants (oil, carbon soot, exhaust residues). Handle with gloves and eye protection.
- Used parts may contain hazardous waste—follow OSHA and local safety regulations.
- Catalytic converters should not be cut or dismantled without proper ventilation and PPE due to potential exposure to alumina substrate dust and precious metal particles.
Storage Conditions
- Store in dry, covered areas to prevent corrosion.
- Keep off the ground using pallets.
- Segregate new, used, and scrap converters to avoid mix-ups and regulatory issues.
H2: Anti-Theft and Traceability
Serial Number Tracking
- New OEM and CARB-certified catalytic converters often have unique serial numbers.
- Maintain a log of serial numbers for high-theft-risk models (e.g., Honda, Toyota hybrids).
- Share serial data with law enforcement or industry databases (e.g., National Insurance Crime Bureau in the U.S.) to deter theft and aid recovery.
Theft Prevention in Transit
- Use tamper-evident packaging.
- Avoid open trailers for long-haul transport.
- Partner with secure, vetted logistics providers.
H2: End-of-Life and Recycling Compliance
Recycling Requirements
- Spent catalytic converters are recyclable but regulated waste.
- Use certified recyclers compliant with:
- RCRA (U.S.)
- WEEE and ELV Directives (EU)
- Local hazardous waste regulations
- Maintain chain-of-custody documentation for recycling transactions.
Documentation for Recyclers
- Provide proof of lawful acquisition (e.g., purchase invoice, dismantling record).
- Include vehicle identification number (VIN) if removed from a specific vehicle (required in some states).
H2: Summary Checklist
| Requirement | Action |
|———–|——–|
| Regulatory Compliance | Verify EPA/CARB/EU certification; avoid anti-tampering violations |
| Packaging | Use durable, moisture-resistant materials; label clearly |
| Customs | Use correct HS codes; provide full documentation |
| Precious Metals | Record serial numbers; comply with state/national reporting |
| Safety | Use PPE; store in dry, secure areas |
| Recycling | Partner with certified recyclers; maintain records |
By adhering to this guide, businesses can ensure legal compliance, reduce shipment risks, and support environmental sustainability in the distribution of exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters.
Conclusion on Sourcing Exhaust Manifold and Catalytic Converter
In conclusion, sourcing exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, compliance, and supply chain reliability. These critical components play a vital role in engine performance, emissions control, and regulatory compliance, making the selection of reliable suppliers paramount.
After evaluating multiple sourcing options—including original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), aftermarket suppliers, and recycled/remanufactured parts—it is evident that OEM-sourced components offer the highest assurance of compatibility, durability, and adherence to emissions standards. However, they often come at a higher cost. Aftermarket alternatives can provide cost-effective solutions, especially for older vehicle models, but require careful vetting to ensure they meet required specifications and environmental regulations.
Geographic sourcing considerations, such as proximity to manufacturing hubs and potential trade restrictions, also influence lead times and total cost of ownership. Additionally, the increasing prevalence of catalytic converter theft due to precious metal content underscores the need for secure supply chains and traceability.
Ultimately, a hybrid sourcing strategy—leveraging OEM parts for critical applications and high-quality aftermarket options where appropriate—can optimize cost-efficiency without compromising performance or compliance. Establishing long-term partnerships with certified suppliers and implementing rigorous quality control measures will ensure consistent supply and support long-term operational reliability.