The global ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industries such as dental materials, adhesives, coatings, and polymer manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global acrylate monomers market—of which EGDMA is a key specialty segment—was valued at USD 14.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is largely fueled by increasing applications in high-performance polymers and dental composites, where EGDMA serves as an essential cross-linking agent. As regulatory standards evolve and manufacturers prioritize low-VOC, durable materials, the demand for high-purity EGDMA has surged. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers lead in production capacity, product quality, and innovation. Based on market presence, technological expertise, and global distribution networks, the following six companies have emerged as the top ethylene glycol dimethacrylate manufacturers shaping the industry’s trajectory.
Top 6 Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wegochem.com
Key Highlights: Wego Chemical Group is an industrial distributor and supplier of Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate , providing supply chain, logistics and warehousing ……
#2 Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA), ≥ 99.7%
Domain Est. 1995
Website: polysciences.com
Key Highlights: Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA) is a difunctional methacrylate monomer widely used as a crosslinking agent in polymer synthesis….
#3 Ethylene-Glycol-Dimethacrylate
Domain Est. 1995
Website: spectrumchemical.com
Key Highlights: 15-day returnsEthylene Glycol Dimethacrylate is a diester that is formed by the condensation of ethylene glycol and methacrylic acid and used primarily in free radical ……
#4 Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate Supplier and Distributor
Domain Est. 1999
Website: gjchemical.com
Key Highlights: GJ Chemical offers Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate, CAS# 97-90-5. Available in various grades, packaging and quantities from LTL to Bulk….
#5 VISIOMER® EGDMA
Domain Est. 2006
Website: evonik.com
Key Highlights: VISIOMER® EGDMA (Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) is a hydrophilic dimethacrylate monomer with low viscosity. Suitable as a crosslinking agent….
#6 EGDMA monomer
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sinocurechem.com
Key Highlights: SINOMER EGDMA (CAS 97-90-5,Diglycol dimethacrylate) is a low viscosity dimethacrylate crosslinker manufactured for polymer synthesis and artificial marble ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate
H2: Market Trends and Outlook for Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA) in 2026
The global market for Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA), a bifunctional crosslinking agent widely used in polymer chemistry, is expected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand across key end-use industries such as dental materials, coatings, adhesives, 3D printing resins, and biomedical applications. Several macroeconomic, technological, and regulatory trends are shaping the EGDMA market landscape over the forecast period leading to 2026.
-
Rising Demand in Dental and Medical Applications
EGDMA is a critical component in the formulation of dental composites, orthodontic adhesives, and prosthetics due to its ability to enhance mechanical strength and durability. The global expansion of dental healthcare services, particularly in emerging economies, coupled with growing consumer preference for cosmetic dentistry, is boosting demand for high-performance methacrylate-based resins. By 2026, the medical-grade EGDMA segment is projected to register above-average growth, supported by advancements in biocompatible polymer systems and increased R&D in hydrogels and drug delivery matrices. -
Growth in 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
The proliferation of photopolymer-based 3D printing technologies—especially stereolithography (SLA) and digital light processing (DLP)—is a major driver for EGDMA. As industries ranging from aerospace to healthcare adopt rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing, demand for high-resolution, durable photopolymer resins is rising. EGDMA’s role as a crosslinker improves the structural integrity and thermal stability of printed parts. By 2026, the integration of EGDMA into specialty 3D printing formulations is expected to expand, particularly in engineering and biomedical modeling applications. -
Expansion in Coatings and Adhesives
The industrial coatings sector is increasingly adopting UV-curable formulations to meet environmental regulations and improve production efficiency. EGDMA is used in these formulations to accelerate curing and enhance scratch and chemical resistance. Demand from automotive, electronics, and packaging industries for faster, eco-friendly coating systems will support market growth. By 2026, regulatory pressure to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions will continue to favor low-VOC, high-solids UV-curable systems where EGDMA plays a pivotal role. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing region for EGDMA by 2026, driven by robust manufacturing activity in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Local production of electronics, automotive components, and medical devices is increasing the regional consumption of advanced polymer materials. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand due to innovation in medical technologies and stringent environmental standards promoting UV-curable systems. However, regulatory scrutiny on certain acrylate monomers may prompt manufacturers to invest in purer, higher-grade EGDMA with improved safety profiles. -
Supply Chain and Sustainability Trends
Raw material availability, particularly methacrylic acid and ethylene oxide, remains a factor influencing EGDMA pricing and supply stability. By 2026, producers are expected to focus on process optimization and sustainable production methods, including recycling initiatives and bio-based alternatives. While fully bio-derived EGDMA is not yet commercially viable, research into greener synthesis routes may influence long-term market positioning. -
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The EGDMA market is characterized by a mix of large chemical companies and specialty monomer producers. Key players are investing in product differentiation through high-purity grades, inhibitor-free formulations, and technical support for niche applications. Strategic partnerships with resin formulators and 3D printing firms are expected to intensify by 2026, enhancing downstream integration and application-specific development.
Conclusion
By 2026, the ethylene glycol dimethacrylate market is poised for moderate but consistent growth, with a CAGR estimated between 4.5% and 5.8%, depending on region and application. Innovation in high-performance materials, regulatory tailwinds for sustainable technologies, and expanding use in advanced manufacturing will define market dynamics. Companies that prioritize quality, application support, and sustainability are likely to gain competitive advantage in the evolving EGDMA landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA), a key crosslinking monomer used in polymers, dental resins, hydrogels, and specialty coatings, involves several critical risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Failure to address these can lead to supply chain disruptions, regulatory non-compliance, or legal exposure.
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Purity and Inhibitor Levels
EGDMA is highly reactive and prone to premature polymerization. Reputable suppliers add inhibitors (e.g., hydroquinone monomethyl ether, MEHQ) to ensure stability. A common pitfall is sourcing material with inconsistent or insufficient inhibitor content, which can result in gelation during storage or transport. Conversely, excessive inhibitor levels may interfere with downstream applications, especially in sensitive formulations like medical devices or adhesives. -
Presence of Impurities (e.g., Methacrylic Acid, Water Content)
Poor manufacturing processes can lead to elevated levels of methacrylic acid or hydrolysis byproducts due to moisture ingress. These impurities affect reactivity, shelf life, and final product performance. Suppliers from non-GMP or non-audited facilities may lack adequate quality control (QC) measures to detect such impurities. -
Lack of Batch-to-Batch Consistency
Variability in viscosity, color, or refractive index between batches can indicate poor process control. This inconsistency is particularly problematic in regulated industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, biomedical devices), where reproducibility is mandatory. -
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Some suppliers—especially those in less-regulated markets—may provide incomplete Certificates of Analysis (CoA), lack raw material traceability, or fail to comply with ISO or REACH requirements. This complicates quality audits and regulatory submissions.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Unauthorized Production or Patent Infringement
Certain high-purity grades or stabilized formulations of EGDMA may be protected by patents, particularly in specialty applications such as dental composites or controlled drug delivery. Sourcing from manufacturers that produce EGDMA using patented processes (e.g., specific purification or stabilization methods) without license can expose the buyer to IP litigation, even if unintentional. -
Use of Generic Labels Masking Proprietary Formulations
Some suppliers market “generic EGDMA” that may contain proprietary additives or blends protected under formulation patents. Buyers assuming these are freely usable may inadvertently infringe on IP rights, especially when used in commercialized end-products. -
Unclear IP Warranty in Supply Agreements
Contracts with suppliers often lack explicit IP indemnification clauses. Without these, the buyer assumes liability if the sourced EGDMA violates third-party patents, particularly in export markets with strong IP enforcement (e.g., U.S., EU, Japan).
Mitigation Strategies
- Source from reputable suppliers with ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (if medical use), or REACH compliance.
- Require full CoAs, including inhibitor content, water levels, and purity (typically >98% for technical grade).
- Conduct supplier audits or request third-party testing for critical applications.
- Perform freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses when using EGDMA in patented processes or formulations.
- Include IP warranty and indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
In conclusion, sourcing EGDMA requires careful due diligence beyond price and availability. Ensuring consistent quality and avoiding IP entanglements are essential to maintaining product integrity and legal compliance.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA)
Hazard Class: H2 – Flammable Liquids
1. Chemical Identification
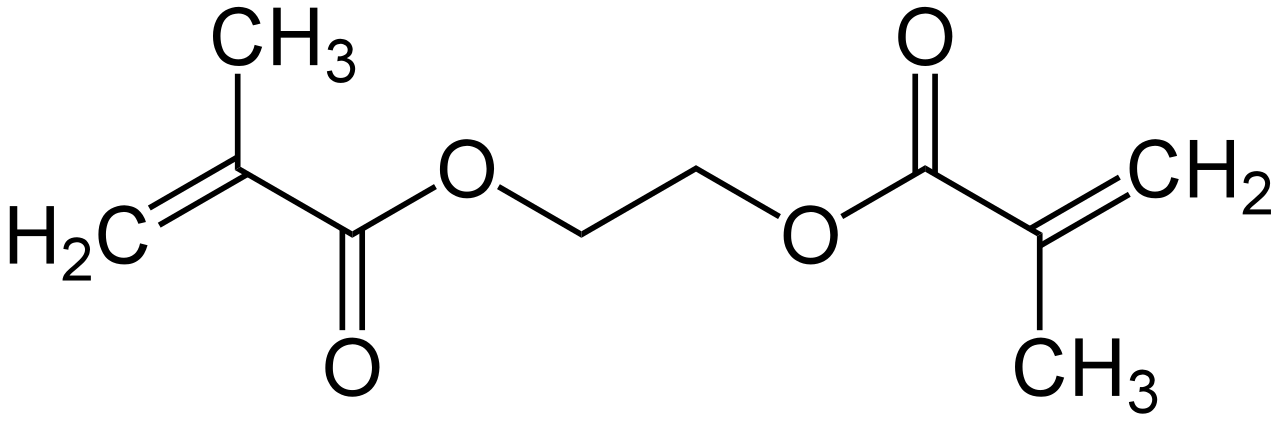
- Chemical Name: Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (EGDMA)
- CAS Number: 108-65-6
- Molecular Formula: C₁₀H₁₄O₄
- UN Number: UN 3271
- Proper Shipping Name: ETHYLENE GLYCOL DIMETHACRYLATE, STABILIZED
- Hazard Class: 3 (Flammable Liquid), PG II (Packing Group II – Medium Danger)
- Stabilizer: Typically contains hydroquinone (HQ) or methoxyhydroquinone (MEHQ) to prevent polymerization during storage and transport.
2. Hazard Classification (GHS / CLP) – H2 Focus
- H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapor
- H315: Causes skin irritation
- H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction
- H319: Causes serious eye irritation
- H335: May cause respiratory irritation
- H361: Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child
- H372: Causes damage to organs (central nervous system) through prolonged or repeated exposure
Note: This guide emphasizes H2 (flammability) as requested.
3. Flammability Properties (H2)
- Flash Point: ~76°C (closed cup) – classified as flammable per GHS (liquids with flash point ≤ 93°C)
- Autoignition Temperature: Approx. 350°C
- Flammable Limits:
- LEL: 1.0%
- UEL: 12.0%
- Vapor Density: >1 (vapors are heavier than air, may accumulate in low-lying areas)
- Combustion Products: Carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and irritating/toxic fumes (e.g., acrid smoke)
Despite a relatively high flash point, EGDMA is classified as Flammable Liquid, Category 3 under GHS, hence H225 applies.
4. Storage Requirements (H2 Focus)
- Storage Temperature: Store in a cool, well-ventilated area below 25°C. Avoid heat, sparks, open flames, and direct sunlight.
- Container: Keep in tightly closed, original, approved containers made of metal or compatible plastic. Ground and bond containers during transfer.
- Segregation:
- Keep away from: Oxidizers (e.g., nitrates, peroxides), strong acids, strong bases, and sources of ignition.
- Do not store near polymerization catalysts (e.g., peroxides, amines).
- Ventilation: Use explosion-proof ventilation in storage areas.
- Fire Protection: Store in flammable liquid storage cabinets or dedicated flammable storage rooms with fire suppression systems.
5. Handling Precautions (H2 Focus)
- No Smoking Policy: Strictly enforced in handling and storage areas.
- Static Control: Use grounding and bonding during transfer operations to prevent static sparks.
- Equipment: Use explosion-proof tools, electrical equipment, and ventilation systems.
- Spill Prevention: Use secondary containment (e.g., spill pallets) to prevent leaks from spreading.
- Minimize Vapor Release: Keep container closed when not in use; use local exhaust ventilation.
6. Transportation (H2 Compliance)
- Regulatory Framework:
- ADR/RID (Europe)
- IMDG Code (Maritime)
- IATA DGR (Air)
- 49 CFR (USA – DOT)
- Classification:
- Class 3: Flammable Liquid
- Packing Group: II
- UN 3271: ETHYLENE GLYCOL DIMETHACRYLATE, STABILIZED
- Labeling:
- Class 3 Flammable Liquid label (flame symbol)
- “Keep Away from Heat” marking
- Stabilizer statement required on package
- Packaging:
- Use UN-approved packaging (e.g., steel drums, composite containers)
- Inner containers must prevent leakage; outer packaging must pass drop and stack tests
- Documentation:
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) required
- Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (air/sea)
- Transport emergency cards (e.g., TREL/ERG)
Air Transport (IATA): Limited quantities may be allowed, but full regulation applies otherwise. Check current IATA DGR for exceptions.
7. Emergency Response (H2 Focus)
- Fire:
- Extinguishing Media: Alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical, CO₂, or water spray (to cool containers).
- Do Not Use: Straight water jets (may spread fire).
- Evacuate area and fight fire from a safe distance.
- Cool exposed containers with water spray.
- Spill Response:
- Eliminate ignition sources.
- Contain spill with inert absorbents (e.g., sand, vermiculite).
- Collect in labeled, closed containers for proper disposal.
- Ventilate area.
- Personal Protection: Wear flame-resistant clothing, self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA), and chemical-resistant gloves.
8. Regulatory Compliance
- OSHA (USA):
- Flammable Liquids Standard (29 CFR 1910.106) applies
- Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200) – SDS and labeling required
- EPA (USA):
- EPCRA Tier II reporting may be required for quantities above thresholds
- REACH/CLP (EU):
- Registration, labeling, and SDS in compliance with Annex II
- Notify in C&L Inventory
- GHS Compliance: Ensure labels and SDS follow H225 and other hazard statements.
9. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Eye/Face Protection: Chemical splash goggles or face shield
- Skin Protection: Nitrile or neoprene gloves, flame-resistant lab coat or apron
- Respiratory Protection: NIOSH-approved organic vapor respirator if vapor levels exceed exposure limits
- Footwear: Closed-toe, chemical-resistant shoes
10. Disposal
- Waste Code (EPA): D001 (Ignitable waste – flash point <60°C, but EGDMA may still qualify depending on formulation)
- Disposal Method: Incineration in permitted hazardous waste facility
- Never dispose of down the drain or in regular trash
Summary: H2 (Flammability) Key Points
- EGDMA is a flammable liquid (H225) — handle as such despite moderate flash point
- Avoid heat, sparks, and ignition sources
- Use bonded/grounded equipment during transfer
- Store in approved flammable liquid storage areas
- Transport under Class 3, PG II regulations
- Ensure emergency plans address flammable liquid fires
Always consult the current Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and local regulations before handling, storing, or transporting.
Review SDS Section 2 (Hazards), Section 7 (Handling/Storage), and Section 14 (Transport) for full compliance.
In conclusion, sourcing ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure reliability, quality, and compliance. It is essential to identify suppliers with a proven track record in providing high-purity EGDMA, particularly for applications in polymer science, dental materials, hydrogels, or biomedical research where consistency is critical. Evaluating suppliers based on product specifications, analytical certifications (such as GC, NMR, and certificate of analysis), regulatory compliance (including REACH, TSCA, and GHS labeling), and supply chain stability is paramount.
Additionally, safety and handling requirements must be taken into account due to EGDMA’s irritant and sensitizing properties, necessitating appropriate storage, transportation, and personal protective measures. Engaging with reputable chemical distributors or direct manufacturers—both domestic and international—can help balance cost-efficiency with quality assurance. Establishing long-term supplier relationships, conducting regular audits, and maintaining alternative sourcing options can further mitigate supply risks.
Ultimately, a strategic and due-diligent approach to sourcing ethylene glycol dimethacrylate will support process reliability, product performance, and regulatory compliance across various industrial and research applications.