The global ester gum market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care industries. According to Grand View Research, the global ester gum market size was valued at USD 68.3 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing consumer preference for natural additives and the expanding use of ester gum as a stabilizer, emulsifier, and clouding agent in beverages and chewing gums. Additionally, rising innovation in clean-label ingredients has prompted manufacturers to invest in sustainable and high-purity ester gum production. As demand escalates, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as key players, combining scalability, regulatory compliance, and technical expertise to lead the market. Based on production capacity, geographic reach, product quality, and innovation, the following nine companies represent the top ester gum manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 9 Ester Gum Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ester Gum
Domain Est. 2009
Website: rosin-factory.com
Key Highlights: It is commonly used as an emulsification stabilizer in beverages and as an ingredient in chewing gum and bubble gum. Additionally, it has various industrial ……
#2 What is ester gum?
Domain Est. 2006
Website: fortunachem.com
Key Highlights: Ester gum, scientifically known as Glycerol Ester of Wood Rosin, is a widely utilized food additive. Its core function is to act as an emulsifier and stabilizer ……
#3 Ester gum or Glycerol ester distributors, manufacturers, exporters …
Domain Est. 2016
Website: vizagchemical.com
Key Highlights: Vizag chemical is one of the leading Ester gum or Glycerol ester distributors, manufacturers, exporters, and suppliers in Visakhapatnam, Mumbai, Surat, ……
#4 Ester Gum 8BG®
Domain Est. 1997
Website: drt.fr
Key Highlights: Ester Gum 8BG is produced from food-grade glycerol (non animal-origin) and refined wood rosin, the latter of which is extracted from pinewood and is produced ……
#5 Ester Gum
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ifpc.com
Key Highlights: Ester gum is a high-quality stabilizing and emulsifying agent used in various industries, particularly in beverages and food products….
#6 PINOVA® ESTER GUM 8BG
Domain Est. 1998
Website: safic-alcan.com
Key Highlights: Clouding- & weighting agent suitable for the beverage industry. It is produced from food-grade glycerol and refined wood rosin….
#7 Glycerol Esters Of Wood Rosin(Ester Gum)
Domain Est. 2004
Website: foodchem.cn
Key Highlights: Foodchem International Corporation has been supplying and exporting Glycerol Esters Of Wood Rosin(Ester Gum) from China for almost 10 years….
#8 Glycerol Ester of Gum Rosin (ESTER GUM)
Domain Est. 2006
Website: foreverest.net
Key Highlights: Glycerol Ester of Gum Rosin (GEGR), also known as Glyceryl Rosinate or Ester Gum, is an oil-soluble food additive made by esterifying rosin with edible ……
#9 Synthomer™ Ester Gum 8WA
Domain Est. 2018
Website: univarsolutions.com
Key Highlights: 3–7 day delivery 14-day returnsSynthomer™ Ester Gum 8WA-M kosher is a pale, thermoplastic glycerol ester of gum rosin. This resin is produced from glycerin from non-animal origin a…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ester Gum

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Ester Gum
Based on current industry dynamics, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences, the market for Ester Gum in the second half of 2026 is expected to be characterized by several key trends, driven primarily by sustainability demands, performance optimization, and regulatory shifts.
1. Accelerated Shift Towards Sustainable & Bio-Based Ester Gums (Dominant Trend):
* Driver: Intensifying pressure from consumers, brands (especially in cosmetics, food, and sustainable packaging), and regulators (e.g., EU Green Deal, extended producer responsibility schemes) for reduced environmental impact and circularity.
* Manifestation: Significant growth in demand for Ester Gums derived from sustainably sourced, non-GMO rosin (e.g., from certified pine plantations) and bio-based alcohols (like bio-glycerol or bio-ethanol). Manufacturers will heavily invest in R&D to improve the yield and cost-competitiveness of bio-based routes.
* H2 2026 Focus: Leading producers will launch new “Next-Gen” bio-ester gum grades with higher bio-content (>90%) and certified low carbon footprints. Transparency in the supply chain (traceability from forest to finished product) will become a critical differentiator and marketing claim.
2. Performance Enhancement & Specialization for Niche Applications:
* Driver: Need for superior functionality in demanding applications and the pursuit of higher-value markets.
* Manifestation: Development and commercialization of Ester Gum variants with tailored properties:
* Higher Purity & Clarity: For premium cosmetics (serums, clear gels), high-end varnishes, and food-grade applications where color and haze are critical.
* Enhanced Stability: Improved heat, UV, and hydrolytic stability for applications in automotive coatings, outdoor wood finishes, and long-shelf-life products.
* Functionalization: Development of ester gums with reactive groups (e.g., acrylated ester gums) for use in radiation-curable coatings (UV/EB), enabling faster curing, lower VOC, and improved adhesion.
* H2 2026 Focus: Market leaders will segment their portfolios, offering standardized grades alongside premium, application-specific solutions commanding price premiums. Demand for technical support and co-development with customers will increase.
3. Regulatory Scrutiny & Supply Chain Resilience:
* Driver: Ongoing global regulatory reviews of food additives, cosmetic ingredients (e.g., EU SCCS opinions), and chemical safety (REACH, TSCA), coupled with geopolitical and climate-related supply chain risks.
* Manifestation:
* Compliance: Manufacturers will invest heavily in generating robust safety and toxicological data dossiers to maintain regulatory approval, particularly for food contact and cosmetic uses. Proactive engagement with regulatory bodies will be essential.
* Supply Chain: Diversification of rosin sourcing (beyond traditional Southeast Asia) and securing long-term contracts with sustainable suppliers will be a priority. Investments in regional manufacturing or tolling might increase to mitigate logistics risks and reduce carbon footprint.
* H2 2026 Focus: “Regulatory intelligence” and robust supply chain risk management will be core competencies. Traceability systems (potentially blockchain-based) will gain traction to verify sustainability and compliance claims.
4. Consolidation & Strategic Partnerships:
* Driver: Need for scale in R&D (especially for sustainable tech), global reach, and navigating complex regulatory landscapes.
* Manifestation: Increased M&A activity or strategic joint ventures between major rosin producers, chemical companies, and specialty additive suppliers. Partnerships between ester gum producers and end-users (e.g., major paint, cosmetic, or adhesive companies) for co-developing sustainable solutions will become more common.
* H2 2026 Focus: The market structure may see further consolidation, potentially leading to a more concentrated supplier base focused on integrated, sustainable solutions rather than just commodity supply.
5. Price Volatility Management:
* Driver: Fluctuations in raw material costs (pine rosin prices influenced by forestry, pulp/paper demand, weather; bio-alcohol feedstocks) and energy costs.
* Manifestation: Producers will increasingly utilize long-term contracts, hedging strategies, and pass-through mechanisms to manage volatility. The premium for sustainable/bio-based grades will persist but may narrow slightly as production scales.
* H2 2026 Focus: Transparency in pricing linked to raw material indices and sustainability premiums will be crucial for customer relationships. Cost-competitiveness of bio-based routes will be a key battleground.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The Ester Gum market in the second half of 2026 will be defined by the imperative of sustainability. Success will hinge on a producer’s ability to offer genuinely sustainable, high-performance, and compliant products backed by transparent supply chains. Innovation will focus on bio-based content, enhanced functionality, and application-specific solutions. While price and supply security remain important, the premium for verifiable sustainability and technical expertise will be the primary driver of market share and profitability. Companies failing to adapt to these trends will face significant competitive pressure.
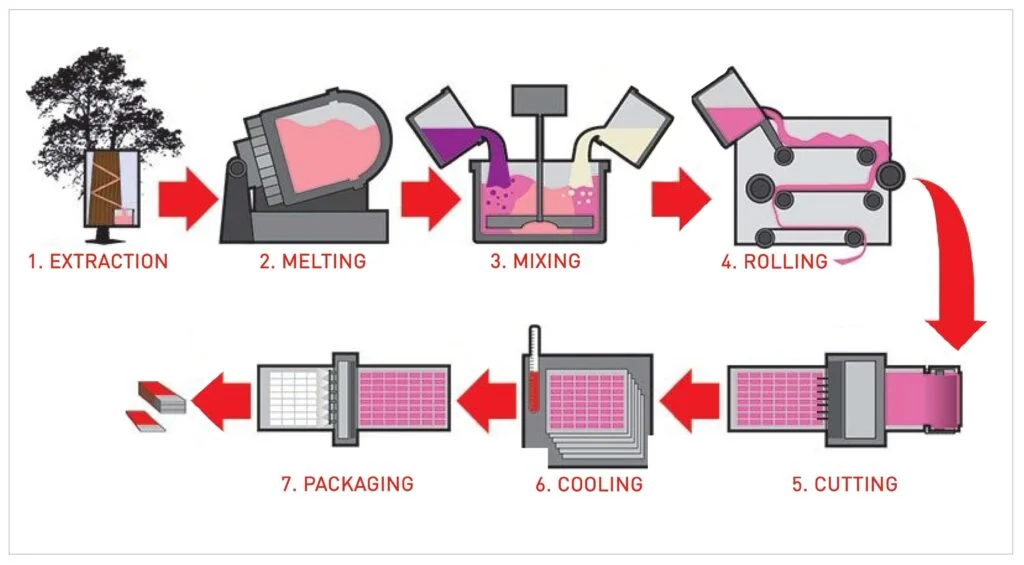
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Ester Gum (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Ester Gum—a natural resin ester used in food, pharmaceuticals, and coatings—requires careful attention to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to supply chain disruptions, regulatory non-compliance, or legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Raw Material Sourcing
Ester Gum is derived from gum rosin, which varies significantly based on the pine species, geographic origin, and harvesting methods. Sourcing from suppliers without strict raw material controls can result in batch-to-batch variability in color, odor, acid value, and ester content—compromising product performance.
2. Inadequate Specification Compliance
Many suppliers claim compliance with food-grade standards (e.g., FCC, USP, or EU regulations), but not all provide verifiable Certificates of Analysis (CoA). Relying on unverified claims risks receiving material that fails to meet required purity, heavy metal limits, or residual solvent specifications.
3. Poor Processing Controls
The esterification process must be tightly controlled to ensure consistent molecular weight, softening point, and solubility. Suppliers with outdated or inconsistent manufacturing processes may produce Ester Gum with off-spec properties, especially regarding clarity in solution or thermal stability.
4. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Without full traceability from forest to finished product, it becomes difficult to verify sustainability practices, allergen-free status, or GMO compliance—critical for food and pharmaceutical applications. Missing or incomplete documentation increases regulatory and reputational risks.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unlicensed Use of Patented Formulations or Processes
Some advanced grades of Ester Gum (e.g., hydrogenated or modified variants) are protected by patents. Sourcing such materials from unauthorized suppliers—or using them in ways that infringe on method-of-use patents—can expose the buyer to legal action, especially in regulated industries.
2. Misrepresentation of Origin or Technology
Suppliers may falsely claim proprietary manufacturing techniques or origin (e.g., “sustainably harvested” or “patent-pending process”) without proper documentation. This can mislead buyers into assuming unique performance benefits or legal safety that do not exist, leading to IP exposure or marketing claims disputes.
3. Inadequate Supplier IP Due Diligence
Failing to assess whether a supplier owns or has licensed rights to the Ester Gum they provide can result in downstream infringement. This is particularly relevant when sourcing from third-party manufacturers or toll processors who may not have full IP clearance.
4. Ambiguous Contractual Terms on IP Ownership
When custom modifications or private labeling are involved, contracts that don’t clearly define IP ownership (e.g., formulations, process improvements) can lead to disputes. Buyers may lose rights to innovations or face restrictions on usage and resale.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Require comprehensive CoAs and conduct independent batch testing.
- Audit supplier facilities for GMP, traceability, and process controls.
- Verify regulatory compliance with relevant pharmacopoeias or food safety standards.
- Conduct IP landscape reviews before sourcing specialty grades.
- Include clear IP indemnification clauses in supply agreements.
- Prioritize suppliers with transparent sourcing and documented IP rights.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, companies can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally secure sourcing of Ester Gum.
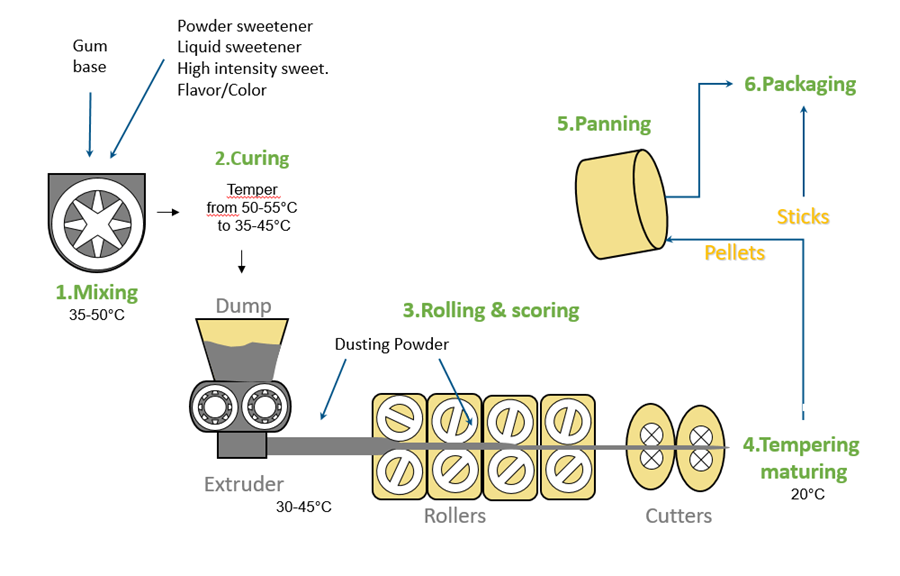
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ester Gum
Overview of Ester Gum
Ester Gum, also known as glyceryl ester of wood rosin or glyceryl abietate, is a modified rosin used in food, cosmetics, and industrial applications. It functions primarily as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and solubilizer, particularly in flavor formulations for beverages. Proper logistics and regulatory compliance are essential due to its use in consumer products and international trade.
Regulatory Classification and Status
Ester Gum is regulated differently depending on the region and application. Key regulatory considerations include:
- Food Use (FDA): Listed in the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations (21 CFR 172.808) as an indirect food additive and permitted for use in food contact adhesives. When used in food, it must comply with specifications outlined in the Food Chemicals Codex (FCC).
- GRAS Status: Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) for specific uses, particularly in flavoring agents under certain conditions.
- EU Regulations: Approved as a food additive (E445) under Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008. Must meet purity criteria defined in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012.
- REACH (EU): Registered under REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) for industrial uses. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) must be compliant with EU REACH requirements.
- Cosmetics (EU & US): Permitted in cosmetic products under both EU Cosmetic Regulation 1223/2009 and FDA guidelines, provided it meets purity standards.
- Other Regions: Check local regulations in countries such as Canada (Health Canada), Australia (FSANZ), Japan (MHLW), and China (NHC) for specific import and usage requirements.
Packaging and Storage Requirements
Proper packaging and storage are critical to maintain quality and ensure safety:
- Packaging: Typically supplied in food-grade polyethylene-lined multi-wall paper bags, drums, or bulk containers. Ensure packaging is sealed to prevent moisture absorption and contamination.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Ideal storage temperature: 15–25°C (59–77°F).
- Shelf Life: Generally 12–24 months when stored properly. Monitor for signs of discoloration or clumping.
- Hygroscopic Nature: Ester Gum can absorb moisture; use desiccants if necessary and avoid humidity exposure.
Transportation and Shipping Guidelines
Ester Gum is generally non-hazardous but requires careful handling during transport:
- Classification: Not classified as hazardous under DOT (49 CFR), IMDG, or ADR regulations. However, verify current SDS for any updates.
- Load Securing: Ensure containers are stacked securely to prevent crushing or leakage.
- Temperature Control: Avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures (>40°C) during transit, which may cause softening or melting.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of analysis (CoA), and SDS. For food-grade shipments, provide a statement of compliance (e.g., FDA 21 CFR or EU Food Contact compliance).
- Import/Export Requirements:
- Certificates: May require phytosanitary certificate (for plant-derived rosin) or certificate of free sale depending on destination.
- Customs Codes: HS Code typically 3806.10 (Rosin and resin acids, esters). Confirm with local customs authority.
- Labeling: Packages must be labeled with product name, batch number, net weight, manufacturer details, and applicable regulatory statements (e.g., “For Food Use” or “Not for Human Consumption” if industrial grade).
Safety and Handling Procedures
Ensure workplace safety during handling and processing:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use gloves, safety goggles, and dust masks when handling powder form to avoid skin/eye irritation or inhalation.
- Ventilation: Use local exhaust ventilation in areas where dust is generated.
- Spill Management: Collect spillage carefully; avoid creating dust. Dispose of waste in accordance with local regulations.
- First Aid Measures: Refer to SDS for specific instructions in case of exposure.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Maintain traceability and compliance through rigorous quality controls:
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): Must include assay, acid value, color, odor, specific gravity, and conformance to FCC or EU specifications.
- Batch Traceability: Implement a system to track raw materials and finished batches.
- Supplier Qualification: Source only from certified suppliers with GMP, ISO 9001, or FSSC 22000 certification when applicable.
Disposal and Environmental Considerations
Dispose of Ester Gum and packaging in compliance with local environmental regulations:
- Waste Classification: Not classified as hazardous waste under RCRA or EU Waste Framework Directive, but confirm locally.
- Disposal Method: Can typically be disposed of in landfill or incinerated in permitted facilities. Avoid release into waterways.
- Sustainability: Consider biodegradability and environmental impact; Ester Gum is derived from renewable pine tree resin.
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure safe and compliant logistics for Ester Gum:
– Confirm regulatory status in target markets.
– Use appropriate food-grade or industrial-grade packaging.
– Maintain temperature and humidity control during storage and transport.
– Provide complete and accurate documentation for customs and quality audits.
– Train personnel on safe handling procedures and emergency response.
Always consult the most recent Safety Data Sheet and regulatory updates from authorities such as FDA, EFSA, and ECHA to ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Ester Gum
In conclusion, sourcing ester gum requires a strategic approach that balances quality, compliance, cost-efficiency, and supply chain reliability. As a key ingredient in food, beverage, and fragrance industries—particularly as an emulsifier and clouding agent in flavored beverages—ensuring the ester gum meets regulatory standards (such as FDA, FEMA, or EU specifications) is critical.
Potential suppliers should be carefully vetted for certifications (e.g., ISO, GMP, Kosher, Halal), consistent product quality, and traceability. Additionally, factors such as pricing stability, minimum order quantities, lead times, and geographic location play a significant role in determining the overall feasibility of a long-term partnership.
Given potential supply chain disruptions and fluctuating raw material costs, establishing relationships with multiple qualified suppliers can enhance resilience. Furthermore, ongoing communication and quality assurance testing are essential to maintain product consistency and compliance.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of ester gum hinges on thorough due diligence, strong supplier collaboration, and a focus on sustainability and regulatory adherence to support product safety and market competitiveness.