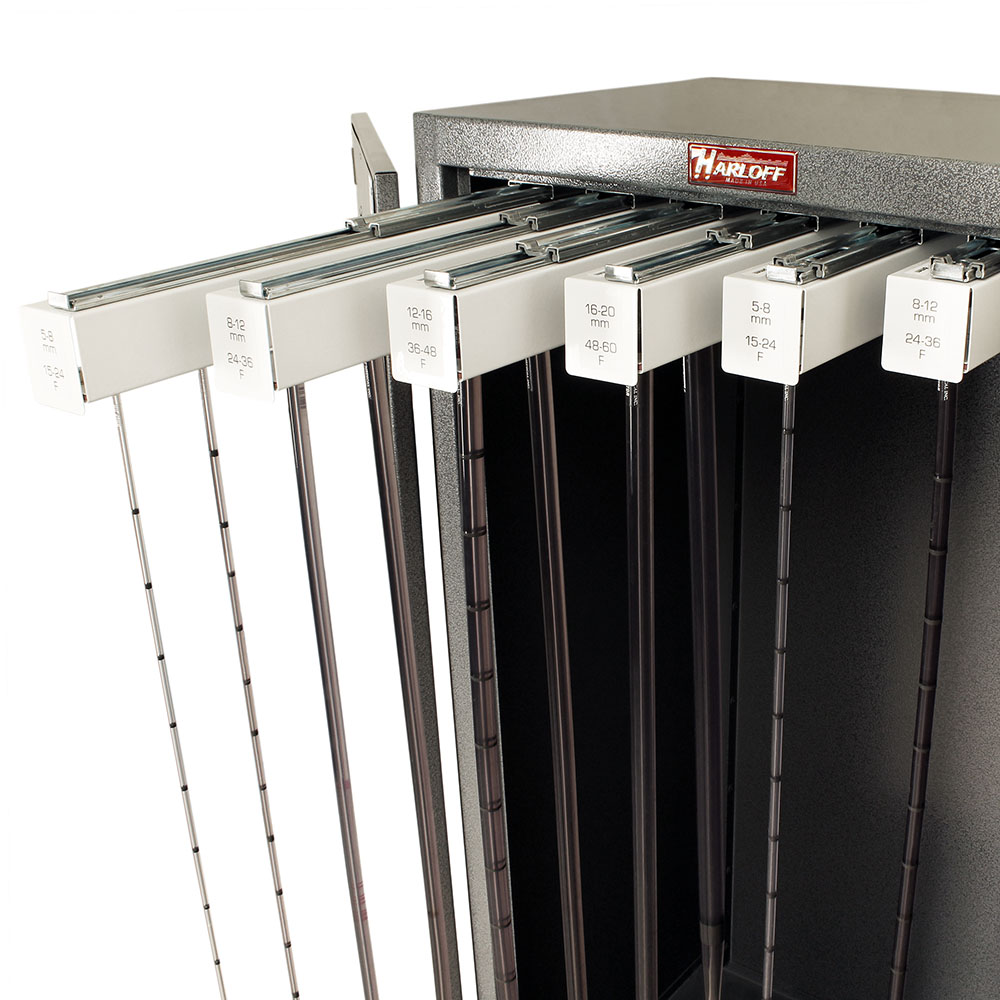
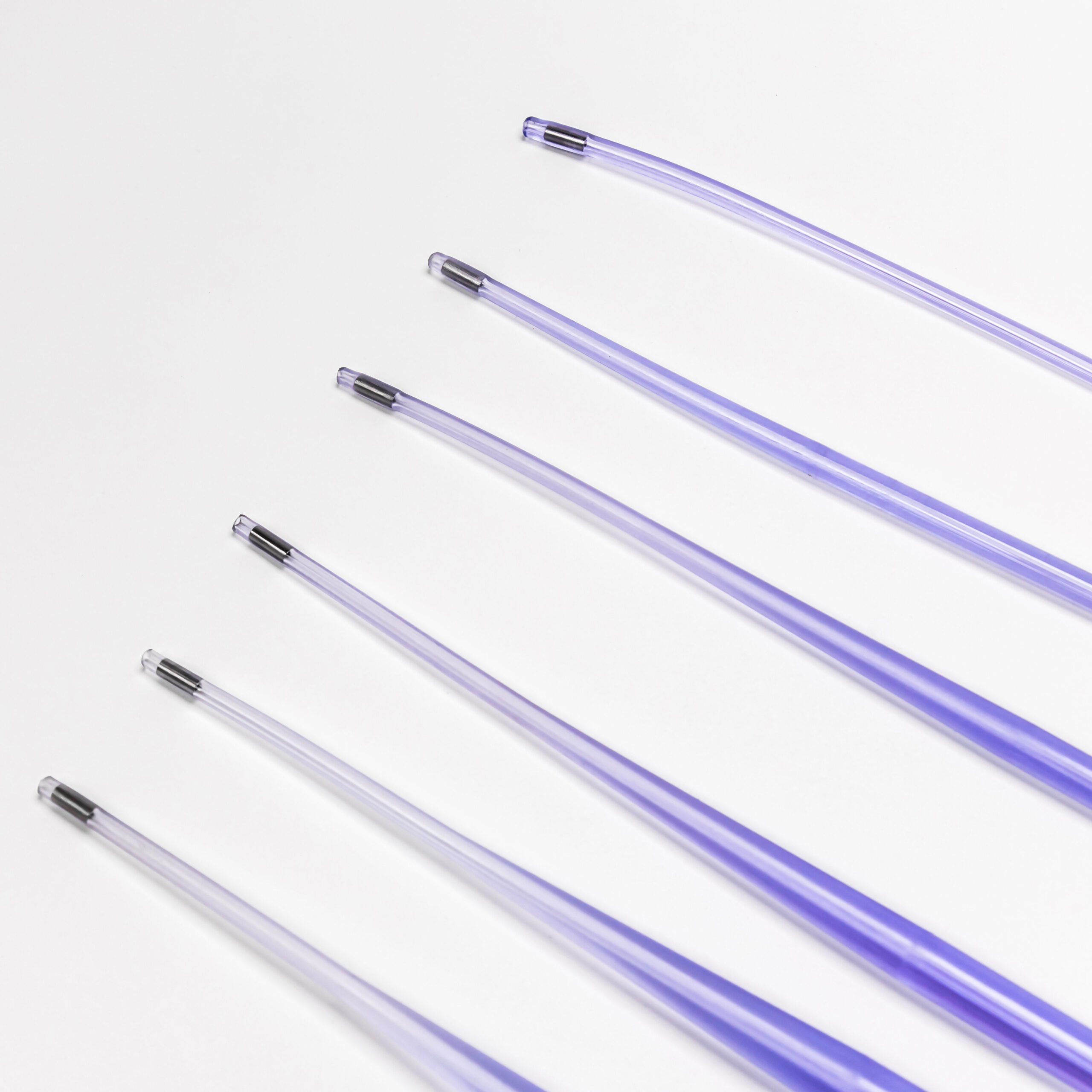
The global esophageal dilator market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing prevalence of esophageal disorders such as strictures, achalasia, and eosinophilic esophagitis. According to Grand View Research, the global market for gastrointestinal devices was valued at USD 4.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030, with minimally invasive therapeutic devices like esophageal dilators contributing significantly to this expansion. Additionally, rising geriatric populations, growing adoption of endoscopic procedures, and technological advancements in dilation systems—such as hydrostatic balloon and bougie dilators—are accelerating demand. As healthcare providers prioritize safe and effective interventions for dysphagia and related conditions, innovation and reliability in device performance have become critical differentiators among manufacturers. In this evolving landscape, a select group of companies are leading the way in product development, regulatory compliance, and global market penetration—setting the benchmark for quality and clinical efficacy in esophageal dilation solutions.
Top 5 Esophageal Dilators Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Esophageal Dilation
Domain Est. 1995
Website: pro.boehringer-ingelheim.com
Key Highlights: Review how esophageal dilation is important to take note of on high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) in patients with connective tissue disease….
#2 Esophageal Dilator Set
Domain Est. 2003
Website: cookmedical.com
Key Highlights: Used for placement of an esophageal bougie or stent during laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair. This product line is serviced by the following clinical division(s):….
#3 Esophageal Dilation
Domain Est. 2016
Website: diversatekhealthcare.com
Key Highlights: SafeGuide® Single OTW Esophageal Dilators A disposable dilator featuring both American and European depth markings to support more precise placement….
#4 GIE Medical
Domain Est. 2018
Website: giemedical.com
Key Highlights: GIE Medical is a clinical stage company conducting trials in the US helping patients who suffer from benign stricture(s) of the esophagus, bowel….
#5 CleanGuide Esophageal Dilators
Domain Est. 1995
Website: conmed.com
Key Highlights: CleanGuide Dilators provide a sterile-packed, disposable solution for rigid, over-the-wire esophageal dilation, eliminating the work and costs associated ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Esophageal Dilators

H2: Market Trends for Esophageal Dilators in 2026
The global market for esophageal dilators is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing prevalence of esophageal disorders, technological advancements in endoscopic devices, and rising geriatric populations. Key trends shaping the industry include a shift toward minimally invasive procedures, integration of smart technologies, and geographic expansion in emerging economies.
One major trend is the growing adoption of hydrostatic balloon dilators and through-the-scope (TTS) systems due to their precision, safety, and compatibility with standard endoscopes. These devices are increasingly preferred over traditional bougie dilators, particularly in ambulatory surgical centers and outpatient clinics. The demand for single-use, sterile esophageal dilators is also rising, fueled by concerns over cross-contamination and healthcare-associated infections.
Another significant development is the integration of real-time monitoring and pressure-sensing technologies in dilator systems. These innovations enhance procedural safety by enabling clinicians to monitor dilation force and tissue response, reducing the risk of perforation. Companies are investing in R&D to develop smart dilators with feedback mechanisms, aligning with broader trends in digital health and connected medical devices.
Regionally, North America dominates the market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure and high diagnosis rates of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and esophageal strictures. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, supported by rising healthcare expenditure, expanding endoscopy services, and increasing awareness of gastrointestinal disorders.
In addition, regulatory support and favorable reimbursement policies in developed markets are facilitating wider adoption. Key players are focusing on strategic partnerships, product innovations, and geographic diversification to strengthen their market position. Overall, the 2026 landscape for esophageal dilators reflects a convergence of clinical need, technological innovation, and market expansion, positioning the sector for sustained growth.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Esophageal Dilators: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Sourcing esophageal dilators from manufacturers lacking adherence to recognized quality management systems (e.g., ISO 13485) can result in inconsistent product performance. Variability in materials, dimensions, or surface finish may compromise patient safety and lead to complications such as mucosal injury or perforation.
Substandard Materials and Biocompatibility
Using non-medical-grade materials or failing to validate biocompatibility (per ISO 10993) increases the risk of adverse reactions, including irritation, inflammation, or allergic responses. Some suppliers may cut costs by using inferior polymers or coatings, which can degrade prematurely during clinical use.
Inadequate Sterility Assurance
Improper sterilization processes or packaging compromises sterility, posing significant infection risks. Suppliers may lack validated sterilization methods (e.g., ethylene oxide or gamma irradiation) or fail to maintain sterile integrity during transport and storage.
Lack of Regulatory Compliance
Dilators sourced from non-compliant manufacturers may not meet essential regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA 510(k), CE marking under MDR). This can result in product recalls, legal liabilities, and market access restrictions.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Infringement of Patented Designs
Many esophageal dilators incorporate patented technologies, such as specific balloon inflation mechanisms, tapered tip designs, or guidewire compatibility features. Sourcing unlicensed copies risks patent infringement lawsuits, leading to financial penalties and supply chain disruptions.
Counterfeit or Unbranded Products
Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or low-cost suppliers increases exposure to counterfeit devices that mimic branded products. These may lack proper IP licensing and often fail to meet safety and performance standards.
Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When working with contract manufacturers on custom dilator designs, failure to establish clear IP ownership in contracts can result in disputes. Suppliers may retain rights to design improvements, limiting exclusivity and future commercialization.
Insufficient Due Diligence on Supplier IP
Failing to verify a supplier’s IP licenses or freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis leaves buyers vulnerable to third-party claims. Conducting IP audits and requesting documentation is essential to mitigate legal and commercial risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Esophageal Dilators
This guide outlines key considerations for the logistics and regulatory compliance associated with the distribution, handling, and use of esophageal dilators—medical devices used to treat esophageal strictures and other narrowing conditions.
Regulatory Classification and Approvals
Esophageal dilators are typically classified as medical devices, often falling under Class II in the United States (regulated by the FDA) and Class IIa or IIb in the European Union (regulated under the Medical Device Regulation, MDR). Before distribution, manufacturers and distributors must ensure:
- FDA 510(k) clearance or premarket approval (PMA), as applicable, is obtained.
- CE marking is affixed, indicating conformity with EU MDR requirements for devices sold in Europe.
- Local regulatory approvals are secured for other target markets (e.g., Health Canada, TGA in Australia, PMDA in Japan).
All documentation, including technical files, declarations of conformity, and certificates, must be current and available for audit.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
Proper labeling and packaging are critical for compliance and safe use:
- Labels must include the device name, model/lot numbers, expiration date (if applicable), sterile status, single-use designation (if applicable), and manufacturer details.
- Symbols per ISO 15223-1 (e.g., sterile, single-use, latex-free) must be correctly used.
- Packaging must maintain sterility during transit and storage. Tamper-evident and protective packaging is required.
- Instructions for Use (IFU) must be included in all required languages and conform to regulatory standards (e.g., FDA’s labeling requirements, EU MDR Annex I).
Storage and Handling
To preserve device integrity:
- Store esophageal dilators in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment per manufacturer specifications (typically 15–30°C).
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
- Maintain a segregated area for medical devices to prevent contamination or damage.
- Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize expiration risks.
Transportation and Distribution
Logistics partners must comply with medical device transport standards:
- Use validated transport methods to maintain storage conditions (e.g., temperature monitoring for sensitive components).
- Ensure packaging is designed to withstand shocks, vibrations, and pressure changes during shipping.
- Distributors and couriers must be ISO 13485-compliant or equivalent where applicable.
- Track and trace systems should be in place to support recalls and inventory management.
Import/Export Compliance
International shipments require adherence to:
- Customs documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Export licenses, if required by the destination country.
- Compliance with import regulations (e.g., FDA prior notice for U.S. imports, EU Authorized Representative requirements).
- Adherence to international shipping regulations for medical devices (e.g., IATA guidelines for air transport).
Post-Market Surveillance and Vigilance Reporting
Ongoing compliance requires proactive monitoring:
- Manufacturers must establish a post-market surveillance (PMS) system to collect and analyze device performance data.
- Report adverse events and field safety corrective actions (FSCAs) to relevant authorities (e.g., FDA MAUDE database, EUDAMED in the EU) per mandatory timelines.
- Maintain complaint handling procedures and conduct root cause analyses when necessary.
Quality Management System (QMS)
All entities in the supply chain should implement a QMS compliant with ISO 13485:
- Document control, risk management (per ISO 14971), and internal audits are required.
- Supplier audits and controls ensure third-party compliance.
- Training programs for staff on regulatory requirements and device handling.
Single-Use and Reuse Policies
Most esophageal dilators are labeled for single use. Reuse is prohibited unless reprocessing instructions are validated and cleared by regulatory bodies. Distributors and healthcare providers must adhere strictly to labeling to avoid compliance violations and patient safety risks.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Dispose of used esophageal dilators according to biohazard and medical waste regulations:
- Follow local, national, and international guidelines (e.g., OSHA, EPA, EU directives) for sharps and contaminated device disposal.
- Provide disposal instructions in the IFU when relevant.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance framework, stakeholders can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient distribution of esophageal dilators while maintaining patient safety and regulatory alignment.
In conclusion, sourcing esophageal dilators requires careful consideration of clinical needs, regulatory compliance, product quality, and supplier reliability. It is essential to select dilators that meet medical standards—such as those set by the FDA or CE marking—ensuring patient safety and procedural efficacy. Factors such as material quality, dilation method (e.g., bougie, balloon, or guidewire-controlled), and compatibility with endoscopic procedures should align with the healthcare facility’s practices. Engaging with reputable suppliers, evaluating cost-effectiveness without compromising on safety, and establishing long-term vendor relationships contribute to a sustainable and efficient supply chain. Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy for esophageal dilators supports optimal patient outcomes and enhances the overall performance of gastrointestinal care services.