The global epoxy resin market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across industrial and consumer applications, including high-performance knife handle manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global epoxy resin market was valued at USD 9.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by epoxy’s superior durability, chemical resistance, and aesthetic versatility—qualities that make it a preferred material for premium knife handles. As the cutlery market increasingly embraces composite and synthetic handle materials for both functional and visual appeal, manufacturers specializing in epoxy resin handles are gaining prominence. Based on production scale, design innovation, material quality, and customer reviews, the following seven manufacturers have emerged as leaders in supplying high-performance epoxy resin knife handles worldwide.
Top 7 Epoxy Resin Knife Handle Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
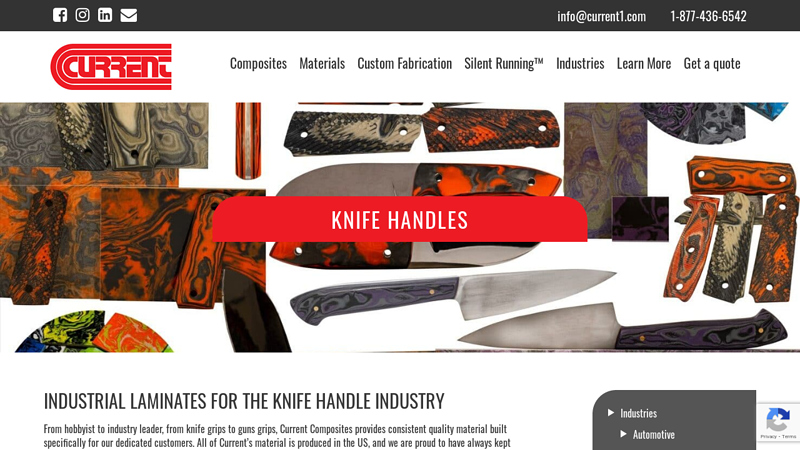
#1 Industrial Laminates for the Knife Handle Industry
Domain Est. 1996
Website: currentcomposites.com
Key Highlights: All our knife material is hand-laid with trusted quality glass fiber and epoxy resin, built specifically to produce a wear resistant, comfortable, and ……
#2 Blade Pro
Domain Est. 1996
#3 Unique Resins
Domain Est. 1998
#4 Resin Casting for Knife Making
Domain Est. 2016
#5 Epoxy for Knife Handles
Domain Est. 2021
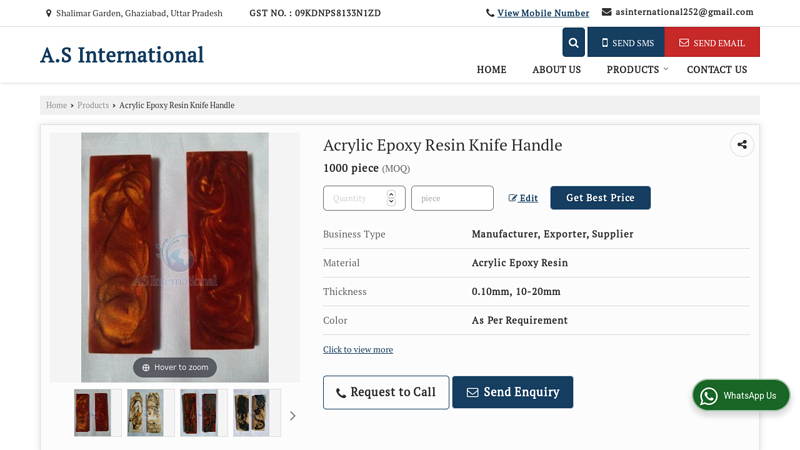
#6 Acrylic Epoxy Resin Knife Handle
Domain Est. 2023
Website: as-international.co.in
Key Highlights: Acrylic Epoxy Resin Knife Handle ; Color, As Per Requirement ; Finishing. Polished ; Feature. Sturdiness, Rust Proof, Perfect Strength, Fine Finished, Durable….
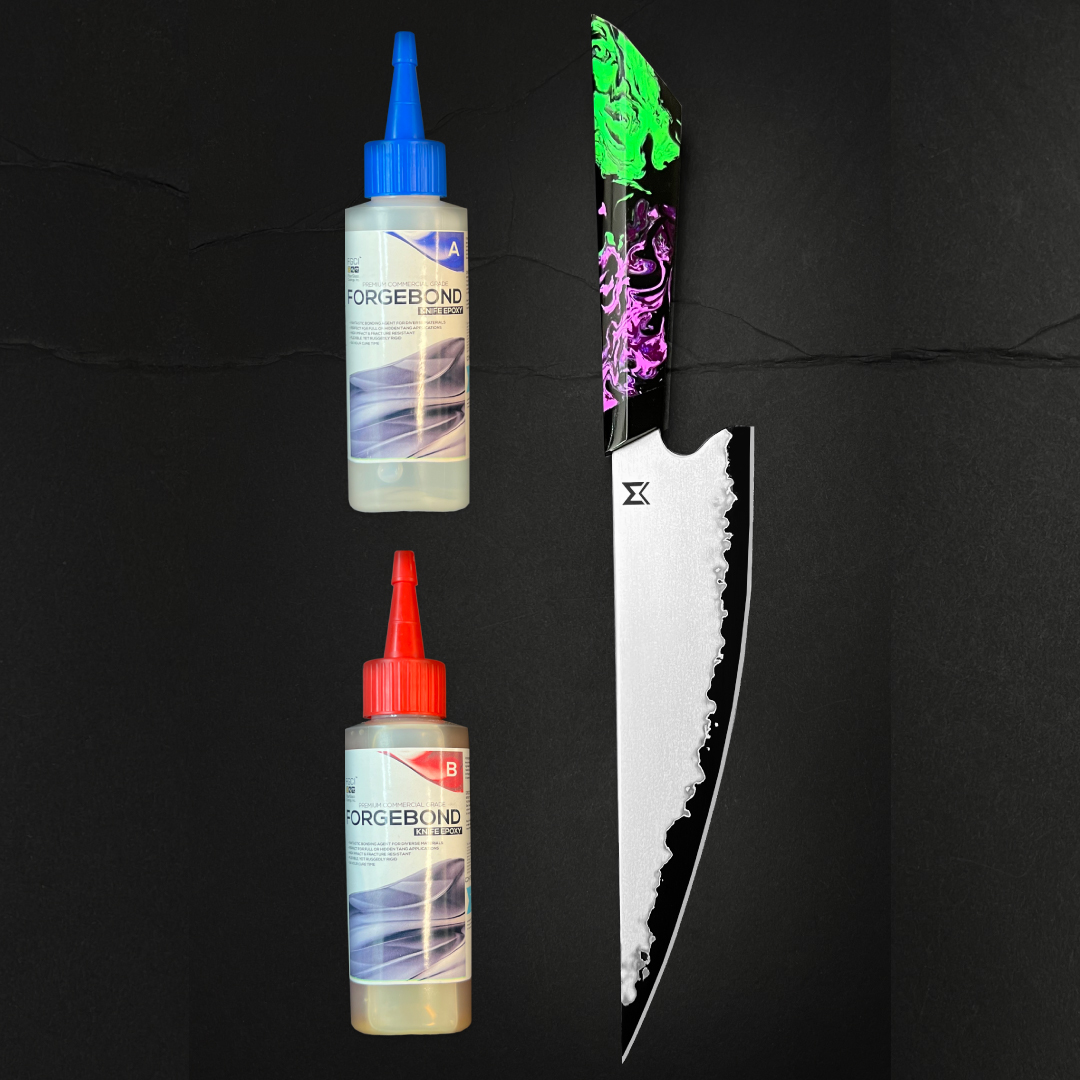
#7 Best Epoxy for Knife Handles
Domain Est. 2019
Website: superepoxysystems.com
Key Highlights: Forgebond Knife Epoxy is the best choice for knife handle applications. Its high-strength bonding capabilities, flexibility, ease of use, and quick cure time…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Epoxy Resin Knife Handle

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Epoxy Resin Knife Handles
The epoxy resin knife handle market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in materials, growing consumer demand for customization, and sustainability concerns. Here’s an in-depth analysis of key trends shaping the industry:
-
Rising Demand for Customization and Aesthetic Appeal
By 2026, personalization will remain a dominant driver in the knife industry. Epoxy resin offers unmatched versatility in color, transparency, and inclusion options (e.g., metallic flakes, wood particles, or glow powders), making it a preferred choice for artisanal and custom knife makers. Consumers increasingly seek unique, handcrafted pieces, and epoxy resin enables bold, one-of-a-kind designs that appeal to collectors and outdoor enthusiasts alike. -
Expansion in DIY and Knife-Making Communities
Online platforms and social media have fueled the growth of DIY knife-making communities. By 2026, the accessibility of epoxy resin kits, molds, and tutorials will further democratize the craft, increasing demand for high-quality, user-friendly epoxy formulations. This grassroots growth will boost market volume, particularly in North America and Europe. -
Improvements in Material Technology
Innovations in epoxy resin formulations—such as enhanced UV resistance, reduced shrinkage, and improved thermal stability—are expected by 2026. These advancements will address previous concerns about durability and yellowing over time, making epoxy more competitive with traditional handle materials like G10 or micarta. Hybrid materials combining epoxy with natural elements (e.g., stabilized wood or composite fibers) may gain traction. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Alternatives
Environmental awareness is reshaping material preferences. While traditional epoxy resins are petroleum-based, the market will see increased demand for bio-based or partially renewable epoxy alternatives. By 2026, manufacturers offering low-VOC, non-toxic, or recyclable resin options are likely to gain a competitive edge, especially in environmentally conscious markets. -
Growth in Premium and Tactical Knife Segments
The premium knife market, including custom tactical and survival knives, is expanding. Epoxy resin’s ability to deliver both ruggedness and visual appeal makes it ideal for high-end applications. Tactical gear enthusiasts value the material’s resistance to moisture and shock, and by 2026, expect to see more collaborations between resin suppliers and tactical knife brands. -
Regional Market Developments
North America and Europe will continue leading in market demand due to strong artisanal knife-making cultures. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific—particularly China and India—may see accelerated growth as local craftsmanship gains international recognition and domestic middle-class consumers adopt premium outdoor and kitchen tools.
In summary, the 2026 epoxy resin knife handle market will be shaped by innovation, personalization, and sustainability. As performance barriers diminish and creative possibilities expand, epoxy resin is expected to solidify its position as a mainstream, high-value material in the knife handle industry.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Epoxy Resin Knife Handles (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing epoxy resin knife handles, whether for in-house manufacturing or private labeling, presents several potential pitfalls—particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these challenges helps mitigate risks and ensures a reliable, legally sound supply chain.
Quality Inconsistencies and Material Deficiencies
One of the most frequent issues is inconsistent product quality. Epoxy resin is sensitive to formulation, mixing ratios, curing conditions, and environmental factors. Suppliers, especially lower-cost or less experienced ones, may use substandard resins, incorrect hardeners, or poor mixing practices, leading to brittle, discolored, or poorly cured handles. Bubbles, cracks, or delamination after curing not only affect aesthetics but also compromise structural integrity and user safety. Furthermore, variations in pigment dispersion or filler integration can result in mismatched colors or textures across batches, undermining brand consistency.
Lack of Durability and Performance Testing
Many sourced epoxy handles fail under real-world conditions due to inadequate testing. Reputable manufacturers conduct tests for water resistance, UV stability, impact strength, and thermal endurance. Without proper validation, handles may yellow, crack, or degrade when exposed to moisture, sunlight, or temperature fluctuations—common hazards in kitchen or outdoor environments. Buyers often overlook requesting test reports or samples subjected to stress conditions, increasing the risk of field failures and customer complaints.
Mold Quality and Dimensional Accuracy
The precision of molds directly impacts the final product. Poorly made or worn molds can cause dimensional inaccuracies, flash lines, or surface defects, requiring extensive post-processing. If molds are not properly maintained or designed with proper draft angles and venting, it results in incomplete fills or trapped air. Sourcing from suppliers without strict mold control processes leads to inconsistent handle shapes, making them incompatible with knife blades or assembly lines.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Using or replicating existing epoxy handle designs—especially those with unique patterns, embedded materials, or artistic inlays—can pose serious IP risks. Many visually striking resin patterns (e.g., “river,” “galaxy,” or branded color swirls) are protected by design patents, copyrights, or trademarks. Sourcing handles that mimic these without authorization can lead to cease-and-desist letters, product seizures, or legal liability. Additionally, if a supplier uses a design you provide, unclear contractual terms may result in disputes over ownership of molds or design files.
Inadequate IP Protection in Supplier Agreements
Even when developing custom designs, failure to secure robust IP clauses in supplier contracts is a major oversight. Without explicit assignment of IP rights, the supplier may retain ownership of molds, digital designs, or production methods. This limits exclusivity and enables the supplier to sell similar designs to competitors. Always ensure contracts include confidentiality provisions, IP ownership transfer, and restrictions on third-party production to safeguard your investment and market differentiation.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers—request material certifications, quality control procedures, and performance test data. Invest in custom tooling and legally binding agreements that clearly define IP ownership and usage rights. Prototyping and batch sampling under real-use conditions are essential steps before full-scale production. By addressing quality and IP concerns proactively, you can ensure durable, unique, and legally compliant epoxy resin knife handles that enhance your product offering.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Epoxy Resin Knife Handles
Product Classification & Regulatory Framework
Epoxy resin knife handles fall under a dual regulatory scope: as a component of a knife (a tool/weapon) and as a chemical product (the cured epoxy resin). Understanding both aspects is critical for compliance.
Harmonized System (HS) Code Determination
The applicable HS code depends on the stage of the product:
– Unassembled Components (epoxy resin + blank handle): Typically classified under Chapter 39 (Plastics and Articles Thereof). A common code may be 3926.30 – “Articles of plastics, for the conveyance or packing of goods”.
– Assembled Knife Handle (as part of a knife): Falls under Chapter 82 (Tools, Cutlery, and General Hardware), likely 8211.92 – “Blades for knives, knife blades, other”.
Accurate classification affects duties, tariffs, and import/export controls. Always verify with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker.
Chemical Compliance (Pre- and Post-Cure)
Uncured epoxy resin is regulated as a chemical substance:
– REACH (EU): Registrants must ensure epoxy components are registered under REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals). Suppliers must provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) compliant with Annex II.
– TSCA (USA): Confirm all chemical substances comply with the Toxic Substances Control Act. Manufacturers/importers must verify substances are listed on the TSCA Inventory.
– GHS Compliance: Label all epoxy resin shipments with GHS-compliant hazard pictograms, signal words (e.g., “Danger”), and precautionary statements. SDS must follow GHS formatting.
Cured epoxy resin is generally inert and non-regulated, but documentation of resin compliance must be retained.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Hazardous Material Classification
Uncured epoxy resin is often classified as:
– UN 1866, Class 3 Flammable Liquid, if volatile organic content (VOC) exceeds thresholds.
– UN 3082, Class 9 Environmentally Hazardous Substance, if ecotoxicological data indicates risk.
Shipping as hazardous material requires:
– UN-certified packaging (e.g., combination packaging with inner containers and outer fiberboard drum).
– Proper hazard labels (Class 3 flammable liquid label, Class 9 miscellaneous label if applicable).
– Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (for air freight under IATA DGR).
– Training certification for personnel preparing shipments (IATA/IMDG/49 CFR as applicable).
Non-Hazardous Shipment (Cured Resin or Finished Handles)
Once fully cured, epoxy resin is typically non-hazardous. Packaging should still:
– Prevent mechanical damage (use bubble wrap, foam inserts).
– Use moisture-resistant outer packaging.
– Clearly label contents and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile – Knife Handle Component”).
Shipping Modes & Restrictions
– Air Freight: Strict rules for flammable liquids. Even small quantities may require full dangerous goods handling.
– Ocean Freight (IMDG): Requires proper container stowage, segregation from incompatible goods (e.g., oxidizers).
– Ground (49 CFR in USA): Segregation, placarding, and documentation based on quantity and classification.
Import/Export Documentation
Essential documents include:
– Commercial Invoice: Must detail product description, value, HS code, country of origin, and Incoterms® (e.g., FOB, DDP).
– Packing List: Itemizes contents per package (weight, dimensions, quantity).
– Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): Contract of carriage.
– Certificate of Origin: Required for tariff preference (e.g., under USMCA, EU trade agreements).
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Mandatory for uncured resin shipments.
– Dangerous Goods Note (DGN): If shipping hazardous materials.
For resin imports, retain supplier compliance documents (REACH registration numbers, TSCA certification).
Labeling & Marking Compliance
Product Labels
– Finished handles or kits must include:
– Manufacturer/importer name and address.
– Batch/lot number.
– GHS-compliant warning labels (for kits including uncured resin).
– Handling instructions (e.g., “Use in well-ventilated area”, “Wear protective gloves”).
Packaging Markings
– UN certification marks (if shipping hazardous).
– Orientation arrows (“This Way Up”).
– Gross/net weight.
– Proper shipping name and UN number (e.g., “EPOXY RESIN, FLAMMABLE LIQUID, N.O.S., UN 1866, Class 3”).
Environmental & Safety Considerations
Waste Disposal & Lifecycle
– Uncured resin waste is hazardous. Dispose of according to local regulations (e.g., EPA in USA, WEEE/CLP in EU).
– Provide end-user guidance: Cured resin is safe, but sanding dust should be collected (respiratory protection advised).
Workplace Safety (Manufacturing)
– Comply with OSHA (USA) or equivalent (e.g., COSHH in UK) for handling resins.
– Provide PPE: Nitrile gloves, respirators with organic vapor cartridges, eye protection.
– Implement ventilation systems (local exhaust).
Risk Mitigation & Best Practices
- Supplier Vetting: Ensure resin suppliers provide full regulatory documentation (SDS, compliance certificates).
- Testing: Conduct migration testing (if applicable) to confirm cured resin is food-safe (e.g., for kitchen knives—note: epoxy is generally not food-contact approved).
- Insurance: Secure cargo and product liability insurance covering chemical and product risks.
- Consult Experts: Engage a regulatory compliance consultant or freight forwarder experienced in chemical logistics.
Adhering to this guide ensures legal compliance, minimizes shipment delays, and enhances supply chain safety and reliability.
In conclusion, sourcing epoxy resin for knife handles requires careful consideration of quality, durability, ease of use, and aesthetic potential. High-quality, UV-resistant, and food-safe epoxy resins ensure long-lasting, visually appealing, and functional knife handles that can withstand everyday use and environmental exposure. It is essential to source materials from reputable suppliers who provide consistent product specifications and safety data. Additionally, evaluating cost-effectiveness and availability helps maintain efficiency in production, whether for commercial manufacturing or artisanal craftsmanship. Ultimately, selecting the right epoxy resin enhances both the performance and visual appeal of knife handles, contributing to a superior end product.