The global electric piston actuator (EPB) market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing automation across industrial, energy, and infrastructure sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global electric actuator market was valued at USD 7.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising demand for precision control, energy efficiency, and integration with smart control systems in industrial processes. As industries prioritize reliability and low maintenance in valve automation, EPB actuators—known for their durability and accurate positioning—are becoming a preferred solution. With market dynamics shaped by technological advancements and regional industrialization trends, identifying leading manufacturers is critical for engineers, procurement teams, and system integrators. Based on market presence, innovation, product range, and global reach, the following nine companies emerge as key players shaping the future of EPB actuator technology.
Top 9 Epb Actuator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 EPB
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: The electronic parking brake replaces the conventional mechanical lever and cable and will provide better assistance to the driver….
#2 Electric Park Brake (EPB)
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zf.com
Key Highlights: Leading market technology with more than 250 million EPB calipers on world roadways. Suited for front and rear wheel applications….
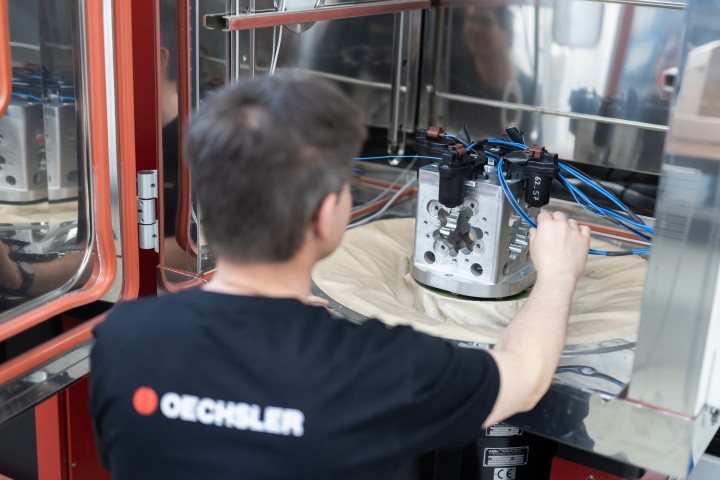
#3 OECHSLER’s Electric Parking Brake
Domain Est. 2015
Website: oechsler-motion.com
Key Highlights: OECHSLER started developing in the field of actuator technology as early as 1995. The EPB itself was developed from 1997 together with a leading supplier for ……
#4 ADVICS Expands Product Lines with Launch of New Electric …
Domain Est. 2018
Website: advicsaftermarket.com
Key Highlights: ADVICS, the leader in advanced braking technology, is expanding its brake system product offerings by adding new EPB actuator kits….
#5 Custom Motors for Automotive Electric Parking Brake
Domain Est. 1996
Website: johnsonelectric.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery5% higher stall torque for high braking force; 60% longer life cycle for frequent operation; 3dBA lower noise and better sound quality ……
#6 Electric parking brake
Domain Est. 1999
Website: infineon.com
Key Highlights: EPB systems are more convenient to use than traditional mechanical parking brakes. They can be engaged and disengaged with the push of a button, rather than ……
#7 Parking Brake Actuators
Domain Est. 2000
Website: standardbrand.com
Key Highlights: This new and growing category is also entirely powertrain-neutral, meaning parking brake actuators are found on gasoline, diesel, hybrid, and electric vehicles….
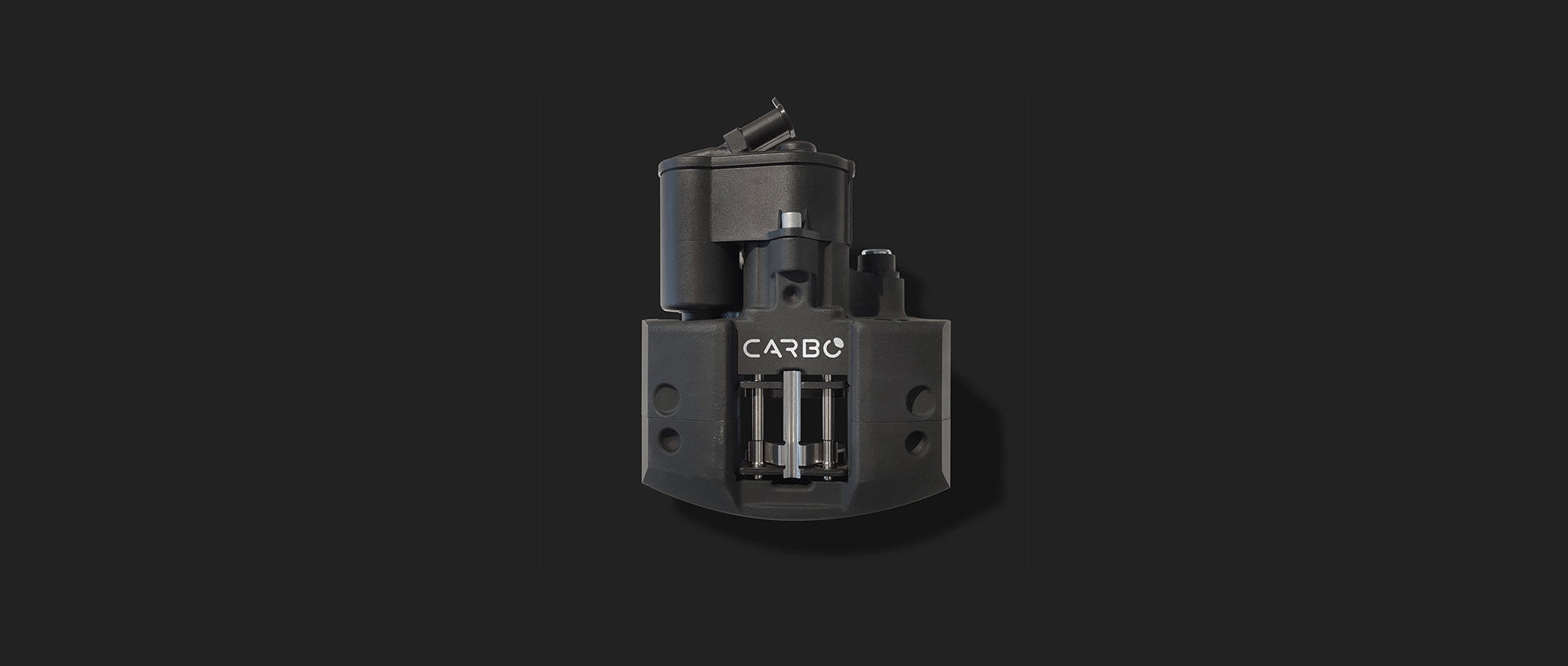
#8 EPB – Carbo™ Brake
Domain Est. 2020
Website: carbobrake.com
Key Highlights: The EPB is used on vehicles to hold the vehicle stationary on grades and flat roads; this function was accomplished traditionally using a manual parking brake….
#9 Electric Parking Brake (EPB)
Website: icnavigator.com
Key Highlights: Learn how EPB systems use power drivers, position sensing and diagnostic paths to meet safety and procurement requirements in automotive assemblies….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Epb Actuator

2026 Market Trends for EPB Actuators
Global Shift Toward Electrification and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
By 2026, the market for Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) actuators is expected to experience robust growth, primarily driven by the automotive industry’s accelerated shift toward electrification and the integration of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). As electric vehicles (EVs) become more prevalent, traditional mechanical parking brake systems are being phased out in favor of compact, lightweight, and software-controllable EPB actuators. These systems offer enhanced compatibility with regenerative braking and automated parking features, making them a critical component in EV architectures. The increasing demand for ADAS features such as auto-hold, hill-start assist, and automated parking further boosts the need for reliable and responsive EPB actuators.
Increased Adoption in Entry-Level and Mid-Tier Vehicle Segments
Historically limited to premium vehicles, EPB actuators are projected to penetrate the entry-level and mid-tier automotive segments by 2026. This expansion is fueled by declining component costs, economies of scale, and heightened consumer demand for modern convenience and safety features. Automakers are leveraging EPB systems not only for functional benefits but also as a differentiator in competitive markets. The integration of EPB actuators into compact cars and economy SUVs is expected to significantly expand the addressable market, particularly in emerging regions such as India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America.
Technological Advancements and Integration with Vehicle Networks
By 2026, EPB actuators will increasingly feature enhanced connectivity with vehicle control units (VCUs) and centralized electronic architectures. Next-generation actuators will support over-the-air (OTA) updates, predictive diagnostics, and seamless integration with autonomous driving platforms. The trend toward software-defined vehicles will push manufacturers to develop smarter actuators that can communicate real-time data on brake health, usage patterns, and fault detection. This shift is likely to stimulate innovation among Tier-1 suppliers, with a focus on miniaturization, energy efficiency, and fail-safe redundancy.
Regulatory and Safety Standards Driving Market Growth
Stringent global safety regulations are expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the EPB actuator market in 2026. Regulatory bodies such as Euro NCAP, NHTSA, and C-NCAP are increasingly emphasizing automated safety functions, including hill-hold control and emergency brake engagement, which rely on EPB systems. The alignment of EPB technology with mandatory safety requirements will compel automakers to adopt these systems across a wider range of models, further accelerating market penetration.
Regional Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to lead global demand for EPB actuators by 2026, driven by strong EV production in China and government incentives promoting smart mobility solutions. Europe will maintain a high adoption rate due to stringent emissions and safety norms, while North America will see steady growth supported by consumer preference for premium features in light-duty vehicles. Key players such as Bosch, Continental, Nissin Kogyo, and Mando are expected to intensify R&D efforts and strategic partnerships to capture market share, particularly in developing integrated brake-by-wire solutions that build upon existing EPB platforms.
In conclusion, the EPB actuator market in 2026 will be shaped by technological convergence, regulatory mandates, and evolving consumer expectations. As vehicles become more automated and electric, EPB actuators will transition from convenience components to essential elements of integrated braking and safety ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing EPB Actuators (Quality and IP)
Sourcing Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) actuators involves navigating complex technical, quality, and intellectual property (IP) challenges. Overlooking these can lead to product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly assess a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, quality management systems (e.g., IATF 16949 certification), and track record in automotive components can result in inconsistent product quality. Suppliers without proven experience in high-reliability automotive systems may deliver actuators prone to premature failure.
Insufficient Testing and Validation
EPB actuators must endure harsh automotive environments, including extreme temperatures, vibration, and moisture. Sourcing actuators without rigorous validation (e.g., life cycle testing, environmental stress screening, functional safety testing per ISO 26262) increases the risk of field failures and safety issues.
Lack of Traceability and Process Control
Poor component traceability and inconsistent production processes can hinder root cause analysis during failures. Suppliers that do not maintain detailed batch records, process controls, or failure reporting systems may compromise long-term reliability and recall management.
Use of Substandard Materials or Components
To cut costs, some suppliers may substitute lower-grade materials or use counterfeit semiconductors and motors. This compromises durability and safety, especially in safety-critical systems like EPB actuators.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed or Infringing Designs
Sourcing from suppliers who use patented technologies (e.g., motor control algorithms, mechanical designs) without proper licensing exposes the buyer to IP infringement claims. This can result in costly litigation, product recalls, or sales bans.
Ambiguous Ownership of Custom Designs
When co-developing or customizing an EPB actuator, unclear contractual terms on IP ownership can lead to disputes. Without explicit agreements, suppliers may retain rights to design improvements, limiting your freedom to manufacture or modify the product.
Reverse-Engineered or Clone Products
Some suppliers offer “compatible” EPB actuators that closely mimic original equipment (OE) designs. These may violate design patents or utility models, creating legal exposure for both the supplier and the buyer.
Insufficient IP Due Diligence
Failing to conduct IP audits or freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses before sourcing increases the risk of adopting infringing technology. This is especially critical when entering new markets with strong IP enforcement.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier audits and require certifications (IATF 16949, ISO 26262 compliance).
- Enforce strict testing protocols and sample validation before mass production.
- Include clear IP clauses in contracts, specifying ownership, licensing, and indemnification.
- Perform IP landscape and FTO analyses, especially for custom or cost-reduced designs.
- Establish long-term partnerships with reputable Tier 1 or Tier 2 suppliers with proven IP integrity.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable, legally compliant EPB actuator sourcing aligned with automotive safety and quality standards.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for EPB Actuator
Overview
The Electronic Park Brake (EPB) Actuator is a critical automotive component governed by stringent logistics and compliance requirements. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, efficient transportation, storage, and regulatory compliance throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Ensure all EPB actuators meet regional and international standards, including but not limited to:
– Automotive Safety Standards: ISO 26262 (Functional Safety), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management)
– Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): ISO 11452 and CISPR 25
– RoHS & REACH Compliance: Restriction of hazardous substances in electronics (EU Directive 2011/65/EU and Regulation EC 1907/2006)
– Country-Specific Approvals: IATF 16949 certification for quality management in automotive production
Documentation must include certificates of compliance, material declarations, and test reports for each batch shipped.
Packaging & Handling
- Use ESD-safe (Electrostatic Discharge) packaging to protect sensitive electronic components
- Secure actuators in rigid, anti-vibration containers with foam or molded inserts to prevent mechanical damage
- Label packages with:
- Part number and revision
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack,” “This Side Up”)
- ESD warning labels
- Avoid exposure to moisture; include desiccant packs if necessary
Storage Conditions
- Temperature: Store between -10°C to +40°C
- Humidity: Maintain relative humidity below 65% to prevent condensation and corrosion
- Shelf Life: Monitor and adhere to manufacturer-specified shelf life; FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management is recommended
- Keep away from direct sunlight, dust, and corrosive atmospheres
Transportation Guidelines
- Use climate-controlled vehicles for long-distance or extreme climate transport
- Secure loads to prevent shifting during transit
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, especially above 60°C or below -20°C
- For international shipments:
- Comply with IMDG Code (if applicable for lithium components)
- Prepare accurate HS codes (e.g., 8708.29 for brake parts)
- Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin
Import/Export Documentation
Maintain complete documentation for customs clearance:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), if required
– Export Control Classification Number (ECCN), if shipping outside free trade zones
Ensure compliance with export regulations such as EAR (Export Administration Regulations) or ITAR, where applicable.
Quality & Traceability
- Implement full traceability using serial or batch numbers
- Maintain records of production date, testing results, and shipping logs for at least 10 years (per automotive industry standards)
- Conduct periodic audits to verify compliance with logistics and quality procedures
Incident Response & Non-Conformance
- Establish a process for reporting and handling damaged, defective, or non-compliant shipments
- Initiate root cause analysis and corrective actions upon non-conformance
- Notify relevant authorities and customers promptly if regulatory breaches occur
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for EPB actuators ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. Regular training for logistics personnel and continuous monitoring of regulatory changes are essential for sustained compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing EPB Actuator
In conclusion, sourcing an EPB (Electric Parking Brake) actuator requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, quality standards, supply chain reliability, and cost-efficiency. As a critical component of modern vehicle braking systems, the EPB actuator must meet stringent safety, durability, and performance requirements to ensure vehicle safety and regulatory compliance.
Key factors in the sourcing decision include selecting suppliers with proven expertise in automotive electronics and mechatronics, adherence to international quality standards such as IATF 16949, and the ability to support just-in-time delivery and long-term after-sales service. Additionally, evaluating the total cost of ownership—beyond unit price—to include reliability, warranty support, and potential integration costs is essential.
Establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers, possibly through a dual-sourcing strategy, mitigates supply chain risks and supports production continuity. Close collaboration during the development and validation phases ensures compatibility with vehicle platforms and facilitates timely integration.
Ultimately, a strategic, risk-aware, and quality-driven approach to sourcing EPB actuators will enhance product reliability, support brand reputation, and contribute to the overall success of the vehicle program.