The global environmental temperature chamber market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for product reliability testing across industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 1.65 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by stringent regulatory standards, rising R&D investments, and the need for climate simulation in product development. As manufacturers prioritize precision, repeatability, and energy efficiency in testing environments, the competition among key players intensifies. In this landscape, nine leading companies have emerged as pioneers, combining technological innovation with global reach to dominate the environmental chamber industry.
Top 9 Environmental Temperature Chamber Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Thermotron
Domain Est. 1996
Website: thermotron.com
Key Highlights: Thermotron is a worldwide temperature chamber, humidity chamber, and vibration testing equipment manufacturer. View our testing equipment today!…
#2 Tenney Environmental
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tenney.com
Key Highlights: Tenney Environmental is the leading manufacturer of environmental and climatic chambers designed to meet temperature, humidity, altitude, and vacuum ……
#3 Parameter
Domain Est. 1998
Website: humiditycontrol.com
Key Highlights: Parameter Generation & Control is an internationally respected manufacturer & innovator of precise humidity control chambers & temperature control systems….
#4 Labworks International: Climate
Domain Est. 2005
Website: labworksinternational.com
Key Highlights: Labworks designs and manufactures environmental test chambers for healthcare, research, pharmaceutical, and industrial use across Canada….
#5 Weiss Technik
Domain Est. 2013
Website: weiss-na.com
Key Highlights: Weiss Technik is an environmental chamber manufacturer that offers pre-engineered & custom equipment for a variety of industries & applications….
#6 ESPEC North America
Domain Est. 1996
Website: espec.com
Key Highlights: ESPEC environmental test chambers create temperature & humidity extremes in chambers from benchtop to drive–in. Standardization allows ESPEC to concentrate ……
#7 Environmental Chambers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: instron.com
Key Highlights: The 3119-600 Series environmental chambers provide extensive temperature testing capabilities for evaluating material properties under non-ambient conditions….
#8 Environmental Test Chambers
Domain Est. 2004
Website: associatedenvironmentalsystems.com
Key Highlights: AES provides precision-engineered environmental test chambers, designed to handle the most demanding requirements with full in-house manufacturing….
#9 environmental test chambers since 1952
Domain Est. 2013 | Founded: 1952
Website: acstestchambers.com
Key Highlights: ACS has been a world leader in the design and manufacture of a wide range of environmental test chambers since 1952, from simple bench-top climatic chambers ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Environmental Temperature Chamber
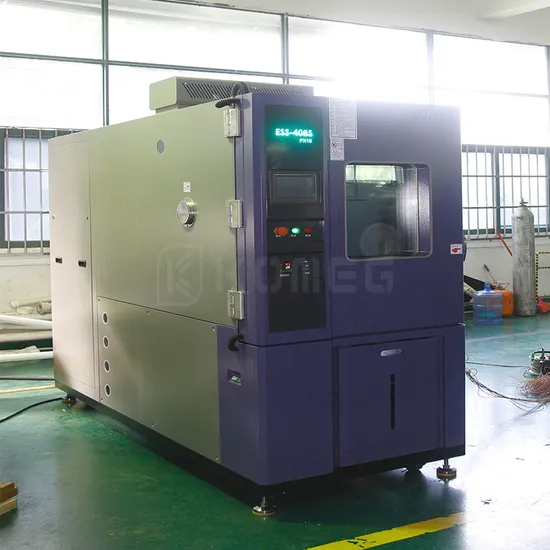

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Environmental Temperature Chambers
The global market for environmental temperature chambers is poised for substantial growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand for product reliability testing across key industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy. These chambers simulate extreme temperature conditions to assess the performance, durability, and safety of materials and products, making them essential tools in quality assurance and R&D.
One of the dominant trends shaping the 2026 landscape is the rising emphasis on product innovation and compliance with stringent international standards. Regulatory bodies are tightening environmental and safety requirements, compelling manufacturers to adopt rigorous testing protocols. This regulatory push is particularly evident in the electric vehicle (EV) and battery technology sectors, where thermal performance under varying climates is critical. As a result, demand for advanced temperature chambers capable of simulating rapid thermal cycling and extended temperature ranges (-70°C to +180°C and beyond) is accelerating.
Another key trend is the integration of smart technologies and Industry 4.0 principles into environmental chambers. By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly offering chambers equipped with IoT connectivity, remote monitoring, real-time data analytics, and predictive maintenance capabilities. These features not only enhance testing accuracy and repeatability but also reduce operational downtime and improve energy efficiency—factors that are becoming central to purchasing decisions.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to lead market growth due to rapid industrialization, expanding electronics manufacturing, and growing investments in R&D by both private and public sectors—particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea. Meanwhile, North America and Europe continue to hold significant market shares, supported by strong aerospace and defense industries and a focus on sustainable testing solutions.
Sustainability is also emerging as a critical market driver. By 2026, manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient designs, eco-friendly refrigerants, and recyclable chamber components to align with global decarbonization goals. This shift is being reinforced by both consumer demand and regulatory incentives.
In summary, the 2026 environmental temperature chamber market will be characterized by technological sophistication, regulatory compliance, regional expansion, and a strong focus on sustainability. Companies that innovate in smart testing solutions and adapt to evolving industry needs are expected to gain a competitive edge in this dynamic and growing market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Environmental Temperature Chambers (Quality and IP)
Sourcing Environmental Temperature Chambers involves significant technical and commercial considerations. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to costly delays, non-compliance, or legal exposure.
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate Testing Validation
One of the most frequent pitfalls is selecting a supplier without thoroughly verifying their quality management systems and testing capabilities. Many low-cost manufacturers may claim compliance with international standards (e.g., IEC, MIL-STD, ASTM) but lack robust internal processes to ensure consistency across units. Buyers may receive chambers that fail to maintain precise temperature uniformity, have poor humidity control, or exhibit calibration drift over time. Without third-party certification or access to detailed performance validation reports (e.g., temperature mapping, recovery time tests), organizations risk investing in equipment that cannot reliably support critical testing protocols.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
A related quality issue involves inadequate documentation. Reputable suppliers provide complete technical files, including calibration certificates, material traceability, and design schematics. When these are missing or poorly maintained, it becomes difficult to validate chamber performance during audits or regulatory inspections (e.g., ISO 17025, FDA 21 CFR Part 11). This lack of traceability not only compromises data integrity but can also invalidate test results used for product certification.
Intellectual Property Risks in Custom Chamber Designs
When sourcing custom-designed environmental chambers, IP ownership is often poorly defined. Buyers may assume that paying for a custom solution automatically grants them full rights to the design, software, or control algorithms. However, many suppliers retain IP rights to proprietary control systems or modular components unless explicitly transferred in the contract. This can restrict the buyer’s ability to modify, service, or replicate the chamber in the future, creating dependency on the original vendor and limiting operational flexibility.
Use of Counterfeit or Non-Compliant Components
Lower-tier suppliers may use counterfeit or substandard components—such as sensors, compressors, or insulation materials—to reduce costs. These components may not meet environmental or safety standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH), posing long-term reliability and compliance risks. In regulated industries like aerospace or medical devices, using chambers with non-compliant parts can invalidate product test data and expose the buyer to regulatory penalties.
Inadequate Software Licensing and Embedded IP
Modern environmental chambers rely heavily on embedded software for control, data logging, and reporting. Buyers often overlook software licensing terms, assuming the software is included outright. In reality, some vendors use licensed third-party software or proprietary code that may require ongoing fees or restrict integration with existing laboratory information management systems (LIMS). Unauthorized use or reverse engineering of such software can trigger IP infringement claims.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, demand comprehensive quality documentation, clearly define IP ownership in contracts, and verify component authenticity and compliance certifications prior to procurement.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Environmental Temperature Chambers
Transporting, installing, and operating Environmental Temperature Chambers (ETCs) requires careful attention to logistics and regulatory compliance to ensure safety, protect equipment, and meet legal requirements. This guide outlines key considerations.
H2: Pre-Shipment & Transportation
- Crating & Packaging: Ensure the chamber is securely crated using robust materials (e.g., wooden skids, protective corner braces, foam padding). Internal components must be immobilized using manufacturer-supplied transit bolts or braces to prevent damage during transit.
- Weight & Dimensions: Verify the chamber’s gross weight (including crate) and external dimensions (L x W x H). Ensure this information is accurate for selecting appropriate freight carriers (e.g., LTL, FTL, air freight) and planning loading/unloading equipment (e.g., forklift capacity, dock height).
- Hazardous Materials (Hazmat): Identify if the chamber contains regulated substances (e.g., refrigerant gases like R-404A, R-134a; hydraulic fluids; batteries). Obtain Safety Data Sheets (SDS). Shipments containing certain refrigerants may require Hazmat classification (e.g., UN1011, UN3159), specific labeling, placarding, and documentation (e.g., Dangerous Goods Declaration). Compliance with IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or 49 CFR (US ground) regulations is mandatory.
- Climate Considerations: For extreme ambient temperatures during transit (especially freezing), consider insulated packaging or climate-controlled transport to prevent condensation or freezing of internal components/fluids.
- Carrier Selection & Insurance: Choose a reputable freight carrier experienced with sensitive scientific equipment. Ensure cargo is adequately insured for its full replacement value.
H2: Receiving & Site Preparation
- Inspection: Immediately inspect the crate upon delivery for visible damage. Note any damage on the carrier’s delivery receipt before signing. Open the crate carefully and inspect the chamber for shipping damage. Document any issues with photos and notify the supplier and carrier immediately.
- Site Requirements: Verify the installation site meets all specifications:
- Floor Load Capacity: Ensure the floor can support the chamber’s weight (check manufacturer specs).
- Clearances: Maintain required clearances around the chamber (front, sides, rear, top) for ventilation, service access, and door swing (refer to manual).
- Power Supply: Confirm voltage, phase, frequency, and amperage requirements are available at the designated outlet(s). Verify grounding is proper. Dedicated circuits are often required.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate room ventilation exists, especially for chambers exhausting heat (e.g., high-temperature operation, refrigerant condensers). Avoid locations near heat sources or in confined spaces.
- Drainage: For chambers with condensate removal (humidity, defrost cycles), ensure a floor drain or condensate pump connection is available and accessible.
- Environment: Site should be clean, dry, level, and free from excessive dust, vibration, and corrosive fumes.
- Unloading & Handling: Use appropriate equipment (e.g., forklift, pallet jack rated for the weight). Follow manufacturer’s handling instructions. Remove transit bolts only after the chamber is in its final position.
H2: Installation & Commissioning
- Professional Installation: Highly recommended, especially for larger chambers or complex utility connections (e.g., chilled water, compressed air, exhaust ducting). Ensures correct setup and voids warranty issues.
- Utility Connections: Connect power, water (if applicable), drain, exhaust (if applicable), and control interfaces (e.g., data logging) strictly according to manufacturer instructions and local codes.
- Leveling: Precisely level the chamber using adjustable feet to ensure door seals properly and internal mechanisms function correctly.
- Initial Power-Up & Checkout: Perform initial power-up as per the manual. Verify controller operation, basic functions, and safety interlocks (door switches, over-temperature protection).
- Performance Verification (IQ/OQ): Conduct Installation Qualification (IQ) and Operational Qualification (OQ) as per regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA 21 CFR Part 11, GxP) or internal quality standards. This typically involves:
- Verifying installation against specifications (IQ).
- Testing temperature (and humidity, if applicable) uniformity, stability, and accuracy across the working volume using calibrated sensors.
- Documenting all procedures and results.
H2: Operational Compliance & Safety
- Regulatory Standards: Ensure operation complies with relevant standards:
- Electrical Safety: UL/CSA 61010-1 (North America), IEC 61010-1 (International).
- EMC/EMI: FCC Part 15 (US), CISPR 11/EN 55011 (International).
- Pressure Equipment: If applicable (e.g., certain refrigeration systems), compliance with ASME BPVC (US) or PED (EU) may be needed.
- Environmental: Compliance with regulations on refrigerant handling (e.g., EPA Section 608, F-Gas Regulation EU No 517/2014) for maintenance, recovery, and disposal.
- User Training: Ensure all operators are trained on safe operation, emergency procedures (e.g., power failure, high-temperature alarm), sample loading/unloading protocols, and basic troubleshooting.
- Safety Features: Never bypass safety interlocks (door switches, over-temperature limits). Ensure emergency stop buttons are accessible and functional. Post clear operating instructions and warnings.
- Sample Safety: Understand limitations regarding flammable, explosive, or toxic materials inside the chamber. Use appropriate safety interlocks or purge systems if required.
- Preventative Maintenance (PM): Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s PM schedule (filter changes, condenser cleaning, refrigerant checks, calibration). Maintain detailed logs. PM is critical for safety, performance, and regulatory compliance.
H2: Decommissioning & Disposal
- Refrigerant Recovery: Mandatory. Refrigerants must be recovered by a certified technician using proper equipment before any disassembly or disposal. Obtain a recovery certificate. Illegal venting is a serious environmental violation.
- Hazardous Waste: Identify and dispose of other hazardous components (e.g., used oils, contaminated filters, batteries) according to local, state/provincial, and federal regulations (e.g., RCRA in the US).
- Recycling: Maximize recycling of metals (steel, copper, aluminum) and other materials. Work with certified e-waste recyclers.
- Data Security: If the chamber has data logging, ensure sensitive data is securely erased from internal memory or connected devices before disposal.
Key Takeaway: Proactive planning for logistics (shipping, site prep, handling) and rigorous adherence to safety, environmental, and operational compliance standards throughout the chamber’s lifecycle are essential for successful and legally sound deployment. Always consult the specific manufacturer’s documentation and relevant local regulations.
Conclusion:
After a thorough evaluation of available options, sourcing an environmental temperature chamber is a critical investment to ensure product reliability, compliance with industry standards, and consistency in quality control processes. The selected chamber must meet specific testing requirements, including accurate temperature range, humidity control (if applicable), uniformity, stability, and data logging capabilities. Key factors such as chamber size, energy efficiency, ease of use, after-sales support, and total cost of ownership played a vital role in the decision-making process.
By carefully assessing vendor credibility, warranty terms, service availability, and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, IEC, MIL-STD), we have identified a solution that balances performance, reliability, and value. Sourcing this environmental chamber will enhance our testing capabilities, support innovation, and ensure long-term operational efficiency. Moving forward, proper installation, staff training, and routine maintenance will be essential to maximize the chamber’s effectiveness and lifespan.