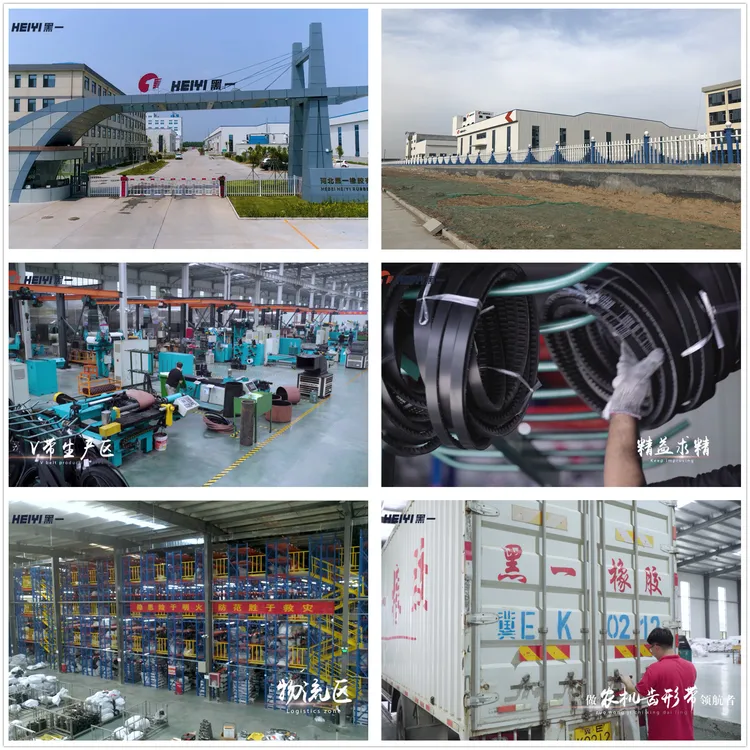
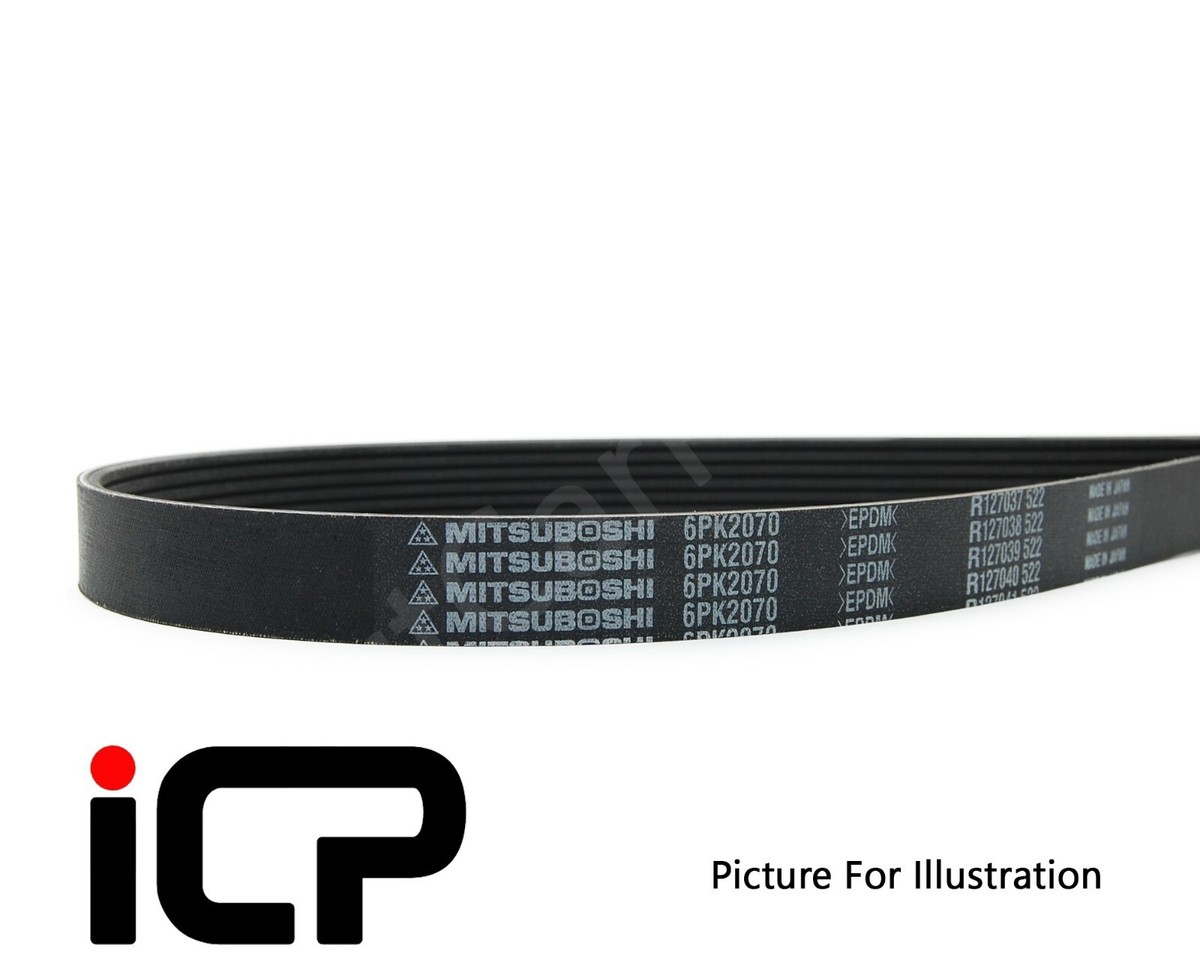
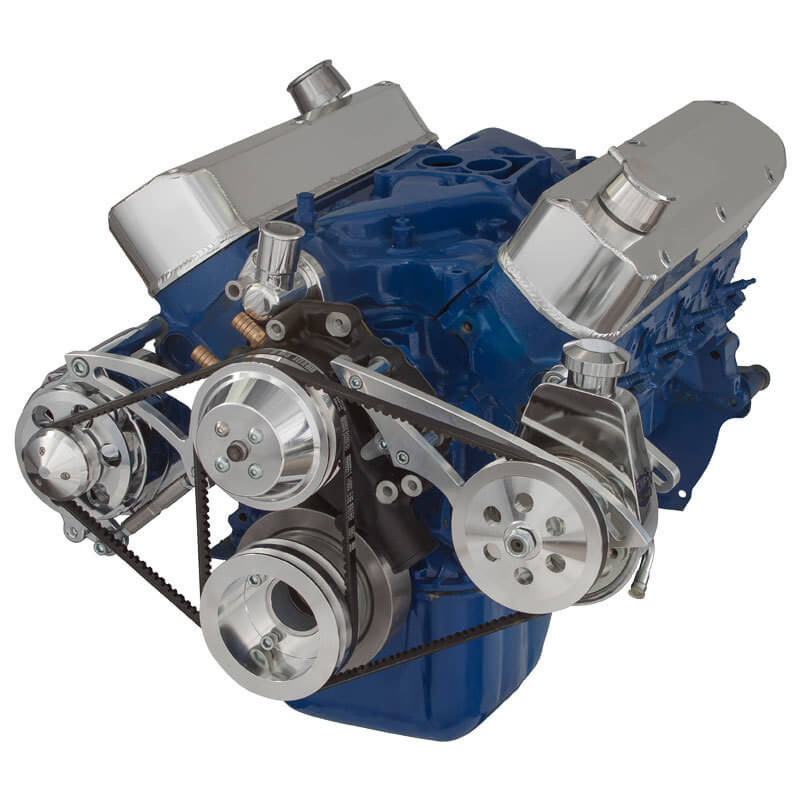
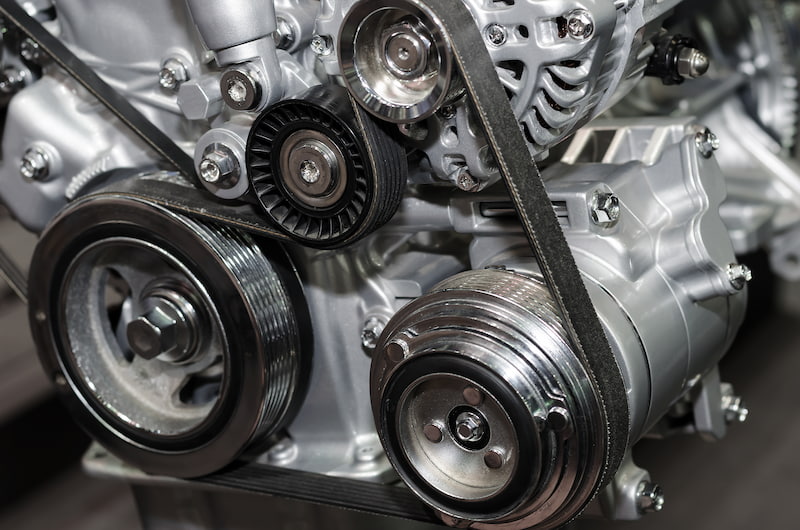
The global automotive alternator belt market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising vehicle production, increasing demand for fuel-efficient powertrains, and the ongoing need for reliable engine accessory drive systems. According to Grand View Research, the global serpentine belt market—encompassing alternator belts—was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by both original equipment manufacturer (OEM) demand and the growing aftermarket segment, particularly in emerging economies. As vehicles become more reliant on electrical systems—from advanced driver assistance technologies to infotainment—the role of high-performance alternator belts in maintaining optimal charging efficiency has become increasingly critical. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, durability, and global supply capabilities to meet stringent automotive standards. Here, we present the top 10 engine alternator belt manufacturers shaping the industry with data-backed performance and market reach.
Top 10 Engine Alternator Belt Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial belt manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: hutchinsontransmission.com
Key Highlights: Industrial belt manufacturer. Hutchinson, Belt drive manufacturer, develops and manufactures complete industrial power transmission systems incorporating ……
#2 Mitsuboshi Belting Ltd.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mitsuboshi.com
Key Highlights: We are a comprehensive manufacturer of rubber and plastics, including transmission belts used in automobiles, precision equipment, agricultural machinery, ……
#3 PIX Power Transmission Belts Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: pixtrans.com
Key Highlights: PIX Transmissions Ltd is the world’s leading manufacturer of V belts, Timing belts, poly v belts and pulleys for nearly every application in the automotive, ……
#4 V
Domain Est. 1999
Website: web.optibelt.com
Key Highlights: High-quality V-belts and timing belts from the german manufacturer Optibelt. We have been setting standards in drive systems with first-class system ……
#5 MBL (USA) Corporation
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mblusa.com
Key Highlights: As the North American division of Mitsuboshi Belting Ltd., we proudly manufacture and distribute premium power transmission belts….
#6 Belt Drive Components
Domain Est. 2010
Website: continental-aftermarket.com
Key Highlights: Belt drive components in OEM quality for the automotive aftermarket….
#7 V
Domain Est. 1994
Website: gates.com
Key Highlights: We’ve designed our V-belts for wear, corrosion, and heat resistance with OE quality fit and construction for reliable, long-lasting performance….
#8 Dayco
Domain Est. 1998
Website: dayco.com
Key Highlights: Dayco is a global leader in the research, design, manufacture and distribution of essential engine drive systems and aftermarket services for automotive, truck, ……
#9 Dayco Aftermarket North America
Domain Est. 2010
Website: na.daycoaftermarket.com
Key Highlights: Dayco’s high-quality belts, front end drive system components, hoses and tools are all designed to enhance vehicle performance and ease of installation….
#10 V
Domain Est. 2018
Website: continental-industry.com
Key Highlights: Wrapped V-belts for demanding drives in all industries and sectors of machine engineering. Available in three performance levels: Standard, Advance and Supreme….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Engine Alternator Belt

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Engine Alternator Belts
The global engine alternator belt market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automotive technology, shifts in vehicle propulsion systems, and evolving emission regulations. As a critical component in internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, the alternator belt transfers mechanical power from the engine crankshaft to auxiliary systems such as the alternator, water pump, air conditioning compressor, and power steering pump. While the long-term outlook for traditional belt-driven systems faces challenges due to electrification, several key trends will shape the market landscape through 2026.
-
Decline in Demand Due to Electrification of Vehicles
The most influential trend impacting the alternator belt market is the global shift toward electric vehicles (EVs). Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) do not use internal combustion engines and therefore do not require alternator belts. With automakers committing to electrify their fleets and governments enforcing stricter carbon emission standards, the proportion of ICE vehicles in new car sales is expected to decline, directly reducing demand for alternator belts. However, hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) still rely on ICEs and will continue to use alternator belts, providing a transitional market. -
Growth in Replacement and Aftermarket Demand
Despite declining new vehicle demand in some regions, the aftermarket for alternator belts remains robust. The global vehicle parc—especially in emerging markets—consists largely of ICE-powered vehicles that require routine maintenance. Alternator belts are wear-and-tear components with typical replacement intervals between 60,000 and 100,000 miles. As the average age of vehicles on the road increases, particularly in North America and Europe, demand for replacement belts will sustain market growth through 2026. -
Material and Design Innovations
Manufacturers are investing in high-performance materials such as ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) and polyurethane to enhance belt durability, heat resistance, and noise reduction. These materials offer longer service life compared to traditional neoprene belts, aligning with consumer demand for reliability and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, the development of multi-ribbed serpentine belts improves efficiency and reduces space requirements, supporting compact engine designs in modern vehicles. -
Regional Market Disparities
Regional trends will diverge significantly. In North America and Europe, market growth will be constrained by EV adoption and declining ICE vehicle production. Conversely, Asia-Pacific—especially India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa—will see continued demand due to rising vehicle ownership, slower EV adoption rates, and a growing fleet of commercial and passenger ICE vehicles. This regional disparity will shift manufacturing and sales focus toward emerging markets. -
Integration with Start-Stop Systems and Mild Hybrids
Many modern ICE vehicles incorporate start-stop technology and mild hybrid systems (e.g., 48V architectures) to improve fuel efficiency. While these systems reduce engine runtime, they do not eliminate the need for alternator belts. In fact, they increase belt stress due to frequent engine cycling, potentially accelerating wear. This trend may lead to higher replacement frequency and demand for reinforced, high-durability belts tailored for start-stop applications. -
Consolidation and Competitive Dynamics
The alternator belt market is seeing consolidation among component suppliers, with major players such as Gates, Continental, and Dayco focusing on innovation, global distribution, and integration with broader engine accessory drive systems. Smaller manufacturers face pressure to differentiate through cost efficiency or niche applications, such as heavy-duty or off-road vehicles.
Conclusion
By 2026, the engine alternator belt market will navigate a complex environment shaped by technological disruption and regional variation. While long-term demand faces pressure from vehicle electrification, the aftermarket, material innovation, and regional growth in developing economies will sustain the industry. Suppliers that adapt to hybrid applications, invest in durable materials, and target high-growth regions will maintain competitiveness in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Engine Alternator Belts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing engine alternator belts—critical components for vehicle electrical systems—can be fraught with challenges, particularly when balancing cost, quality, and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Materials and Construction
Many low-cost alternator belts on the market use substandard rubber compounds and reinforcement fibers, leading to premature cracking, glazing, or delamination. Inferior manufacturing processes may result in inconsistent tension cords or improper curing, reducing belt life and reliability. These defects can cause alternator failure, battery charging issues, or even complete drive system breakdowns, increasing downtime and repair costs.
Lack of OEM or Aftermarket Certification
Sourcing belts without proper OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) specifications or recognized aftermarket certifications (such as ISO 9001, SAE J1459, or DIN 7753) increases the risk of incompatibility and performance issues. Belts that don’t meet OEM specs may not fit correctly or handle the required load, leading to slippage or excessive wear. Always verify documentation and traceability to ensure compliance.
Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Products
The automotive aftermarket is rife with counterfeit alternator belts that mimic branded products (e.g., Gates, Dayco, Continental) but lack the intellectual property rights or technical approval. These products often infringe on patents, trademarks, and design rights, exposing buyers to legal and reputational risks. Furthermore, counterfeit belts typically offer inferior performance and safety, undermining reliability.
Inadequate IP Due Diligence in Supply Chain
When sourcing from third-party manufacturers, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, buyers may unknowingly procure belts that violate IP rights. This includes unauthorized use of patented belt designs, tread patterns, or proprietary rubber formulations. Failure to conduct proper due diligence—such as supplier audits or IP clearance searches—can result in customs seizures, legal disputes, or product recalls.
Inconsistent Sizing and Compatibility
Generic or unbranded alternator belts may list incorrect dimensions or compatibility data, leading to fitment issues. Even minor deviations in length, width, or rib count can affect tension, alignment, and power transmission. Poorly sourced belts often lack detailed application guides, increasing the risk of installation errors and system damage.
Shortened Service Life and Increased Warranty Claims
Low-quality or IP-infringing belts typically exhibit shorter service lives, requiring more frequent replacements. This not only increases operational costs but also leads to higher warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction. Using non-compliant products may void equipment warranties, further escalating financial liabilities.
Supply Chain Reliability and Traceability Gaps
Unverified suppliers may lack consistent production capacity or quality control, resulting in batch-to-batch variability. Without proper traceability (e.g., lot numbering, material certifications), diagnosing failures or managing recalls becomes extremely difficult, especially in regulated industries or fleet operations.
To mitigate these pitfalls, prioritize suppliers with verifiable quality management systems, clear IP compliance, and transparent documentation. Always request test reports, material specifications, and proof of licensing when applicable.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Engine Alternator Belt
Product Overview
The Engine Alternator Belt is a critical component in automotive and industrial engine systems, responsible for transferring power from the engine crankshaft to the alternator, enabling electrical charging. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to maintain product integrity, ensure timely delivery, and meet regulatory requirements across regions.
Classification and HS Code
The Engine Alternator Belt typically falls under the following Harmonized System (HS) Code:
– HS Code: 8708.93.60 – Belts for motor vehicle engines (specific classification may vary by country; confirm with local customs authorities).
This classification is used globally for customs declaration, duty assessment, and import/export control.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
- Packaging: Alternator belts must be packaged in moisture-resistant, durable materials (e.g., sealed polybags inside corrugated cardboard boxes) to prevent damage from humidity, dust, and physical stress.
- Labeling: Each package must include:
- Product name and part number
- Manufacturer details
- Batch/lot number
- Country of origin
- Net weight and dimensions
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Do Not Stack,” “Keep Dry”)
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–25°C / 59–77°F), away from direct sunlight and ozone sources (e.g., electric motors).
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, air, and sea freight. Use non-reactive pallets (e.g., plastic or heat-treated wood) to prevent contamination.
- Stacking Limits: Adhere to manufacturer stacking heights to avoid crushing lower layers.
- Temperature Control: Avoid extreme temperatures during transit; prolonged exposure to heat or freezing conditions may degrade rubber compounds.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin.
Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU): Confirm that belt materials (e.g., rubber, fabric, additives) comply with REACH regulations regarding restricted substances (e.g., SVHCs).
- RoHS (EU & Others): Although primarily for electronics, ensure any metallic components (tensioners, pulleys if included) meet RoHS limits for hazardous substances.
- DOT / FMVSS (USA): While not directly regulated, belts used in vehicles must support compliance with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards when installed.
- Country-Specific Approvals: Some markets may require local certifications (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, CCC in China) for auto parts—verify based on destination.
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure the following documents are prepared and accurate:
– Commercial Invoice (with declared value, currency, Incoterms®)
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin (preferably Form A for preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Export Declaration (if required by exporting country)
– Import License (if applicable in destination country)
Incoterms® Recommendations
- FCA (Free Carrier): Recommended for flexibility; seller delivers goods to a carrier nominated by the buyer.
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To): Suitable for international shipments where buyer wants seller to arrange freight and insurance.
- Avoid EXW for inexperienced importers due to full buyer responsibility for export clearance.
Quality and Traceability
- Maintain lot traceability through batch numbering and production records.
- Retain quality inspection reports (e.g., tensile strength, dimensional checks) for at least 5 years.
- Support returns and recalls with documented tracking from manufacturing to delivery.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- End-of-life belts should be disposed of in accordance with local waste management regulations.
- Promote recycling programs where rubber recovery is available.
- Avoid landfill disposal where restricted (e.g., EU Landfill Directive).
Conclusion
Efficient logistics and strict compliance are crucial for the global distribution of Engine Alternator Belts. Adherence to packaging, transportation, and regulatory standards ensures product reliability, reduces supply chain risks, and supports market access worldwide. Regular audits and updates to compliance protocols are recommended to adapt to evolving regulations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Engine Alternator Belt:
Sourcing the correct engine alternator belt is a critical step in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of a vehicle’s charging system. A thorough understanding of the engine specifications, OEM part numbers, belt type (such as V-belt, serpentine, or poly-V), dimensions, and compatibility with the make and model is essential to avoid premature wear, power loss, or system failure. By evaluating reputable suppliers, considering quality certifications, comparing pricing and lead times, and verifying material durability and performance standards, organizations can make informed procurement decisions. Additionally, maintaining accurate inventory records and establishing long-term relationships with dependable vendors contributes to minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Ultimately, proper sourcing of the engine alternator belt supports optimal vehicle performance, longevity, and operational safety.