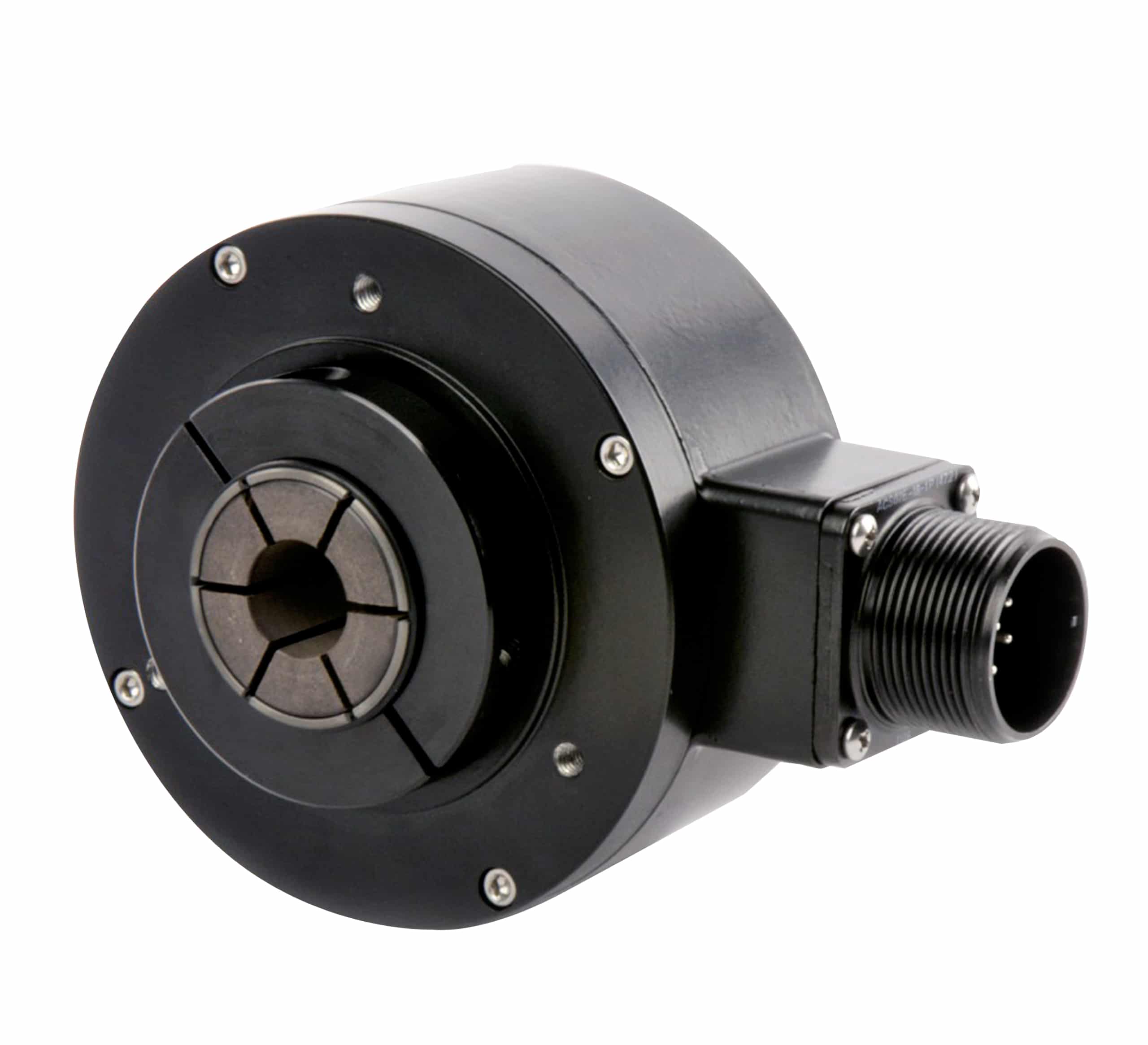
The global encoder market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision motion control across industries such as manufacturing, robotics, automotive, and renewable energy. According to Mordor Intelligence, the encoder market was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 3.1 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.2% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by the increasing adoption of automation technologies, Industry 4.0 initiatives, and the integration of advanced sensing systems in industrial equipment. As demand intensifies, leading encoder manufacturers are focusing on innovation, miniaturization, and enhanced accuracy to meet evolving application requirements. In this landscape, eight manufacturers have emerged as key players, combining technological leadership, global reach, and strong R&D capabilities to dominate market share and shape the future of motion sensing.
Top 8 Encoder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Encoder Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: quantumdev.com
Key Highlights: Quantum Devices, a United States based encoder manufacturer, designs and manufactures high quality, high performance incremental optical rotary encoders….
#2 Absolute Encoder Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: netzerprecision.com
Key Highlights: Contact Netzer or find an encoder distributor near you. Netzer is a leading absolute encoder manufacturer, delivering precision and innovation across ……
#3 Dynapar Encoders
Domain Est. 2001
Website: dynapar.com
Key Highlights: Dynapar: a manufacturer of encoders – absolute encoder & rotary encoder. Dynapar, Northstar, and Harrowe brands for every encoder application….
#4 Hohner Automation
Domain Est. 2013
Website: encoderhohner.com
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer of incremental and absolute encoders, inclinometers, potentiometers, linear measurement solutions and accessories….
#5 US Digital
Domain Est. 1995
Website: usdigital.com
Key Highlights: American-designed encoders, shipping most orders the same day. Motor encoder, incremental encoder, absolute encoder, optical encoder, magnetic encoder….
#6 Encoder Products Company
Domain Est. 1996
Website: encoder.com
Key Highlights: At Encoder Products Company (EPC), we take pride in designing, manufacturing, and assembling high-quality rotary encoders right here in Sagle, Idaho, USA….
#7 HEIDENHAIN
Domain Est. 1996
Website: heidenhain.com
Key Highlights: HEIDENHAIN develops and manufactures linear and angle encoders, rotary encoders, digital readouts, and CNC controls for demanding positioning tasks….
#8 Custom Encoders
Domain Est. 1998
Website: smac-mca.com
Key Highlights: The compact optical encoder can be customized according to your applications. Design, prototype and fast turnaround for drop-in replacement products….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Encoder
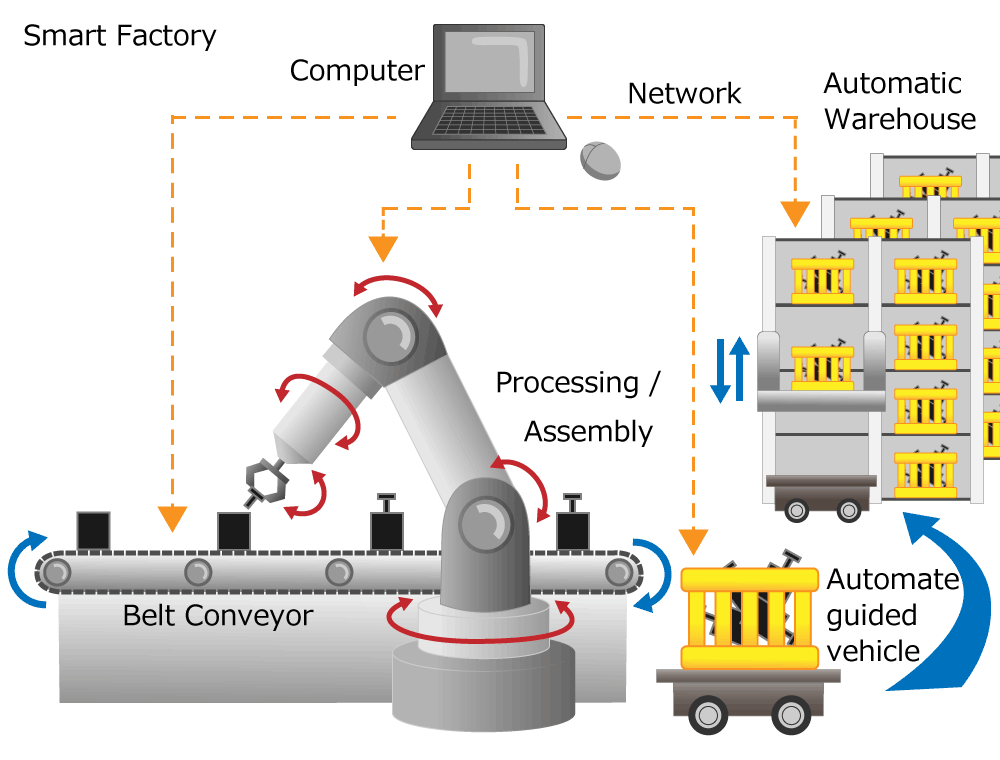
H2: Market Trends for Encoders in 2026
As the global industrial and technological landscape evolves, encoder technology is poised for significant transformation and expansion by 2026. Encoders—devices that convert motion into electrical signals for position, velocity, and direction feedback—are critical components in automation, robotics, renewable energy, electric vehicles (EVs), and advanced manufacturing. The following analysis outlines key market trends shaping the encoder industry in 2026, with a focus on technological advancements, sectoral demand, regional dynamics, and competitive positioning.
1. Accelerated Adoption in Industrial Automation and Industry 4.0
The continued rollout of Industry 4.0 principles is driving demand for high-precision encoders. By 2026, smart factories will rely increasingly on real-time data acquisition and closed-loop control systems, where encoders play a foundational role. Absolute and incremental encoders with digital interfaces (e.g., EnDat, BiSS, and SSI) are being integrated into collaborative robots (cobots), CNC machines, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). Demand is further amplified by the need for predictive maintenance and system diagnostics, with encoders embedded with IoT capabilities providing valuable operational insights.
2. Growth in Electric Vehicles and E-Mobility
The EV revolution is a major growth catalyst. By 2026, encoders—particularly rotary and magnetic types—are expected to be standard in traction motor control systems for electric cars, e-bikes, and commercial EVs. These encoders ensure precise torque and speed measurement, essential for motor efficiency and battery optimization. The shift toward higher-resolution, compact, and temperature-resilient encoders is evident, driven by demands for performance under harsh automotive conditions.
3. Technological Innovation: Miniaturization, Wireless, and Absolute Positioning
Encoder technology is advancing rapidly:
– Miniaturization: Demand for compact encoders is rising in medical devices, drones, and robotics, where space constraints are critical.
– Wireless Encoders: Emerging applications in rotating machinery and remote monitoring are beginning to adopt wireless solutions, reducing cabling complexity and improving system flexibility.
– Absolute Encoders: These are gaining preference over incremental types due to their ability to retain position data during power loss—a crucial feature in industrial safety and automation continuity.
Optical, magnetic, and capacitive sensing technologies are being refined for higher accuracy, durability, and resistance to contaminants like dust, moisture, and vibration.
4. Expansion in Renewable Energy and Smart Infrastructure
The renewable energy sector, especially wind turbines, continues to be a strong end-user of encoders. Pitch and yaw control systems in wind turbines rely on robust encoders to maximize energy capture and ensure mechanical safety. By 2026, increased global investments in offshore wind and solar tracking systems will boost demand for rugged, high-reliability encoders capable of withstanding extreme environmental conditions.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific Dominance: China, Japan, South Korea, and India are expected to lead encoder consumption by 2026, fueled by industrial automation, electronics manufacturing, and government initiatives like “Made in China 2025” and “Smart India.”
- North America: Growth is driven by advanced robotics, aerospace, and defense applications, along with rising EV production.
- Europe: Strong emphasis on sustainability and green manufacturing supports encoder use in high-precision machinery and EVs, with Germany and France remaining key markets.
6. Competitive Landscape and Supply Chain Shifts
The encoder market is consolidating, with key players like TE Connectivity, Panasonic, Broadcom, Renishaw, and HEIDENHAIN investing in R&D and acquiring niche innovators. Localized manufacturing and supply chain resilience are becoming priorities post-pandemic, prompting companies to diversify production bases and adopt nearshoring strategies, particularly in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe.
7. Sustainability and Regulatory Influence
Environmental regulations are influencing encoder design. By 2026, there will be greater demand for RoHS-compliant, energy-efficient, and recyclable encoder components. Additionally, functional safety standards such as ISO 13849 and IEC 61508 are pushing manufacturers to integrate safety-rated encoders into machinery, especially in automotive and industrial automation.
Conclusion
By 2026, the global encoder market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6–8%, reaching an estimated value of USD 2.5–3 billion. The convergence of automation, electrification, and digitalization will continue to propel innovation and adoption. Companies that prioritize smart, compact, and resilient encoder solutions—especially those compatible with IoT and Industry 4.0 ecosystems—will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Encoders (Quality, IP)
Sourcing the right encoder for an industrial or automation application involves more than just matching basic specifications. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings can lead to premature failure, system downtime, and increased maintenance costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Choosing Low-Quality Encoders to Cut Costs
Opting for cheaper, low-quality encoders may seem cost-effective initially, but these often suffer from poor mechanical tolerances, inconsistent signal output, and shorter lifespans. Substandard materials and manufacturing processes can result in unreliable performance, especially under load or in dynamic environments.
Misunderstanding IP Ratings and Environmental Needs
Many engineers assume a higher IP rating is always better, but fail to consider the specific environmental conditions. For example, selecting an IP65 encoder for a washdown environment when IP67 or IP69K is required can lead to water ingress and failure. Conversely, over-specifying can increase costs unnecessarily.
Ignoring Mechanical Stress and Mounting Conditions
Encoders are sensitive to misalignment, shaft loading, and vibration. Sourcing an encoder without considering shaft runout, coupling alignment, or external forces can cause bearing wear and internal damage, even if the IP rating is adequate for the environment.
Overlooking Sealing Integrity Over Time
Even encoders with high initial IP ratings may degrade due to poor sealing design or material fatigue. Gaskets can harden, seals can crack, and housing joints may loosen under thermal cycling or mechanical stress, compromising protection.
Failing to Verify Manufacturer Claims with Certifications
Not all manufacturers provide accurate or verified IP ratings. Some may self-certify without third-party testing. Always request test reports or certifications (e.g., IEC 60529 compliance) to ensure the encoder meets stated protection levels.
Neglecting Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Protection
While not directly related to IP, EMI can disrupt encoder signals. Low-quality encoders often lack proper shielding and filtering, leading to signal errors in electrically noisy environments. This can be mistaken for mechanical or environmental failure.
Assuming All “Industrial” Encoders Are Equal
The term “industrial-grade” is often used loosely. Some encoders marketed as such may not withstand real-world conditions. Evaluate build quality, materials (e.g., metal vs. plastic housings), and proven performance in similar applications.
Not Considering Long-Term Service and Support
Low-cost encoders may come from suppliers with limited technical support or short product lifecycles. This creates challenges for maintenance, spare parts availability, and system upgrades, increasing total cost of ownership.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in evaluating both the technical specifications and the reliability of the supplier. Prioritize quality, verify environmental ratings, and consider the total lifecycle cost rather than initial price.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Encoder
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling, transportation, and deployment of Encoder devices. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational reliability.
Product Classification and Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all Encoder models are classified correctly under international trade and safety regulations. Verify compliance with relevant standards, including but not limited to:
– CE Marking (Europe): Conformity with EU directives such as EMC (2014/30/EU) and RoHS (2011/65/EU).
– FCC Certification (USA): Compliance with Part 15 of the FCC rules for electromagnetic interference.
– REACH & RoHS: Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment.
– IEC 61000-6-2/6-4: Electromagnetic compatibility standards for industrial environments.
Documentation, including Declarations of Conformity and test reports, must accompany each shipment and be retained for audit purposes.
Packaging and Handling
Encoders must be packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use anti-static materials where applicable and ensure packaging meets ISTA 3A standards for vibration and drop resistance. Include:
– Protective foam or cushioning to secure the device.
– Moisture barrier for humidity-sensitive environments.
– Clearly labeled orientation and fragile indicators.
Handle encoders with ESD-safe practices in warehouses and during installation to prevent electrostatic discharge damage.
Shipping and Transportation
Ship encoders via certified logistics partners experienced in handling sensitive electronic components. Key requirements:
– Maintain temperatures between -20°C and +60°C during transit.
– Avoid exposure to condensation, dust, and corrosive environments.
– Use tracked and insured shipping with real-time monitoring where possible.
– For international shipments, provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
Classify encoders under the correct HS Code (e.g., 8543.70 for electrical transducers) to ensure accurate customs clearance.
Import/Export Controls
Verify whether encoders or their components are subject to export restrictions under regulations such as:
– EAR (Export Administration Regulations) – U.S. Department of Commerce.
– ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) – If used in defense applications.
– Dual-Use Regulations – Especially for high-precision industrial encoders.
Obtain necessary export licenses or authorizations before shipping to controlled destinations. Maintain records of all export transactions for a minimum of five years.
Inventory Management and Traceability
Implement a serial-number-based tracking system for all encoders to ensure full traceability from manufacture to end-user. Log key data including:
– Batch/lot numbers
– Manufacturing date
– Calibration information
– Shipping and delivery details
This supports warranty claims, recalls, and compliance audits.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Ensure installation follows manufacturer specifications and local electrical safety codes (e.g., NEC, IEC 60364). Include:
– Proper grounding and shielding to avoid noise interference.
– Use of recommended cable types and connectors.
– Verification of ingress protection (IP) rating suitability for the environment (e.g., IP67 for wet/dusty areas).
Provide end-users with installation manuals and safety data sheets (SDS) if applicable.
End-of-Life and Recycling
Dispose of encoders in accordance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives. Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to ensure:
– Safe dismantling and material recovery.
– Proper handling of hazardous components.
– Documentation of recycling for compliance reporting.
Audit and Documentation Retention
Conduct annual compliance audits covering logistics, export controls, and environmental regulations. Retain all relevant records—including shipping documents, compliance certificates, and transaction logs—for the legally required period (typically 5–7 years).
Adhering to this guide ensures operational efficiency, legal compliance, and customer trust in the Encoder supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Encoder:
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate encoder requires a thorough evaluation of application requirements, including resolution, accuracy, environmental conditions, installation constraints, and communication protocols. Both rotary and linear encoders offer distinct advantages depending on the use case, and the choice between absolute and incremental types should align with system needs for position tracking and power cycling. After assessing technical specifications, reliability, and cost-effectiveness from multiple suppliers, it is recommended to select an encoder that balances performance with long-term durability and compatibility with existing control systems. Engaging with reputable manufacturers and considering support, lead times, and scalability will ensure a reliable supply chain and optimal integration into the overall system. Ultimately, a well-sourced encoder contributes significantly to system precision, efficiency, and operational success.