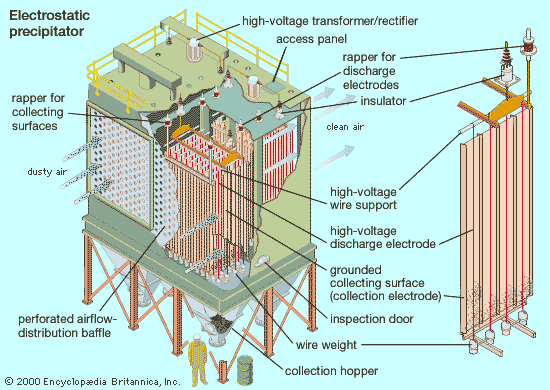
The global electrostatic precipitator market is experiencing robust growth, driven by escalating air pollution concerns and stringent environmental regulations across key industries such as power generation, cement, and metallurgy. According to Grand View Research, the market size was valued at USD 14.9 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts steady expansion, citing increased adoption of clean coal technologies and industrialization in emerging economies as key growth catalysts. With governments worldwide tightening emission norms, particularly for particulate matter, demand for high-efficiency air pollution control systems like electrostatic precipitators is surging. This growth trajectory has intensified competition among manufacturers, leading to significant technological advancements in collection efficiency, energy consumption, and system durability. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as industry leaders, setting benchmarks in innovation, global reach, and performance reliability. Here, we present the top 10 electrostatic precipitator manufacturers shaping the future of industrial emission control.
Top 10 Electrostatic Participator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Leading Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) Supplier
Domain Est. 1995
Website: babcock.com
Key Highlights: OEM electrostatic precipitators (ESP), along with engineered rebuilds and upgrades, provide effective particulate control in a wide range of utility and ……
#2 Electrostatic Precipitators (ESP) Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nwl.com
Key Highlights: NWL is a leading manufacturer of Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) products, including power supplies/ancillaries and controls for ESPs….
#3 Electrostatic Precipitator Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
#4 Electrostatic Precipitators Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2003
Website: himenviro.com
Key Highlights: HIMENVIRO has installed numerous electrostatic precipitators in various fields of application. We have built more than 200 precipitators within last 5 years….
#5 Electrostatic precipitator / dry and wet gas cleaning
Domain Est. 1995
Website: gea.com
Key Highlights: GEA’s Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) uses electrostatic force to remove particulates from a flue gas stream. The physical principle applied in ESP sets no ……
#6 Electrostatic Precipitator
Domain Est. 1998
Website: power.mhi.com
Key Highlights: Electrostatic Precipitators (EPs) contribute to the preservation of the air environment in a wide range of fields, including thermal power plants….
#7 Beltran Technologies Wet Electrostatic Precipitator Air Pollution …
Domain Est. 2007
Website: beltrantechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Beltran systems include: Advanced wet and dry electrostatic precipitators, scrubbers, fume coalescers, biomass gasification with syngas cleaning….
#8 Electrostatic precipitators (Omnivise electrical solutions)
Domain Est. 2007
Website: siemens-energy.com
Key Highlights: Electrostatic precipitators (ESP) collect dust in the flue gas produced by the boiler and other components. They support air pollution control at thermal power ……
#9 Electrostatic Precipitator
Domain Est. 2013
Website: antaichina.com
Key Highlights: Electrostatic precipitator-ESP dust collector. Product List. Contact Us. Tel: +86-532-88138566. Mobile(Whatsapp): +86-15753219207….
#10 Electrostatic Precipitators
Website: shi.co.jp
Key Highlights: The SHI Group has made numerous deliveries of electrostatic precipitators, exceeding 500 units in wide range of fields that include electric power, steel ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electrostatic Participator
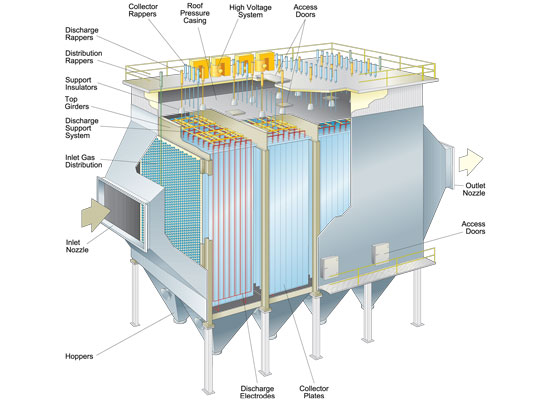
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electrostatic Precipitators
The global market for electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) is projected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing environmental regulations, industrial expansion, and a heightened focus on air quality management. Key trends shaping the electrostatic precipitator market in 2026 include:
-
Stringent Emission Regulations: Governments worldwide, particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific, are enforcing tighter air pollution control standards. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Union’s Industrial Emissions Directive are mandating reduced particulate matter (PM) emissions from power plants, cement kilns, and steel manufacturing facilities. This regulatory push is driving demand for high-efficiency ESPs.
-
Growth in Power Generation and Heavy Industries: Despite the shift toward renewable energy, coal- and gas-fired power plants remain significant in emerging economies such as India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. These facilities continue to rely on ESPs for flue gas cleaning. Additionally, the expansion of heavy industries—including cement, metallurgy, and glass manufacturing—supports sustained demand for electrostatic precipitation technology.
-
Technological Advancements and Hybrid Systems: By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly integrating advanced control systems, pulse energization, and hybrid designs (e.g., combining ESPs with fabric filters or wet scrubbers) to enhance efficiency, especially for fine particulate (PM2.5) and ultrafine particle capture. IoT-enabled monitoring and predictive maintenance are becoming standard, improving operational reliability and reducing downtime.
-
Rise of Wet Electrostatic Precipitators (WESPs): WESPs are gaining traction due to their ability to remove sub-micron particles, aerosols, and acid mists—particularly in applications involving high moisture content or sticky particulates. Industries such as waste incineration, chemical processing, and biomass energy are increasingly adopting WESPs to meet emission compliance.
-
Asia-Pacific as a Dominant Market: The Asia-Pacific region is expected to lead the global ESP market in 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and government initiatives to combat air pollution in countries like China and India. China’s “Blue Sky” campaign and India’s National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) are accelerating ESP adoption in industrial and utility sectors.
-
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus: As industries aim to lower their carbon footprint, ESP manufacturers are focusing on energy-efficient designs that reduce power consumption without compromising collection efficiency. Innovations such as smart power control and low-temperature ESPs contribute to improved sustainability profiles.
-
Market Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships: The competitive landscape is witnessing consolidation, with key players such as Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Thermax, and GE Steam Power expanding their portfolios through acquisitions and joint ventures. These collaborations aim to deliver integrated air pollution control solutions and enhance global reach.
-
Aftermarket and Retrofit Demand: A significant portion of the 2026 market growth is expected to come from retrofitting older ESP units to meet modern emission standards. Upgrades often include installing advanced electrodes, control systems, and rapping mechanisms to improve performance and extend equipment lifespan.
In conclusion, the 2026 electrostatic precipitator market reflects a convergence of regulatory pressure, technological innovation, and industrial demand. As air quality becomes a critical public and corporate priority, ESPs will remain a cornerstone technology in industrial emission control, with evolving capabilities to meet future environmental challenges.
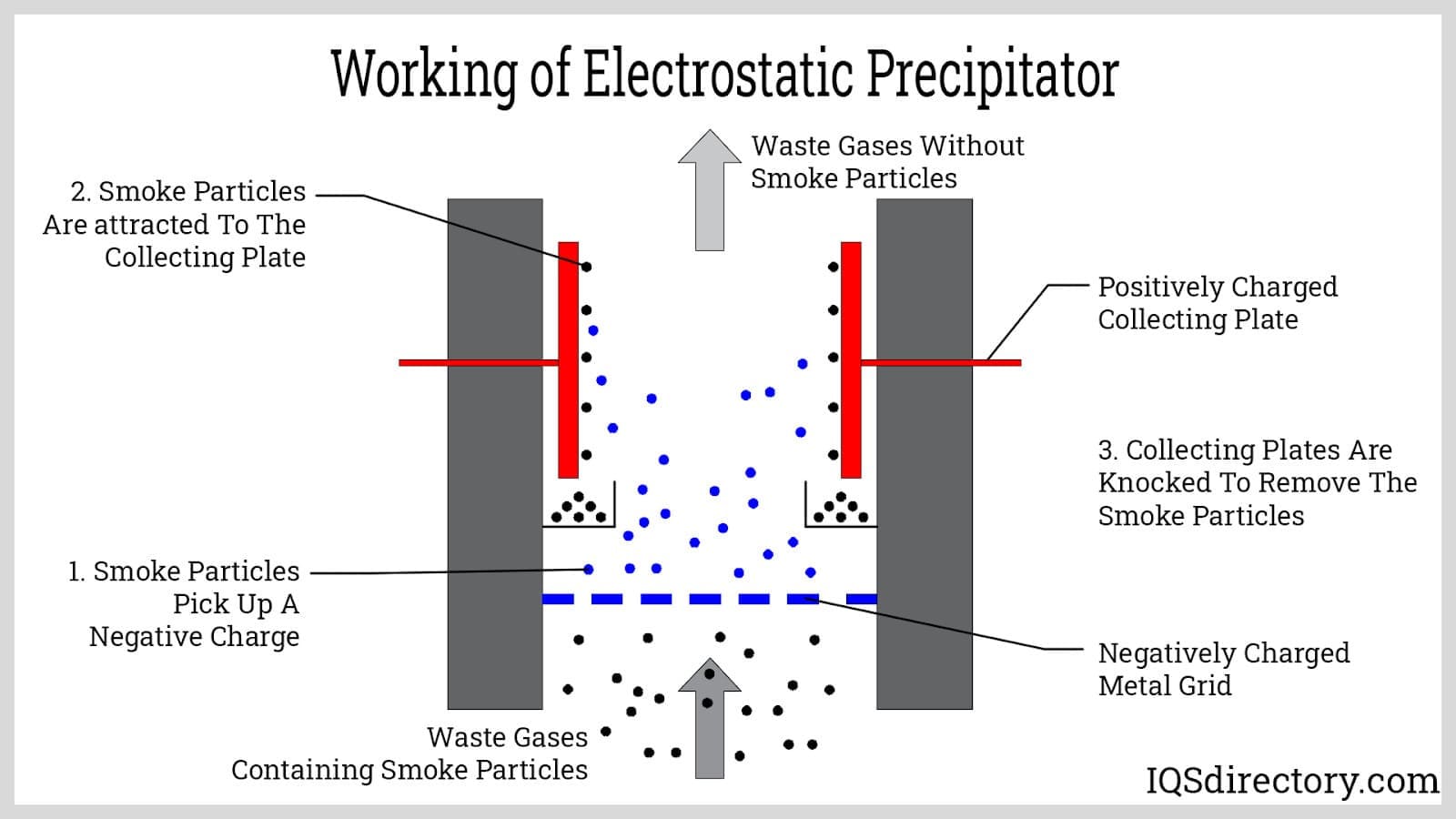
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Electrostatic Precipitators: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) involves navigating several critical challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and significant financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Performance Specifications
Procuring ESPs without clearly defined performance criteria—such as collection efficiency, gas flow rates, temperature tolerance, and particulate size removal—can result in underperforming systems. Suppliers may meet minimum contractual terms but deliver units unsuitable for specific industrial applications, leading to non-compliance with environmental regulations.
Substandard Materials and Construction
To reduce costs, some suppliers use inferior materials (e.g., low-grade steel, inadequate insulation, or poor electrode coatings), which compromise longevity and reliability. These shortcomings often surface only after prolonged operation, resulting in frequent maintenance, unplanned downtime, and shortened equipment lifespan.
Lack of Third-Party Certification and Testing
Failing to verify certifications (such as ISO, CE, or industry-specific standards) or to require factory acceptance tests (FAT) increases the risk of receiving non-compliant equipment. Without independent validation, performance claims remain unverified, exposing buyers to operational and regulatory risks.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Documentation
Poor technical documentation, lack of spare parts availability, and limited access to qualified service engineers can severely impact maintenance and troubleshooting. This is especially problematic when sourcing from overseas suppliers with weak local support networks.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Use of Patented Technology
Some suppliers may incorporate patented designs, control systems, or proprietary electrode configurations without proper licensing. Buyers risk becoming complicit in IP infringement, potentially facing legal action, import bans, or forced equipment modification.
Reverse-Engineered or “Knock-Off” Designs
Low-cost ESPs may be based on reverse-engineered versions of established OEM equipment. These clones often lack the original design integrity, performance optimizations, and safety features, increasing failure risks and voiding warranties.
Ambiguous Ownership of Custom Designs
When commissioning custom ESPs, unclear contractual terms regarding IP ownership can lead to disputes. Suppliers may retain rights to design improvements or use the custom design for competing clients, undermining the buyer’s competitive advantage.
Limited Access to Firmware and Software
Modern ESPs rely on proprietary control software for optimal operation. Suppliers may restrict access to source code, firmware updates, or configuration tools, creating vendor lock-in and reducing operational flexibility.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Define detailed technical specifications and performance guarantees.
– Conduct supplier audits and request proof of certifications.
– Include IP clauses in contracts to ensure freedom to operate and clarify ownership.
– Require transparency in design sources and component origins.
– Engage independent engineering consultants for pre-purchase review.
Proactively addressing quality and IP issues during procurement ensures reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection against legal and operational vulnerabilities.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electrostatic Precipitator
Overview
An Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) is an industrial emission control device used to remove fine particulate matter, such as dust and smoke, from exhaust gases using electrostatic forces. Proper logistics and compliance management are critical to ensure safe handling, transportation, installation, and regulatory adherence throughout the ESP’s lifecycle.
Transportation & Handling
- Packaging: ESP components (e.g., discharge electrodes, collection plates, insulators, high-voltage transformers) must be securely packaged in weather-resistant crates with shock-absorbing materials to prevent deformation or contamination.
- Labeling: Clearly label all packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “High Voltage Equipment”) and include shipment manifests with part numbers and weights.
- Transportation Mode: Use flatbed trucks or container freight depending on component size. Over-dimensional loads may require special permits and route planning.
- On-site Handling: Use cranes or forklifts with appropriate lifting fixtures. Avoid dragging or tilting sensitive components. Follow OEM-recommended lifting points and safety protocols.
Installation Requirements
- Site Preparation: Ensure foundation design meets load-bearing specifications. Confirm proper alignment, leveling, and anchoring as per engineering drawings.
- Clearance & Access: Maintain required clearance around the ESP for maintenance, electrical access, and safety egress. Include space for rapping systems and hopper discharge.
- Electrical Connections: Install high-voltage cables in protected conduits. Bond and ground all metallic parts to prevent static discharge. Use certified electricians compliant with NFPA 70 (NEC) or IEC 60364 standards.
- Ductwork Integration: Align inlet and outlet ducts precisely to avoid gas flow turbulence. Use expansion joints to accommodate thermal movement.
Regulatory Compliance
- Emissions Standards: ESPs must comply with local and international air quality regulations (e.g., U.S. EPA Clean Air Act, EU Industrial Emissions Directive). Verify ESP performance meets required particulate matter (PM) removal efficiency (typically ≥99%).
- Permitting: Obtain necessary environmental permits prior to operation. Include ESP specifications in permit applications and conduct stack testing for compliance verification.
- Electrical Safety: Comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.303 (electrical installations) and IEEE 516 (live-line work). Use lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance.
- Hazardous Locations: In explosive environments (e.g., combustible dust), ensure ESP design meets ATEX (EU) or NEC Class I/II Divisions (U.S.) standards.
Operational & Maintenance Compliance
- Monitoring Systems: Install continuous opacity monitors (COM) or particulate matter (PM) CEMS to ensure ongoing compliance. Calibrate regularly per EPA Method 9 or EN 13284-1.
- Inspection Schedule: Conduct routine visual and electrical inspections. Check for electrode alignment, insulator cleanliness, and rapping system functionality.
- Waste Handling: Collected particulate (fly ash) may be classified as hazardous waste. Analyze material per TCLP (U.S.) or Waste Framework Directive (EU) and dispose of through licensed facilities.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain logs of inspections, emissions data, maintenance activities, and component replacements for audit purposes (retain minimum 5 years).
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Leak Prevention: Seal all flanges and access doors to prevent fugitive emissions. Conduct annual leak detection audits.
- Worker Protection: Provide PPE for high-voltage work (e.g., dielectric gloves, face shields). Train personnel on arc flash hazards and emergency shutdown procedures.
- Decommissioning: When retiring an ESP, de-energize and ground all electrical systems. Decontaminate components and recycle metals where possible in accordance with WEEE or RCRA regulations.
Documentation & Certification
- Maintain copies of:
- Equipment manuals and as-built drawings
- Third-party certification (e.g., CE, UL)
- Emissions test reports
- Electrical safety inspection records
- Operator training certifications
Ensure all documentation is accessible for regulatory audits and facility transfers.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Electrostatic Precipitator
In conclusion, sourcing an electrostatic precipitator (ESP) requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, operational requirements, cost-effectiveness, and long-term maintenance needs. The selection process should align with the specific industrial application, emission control standards, and air quality goals. Key factors such as gas flow rate, particle characteristics, space constraints, energy efficiency, and compliance with environmental regulations must be carefully assessed.
Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer proven designs, robust after-sales support, and performance guarantees is essential to ensure reliable and efficient operation. Additionally, considering scalability and future regulatory changes can enhance the long-term viability of the investment.
Ultimately, a well-sourced electrostatic precipitator not only contributes to cleaner air and regulatory compliance but also supports sustainable industrial operations by minimizing environmental impact and optimizing operational efficiency.