The global electrophoresis equipment market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in genomics, proteomics, and biopharmaceutical research. According to Mordor Intelligence, the electrophoresis market was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in molecular biology techniques and increasing investments in life sciences research. Electrophoresis power supplies, as critical components of these systems, play a pivotal role in ensuring consistent and reproducible results. With expanding applications in clinical diagnostics, academic research, and drug discovery, the demand for reliable, high-performance power supplies has intensified. This growth trajectory has attracted key players worldwide, fostering innovation and competition. Based on market presence, technological advancements, and product portfolios, the following is a data-driven overview of the top 10 electrophoresis power supply manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 10 Electrophoresis Power Supply Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Electrophoresis
Domain Est. 1995
Website: spellmanhv.com
Key Highlights: Spellman teamed with a leading global partner to design a hot-switch power supply that provides ±30kV at 300µA, and has the capability to switch from positive ……
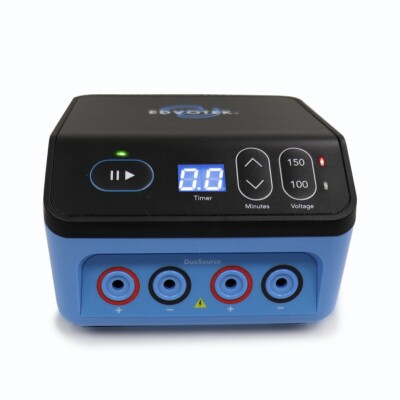
#2 DuoSource Power Supply
Domain Est. 1997
Website: edvotek.com
Key Highlights: The DuoSource™ electrophoresis power supply has been reimagined and now includes a built-in timer. Run gels quickly in only 20-30 minutes at 150 V!…
#3 Electrophoresis Power Supply
Domain Est. 1999
Website: fison.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.9 (657) · Free deliveryFison Power Supply provides a stable and adjustable electrical current for running gel electrophoresis experiments. They provide precise voltage…
#4 Electrophoresis Power Supplies
Domain Est. 2001
Website: netascientific.com
Key Highlights: At Neta Scientific, we enable your mission by centralizing superior lab supplies and supply chain management with our unique ability to provide ……
#5 Electrophoresis Power Supplies
Domain Est. 2006
Website: thermofisher.com
Key Highlights: We offer a range of powerful, easy-to-use electrophoresis power supplies for protein electrophoresis and nucleic acid electrophoresis applications….
#6 Electrophoresis Power Supply
Domain Est. 2009
Website: majorsci.com
Key Highlights: Our power supplies are ideal for nucleic acid and protein electrophoresis as well as blotting. CE and ETL certificated power supplies are available to fit ……
#7 EC
Domain Est. 2012
Website: marshallscientific.com
Key Highlights: In stock $39 deliveryThe EC Apparatus Electrophoresis Power Supply EC-135. Specifications: Maximum Voltage 250V, Voltage Steps Low Range Setting: 20-130V (Increments of 10V)…
#8 Biologix® Mini 300V Electrophoresis Power Supply, 1 Piece/Pack
Domain Est. 2013
Website: biologixusa.com
Key Highlights: In stock 30-day returnsThese Power Supplies are ideal for a variety of DNA, RNA, and protein electrophoresis, as well as blotting. Features: • Compact, user-friendly design….
#9 Universal Electrophoresis Power Supply
Domain Est. 2016
Website: nusep.us
Key Highlights: In stock 12-day deliverySuited for vertical gel electrophoresis and mini vertical gel electrophoresis. Features. Output: constant voltage, constant current and constant power….
#10 Gel Electrophoresis Power Supplies
Domain Est. 2023
Website: scitekglobal.com
Key Highlights: The electrophoresis power supply features a backlit LCD touch screen that is user friendly and easy to use. The touchscreen and user interface design makes ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electrophoresis Power Supply

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electrophoresis Power Supplies
The global electrophoresis power supply market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by advancements in life sciences research, rising demand for protein and nucleic acid analysis, and the expansion of biopharmaceutical development. Several key trends are shaping the market landscape:
-
Increased Demand from Biopharmaceutical and Academic Research
The growing focus on personalized medicine, genomics, and proteomics is fueling demand for precise and reliable electrophoresis systems. Electrophoresis power supplies—critical for DNA, RNA, and protein separation—are seeing heightened adoption in pharmaceutical R&D and academic laboratories. As biologics and gene therapies advance, so does the need for high-precision electrophoretic techniques, supporting market expansion. -
Integration of Smart Technology and Automation
By 2026, a significant trend is the integration of digital interfaces, programmable protocols, and IoT-enabled features in electrophoresis power supplies. Vendors are launching models with touchscreen controls, cloud connectivity, and remote monitoring capabilities, improving reproducibility and user convenience. This shift toward smart laboratory equipment aligns with broader trends in lab automation and digitalization. -
Miniaturization and Portability
There is a growing demand for compact, benchtop, and portable electrophoresis power supplies—especially in field research, point-of-care diagnostics, and resource-limited settings. These systems offer energy efficiency and ease of use without compromising performance, making them ideal for educational institutions and smaller labs. -
Focus on Safety and Energy Efficiency
Manufacturers are prioritizing safety features such as over-voltage protection, short-circuit prevention, and temperature monitoring. Additionally, energy-efficient designs are being adopted to meet sustainability goals and reduce operational costs, aligning with green laboratory initiatives. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and South Korea, is expected to register the highest growth rate due to rising investments in life sciences infrastructure, increasing government funding for research, and the expansion of contract research organizations (CROs). Local manufacturing and cost-effective product offerings are further accelerating market penetration. -
Customization and Multi-Functionality
End-users are demanding power supplies that support a wide range of electrophoresis techniques (e.g., agarose, SDS-PAGE, native gels) with adjustable voltage, current, and power settings. Multi-mode power supplies capable of constant voltage, current, or power output are becoming standard, enhancing versatility across applications. -
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Collaborations
Leading players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bio-Rad Laboratories, and GE Healthcare are investing in R&D and forming strategic partnerships with academic and biotech institutions. Mergers and product innovation are key strategies to capture market share and address evolving customer needs.
In conclusion, the 2026 electrophoresis power supply market reflects a convergence of technological innovation, expanding application areas, and geographic diversification. As research complexity increases and laboratories demand smarter, safer, and more efficient tools, electrophoresis power supplies will remain a foundational component in molecular biology workflows.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Electrophoresis Power Supplies: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing electrophoresis power supplies requires careful evaluation beyond basic specifications to ensure performance, safety, and legal compliance. Overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to significant operational, financial, and reputational risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Compromising on Build Quality and Component Reliability
A common mistake is prioritizing low cost over long-term durability and precision. Low-quality power supplies often use substandard components (e.g., capacitors, transformers, cooling systems) that degrade quickly under continuous use, leading to inconsistent voltage/current output and premature failure. Poor thermal management can cause overheating, affecting gel resolution and creating safety hazards.
Impact: Unreliable results, increased downtime, higher total cost of ownership due to frequent replacements or repairs.
Best Practice: Source from manufacturers with proven track records, request third-party test reports (e.g., CE, UL, ISO certifications), and evaluate warranty terms and service support.
2. Inadequate Safety and Compliance Features
Some suppliers, especially lesser-known or non-specialist brands, may omit essential safety protections such as over-voltage, over-current, over-temperature, and short-circuit safeguards. These omissions increase the risk of equipment damage, sample loss, or even fire.
Impact: Risk to personnel, lab equipment, and experimental integrity. Non-compliance with local safety regulations (e.g., IEC 61010) may void insurance or fail audits.
Best Practice: Verify that units meet international safety standards and include comprehensive protection circuits. Ensure documentation is available in your region’s language and complies with regulatory requirements.
3. Falsified or Inaccurate Specifications
Some suppliers, particularly on e-commerce platforms, may exaggerate technical capabilities—such as maximum voltage, current, or power output—or omit critical limitations like duty cycle or load regulation. This can result in underperforming equipment that fails during high-demand runs.
Impact: Inability to run standard protocols (e.g., high-voltage PAGE or large-format gels), leading to failed experiments and wasted reagents.
Best Practice: Request detailed technical datasheets, verify specs with independent reviews or lab testing, and favor suppliers that provide traceable calibration certificates.
4. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers that replicate designs or firmware from established brands (e.g., Bio-Rad, Thermo Fisher, Hoefer) without proper licensing exposes buyers to legal and ethical risks. Counterfeit or cloned units may violate patents, trademarks, or software copyrights.
Impact: Potential legal liability, lack of technical support, no access to firmware updates, and compromised data integrity due to unverified control algorithms.
Best Practice: Purchase directly from authorized distributors or reputable OEMs. Conduct due diligence on supplier legitimacy, including checking for registered trademarks, patents, and original design documentation.
5. Lack of Software and Firmware Transparency
Modern electrophoresis power supplies often include programmable methods and digital interfaces. Cloned or low-cost units may use pirated or reverse-engineered firmware, which can introduce bugs, lack security updates, or fail to comply with data integrity standards (e.g., ALCOA+ for regulated environments).
Impact: Non-compliance in GLP/GMP labs, unreliable method reproducibility, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
Best Practice: Choose suppliers that openly disclose firmware versioning, offer update paths, and adhere to software licensing agreements.
6. Poor After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if initial quality appears acceptable, sourcing from suppliers without local service networks or long-term parts availability can render equipment unusable after minor failures.
Impact: Extended downtime, forced replacement of functional systems, and increased waste.
Best Practice: Evaluate service response times, spare parts lead times, and availability of technical documentation before purchase.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, laboratories can ensure they invest in reliable, safe, and legally compliant electrophoresis power supplies that support accurate and reproducible research.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electrophoresis Power Supply
Regulatory Compliance
Electrophoresis power supplies are electrical laboratory instruments that must meet specific regulatory requirements for safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and environmental standards. Compliance ensures user safety, legal market access, and environmental responsibility.
Safety Standards
- IEC 61010-1: This international standard governs safety requirements for electrical equipment used in measurement, control, and laboratory use. Electrophoresis power supplies must comply with insulation, protection against electric shock, and mechanical hazard provisions.
- UL 61010-1 (USA): The U.S. adoption of IEC 61010-1, required for market entry in North America. Products should bear UL or CSA certification marks.
- EN 61010-1 (Europe): Mandatory for CE marking under the EU’s Low Voltage Directive (LVD). Compliance ensures electrical safety within the European Economic Area.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- IEC/EN 61326-1: Specifies EMC requirements for electrical equipment used in laboratory, industrial, and other environments. Ensures the power supply does not emit excessive electromagnetic interference and is immune to common disturbances.
- Devices must undergo radiated and conducted emission testing, as well as immunity testing (e.g., electrostatic discharge, surges).
Environmental & Chemical Compliance
- RoHS (EU Directive 2011/65/EU): Restricts the use of hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium in electrical equipment. Electrophoresis power supplies must be RoHS-compliant for sale in the EU.
- REACH (EC 1907/2006): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) in products. Suppliers must ensure compliance and provide safety data if requested.
- WEEE (Directive 2012/19/EU): Mandates proper recycling and disposal of electronic equipment. Manufacturers must register and provide take-back options in EU countries.
Regional Certification Marks
- CE Marking: Required for sale in the EU. Demonstrates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- FCC Part 15 (USA): Regulates electromagnetic emissions. Class A or B compliance may be required depending on the intended environment (industrial vs. residential).
- PSE Mark (Japan): Required for electrical products sold in Japan under the DENAN Law.
- KC Mark (South Korea): Mandatory for electrical safety and EMC compliance.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Proper packaging and shipping practices are essential to prevent damage during transit and ensure regulatory compliance.
Packaging Standards
- Use anti-static and shock-absorbent materials to protect sensitive electronic components.
- Include moisture barrier bags if shipping to humid climates or for long-term storage.
- Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators.
- Include all necessary documentation (user manual, safety sheets, compliance certificates) in a sealed internal pouch.
Shipping Documentation
- Commercial invoice specifying product description, HS code, value, and country of origin.
- Packing list detailing contents, weights, and dimensions.
- Certificate of Compliance (CoC) confirming adherence to IEC 61010-1, RoHS, and other relevant standards.
- Material Declaration (e.g., RoHS, REACH) upon request from importers.
Import Considerations
- HS Code: Typically 9027.50 (instruments for physical or chemical analysis) or 8543.70 (electrical machines with individual functions). Confirm with local customs authorities.
- Import duties and taxes vary by country; consult local regulations.
- Some countries require additional registration (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, SONCAP in Nigeria).
Installation & User Compliance
End users must follow manufacturer guidelines to maintain compliance and ensure safe operation.
Site Requirements
- Stable power supply with proper grounding (earth connection).
- Operate within specified environmental conditions (temperature: 10–40°C, humidity: <80% non-condensing).
- Adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
User Responsibilities
- Perform regular electrical safety checks (e.g., inspect cables, test grounding).
- Use only manufacturer-approved accessories and consumables.
- Adhere to local biosafety and electrical safety protocols, especially in shared lab environments.
Disposal & End-of-Life
Electrophoresis power supplies are classified as electronic waste and must be disposed of responsibly.
- Follow WEEE directives in the EU: Return to designated e-waste collection points or use manufacturer take-back programs.
- Do not dispose of in regular trash.
- Data security: Reset or remove any user-programmable settings before disposal.
Summary
Compliance for electrophoresis power supplies spans safety, environmental, and regional regulations. Proper logistics—from packaging and documentation to end-of-life disposal—ensures legal operation, user safety, and environmental sustainability. Always verify local requirements before shipping or installing equipment.
Conclusion for Sourcing Electrophoresis Power Supply
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, supplier credibility, cost-efficiency, and long-term reliability, sourcing an electrophoresis power supply requires a balanced approach that prioritizes performance, safety, and compatibility with laboratory applications. The selected power supply must meet essential specifications such as voltage, current, and power output ranges appropriate for the intended electrophoresis techniques (e.g., agarose gel, SDS-PAGE, or DNA sequencing). Features like programmable run settings, safety protections (e.g., over-voltage, over-current, and overheating), digital displays, and consistent output stability are critical for reproducible results and user safety.
Furthermore, sourcing from reputable manufacturers or suppliers with strong technical support, warranty services, and compliance with international safety standards (such as CE, UL, or ISO) ensures durability and regulatory compliance. While cost is an important consideration, it should not compromise quality, especially in research or diagnostic environments where reliability directly impacts data integrity.
In conclusion, the ideal electrophoresis power supply should be sourced based on a comprehensive assessment of technical specifications, user requirements, service support, and total cost of ownership. Investing in a high-quality, versatile unit from a trusted supplier ultimately enhances experimental accuracy, lab efficiency, and long-term operational savings.