The global electron beam welding (EBW) machine market is witnessing steady expansion, driven by rising demand for high-precision welding in aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. According to Mordor Intelligence, the industrial welding equipment market—of which electron beam welding is a critical niche—is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. Grand View Research further highlights that advancements in vacuum technology and the increasing adoption of automation in production lines are accelerating the uptake of electron beam welding systems, with the global EBW market expected to expand significantly over the same period. As industries prioritize weld integrity, repeatability, and minimal distortion in critical components, leading manufacturers are innovating to deliver more efficient, compact, and digitally integrated solutions. In this evolving landscape, the following ten companies have emerged as key players, shaping the future of electron beam welding technology with robust engineering and global reach.
Top 10 Electron Welding Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Sciaky, Inc.
Founded: 1939
Website: sciaky.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1939, Sciaky is the worldwide leader in industrial 3D metal printing technology and the most trusted name in electron beam welding….
#2 Electron Beam Welding
Website: ptreb.com
Key Highlights: PTR manufactures and services Electron Beam Welders and provides electron beam welding job shop services in the US with the most modern EB welding machines….
#3 Electron Beam Welding Solutions
Website: sst-ebeam.com
Key Highlights: As a global medium-sized company, we are one of the leading developers and manufacturers of electron beam machines. These include electron beam welding machines ……
#4 Acceleron Inc.
Website: acceleroninc.com
Key Highlights: Acceleron Inc is at the forefront of cutting-edge welding technologies, specializing in electron beam welding services that outperform traditional welding ……
#5 Homepage
Website: pro-beam.com
Key Highlights: The pro-beam Group is a company in the field of electron beam and laser technology. It specializes in electron beam welding, hardening and drilling….
#6 Cambridge Vacuum Engineering
Website: camvaceng.com
Key Highlights: ELECTRON BEAM WELDING MACHINES. Electron beam welding (EBW) is a fusion welding process that uses a high-velocity electron beam to join two materials ……
#7 Electron Beam Equipment
Website: electronbeamwelding.com
Key Highlights: Electron Beam Engineering Services (EBES) provides electron beam welding and laser beam welding systems and weld tooling accessories….
#8 EB Industries: Electron Beam Welding
Website: ebindustries.com
Key Highlights: We are the preeminent supplier of Electron Beam Welding, Laser Beam Welding, and Laser Hermetic Sealing in North America. All industries served, NADCAP, ……
#9 Electron Beam Welding Experts
Website: ebpglobal.com
Key Highlights: EBP is Europe’s most experienced electron beam welding specialist. As an increasing number of our customers have asked us to provide the hardware for their ……
#10 Electron Beam Welding, LLC
Founded: 1966
Website: electronbeamweldinginc.com
Key Highlights: A leading edge electron beam welding company since 1966, we partner with our customers to provide high performance quality results….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electron Welding Machine

H2: Market Trends in Electron Beam Welding Machines (2026 Outlook)
The global electron beam welding (EBW) machine market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising demand for high-precision welding in critical industries, and the ongoing shift toward automation and sustainable production. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Increased Adoption in Aerospace and Defense
By 2026, the aerospace and defense sectors are expected to remain the largest end-users of electron beam welding machines. The need for lightweight, high-strength materials and precision joining of complex components—such as turbine blades, engine parts, and satellite structures—is fueling demand. EBW’s ability to produce deep, narrow welds with minimal distortion makes it indispensable in these high-value applications. -
Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Battery Manufacturing
The surge in electric vehicle production is creating new opportunities for electron beam welding, particularly in battery pack assembly and powertrain components. EBW offers superior weld quality in conductive materials like copper and aluminum, essential for high-efficiency EV systems. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to increasingly integrate EBW into automated battery production lines to ensure reliability and thermal stability. -
Advancements in Vacuum and Non-Vacuum EBW Systems
Technological innovations are reducing the limitations of traditional vacuum-based EBW systems. Non-vacuum (or low-pressure) electron beam welding is gaining traction due to lower operational costs and greater flexibility in handling large or complex parts. By 2026, hybrid systems that combine vacuum efficiency with atmospheric adaptability are expected to capture a growing market share, especially in automotive and industrial manufacturing. -
Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Electron beam welding machines are becoming smarter through integration with IoT, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven process optimization. By 2026, predictive maintenance, digital twin modeling, and closed-loop control systems will enhance precision, reduce downtime, and improve quality assurance—making EBW a key enabler of smart factories. -
Regional Market Expansion
While North America and Europe continue to lead in EBW adoption due to advanced aerospace and R&D infrastructure, the Asia-Pacific region—particularly China, Japan, and South Korea—is expected to witness the highest growth rate by 2026. This is attributed to rising industrial automation, government support for high-tech manufacturing, and expanding defense and EV sectors. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
With increasing emphasis on green manufacturing, electron beam welding is gaining favor for its high energy efficiency and low material waste compared to traditional welding methods. Manufacturers are investing in energy-optimized EBW systems and recycling vacuum components to meet environmental regulations, a trend that will accelerate through 2026.
In conclusion, the electron beam welding machine market in 2026 will be defined by technological innovation, sector-specific customization, and digital integration. As industries demand higher precision and efficiency, EBW is set to evolve from a niche technique into a cornerstone of advanced manufacturing.
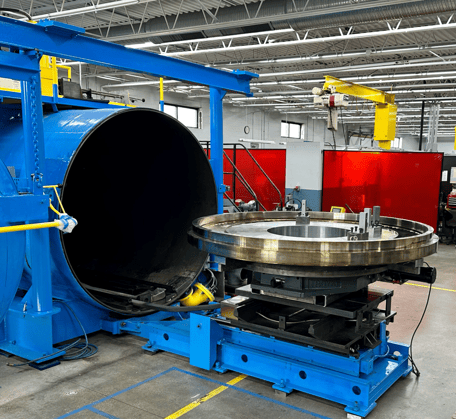
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Electron Beam Welding Machines (Quality & IP)
Sourcing an Electron Beam (EB) Welding machine is a significant investment requiring careful due diligence. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to major operational, financial, and legal risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Machine Quality and Performance
1. Inadequate Vacuum System Performance
A substandard vacuum system leads to poor beam stability, contamination, and weld defects. Pitfalls include under-specified pumps, leaky chambers, or insufficient maintenance support, resulting in high downtime and inconsistent weld quality.
2. Unreliable Electron Gun and Beam Control
Low-quality electron guns may suffer from short lifespans, beam instability, or inaccurate focusing. This compromises weld precision and repeatability, especially critical in aerospace or medical applications.
3. Incomplete or Poorly Integrated Safety Systems
EB machines generate high voltage and X-rays. Sourcing from suppliers with inadequate radiation shielding, interlock systems, or safety certifications (e.g., CE, ANSI) poses serious safety and compliance risks.
4. Lack of Calibration and Repeatability Documentation
Without traceable calibration records and performance validation (e.g., beam alignment, power consistency), ensuring long-term process reliability becomes difficult. This undermines quality assurance in regulated industries.
5. Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many suppliers, especially lesser-known or offshore manufacturers, lack local service networks. Delays in technical support or spare parts can halt production for extended periods.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Compliance Risks
1. Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Some suppliers use cloned or unauthorized versions of critical components (e.g., control systems, power supplies). This not only affects reliability but may expose the buyer to IP infringement claims.
2. Unclear or Missing IP Ownership in Custom Solutions
When machines are customized, unclear contracts may leave IP ownership—such as software algorithms or process parameters—ambiguous. This can restrict your ability to modify, service, or scale the technology.
3. Non-Compliance with Export Controls and Regulations
EB welding technology may be subject to export controls (e.g., ITAR, EAR) due to dual-use potential. Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers risks shipment delays, legal penalties, or operational restrictions.
4. Proprietary Software Lock-In
Some suppliers use closed-source, proprietary software with restrictive licensing. This limits your ability to integrate with factory systems, perform in-house diagnostics, or switch service providers.
5. Hidden IP in Consumables and Consumable Processes
Patented filament designs, chamber liner materials, or process recipes may be embedded in the machine. Unlicensed use could lead to infringement if the supplier does not grant appropriate rights.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough technical audits and factory acceptance testing (FAT).
- Verify supplier certifications (ISO, AS9100, etc.) and request references.
- Perform IP due diligence—review contracts, component sourcing, and software licenses.
- Ensure export compliance documentation is provided upfront.
- Negotiate clear IP ownership and service rights in procurement agreements.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures you acquire a reliable, compliant, and legally secure electron beam welding solution.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electron Beam Welding Machines
Electron beam welding (EBW) machines are high-precision, high-vacuum industrial systems used for deep-penetration, low-distortion welding in aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. Due to their complexity, radiation-emitting components, and international trade sensitivities, shipping and operating these machines require strict adherence to logistics and compliance protocols.
Regulatory Compliance
Electron beam welding machines are subject to multiple regulatory frameworks due to their use of high-voltage electrical systems, vacuum technology, and controlled radiation sources.
Radiation Safety Regulations
EBW machines generate X-rays as a byproduct of electron beam operation. Compliance with radiation protection standards is mandatory:
– IAEA Safety Standards (GSR Part 3): Applies to radiation-generating equipment design and operation.
– National Regulations (e.g., NRC in the U.S., ARPANSA in Australia, BfS in Germany): Requires registration of EBW equipment, radiation shielding certification, and operator licensing.
– Local Workplace Safety (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., HSE in the UK): Mandates radiation monitoring, controlled access zones, and safety interlocks.
Electrical and Equipment Standards
Electron beam systems operate at high voltages (typically 30–150 kV), requiring compliance with:
– IEC 60204-1: Safety of machinery – Electrical equipment of machines.
– UL/CSA/CE Marking: Required for sale and operation in North America and the European Union.
– EMC Compliance (IEC 61326): Ensures electromagnetic compatibility with surrounding equipment.
Export Controls and Trade Compliance
Due to dual-use potential (civilian and military applications), EBW machines may be subject to export control regulations:
– Wassenaar Arrangement: Controls export of dual-use goods and technologies, including high-energy beam welding systems.
– U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR): Check ECCN 2B225 for electron beam welding equipment; licenses may be required for certain destinations.
– EU Dual-Use Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2021/821): Requires export authorization for controlled technologies.
– Sanctions Screening: Verify end-user and destination against OFAC, UN, and EU sanctions lists.
Transportation and Logistics
Shipping an electron beam welding machine demands specialized handling due to its weight, sensitivity, and hazardous components.
Packaging and Handling
– Use custom-built wooden crates with shock-absorbing foam or air-ride suspension systems.
– Secure all moving parts (manipulators, vacuum chambers) with braces to prevent internal damage.
– Protect optical components and electron gun assemblies with sealed, anti-static packaging.
– Label crates with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators.
Shipping Modes
– Air Freight: For urgent or international shipments; requires IATA-compliant packaging and documentation. Limited by size/weight constraints.
– Sea Freight (FCL/LCL): Most common for heavy equipment; use 20’ or 40’ containers with climate control if needed.
– Overland Transport: Requires low-bed trailers and route planning to avoid low bridges or weight-restricted roads.
Customs Documentation
– Commercial Invoice with detailed technical specifications.
– Packing List with gross/net weights and dimensions.
– Certificate of Origin.
– Export License (if applicable under EAR or EU dual-use rules).
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill.
– Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for incidental hazardous materials (e.g., vacuum pump oils).
Installation, Site Preparation, and Commissioning
Proper site setup ensures compliance and operational safety.
Facility Requirements
– Floor Loading: Minimum 1,000 kg/m² (verify with manufacturer).
– Power Supply: Stable 3-phase power (e.g., 400V, 50/60 Hz) with dedicated circuit; voltage fluctuations must be <±5%.
– Cooling System: Chilled water supply (typically 15–25°C) with sufficient flow rate and pressure.
– Ventilation: Required for ozone and metal fumes; install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) near welding chamber.
Radiation Shielding and Safety Zones
– Install lead-lined walls or concrete enclosures as per radiation safety assessment.
– Mark controlled areas with warning signs (e.g., “Caution: X-Ray Radiation”).
– Conduct pre-operational radiation survey by certified health physicist.
Commissioning and Certification
– Perform vacuum integrity and high-voltage tests under manufacturer supervision.
– Calibrate beam alignment and control systems.
– Obtain operational license from national radiation authority before full operation.
Maintenance and Ongoing Compliance
Regular maintenance ensures safety and regulatory adherence.
Scheduled Maintenance
– Replace vacuum pump oil and filters per manufacturer guide.
– Inspect high-voltage cables and connectors for wear.
– Test safety interlocks, emergency stops, and radiation shielding annually.
Recordkeeping
– Maintain logs of radiation surveys, maintenance, operator training, and incident reports.
– Retain export documentation for at least 5 years (per EAR requirements).
Operator Training
– Provide certified training on EBW operation, radiation safety, and emergency procedures.
– Document training completion for regulatory audits.
Adherence to this guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient deployment of electron beam welding machines across global operations. Always consult local authorities and the equipment manufacturer for site-specific requirements.
Conclusion on Sourcing an Electron Beam Welding Machine
Sourcing an electron beam (EB) welding machine is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance manufacturing capabilities, particularly for high-precision, high-integrity applications in industries such as aerospace, medical devices, automotive, and advanced research. After evaluating technical specifications, supplier reliability, cost implications, maintenance requirements, and operational safety, it is evident that selecting the right EB welding system requires a comprehensive approach.
Key considerations include the required vacuum chamber size, beam power, control systems, automation integration, and compliance with safety and regulatory standards. It is crucial to partner with reputable suppliers offering proven technology, strong technical support, and training to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
While the initial capital investment and operational complexity of EB welding machines are higher compared to conventional welding systems, the benefits—such as deep penetration, minimal distortion, and superior weld quality in refractory and dissimilar metals—justify the cost for applications demanding the highest standards of precision and reliability.
In conclusion, sourcing an electron beam welding machine should align with long-term production goals, quality requirements, and technological advancement strategies. A thorough evaluation process, including site visits, supplier assessments, and pilot testing, will ensure the successful integration of this advanced technology into the manufacturing workflow, ultimately driving innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage.