The global electron beam welding (EBW) equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining solutions in aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial welding equipment market, which includes electron beam welding technologies, was valued at USD 17.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence further highlights the rising adoption of automated and advanced welding systems, projecting steady growth in the EBW segment due to its superiority in deep-penetration welding with minimal distortion. As industries prioritize precision, efficiency, and material integrity, leading manufacturers are investing in next-generation EBW systems featuring vacuum automation, real-time monitoring, and integration with Industry 4.0 platforms. Against this backdrop, the following nine companies have emerged as key players, driving innovation and capturing significant market share in the electron beam welding equipment landscape.
Top 9 Electron Beam Welding Equipment Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Electron Beam Welding
Website: ptreb.com
Key Highlights: PTR manufactures and services Electron Beam Welders and provides electron beam welding job shop services in the US with the most modern EB welding machines….
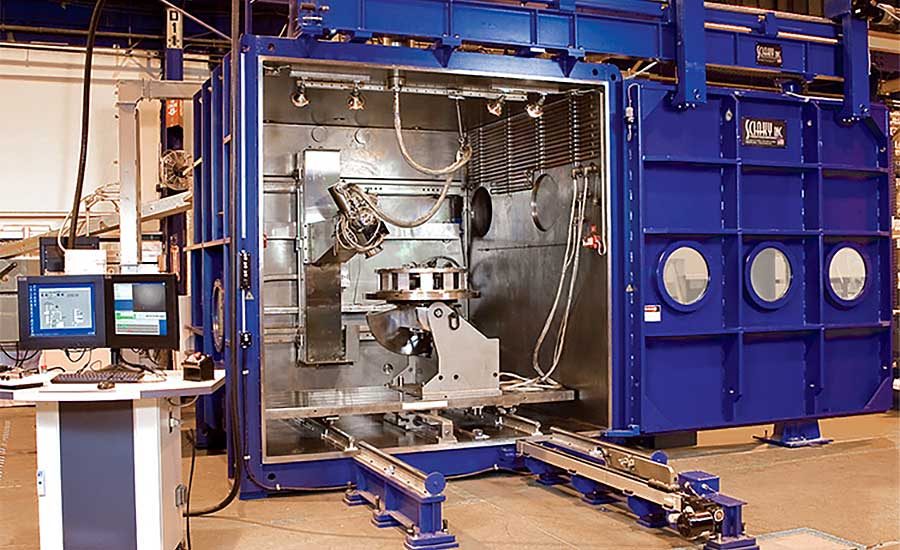
#2 Electron Beam Welding Systems
Website: sciaky.com
Key Highlights: Sciaky provides the highest-quality Electron Beam Welding Systems and EB Welding Services in the world. Learn more about our capabilities and track record….
#3 Electron Beam Welding, LLC
Founded: 1966
Website: electronbeamweldinginc.com
Key Highlights: A leading edge electron beam welding company since 1966, we partner with our customers to provide high performance quality results….
#4 Electron Beam Equipment
Website: electronbeamwelding.com
Key Highlights: Electron Beam Engineering Services (EBES) provides electron beam welding and laser beam welding systems and weld tooling accessories….
#5 EB Industries: Electron Beam Welding
Website: ebindustries.com
Key Highlights: We are the preeminent supplier of Electron Beam Welding, Laser Beam Welding, and Laser Hermetic Sealing in North America. All industries served, NADCAP, ……
#6 Electron Beam Welder
Website: electronbeamwelder.net
Key Highlights: Electron beam welder is a relatively sophisticated welding equipment that uses the principle of high-speed moving electron beam bombardment of the workpiece ……
#7 Electron Beam (EB) Welding Service, Precision Micro Welding …
Website: ebiweld.com
Key Highlights: Electron Beam Industries provides sub-contract electron beam welding services including EB welders, micro and precision welding as well as other services….
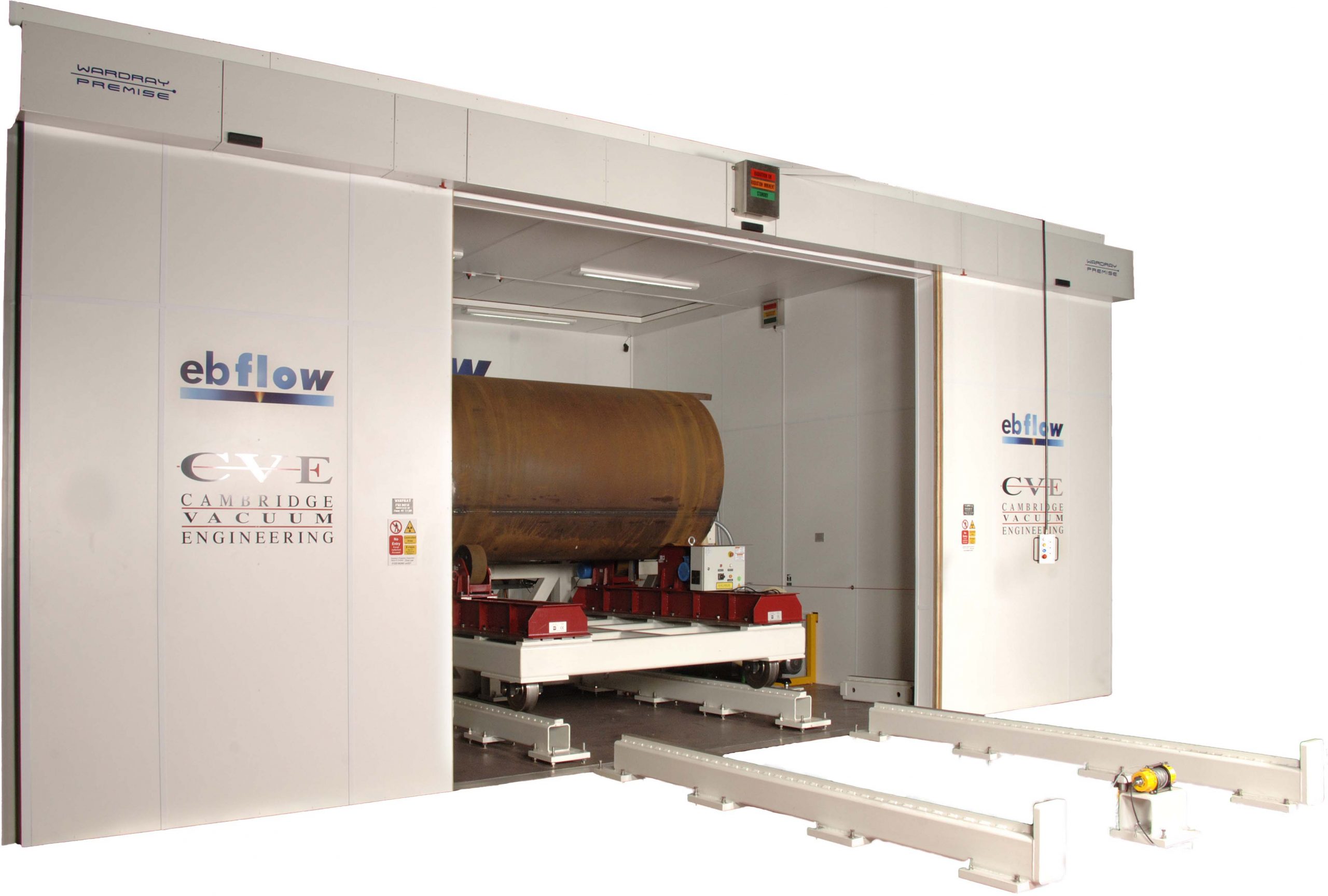
#8 Cambridge Vacuum Engineering
Website: camvaceng.com
Key Highlights: ELECTRON BEAM WELDING MACHINES. Electron beam welding (EBW) is a fusion welding process that uses a high-velocity electron beam to join two materials ……
#9 Electron Beam Welding Associates
Website: ebwelding.com
Key Highlights: Our electron beam welding services are useful in producing parts for all types of engines. We have proficiency in electron beam welding pressure vessels, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electron Beam Welding Equipment

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electron Beam Welding Equipment
The global electron beam welding (EBW) equipment market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising demand from high-precision industries, and growing emphasis on automation and sustainability. This analysis explores key trends shaping the EBW equipment landscape in 2026 under the H2 heading structure.
H2: Rising Adoption in Aerospace and Defense Sectors
One of the most prominent drivers of the EBW equipment market in 2026 is the increasing adoption within the aerospace and defense industries. These sectors demand high-strength, precision welds for components such as turbine blades, engine parts, and structural assemblies. Electron beam welding offers deep penetration, minimal distortion, and the ability to weld refractory and dissimilar metals—qualities essential for mission-critical applications. By 2026, continued investment in next-generation aircraft, space exploration technologies, and defense modernization programs is expected to fuel demand for advanced EBW systems, particularly vacuum chamber and local vacuum variants.
H2: Expansion in Electric Vehicle and Battery Manufacturing
The global shift toward electric mobility is creating new opportunities for EBW technology. In 2026, electron beam welding is gaining traction in the production of electric vehicle (EV) powertrain components and high-capacity battery systems. EBW enables precise, clean welds on aluminum and copper materials used in battery interconnects and motor components, improving thermal performance and reliability. As EV manufacturers scale production and strive for higher energy density and safety standards, EBW equipment is increasingly integrated into automated production lines, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America.
H2: Technological Advancements and Automation Integration
By 2026, electron beam welding equipment is becoming more intelligent and connected, integrating Industry 4.0 principles. Key technological trends include the adoption of CNC-controlled beam manipulation, real-time monitoring via sensors, and AI-driven process optimization. Automated EBW cells with robotic handling are enhancing throughput and consistency in high-volume manufacturing environments. Moreover, developments in non-vacuum (atmospheric) electron beam welding are reducing operational costs and expanding the technology’s applicability to larger and more complex parts, further broadening its industrial footprint.
H2: Regional Market Growth and Competitive Landscape
The geographic distribution of EBW equipment demand is shifting in 2026. While North America and Europe remain strong markets due to mature aerospace and automotive sectors, the Asia-Pacific region—especially China, Japan, and South Korea—is witnessing accelerated growth. This is fueled by government support for advanced manufacturing, expanding defense budgets, and booming EV production. Leading equipment manufacturers are responding with localized production, strategic partnerships, and R&D investments in compact and modular EBW systems tailored to regional needs.
H2: Sustainability and Cost-Efficiency Pressures
Sustainability concerns are influencing EBW adoption as manufacturers seek energy-efficient and low-waste joining methods. Electron beam welding produces minimal heat-affected zones and reduces material waste compared to traditional welding techniques, aligning with green manufacturing goals. In 2026, equipment vendors are focusing on improving energy efficiency, reducing helium usage in vacuum systems, and developing recyclable component designs. These innovations not only support environmental regulations but also lower total cost of ownership, making EBW more accessible to mid-tier industrial players.
In conclusion, the 2026 electron beam welding equipment market is characterized by technological innovation, sector diversification, and global expansion. As industries demand higher precision and efficiency, EBW is transitioning from a niche process to a strategic manufacturing solution, with sustained growth expected across aerospace, automotive, and high-tech industrial applications.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Electron Beam Welding Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Electron Beam Welding (EBW) equipment involves significant technical, financial, and legal considerations. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to costly failures, production delays, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Equipment Specifications and Verification
Failing to define precise technical requirements or neglecting independent verification can result in equipment that doesn’t meet performance expectations. Buyers may receive machines with substandard vacuum systems, unstable electron beam control, or insufficient power output, leading to poor weld quality and process inconsistency.
Insufficient Supplier Qualification
Choosing suppliers based solely on price without evaluating their manufacturing standards, track record, or after-sales support increases the risk of receiving poorly engineered or unreliable equipment. Unproven vendors may lack the expertise to deliver robust EBW systems suitable for critical applications in aerospace or medical industries.
Lack of Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT)
Skipping rigorous FAT protocols allows undetected flaws to go unnoticed until installation. Without witnessing performance tests under simulated operating conditions, buyers risk discovering defects only after commissioning, resulting in downtime and costly rectifications.
Overlooking Component Provenance and Reliability
EBW systems rely on high-precision components like electron guns, high-voltage generators, and vacuum pumps. Sourcing equipment with unverified or counterfeit parts can compromise long-term reliability and safety. Ensuring traceability and OEM authenticity is essential.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unverified IP Ownership and Infringement Risks
Acquiring EBW equipment that incorporates patented technologies without proper licensing exposes the buyer to infringement claims. Suppliers may unknowingly or deliberately use protected designs, software, or control systems, potentially leading to litigation or equipment seizure.
Ambiguous Software Licensing and Restrictions
EBW systems often include proprietary control software with restrictive licenses. Buyers may face limitations on usage, updates, or integration with other systems. Failure to review software terms can result in unexpected costs or operational constraints.
Inadequate IP Protection in Contracts
Purchase agreements that lack clear clauses on IP ownership, indemnification, and warranty for non-infringement leave buyers vulnerable. Without explicit protections, the buyer may bear liability if the equipment infringes third-party IP rights.
Exposure to Trade Secret Misappropriation
When customizing EBW systems or sharing proprietary welding parameters, buyers risk unintentionally exposing their own trade secrets. Suppliers without robust confidentiality safeguards may mishandle sensitive data, leading to potential IP leakage.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including site visits and reference checks.
– Define comprehensive technical specifications and include performance guarantees.
– Require independent FAT and documentation of component sourcing.
– Engage legal counsel to review IP clauses and software licenses.
– Insist on warranties and indemnification against IP infringement.
– Implement confidentiality agreements when sharing proprietary information.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure they acquire reliable, compliant, and legally sound Electron Beam Welding equipment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electron Beam Welding Equipment
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Electron Beam (EB) welding equipment is highly sensitive and requires careful handling during transportation. The vacuum chamber, electron gun, high-voltage power supply, and control systems are precision components vulnerable to shock, vibration, and contamination. Use only certified rigging professionals and specialized crating designed for heavy industrial machinery. Secure all moving parts, cover optical and electrical connections, and ensure the equipment remains upright during transit. Climate-controlled transport is recommended to prevent condensation and thermal stress. Always follow the manufacturer’s transport instructions strictly to avoid voiding warranties or causing operational damage.
Import and Export Regulations
EB welding systems are subject to international trade controls due to their high-voltage and vacuum technologies. Export classifications may fall under dual-use regulations such as the Wassenaar Arrangement or national frameworks like the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL), particularly under ECCN 2B232 for vacuum equipment and electron beam systems. Prior to shipment, obtain proper export licenses or validate eligibility for license exceptions. Importing countries may impose additional requirements, including customs documentation, conformity assessments, and local registration. Engage a qualified trade compliance officer or customs broker to ensure adherence to ITAR, EAR, or equivalent regional regulations.
Electrical and Safety Standards Compliance
EB welding equipment must comply with regional electrical safety standards such as IEC 60204-1 (Safety of Machinery – Electrical Equipment of Machines) and UL/CSA standards in North America. High-voltage components (typically 30–150 kV) require proper shielding and interlocks to prevent exposure to X-ray radiation, which is generated during operation. Equipment must be designed and certified to meet radiation safety standards, including IEC 61331 for protective devices and local regulations such as 21 CFR 1020.40 in the U.S. or the EURATOM Basic Safety Standards Directive in the EU. Regular radiation leakage testing and certification by accredited bodies are mandatory.
Installation Site Preparation and Requirements
Proper site planning is critical for EB welding system installation. The facility must have a stable concrete foundation capable of supporting the equipment’s weight (often exceeding several tons) and minimizing vibration. Maintain a clean, dry environment with controlled ambient temperature (typically 18–24°C) and humidity (<60% RH) to protect vacuum and electronic components. Ensure adequate electrical supply (three-phase, stable voltage, proper grounding) and cooling water systems with specified flow rate, pressure, and purity. Allow sufficient clearance around the machine for maintenance, radiation shielding, and emergency access. Conduct a site audit prior to delivery to verify compliance with manufacturer specifications.
Environmental and Waste Management
Vacuum pumps used in EB systems—particularly oil diffusion or turbomolecular pumps—require proper handling of lubricants and contaminated oils. Used pump oil may be classified as hazardous waste depending on local regulations (e.g., EPA in the U.S., REACH/CLP in the EU) and must be disposed of through licensed waste management services. Prevent oil mist emissions using cold traps or filtration systems. Additionally, manage ozone generation near high-voltage areas through adequate ventilation. Facilities must comply with environmental protection laws including ISO 14001, where applicable, and maintain records of waste disposal and emissions control.
Operator Training and Certification
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate EB welding equipment. Comprehensive training programs must cover equipment operation, vacuum procedures, high-voltage safety, radiation hazards, and emergency shutdown protocols. Certification should align with internal safety policies and, where required, national occupational health standards such as OSHA 29 CFR 1910 in the U.S. or the EU’s Directive 89/391/EEC. Maintain training records and conduct regular refresher courses. Implement a lockout/tagout (LOTO) program to ensure safety during maintenance and repairs.
Regulatory Documentation and Audits
Maintain complete technical and compliance documentation including CE marking files (for EU), Factory Inspection Reports, radiation safety certificates, electrical compliance test results, and import/export licenses. These records must be readily available for audits by regulatory bodies such as OSHA, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), or national radiation protection agencies. Establish a compliance management system to track certification expiration dates, inspection schedules, and regulatory updates. Regular internal audits help ensure ongoing adherence to all applicable standards and reduce the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Conclusion for Sourcing Electron Beam Welding Equipment
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, production needs, supplier capabilities, and total cost of ownership, sourcing electron beam (EB) welding equipment represents a strategic investment in precision, quality, and long-term manufacturing efficiency. Electron beam welding offers unparalleled advantages in deep penetration, minimal distortion, and the ability to join high-performance and dissimilar materials—making it ideal for industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and power generation.
Key considerations in the sourcing decision include equipment specifications (voltage, beam power, vacuum chamber size), automation integration, maintenance support, and the supplier’s technical expertise and service reliability. Selecting a reputable manufacturer with a proven track record ensures access to robust engineering support, training, and spare parts—critical for minimizing downtime and ensuring consistent weld quality.
Furthermore, while the initial capital investment may be significant, the long-term benefits in product performance, reduced post-weld processing, and enhanced process repeatability justify the expenditure, particularly for high-value, low- to medium-volume production environments.
In conclusion, by carefully aligning equipment capabilities with operational goals and partnering with a trusted supplier, sourcing electron beam welding technology will significantly elevate manufacturing capabilities, support innovation, and contribute to a competitive advantage in high-integrity metal joining applications.