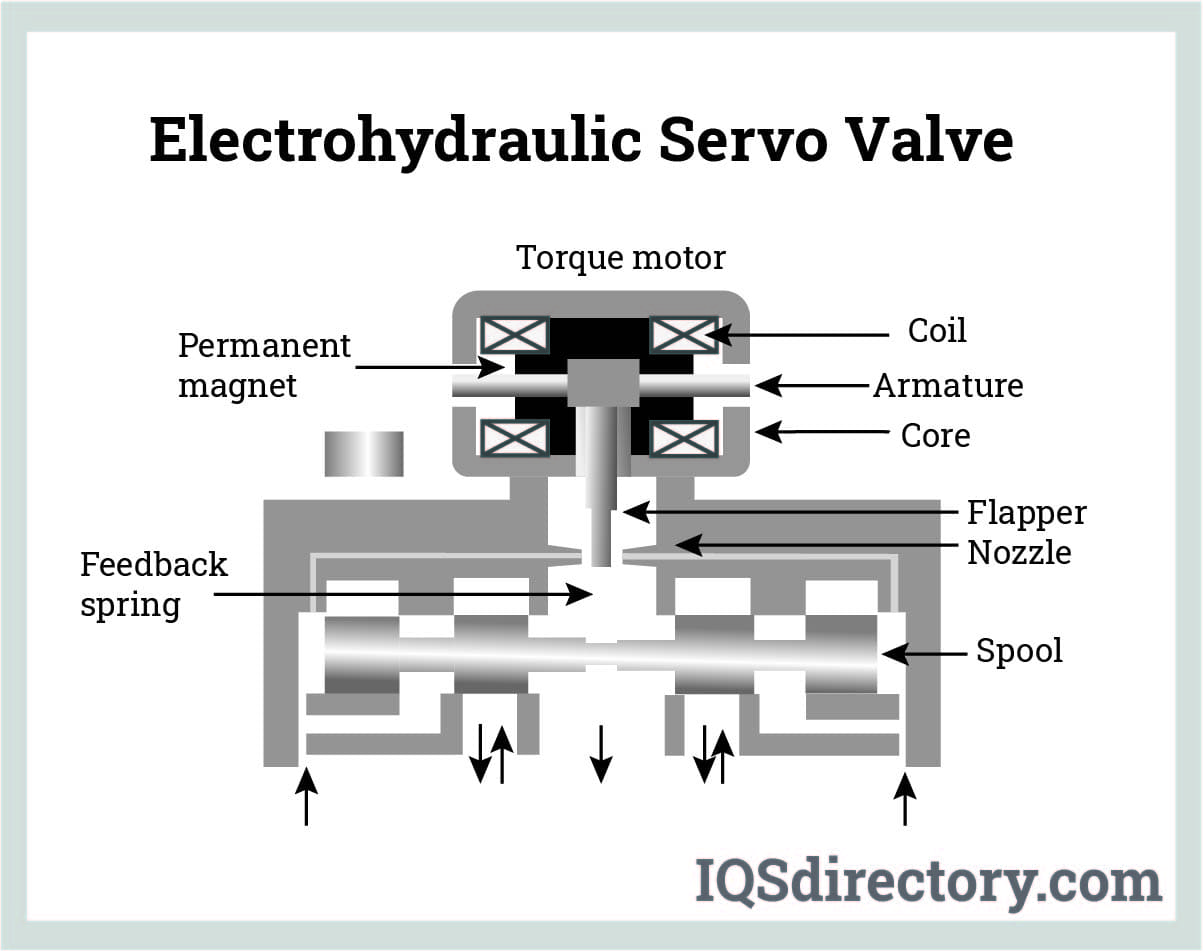
The global electrohydraulic servo valve market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision control systems in aerospace, defense, industrial automation, and heavy machinery. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 1.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by advancements in hydraulic actuation technologies, rising investments in smart manufacturing, and the integration of servo valves in electric and hybrid vehicles. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights the growing adoption of energy-efficient hydraulic systems as a key growth catalyst, particularly in emerging economies. As industries prioritize accuracy, responsiveness, and reliability, the competitive landscape has intensified, with a select group of manufacturers leading innovation and market share. The following list identifies the top eight electrohydraulic servo valve manufacturers shaping the future of fluid power systems.
Top 8 Electrohydraulic Servo Valve Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
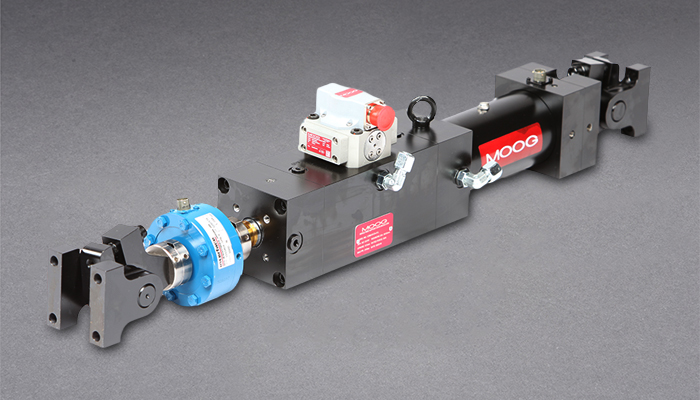
#1 Moog Electrohydraulic Servo Actuators
Domain Est. 1990
Website: moog.com
Key Highlights: Moog is the premier manufacturer of electrohydraulic actuators for Industrial, Aerospace, and Defense applications….
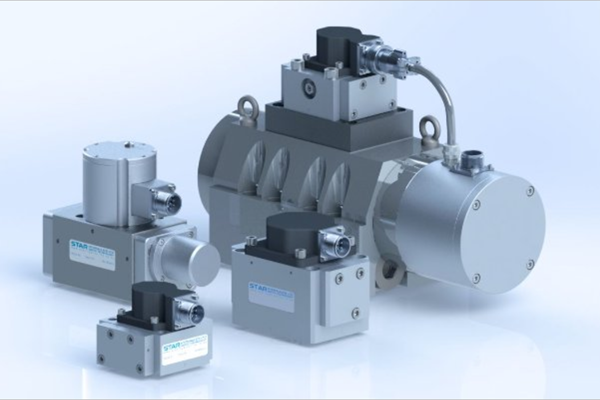
#2 Electro-hydraulic Servo Valves
Domain Est. 1998
Website: star-hydraulics.co.uk
Key Highlights: At STAR HQ based in Tewkesbury, UK, we design and manufacture durable, high quality Electro-Hydraulic Servo Valves using our world famous sapphire technology….
#3 Servo Valves
Domain Est. 1988
Website: aerospace.honeywell.com
Key Highlights: An electro-hydraulic servo valve (EHSV) is a device that uses an electrical input signal to control flow of a gas or liquid….
#4 Servovalves
Domain Est. 1992
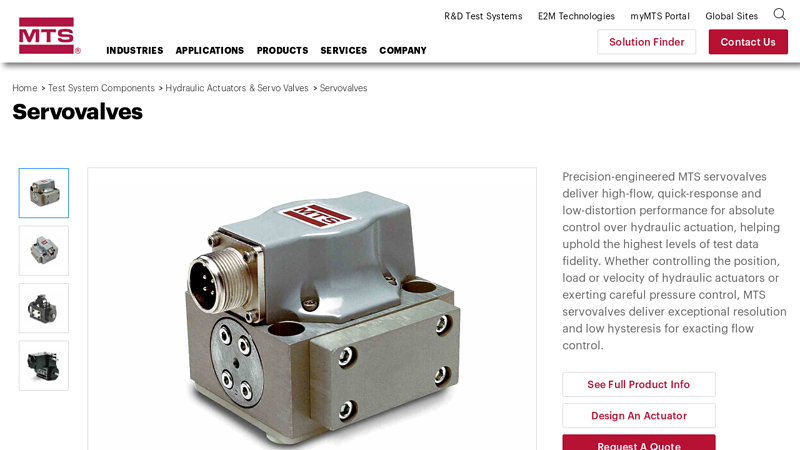
Website: mts.com
Key Highlights: Precision-engineered MTS servovalves deliver high-flow, quick-response and low-distortion performance for absolute control over hydraulic actuation….
#5 Electrohydraulic and Pneumatic Servo Valves
Domain Est. 1999
Website: servotronics.com
Key Highlights: Premier single and two-stage servo valves configured to meet the strict performance, quality, and commercial specifications of our aerospace customers….
#6 hydraulic Servo valves
Domain Est. 2021
Website: schneider-servohydraulics.com
Key Highlights: Servo valves from Schneider Servohydraulics are renowned for reliability and easy maintenance. Our servo valve programme includes valves in one-stage, two-stage ……
#7 Servo valves EMG SV
Website: emg.elexis.group
Key Highlights: Servo valves are the most important components in any electro-hydraulic control system. Our rotary slide design with gap adjustment ensures minimum friction ……
#8 Servo Valve,Electro
Website: servovalvepro.com
Key Highlights: Electro hydraulic servo valve is a key component in electro-hydraulic servo control. It is a hydraulic control valve that receives analog electrical signals ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electrohydraulic Servo Valve
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Electrohydraulic Servo Valves
The global Electrohydraulic Servo Valve (EHSV) market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and strategic sectoral growth. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Accelerated Demand from Automation & Industry 4.0: The relentless push towards smart manufacturing and industrial automation will be a primary growth driver. EHSVs, essential for precise motion control in robotics, CNC machines, and automated assembly lines, will see increased adoption as factories implement IoT-connected systems requiring high-precision, responsive hydraulics. Integration with digital twins and predictive maintenance platforms will enhance their value proposition.
2. Dominance of the Aerospace & Defense Sector: This sector will remain the largest consumer of high-performance EHSVs. The continued production and modernization of military aircraft (fighters, UAVs), commercial airliners (fly-by-wire systems), and defense systems (turrets, missile guidance) demand valves with extreme reliability, high bandwidth, and fault tolerance. Geopolitical tensions and defense spending increases in key regions will sustain this demand.
3. Rapid Growth in Renewable Energy & Heavy Machinery: The expansion of offshore wind energy will significantly boost demand for EHSVs in pitch and yaw control systems for wind turbine blades, where precise, reliable hydraulic actuation is critical in harsh marine environments. Similarly, advancements in mining, construction, and agricultural equipment (e.g., autonomous excavators, precision harvesters) will drive adoption for enhanced control and efficiency.
4. Technological Innovation Focus: Miniaturization, Efficiency & Digitalization: Key R&D efforts will focus on:
* Miniaturization & Weight Reduction: Crucial for aerospace and mobile robotics.
* Improved Energy Efficiency: Reducing heat generation and power consumption through advanced designs (e.g., pressure-compensated valves, optimized flow paths).
* Integrated Electronics & Smart Features: Valves with built-in sensors (position, pressure) and digital communication protocols (e.g., CAN bus, Ethernet/IP) for real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and seamless integration into control networks.
* Enhanced Materials & Durability: Development of corrosion-resistant materials and improved contamination tolerance for harsh environments.
5. Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization: Ongoing global supply chain challenges will push manufacturers towards regionalization and nearshoring, particularly in North America and Europe. This trend will favor established players with local production capabilities and robust supplier networks, potentially reshaping competitive dynamics.
6. Competitive Landscape: Consolidation & Niche Specialization: The market will likely see continued consolidation among mid-tier players, while leading manufacturers (e.g., Moog, Parker Hannifin, Bosch Rexroth, Eaton) strengthen their positions through innovation. Simultaneously, niche players will emerge, focusing on specific applications (e.g., medical robotics, semiconductor manufacturing) or offering highly customized solutions.
7. Sustainability & Environmental Pressures: While hydraulics inherently face scrutiny regarding fluid leakage and energy use, EHSV manufacturers will emphasize the efficiency gains and longevity of their products. Development of valves compatible with biodegradable hydraulic fluids may gain traction in environmentally sensitive applications.
In conclusion, the 2026 EHSV market will be characterized by robust growth fueled by automation and key industrial sectors, underpinned by continuous technological innovation focused on intelligence, efficiency, and integration. Success will depend on a manufacturer’s ability to innovate, ensure supply chain security, and meet the increasingly sophisticated demands of aerospace, industrial automation, and renewable energy applications.
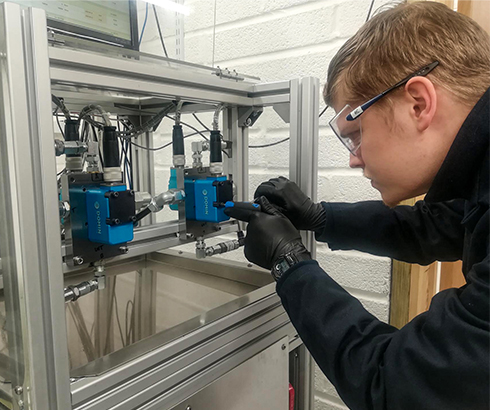

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Electrohydraulic Servo Valves (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Electrohydraulic Servo Valves (EHSVs) requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, safety risks, and legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate Testing
One of the most critical risks is selecting a supplier that lacks rigorous quality assurance processes. EHSVs are precision components where even minor deviations can lead to system instability or failure.
- Inconsistent manufacturing tolerances: Low-quality valves may not meet specified flow, pressure, or response time parameters due to poor machining or assembly.
- Lack of traceability: Absence of component-level traceability makes it difficult to diagnose field failures or conduct root cause analysis.
- Insufficient environmental testing: Valves not tested under real-world conditions (e.g., temperature extremes, vibration, contamination) may fail prematurely in operation.
Mitigation: Require suppliers to provide certification (e.g., ISO 9001), full performance test reports, and evidence of batch traceability. Conduct on-site audits when possible.
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
The high value and technical complexity of EHSVs make them targets for counterfeiting. Some suppliers may offer “compatible” or “replacement” valves that are reverse-engineered copies.
- Performance discrepancies: Reverse-engineered valves often fail to match OEM specifications, particularly in response linearity, hysteresis, and bandwidth.
- Material substitutions: Inferior materials may lead to rapid wear, internal leakage, or failure under high-pressure conditions.
- Hidden defects: Counterfeits may use substandard coils or feedback sensors, increasing the risk of sudden failure.
Mitigation: Source directly from OEMs or authorized distributors. Verify part numbers, markings, and packaging. Use independent testing to validate performance.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Using non-OEM EHSVs can expose your organization to legal liability if the valve infringes on patented designs, control algorithms, or proprietary technologies.
- Patented internal geometries: Flow spool designs, pilot stages, and nozzle-flapper mechanisms are often protected by patents.
- Embedded firmware/IP: Some digital servo valves include proprietary control logic or calibration routines protected under IP law.
- Indirect liability: Even if you’re not manufacturing the valve, using a component known to infringe may lead to legal action in certain jurisdictions.
Mitigation: Conduct IP due diligence when evaluating alternative suppliers. Request documentation confirming freedom to operate (FTO). Avoid “clone” products with no IP clearance.
Inadequate Documentation and Support
Low-quality suppliers may provide incomplete or inaccurate technical documentation, complicating integration and maintenance.
- Missing calibration data: Each servo valve typically requires individual performance calibration; without it, system tuning becomes guesswork.
- Lack of spare parts or long-term support: Some suppliers disappear or discontinue support, leaving systems stranded.
- Poor software compatibility: Digital valves may require specific configuration tools or firmware updates not provided by third parties.
Mitigation: Ensure access to full technical manuals, calibration certificates, and long-term service agreements before procurement.
Overlooking Environmental and Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
EHSVs used in harsh environments must meet appropriate Ingress Protection (IP) standards, but not all suppliers accurately represent or test for these.
- Misrepresented IP ratings: A valve labeled IP65 may lack proper sealing or have inferior connectors, leading to moisture or dust ingress.
- Insufficient protection for industrial use: Valves without proper sealing may fail in washdown, outdoor, or high-contamination environments.
- Compromised coil enclosures: Poor sealing around solenoid coils can lead to electrical shorts or corrosion.
Mitigation: Verify IP ratings through independent testing or certification bodies. Inspect seals, connectors, and housing materials during evaluation.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—focusing on quality validation, IP compliance, and environmental suitability—organizations can ensure reliable, legally sound, and high-performance electrohydraulic systems.
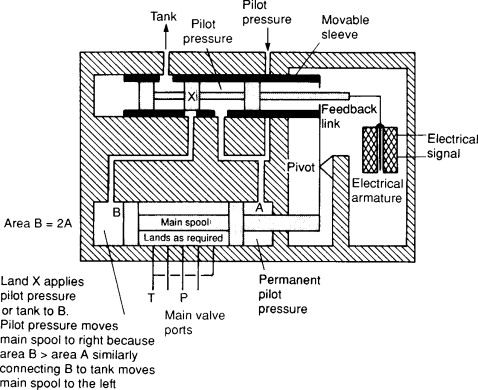
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electrohydraulic Servo Valve
Overview
Electrohydraulic servo valves are precision control components used in high-performance hydraulic systems, commonly found in aerospace, industrial automation, and mobile machinery. Due to their sensitivity, precision engineering, and potential inclusion of regulated materials, proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential for safe, legal, and efficient international and domestic shipping.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Electrohydraulic servo valves require protective packaging to prevent damage during transit. Use anti-static, shock-absorbent materials such as foam-lined boxes and sealed plastic enclosures. Always cap all ports to prevent contamination. Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators. Avoid stacking heavy items on top of valve shipments. Handle with clean gloves to prevent oil or particulate contamination.
Transportation Modes and Conditions
These valves can be shipped via air, ocean, or ground freight depending on urgency and destination. Maintain a stable temperature range (typically 5°C to 40°C) and avoid exposure to extreme humidity, vibration, or magnetic fields. For air transport, ensure compliance with IATA regulations if batteries or electronic components are included. Use climate-controlled containers for sensitive environments.
Import and Export Regulations
Electrohydraulic servo valves may be subject to dual-use export controls under international frameworks such as the Wassenaar Arrangement due to their application in advanced industrial and defense systems. Verify the Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) — commonly EAR99 or 2B201 depending on specifications. Obtain required export licenses from authorities like the U.S. Department of Commerce (BIS) or equivalent bodies in other countries.
Customs Documentation
Prepare accurate shipping documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and Certificate of Origin. Include detailed technical specifications such as flow rate, response time, and voltage requirements. If applicable, provide a Technical Data Disclosure Authorization (TDDA) or license exception documentation (e.g., LVS, AVS, or NLR). Misclassification or incomplete paperwork may lead to customs delays or penalties.
Product Compliance Standards
Ensure servo valves comply with relevant international standards such as ISO 10770 (hydraulic fluid power — servo valves), ISO 9001 (quality management), and IEC 61326 (EMC for industrial equipment). For use in the EU, confirm CE marking compliance including directives such as the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU and Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC. In North America, adherence to UL/CSA standards may be required.
Hazardous Materials and Restrictions
While most servo valves are not classified as hazardous, verify whether components contain restricted substances under RoHS (EU), REACH, or the U.S. TSCA. Avoid shipping with flammable or corrosive materials. If the valve includes hydraulic fluid for testing, declare it appropriately — mineral oil may require hazardous materials labeling (UN1202) under DOT or ADR regulations.
End-Use and End-User Verification
Conduct end-user screening to prevent diversion to unauthorized or embargoed entities. Screen against government watchlists (e.g., U.S. OFAC, BIS Denied Persons List). For shipments to sanctioned countries (e.g., Iran, North Korea, Crimea), obtain prior authorization. Document due diligence to support audit readiness and compliance with anti-boycott and anti-corruption laws.
Storage and Shelf-Life Considerations
Store servo valves in a clean, dry, temperature-stable environment. Avoid prolonged storage in uncontrolled conditions — seals and internal components may degrade. Check manufacturer guidelines for maximum shelf life and recommended preservation methods (e.g., nitrogen sealing). Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) principles.
Returns and Repair Logistics
Establish a clear returns process for defective or out-of-spec units. Use reverse logistics partners familiar with high-value industrial components. For repairs, ensure service centers are authorized and comply with data security and export control protocols, especially if units are returned across borders.
Summary
Successful logistics and compliance for electrohydraulic servo valves demand attention to packaging, regulatory classification, documentation, and end-to-end chain-of-custody controls. Partner with experienced freight forwarders and legal advisors to navigate evolving international trade requirements and ensure uninterrupted supply chain operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Electrohydraulic Servo Valves
In conclusion, sourcing electrohydraulic servo valves requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, reliability, cost, and supplier credibility. These high-precision components are critical in applications demanding accurate control of hydraulic systems—such as aerospace, industrial automation, and heavy machinery—making quality and consistency non-negotiable.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include technical specifications (flow rate, response time, pressure rating), compatibility with existing hydraulic systems, compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, SAE, or MIL-SPEC), and the supplier’s track record for quality assurance and after-sales support. Additionally, evaluating lead times, scalability of supply, and long-term maintenance and service availability is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring operational continuity.
Opting for reputable manufacturers with proven engineering expertise and robust testing procedures ensures enhanced system performance, longevity, and safety. While initial costs may be higher with premium suppliers, the total cost of ownership is often lower due to improved efficiency and reduced failure rates.
Therefore, a well-informed sourcing decision—grounded in thorough technical evaluation and supplier assessment—will ensure the reliable and efficient operation of electrohydraulic systems, supporting overall project success and system integrity.