The global electric forklift market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable material handling solutions across logistics, warehousing, and manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global electric forklift market size was valued at USD 8.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by stringent environmental regulations, rising adoption of automation, and the shift toward electrification in industrial equipment. As electric forklifts rely heavily on high-performance motors for efficiency, reliability, and reduced maintenance, the role of motor manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. With Asia Pacific dominating market share due to rapid industrialization and e-commerce growth—supported by trends cited in Mordor Intelligence reports—innovation in motor technology is accelerating. The following list highlights the top eight electric forklift motor manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape through advanced engineering, scalable production, and strategic partnerships with leading forklift OEMs.
Top 8 Electric Forklift Motor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Heavy Duty Forklifts Manufacturers, Lift Trucks Suppliers
Domain Est. 2008
Website: unforklift.com
Key Highlights: Zhejiang UN Forklift Co., Ltd. is professional China heavy duty forklifts manufacturers and lift trucks suppliers, our factory integrating R&D, production, ……
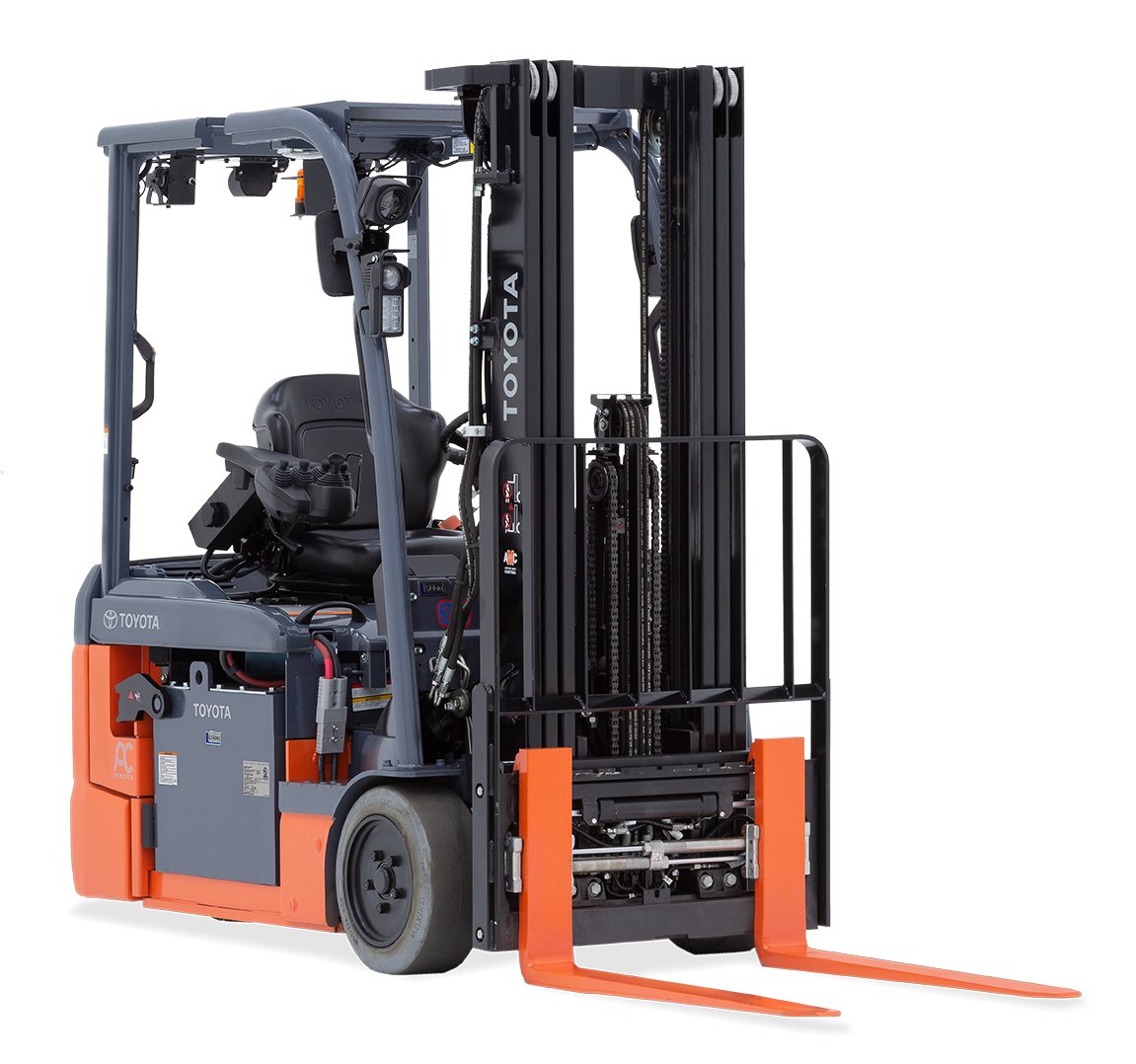
#2 Toyota Forklifts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: toyotaforklift.com
Key Highlights: Toyota’s 3-Wheel Electric Forklift is designed with efficiency and durability in mind to help you tackle all of your material handling challenges. With this ……
#3 Forklift
Domain Est. 1996
Website: en.byd.com
Key Highlights: With rapid, restriction-free charging, BYD electric tractors operate across multiple shifts without the need to change or replace batteries….
#4 CLARK Material Handling Company
Domain Est. 1996
Website: clarkmhc.com
Key Highlights: CLARK offers products in all five classes, including powered pallet jacks, electric standup forklifts, narrow aisle forklifts, walkie pallet stackers, order ……
#5 Big Joe Forklifts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bigjoeforklifts.com
Key Highlights: Discover Big Joe’s innovative lithium-ion forklifts and autonomous solutions, backed by expert support and engineering, for efficient material handling ……
#6 Mitsubishi Forklift Trucks
Domain Est. 1999
Website: mitforklift.com
Key Highlights: Our class-leading diesel and LPG forklifts trucks deliver powerful, efficient and reliable performance. Handling up to 16.0 tonnes….
#7 Electric forklift trucks from Linde Material Handling
Domain Est. 2001
Website: linde-mh.com
Key Highlights: Linde Material Handling offers a wide range of electric forklift trucks for loads weighing in at between 1000 and 8000 kilograms and for virtually any ……
#8 TCM Forklift Trucks
Website: tcm.eu
Key Highlights: TCM forklifts are designed with the operator in mind for maximum safety, productivity & operator comfort. We operate in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electric Forklift Motor

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electric Forklift Motors
The global market for electric forklift motors is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, environmental regulations, and shifting industrial logistics demands. Several key trends are shaping the trajectory of this sector:
1. Surge in Battery-Electric and Lithium-Ion Adoption
By 2026, lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery-powered electric forklift motors are expected to dominate the market, displacing traditional lead-acid batteries. Advantages such as faster charging, longer lifespan, higher energy density, and reduced maintenance are accelerating adoption across warehousing, manufacturing, and distribution centers. Major forklift OEMs are increasingly integrating Li-ion-compatible motors into new models to meet demand for zero-emission material handling solutions.
2. Integration of Smart Motor Technologies
Electric forklift motors are becoming more intelligent with the integration of IoT-enabled sensors and predictive maintenance algorithms. By 2026, a growing number of motors will feature real-time performance monitoring, energy consumption analytics, and remote diagnostics. This trend supports Industry 4.0 initiatives, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime in automated logistics environments.
3. Growth in Automation and AGV Compatibility
The rise of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) is driving demand for compact, high-efficiency electric motors tailored for seamless integration. These motors require precise torque control, regenerative braking, and compatibility with navigation systems. As warehouse automation expands, especially in e-commerce fulfillment centers, motor manufacturers are focusing on modular designs that support scalability and interoperability.
4. Regional Regulatory Pressures and Emissions Standards
Stringent emissions regulations in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific are pushing companies to transition from internal combustion (IC) forklifts to electric alternatives. By 2026, urban logistics hubs and indoor facilities in regions like the EU and China are expected to operate almost exclusively on electric forklifts, directly boosting demand for advanced electric motors.
5. Expansion of Charging Infrastructure and Energy Efficiency Standards
Supporting the growth of electric forklifts, investments in workplace charging infrastructure and energy management systems are rising. Motor manufacturers are aligning with global energy efficiency standards (e.g., IE4 and IE5 efficiency classes), developing motors with optimized power output and thermal performance to reduce operational costs and improve sustainability metrics.
6. Competitive Landscape and Supply Chain Dynamics
By 2026, the electric forklift motor market will see increased competition between established players (e.g., Bosch Rexroth, Siemens, ABB) and emerging EV motor specialists. Strategic partnerships between motor suppliers and forklift OEMs are expected to intensify, alongside localized production to mitigate supply chain risks and meet regional demand more efficiently.
Conclusion
The 2026 outlook for electric forklift motors is characterized by rapid electrification, digitalization, and automation. As sustainability and operational efficiency become top priorities for industrial operators, the demand for high-performance, intelligent electric motors will continue to grow, positioning this segment as a critical component of the future of material handling.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Electric Forklift Motors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing electric forklift motors involves several critical considerations, particularly around quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational failures, legal disputes, and significant financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is selecting motors based solely on price without verifying quality standards. Low-cost suppliers may use substandard materials, inconsistent manufacturing processes, or lack proper testing protocols. This can result in premature motor failure, increased downtime, and higher total cost of ownership. Always demand detailed technical specifications, performance certifications (e.g., ISO, IEC), and test reports such as thermal, load, and insulation resistance tests. Conducting factory audits or third-party inspections prior to purchase can help verify production capabilities and quality management systems.
Misunderstanding IP Protection and Risk of Counterfeiting
Electric forklift motors often incorporate proprietary designs, control algorithms, or patented technologies. Sourcing from unauthorized manufacturers or suppliers without proper IP clearance exposes buyers to legal risks, including infringement claims. Counterfeit or cloned motors may appear identical but lack reliability, safety features, or compliance with regional regulations. To mitigate this risk, ensure suppliers provide proof of IP ownership or licensing agreements. Work with reputable manufacturers and avoid gray-market components that may infringe on patents or trademarks.
Inadequate IP Rating for Operating Environment
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating indicates a motor’s resistance to dust and moisture—critical in industrial environments where forklifts operate. A common mistake is selecting motors with insufficient IP ratings (e.g., IP54 instead of IP65 or higher), leading to premature corrosion, electrical faults, or failure in wet or dusty conditions. Always match the motor’s IP rating to the specific operational environment—such as food processing (wet washdowns) or construction sites (dust and debris). Verify that the IP rating applies to the complete motor assembly, including connectors and cooling systems.
Lack of Traceability and After-Sales Support
Poor documentation and lack of serial traceability can complicate warranty claims, recalls, or performance monitoring. Without clear part numbering, manufacturing dates, and supplier records, identifying counterfeit products or resolving defects becomes difficult. Additionally, unreliable after-sales support—such as limited access to spare parts, repair services, or technical documentation—can disrupt operations. Prioritize suppliers who offer full traceability, comprehensive documentation, and established service networks.
Non-Compliance with Regional Safety and Environmental Standards
Electric motors must comply with regional regulations like CE (Europe), UL (North America), or CCC (China). Sourcing motors that lack proper certification or use non-compliant materials (e.g., hazardous substances under RoHS/REACH) can result in shipment rejections, fines, or liability in case of accidents. Ensure suppliers provide valid compliance certificates and conduct regular audits to confirm ongoing adherence to legal and environmental standards.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, clear procurement criteria, and proactive engagement with trusted suppliers who prioritize quality, compliance, and IP integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electric Forklift Motors
Overview
Electric forklift motors are critical components in material handling equipment, requiring careful handling, transportation, and compliance with international and regional regulations due to their classification as electrical, industrial, and sometimes hazardous goods. This guide outlines best practices for logistics and regulatory compliance when shipping and managing electric forklift motors.
Classification and Identification
Electric forklift motors are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) code 8501.31 or 8501.32, depending on power output and design. Accurate classification is essential for customs clearance, tariff assessment, and import/export compliance. Ensure motors are labeled with manufacturer details, model numbers, voltage, power rating, and certification marks (e.g., CE, UL, CCC).
Packaging Requirements
Use robust, moisture-resistant packaging to prevent physical damage and corrosion during transit. Motors should be:
– Packed in original manufacturer crates or custom wooden boxes
– Secured with anti-vibration materials (e.g., foam inserts, bubble wrap)
– Protected against dust and moisture using sealed plastic wrapping or desiccants
– Clearly labeled with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry,” “This Side Up”)
Transportation and Handling
Electric forklift motors are heavy and sensitive to shock and moisture:
– Use forklifts or pallet jacks for loading/unloading; avoid manual lifting
– Secure motors on pallets with strapping or shrink wrap
– Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or direct sunlight
– Maintain upright orientation during transport to protect internal components
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations:
– CE Marking (EU): Comply with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU)
– UL Certification (USA): Required for electrical safety under UL 1004 or UL 60079 standards
– CCC Mark (China): Mandatory for motors sold in China under GB standards
– RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm absence of restricted hazardous substances
– Energy Efficiency: Comply with local energy performance standards (e.g., MEPS in Australia, DOE rules in the U.S.)
Export and Import Documentation
Prepare complete documentation for smooth customs clearance:
– Commercial invoice with detailed product description, value, and HS code
– Packing list specifying weight, dimensions, and quantity
– Certificate of Origin
– Test reports or conformity certificates (e.g., CE, UL)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Export license (if required by destination country)
Hazardous Materials Considerations
While electric motors themselves are generally not classified as hazardous, associated components (e.g., lubricants, batteries if integrated) may require special handling. Confirm with the manufacturer whether any parts fall under IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations. If motors contain permanent magnets, consider magnetic field shielding and labeling per IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (Class 9 – Miscellaneous).
Storage Guidelines
Store motors in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment:
– Avoid condensation and temperature extremes
– Keep away from corrosive chemicals or conductive dust
– Place on pallets off the floor to prevent moisture absorption
– Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) to prevent obsolescence
End-of-Life and Recycling Compliance
Electric forklift motors contain copper, steel, and rare earth materials. Follow local WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives for proper disposal or recycling. Ensure compliance with environmental regulations in the destination country regarding electronic waste handling.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for electric forklift motors ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency. Partner with certified freight forwarders and stay updated on evolving international standards to minimize delays and avoid penalties.
In conclusion, sourcing an electric forklift motor requires a comprehensive evaluation of performance specifications, quality, reliability, and total cost of ownership. Prioritizing motors from reputable manufacturers with proven track records in electric material handling equipment ensures durability, efficiency, and compatibility with existing systems. Key factors such as power output, voltage requirements, duty cycle, thermal protection, and maintenance needs must align with operational demands. Additionally, considering after-sales support, warranty coverage, and access to spare parts contributes to long-term operational uptime and reduced downtime. Sustainability and energy efficiency are further advantages of choosing a high-quality electric motor, supporting both environmental goals and cost savings over time. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing decision enhances productivity, safety, and return on investment in electric forklift operations.