The global electric motor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions across industrial, automotive, and consumer sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 128.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 186.1 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 6.3% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by rising adoption of electric vehicles, stringent energy efficiency regulations, and advancements in motor technologies such as permanent magnet and brushless DC motors. As industries worldwide pivot toward electrification and automation, the role of leading electric motor manufacturers becomes increasingly critical in shaping the future of sustainable power solutions. Below, we explore the top 10 electric motor manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, market share, and technological advancement in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Top 10 Electic Moter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 McMillan Electric
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1976
Website: mcmillanelectric.com
Key Highlights: McMillan is an electric motor manufacturer in the USA. Founded in 1976, we started making motors here in Woodville, Wisconsin in a small factory with ten people ……
#2 Baldor.com
Domain Est. 1995
Website: baldor.com
Key Highlights: ABB is the world’s number-one manufacturer of NEMA motors, and we’re proud to support you locally with the Baldor-Reliance product brand….
#3 Custom Electric Motors and Gear Motor Design & Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1998
Website: powerelectric.com
Key Highlights: We develop and deliver high-quality, cost-effective electric motors & gear motors for North American OEMs. Utilizing our engineering and manufacturing expertise ……
#4 WorldWide Electric Corporation
Domain Est. 1999
Website: worldwideelectric.com
Key Highlights: WorldWide Electric manufactures electric motors, gear reducers, controls, & generators – backed by our reliable service and fast shipping….
#5 Leading Industry Standard Electric Motors and Pumps Supplier
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1994
Website: electricmotors.com
Key Highlights: Since 1994, ElectricMotors.com has been your electric motor super store. We offer fast, free shipping to the continental US!…
#6 US Motors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: acim.nidec.com
Key Highlights: Build America, Buy America. Compliant Motors. View our quick reference guide to compliant Vertical AC motors built in our Mena, Arkansas facility….
#7 TECO-Westinghouse
Domain Est. 1999
Website: tecowestinghouse.com
Key Highlights: Browse Our Products & Services · Green Energy · Stock Motors · Custom Motors · Drives & Controls · Service and Repair….
#8 Franklin Electric
Domain Est. 2000
Website: franklin-electric.com
Key Highlights: Every day, Franklin Electric manufactures approximately 20,000 pumps, motors, drives, and controls to move the 3 trillion gallons of fresh water used worldwide ……
#9 WEG
Domain Est. 2004
Website: weg.net
Key Highlights: WEG provides global solutions for electric motors, variable frequency drives, soft starters, controls, panels, transformers, and generators….
#10 Wolong Electric America
Domain Est. 2023
Website: wolongamerica.com
Key Highlights: Wolong Electric America manufactures GE branded AC motors, DC motors, and NEMA low voltage and medium voltage electric motors. We serve heavy industries ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Electic Moter

H2 2026 Market Trends for Electric Motors
As we approach the second half of 2026, the global electric motor market is experiencing transformative shifts driven by decarbonization mandates, technological innovation, and evolving industrial and consumer demands. Here’s a breakdown of key H2 2026 trends:
1. Accelerated Adoption in Transportation
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): The EV sector remains the primary growth engine for high-efficiency electric motors. By H2 2026, demand for permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) and switched reluctance motors (SRMs) is surging, particularly in mid- to high-tier EVs. Automakers are focusing on motors with higher power density, reduced rare-earth content, and integrated powertrain designs.
- E-Mobility Expansion: Beyond cars, electric motors are powering e-bikes, scooters, and last-mile delivery vehicles, especially in urban centers across Asia, Europe, and North America. Regulatory pressure and infrastructure development are fueling this trend.
2. Industrial Automation and Energy Efficiency
- Regulatory Push: Stricter global energy efficiency standards (e.g., IE5 and emerging IE6 classifications) are mandating the replacement of legacy motors in industrial applications. By H2 2026, IE4 and IE5 motors account for over 40% of new industrial motor installations.
- Smart Motor Systems: Integration with IoT and Industry 4.0 is driving demand for intelligent motors with embedded sensors, predictive maintenance capabilities, and real-time performance monitoring. These systems reduce downtime and optimize energy use in manufacturing and process industries.
3. Renewables and Grid Infrastructure
- Wind Turbines: Direct-drive permanent magnet generators are gaining dominance in offshore wind farms due to higher reliability and lower maintenance. The global push for renewable energy ensures steady demand for large-scale electric motors and generators.
- Grid Stability Solutions: Motor-driven flywheels and synchronous condensers are being deployed to support grid stability amid increased intermittent renewable generation, creating niche but growing markets for specialized motor technologies.
4. Material Innovation and Supply Chain Resilience
- Rare-Earth Reduction: With geopolitical risks and price volatility in rare-earth elements (e.g., neodymium), manufacturers are advancing rare-earth-free or reduced-content motor designs, such as advanced induction and SRMs.
- Supply Chain Localization: Post-pandemic and geopolitical tensions have accelerated regionalization of motor production, particularly in North America and Europe, driven by incentives like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and EU Green Deal.
5. Advancements in Motor Technology
- SiC and GaN Inverters: Wider adoption of wide-bandgap semiconductors enables higher switching frequencies, improving motor efficiency and enabling smaller, lighter motor drives.
- Modular and Scalable Designs: OEMs are shifting toward modular motor platforms that can be adapted across vehicle or industrial models, reducing R&D costs and speeding time-to-market.
6. Sustainability and Circular Economy
- Recycling and Reuse: By H2 2026, end-of-life motor recycling—especially for magnets and copper—is becoming standardized, supported by new regulations and corporate ESG goals.
- Lifecycle Analysis (LCA): Buyers increasingly demand motors with full lifecycle carbon footprint assessments, influencing procurement decisions in both public and private sectors.
Conclusion
In H2 2026, the electric motor market is defined by convergence: sustainability regulations, digital integration, and electrification across sectors are creating unprecedented demand. Companies that innovate in efficiency, materials, and smart functionality—while ensuring supply chain resilience—will lead the market. The electric motor is no longer just a component; it is a strategic enabler of the global energy transition.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Electric Motors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing electric motors involves several critical considerations, particularly concerning quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking key factors can lead to performance issues, safety hazards, and increased lifecycle costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Verification of Quality Standards
Many buyers assume that motor specifications match actual performance without independent verification. This can result in receiving motors with subpar materials, poor winding practices, or inconsistent manufacturing. Always request test reports, certifications (e.g., ISO, IEC, NEMA), and consider third-party inspections or sample testing before large-scale procurement.
Misunderstanding or Overlooking IP Ratings
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating indicates a motor’s resistance to dust and water. A common mistake is selecting a motor with an insufficient IP rating for the operating environment—such as using an IP54 motor in a washdown or outdoor setting where IP65 or higher is required. Conversely, over-specifying (e.g., IP68 in a dry environment) increases cost unnecessarily.
Assuming IP Rating Guarantees Long-Term Durability
While a high IP rating suggests good sealing, it doesn’t ensure longevity under continuous exposure to harsh conditions. Seals degrade over time, especially with temperature cycling or chemical exposure. Buyers should assess the quality of sealing materials and gaskets, not just the IP code.
Ignoring Thermal and Environmental Compatibility
An electric motor may meet IP and efficiency standards but fail prematurely if it’s not rated for the ambient temperature, humidity, or corrosive elements in the application. Always cross-check the motor’s insulation class, duty cycle, and environmental specifications with real-world operating conditions.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Poor documentation—such as missing serial numbers, unclear manufacturing dates, or incomplete compliance certificates—can create issues in quality tracking, warranty claims, or recalls. Ensure suppliers provide full traceability and standardized documentation.
Overlooking Supplier Reliability and Support
Choosing a vendor based solely on price can lead to inconsistent quality and lack of technical support. Verify the supplier’s track record, manufacturing capabilities, and after-sales service, especially for warranty handling and spare parts availability.
Failing to Validate Motor Efficiency Claims
Some suppliers may exaggerate efficiency ratings (e.g., IE3, IE4). Without proper certification from accredited labs, motors may consume more energy than expected, increasing operational costs. Always demand valid efficiency test reports aligned with IEC 60034-2-1.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, buyers can ensure they source reliable, high-quality electric motors suited to their application’s environmental and performance demands.
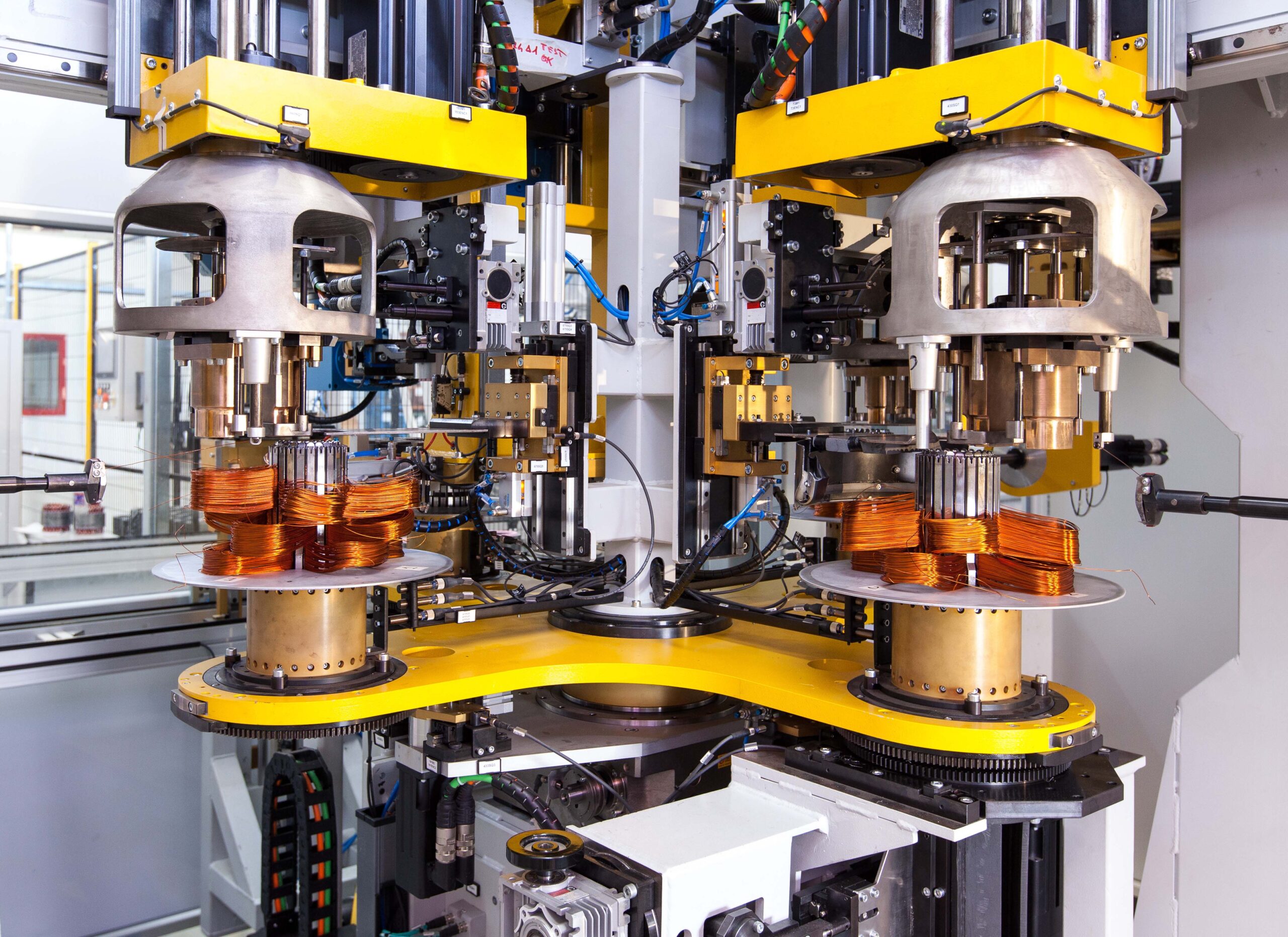
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Electric Motors
Electric motors play a critical role in various industries, from automotive and manufacturing to renewable energy and consumer electronics. Ensuring their safe, efficient, and compliant transportation and handling is essential. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for electric motors across the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
Electric motors are subject to various international, national, and regional regulations depending on their design, application, and destination. Key compliance areas include:
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Many countries (e.g., EU Ecodesign Directive, U.S. DOE regulations) require electric motors to meet minimum efficiency levels (e.g., IE3, IE4). Ensure motors are labeled and certified accordingly.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Motors must comply with EMC directives (e.g., EU EMC Directive 2014/30/EU) to avoid interfering with other electronic equipment.
- RoHS and REACH (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulations apply to materials used in motor manufacturing.
- Export Controls: High-performance or specialized motors may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S., Dual-Use Regulation in the EU) due to potential military applications.
- Product Certification: Required certifications such as CE (Europe), UL (North America), CCC (China), or IECEx (for hazardous environments) must be obtained prior to market entry.
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging is vital to protect electric motors during transit and prevent damage:
- Use robust, moisture-resistant packaging with internal cushioning (e.g., foam inserts) to prevent vibration and impact damage.
- Secure rotors and moving parts with locking mechanisms or transit bolts to prevent internal damage.
- Clearly label packages with handling instructions: “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack.”
- Include desiccants in sealed packaging to prevent moisture ingress, especially for海运 or humid environments.
Transportation Requirements
Electric motors vary in size and weight, influencing the mode and method of transport:
- Road Transport: Use padded straps and load stabilizers. Heavy motors require forklifts or cranes for loading/unloading.
- Sea Freight: Motors must be secured in containers to prevent shifting. Use corrosion-resistant coatings or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) packaging for long voyages.
- Air Freight: Subject to IATA regulations. Motors containing magnets may be classified as “Magnetized Material” and require special documentation and labeling (e.g., Class 9 hazard label if magnetic field strength exceeds limits).
- Battery-Integrated Motors: If the motor includes a battery (e.g., in e-mobility applications), UN38.3 testing and hazardous material classification (e.g., UN3480) apply.
Storage Conditions
Improper storage can degrade motor performance:
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 5°C to 40°C).
- Avoid condensation; use climate-controlled warehouses if necessary.
- Keep motors on wooden pallets or racks to prevent ground moisture absorption.
- Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) to prevent aging and obsolescence.
Documentation and Traceability
Accurate documentation supports compliance and logistics efficiency:
- Include technical specifications, conformity declarations (DoC), and test reports with shipments.
- Maintain records of certifications, batch numbers, and serial numbers for full traceability.
- For international shipments, prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Use proper HS codes (e.g., 8501.31, 8501.32 for AC motors) for customs clearance.
End-of-Life and Recycling
Electric motors contain recyclable materials (copper, aluminum, steel) and may fall under WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU:
- Design for disassembly and recycling where possible.
- Partner with certified e-waste recyclers.
- Provide take-back programs or disposal guidance to customers.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for electric motors ensures legal adherence, product integrity, and customer satisfaction. By following these guidelines—from design and packaging to transportation and end-of-life—manufacturers and logistics providers can mitigate risks and support sustainable operations. Always consult local regulations and update procedures as standards evolve.
Conclusion for Sourcing Electric Motors
In conclusion, sourcing electric motors requires a strategic approach that balances performance, cost, reliability, and sustainability. The selection process should be driven by a clear understanding of application requirements, including power rating, efficiency, size, and environmental conditions. Evaluating multiple suppliers based on technical capabilities, quality certifications, production capacity, and after-sales support ensures long-term supply chain stability and product performance.
Global sourcing offers cost advantages and access to advanced technologies, but it also introduces risks related to logistics, lead times, and quality control. Therefore, establishing strong supplier relationships, conducting rigorous audits, and implementing effective quality assurance protocols are essential. Additionally, considering trends such as energy efficiency standards (e.g., IE4, IE5), Industry 4.0 integration, and the shift toward electrification in transportation and manufacturing can future-proof sourcing decisions.
Ultimately, a well-planned electric motor sourcing strategy not only reduces total cost of ownership but also supports innovation, operational efficiency, and sustainability goals within the organization.