The global elastomeric pump market is experiencing steady growth, driven by the rising demand for ambulatory drug delivery systems in chronic disease management, oncology, and pain control. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the elastomeric pump market was valued at approximately USD 490 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of home-based and ambulatory infusion therapies, expanding healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies, and the need for precise, cost-effective drug delivery solutions with minimal risk of infection. As patient-centric care models gain traction, elastomeric pumps—known for their reliability, portability, and consistent flow rates without the need for electricity—have become essential in outpatient settings. With technological advancements enhancing safety and usability, manufacturers are investing in innovation and regulatory compliance to capture growing market opportunities. This increasing demand underscores the importance of identifying the leading players shaping the industry.
Top 8 Elastomeric Pump Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
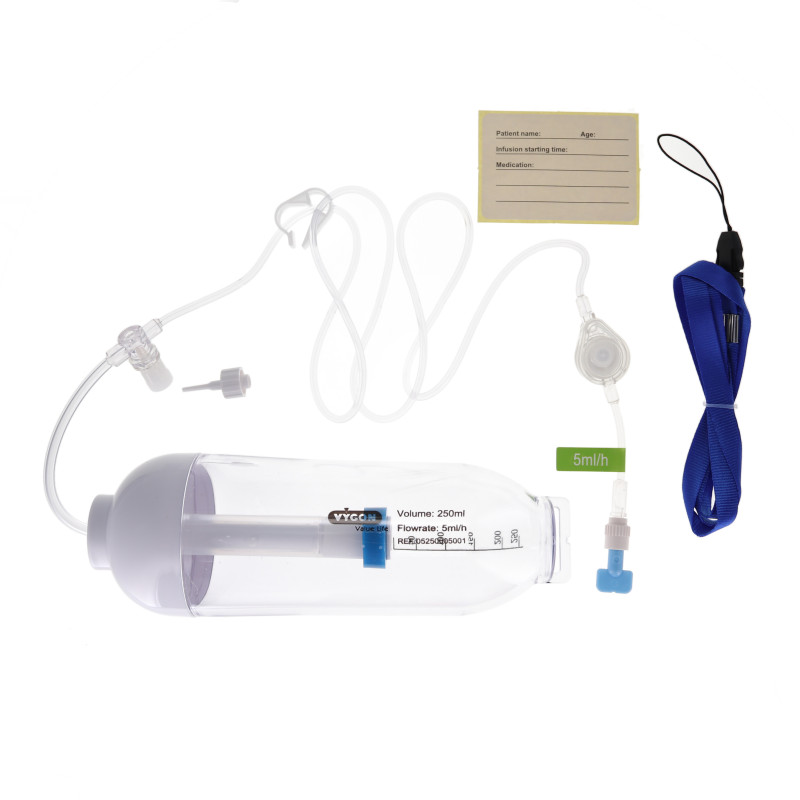
#1 Runqiang Elastomeric Pumps
Domain Est. 1997
Website: vygon.com
Key Highlights: Disposable Infusion Pump for infusion of cytotoxic drugs for cancer treatment, antibiotherapy, pain management in homecare setting or in healthcare centre….
#2 EPIC
Domain Est. 1999
Website: progressivemedinc.com
Key Highlights: SMARTeZ disposable elastomeric pumps are intended for intermittent and continuous antibiotic infusion, chemotherapy, pain management and general infusion ……
#3 IMed EZ
Domain Est. 2000
Website: integratedmedsys.com
Key Highlights: EZ-FLOW™ Elastomeric Pumps are a convenient alternative to electronic infusion pumps. The EZ-FLOW™ offers a safe and effective way to deliver medications ……
#4 Elastomeric infusion pumps
Domain Est. 2012
Website: promecon-medical.com
Key Highlights: Elastomeric infusion pumps for single-use, work independently from external energy sources, and allow for safe and continuous application of medication in ……
#5 Elastomeric Pump Market
Domain Est. 2014
Website: delveinsight.com
Key Highlights: An Elastomeric Pump is a type of infusion pump referred to as a ball pump or a balloon pump. It is a medical device used for infusing medication….
#6 Elastomeric pumps: nursing management
Domain Est. 2017
Website: deltamed.it
Key Highlights: Elastomeric pumps are devices for continuous and constant infusion of drugs intravenously or subcutaneously. These instruments are lightweight, sterile, and ……
#7 First Medical Source (FMS)
Domain Est. 2020
Website: infulife.com
Key Highlights: InfuLife® offers advanced elastomeric infusion pumps for chemotherapy & pain management. Contact us for details on our innovative solutions….
#8 Epic Health EMEA
Website: epichealth.eu
Key Highlights: Epic’s product portfolio ensures a seamless journey from Vial to Vein, offering advanced infusion solutions for every need….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Elastomeric Pump

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Elastomeric Pumps
The global elastomeric pump market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by evolving healthcare needs, technological advancements, and shifting clinical preferences. These disposable, ambulatory infusion devices, known for their portability, precision, and cost-effectiveness, are gaining traction across oncology, pain management, and home healthcare settings. The following trends are anticipated to shape the elastomeric pump landscape in 2026:
-
Increased Adoption in Ambulatory and Home-Based Care
With the global shift toward decentralized healthcare delivery, elastomeric pumps are expected to play a crucial role in enabling outpatient treatments. Their ease of use, portability, and lack of reliance on electricity make them ideal for home infusion therapies. The growing elderly population and rising prevalence of chronic diseases—such as cancer and chronic pain—are fueling demand for patient-centric solutions, positioning elastomeric pumps as a preferred choice for long-term infusion therapy outside hospital settings. -
Growth in Oncology and Pain Management Applications
Elastomeric pumps are extensively used for continuous delivery of chemotherapy agents and analgesics. By 2026, the oncology segment is projected to remain the largest application area due to the rising global cancer burden and the need for outpatient chemotherapy regimens. Similarly, in pain management—especially for post-surgical and palliative care—elastomeric pumps offer controlled, steady infusion, reducing opioid dependency and improving patient comfort. These clinical advantages are expected to sustain strong market growth in these therapeutic areas. -
Technological Innovations and Enhanced Safety Features
Manufacturers are investing in R&D to improve dose accuracy, flow consistency, and user safety. By 2026, next-generation elastomeric pumps are likely to feature integrated flow indicators, anti-siphon mechanisms, and compatibility with smart monitoring systems. While not fully “smart” like electronic pumps, hybrid models with basic telemetry or connectivity for dose tracking may emerge, bridging the gap between mechanical simplicity and digital health integration. -
Regulatory and Reimbursement Dynamics
Regulatory approvals and favorable reimbursement policies in regions like North America and Europe will continue to support market expansion. The U.S. FDA and European EMA have established clear pathways for Class II medical devices like elastomeric pumps, facilitating faster market entry. However, pricing pressures and cost-containment initiatives in public healthcare systems may challenge premium pricing strategies, pushing manufacturers toward cost-efficient production and value-based offerings. -
Geographic Expansion and Emerging Market Opportunities
While North America and Europe dominate the current market, Asia-Pacific—particularly India, China, and Southeast Asia—is expected to witness the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) by 2026. Increasing healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness of advanced infusion therapies are key growth drivers in these regions. Local manufacturing and partnerships with regional distributors will be critical for global players to capture emerging market share. -
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
As healthcare sustainability gains attention, the single-use nature of elastomeric pumps may face scrutiny. By 2026, manufacturers may respond with eco-friendly materials, recyclable components, or take-back programs to address environmental concerns. Regulatory bodies and healthcare providers may also prioritize suppliers with sustainable practices, influencing procurement decisions.
In conclusion, the elastomeric pump market in 2026 will be shaped by a confluence of clinical demand, technological refinement, and evolving care models. While challenges related to cost, competition from electronic pumps, and environmental impact persist, the inherent advantages of elastomeric devices—particularly in ambulatory and resource-limited settings—ensure their continued relevance and growth in the global infusion therapy ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Elastomeric Pumps (Quality, IP)
Sourcing elastomeric pumps—commonly used in ambulatory drug delivery—requires careful attention to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to regulatory setbacks, supply chain disruptions, product failures, or legal liabilities. Below are the critical pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Supplier Qualification and Audits
Relying solely on supplier-provided certifications (e.g., ISO 13485) without conducting thorough on-site audits can result in sourcing from manufacturers with inconsistent quality control. Hidden issues such as poor cleanroom practices, undocumented process changes, or substandard raw material sourcing may not be evident from paperwork alone.
2. Inconsistent Flow Rate Accuracy and Performance
Elastomeric pumps rely on the controlled expansion of an elastomer to deliver medication at a precise rate. Sourcing pumps with inconsistent flow rates—due to variations in elastomer composition, wall thickness, or manufacturing tolerances—can compromise patient safety and therapeutic efficacy. Lack of batch-to-batch consistency testing increases this risk.
3. Poor Material Biocompatibility and Leachables
Using elastomers or adhesives that are not properly tested for biocompatibility (ISO 10993) can lead to patient adverse reactions. Additionally, failure to assess extractables and leachables (per USP <1663> or ISO 10993-18) may result in toxic compounds migrating into the drug solution, especially with long-term infusions.
4. Insufficient Packaging and Sterilization Validation
Improper packaging can compromise sterility or cause device damage during transport. Sourcing pumps without validated sterilization methods (e.g., ethylene oxide, gamma irradiation) or inadequate sterility assurance levels (SAL) increases the risk of microbial contamination.
5. Lack of Regulatory Compliance Documentation
Procuring pumps without full technical documentation (Design Dossier, Risk Management File per ISO 14971, Clinical Evaluation Report) can delay regulatory submissions (e.g., FDA 510(k), CE Marking under MDR). Suppliers may claim compliance but fail to provide necessary evidence.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Designs or Technologies
Many elastomeric pump designs, flow control mechanisms, or connector systems are protected by patents. Sourcing from manufacturers using patented technologies without proper licensing exposes the buyer to infringement lawsuits. Conducting freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses is essential but often overlooked.
2. Unclear Ownership of Customized Designs
When working with contract manufacturers on custom pump designs, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can result in disputes. Suppliers may claim rights to design improvements or tooling, limiting your ability to switch vendors or scale production.
3. Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products
Some low-cost suppliers offer “compatible” or “generic” elastomeric pumps that replicate branded devices. These may be reverse-engineered without IP clearance, exposing the buyer to legal action—even if unintentional. Due diligence on the supplier’s IP portfolio and design origins is critical.
4. Inadequate Protection of Trade Secrets and Know-How
Sharing proprietary drug compatibility data or usage protocols with suppliers without robust confidentiality agreements (NDAs) risks unauthorized disclosure or misuse. This is particularly important when co-developing application-specific pump solutions.
5. Reliance on Suppliers with Weak IP Portfolios
Choosing a supplier with limited or expired IP protection may seem cost-effective but increases vulnerability to competition and reduces long-term exclusivity. It may also indicate lower innovation capacity or reliance on outdated technology.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct comprehensive supplier audits, including quality systems and manufacturing processes.
- Require full biocompatibility and extractables/leachables testing reports.
- Perform independent performance validation (flow rate, priming time, occlusion pressure).
- Engage IP counsel to conduct FTO searches before finalizing sourcing decisions.
- Clearly define IP ownership and usage rights in supply agreements.
- Prioritize suppliers with strong regulatory track records and transparent documentation.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable, compliant, and legally secure sourcing of elastomeric pumps for safe and effective patient care.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Elastomeric Pumps
Regulatory Classification and Approval Requirements
Elastomeric pumps are typically classified as medical devices and are subject to stringent regulatory oversight. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates these devices under the Medical Device Classification system, often falling under Class II (e.g., infusion pumps), requiring 510(k) premarket notification. In the European Union, elastomeric pumps must comply with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) (EU) 2017/745 and bear the CE marking. Manufacturers and distributors must ensure devices have valid technical documentation, clinical evaluations, and quality management systems (e.g., ISO 13485 certification). Country-specific requirements in other markets (e.g., Health Canada, TGA in Australia, PMDA in Japan) must also be verified prior to distribution.
Labeling and Packaging Compliance
All elastomeric pumps must be labeled in accordance with applicable regulations, including device identification, intended use, contraindications, warnings, and precautions. Labels must be legible, permanent, and provided in the official language(s) of the destination country. The packaging must maintain sterility and integrity during transport and storage. Each unit should include a Unique Device Identifier (UDI) as required by FDA and EU MDR for traceability. Instructions for Use (IFU) must be included in the packaging and updated to reflect current regulatory standards and clinical guidance.
Storage and Environmental Controls
Elastomeric pumps must be stored in a controlled environment to preserve functionality and sterility. Recommended storage conditions typically include a temperature range of 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) and relative humidity below 60%. Exposure to extreme temperatures, direct sunlight, or high humidity can compromise the elastomeric reservoir and affect dosing accuracy. Storage areas must be clean, dry, and secure, with documented environmental monitoring where applicable. Products should be stored off the floor and rotated using a first-expiry, first-out (FEFO) system.
Transportation and Distribution Protocols
During transportation, elastomeric pumps must be protected from physical damage, temperature extremes, and moisture. Use of validated packaging and insulated shipping containers with temperature monitors (e.g., data loggers) is recommended, especially for international or long-distance shipments. Transport must comply with IATA regulations if shipped by air, particularly when accompanied by pharmaceuticals. Cold chain requirements do not typically apply unless the pump is pre-filled with a temperature-sensitive drug. Carriers must be qualified and compliant with Good Distribution Practice (GDP) standards.
Import/Export Documentation and Customs Clearance
Exporters and importers must prepare accurate and complete documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and regulatory certificates (e.g., Certificate to Foreign Government, Certificate of Free Sale). For controlled substances or combination products, additional permits may be required. Harmonized System (HS) codes must be correctly applied to ensure proper tariff classification and customs clearance. Importers must confirm that the destination country recognizes the CE mark or equivalent and that local authorizations (e.g., import licenses) are obtained in advance.
Post-Market Surveillance and Adverse Event Reporting
Manufacturers and authorized representatives are responsible for establishing a post-market surveillance (PMS) system to monitor device performance and safety. Any malfunction, adverse event, or serious incident involving an elastomeric pump must be reported to relevant authorities within mandated timelines (e.g., 10–15 days under EU MDR, 30 days for FDA via MedWatch). Trend reporting and periodic safety update reports (PSURs) may also be required. Distributors must cooperate in field safety corrective actions (FSCAs), including recalls or safety alerts.
Training and Competency for Handling Personnel
All personnel involved in the logistics, handling, or distribution of elastomeric pumps must receive appropriate training on medical device regulations, GDP, and product-specific handling procedures. Training records must be maintained and updated regularly. Staff should be aware of the importance of maintaining sterility, proper storage, and incident reporting protocols. Competency assessments should be conducted periodically to ensure compliance and product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Elastomeric Pumps
In conclusion, sourcing elastomeric pumps requires a comprehensive evaluation of clinical needs, regulatory compliance, cost-effectiveness, reliability, and supplier capability. These single-use, portable infusion devices offer significant advantages in ambulatory and home-based care settings due to their simplicity, accuracy, and lack of reliance on electrical power. However, successful sourcing depends on selecting suppliers who demonstrate consistent product quality, adherence to international standards (such as ISO 13485 and FDA/CE requirements), and strong post-market support.
Key considerations include compatibility with prescribed medications, flow rate accuracy, duration of infusion, patient comfort, and ease of use for both clinicians and patients. Conducting thorough due diligence—comprising supplier audits, product validation, cost-benefit analysis, and stakeholder consultation—ensures optimal device performance and patient safety.
Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach that balances clinical efficacy, regulatory assurance, and economic sustainability will enhance patient outcomes and support efficient healthcare delivery. Partnering with reputable manufacturers and maintaining ongoing monitoring of product performance post-implementation will further strengthen the long-term success of elastomeric pump integration into clinical practice.