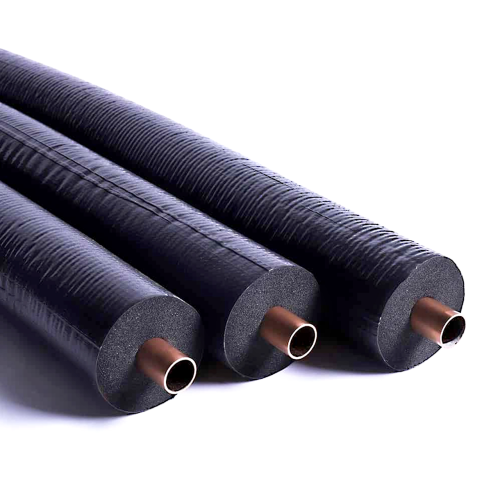
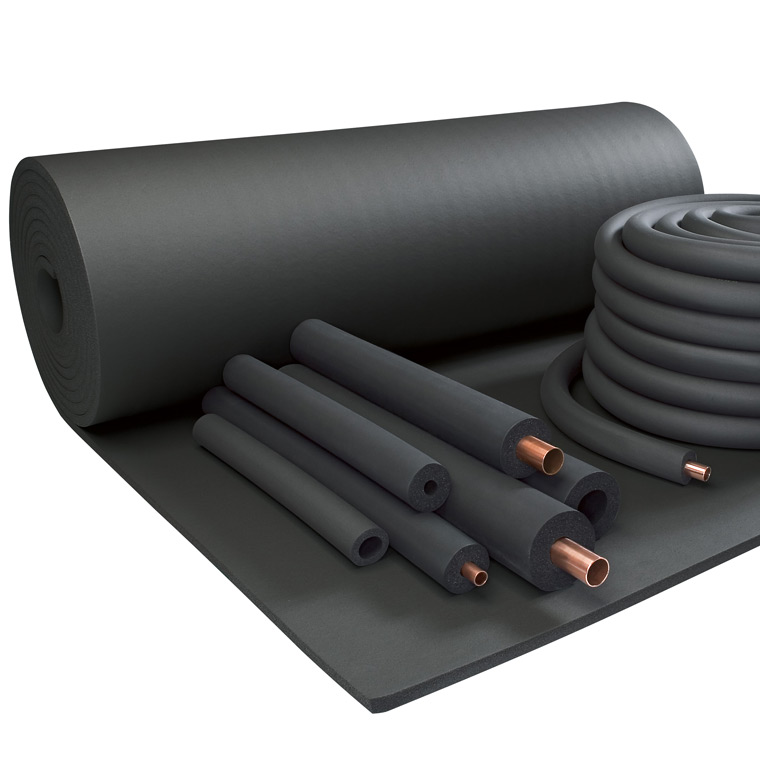
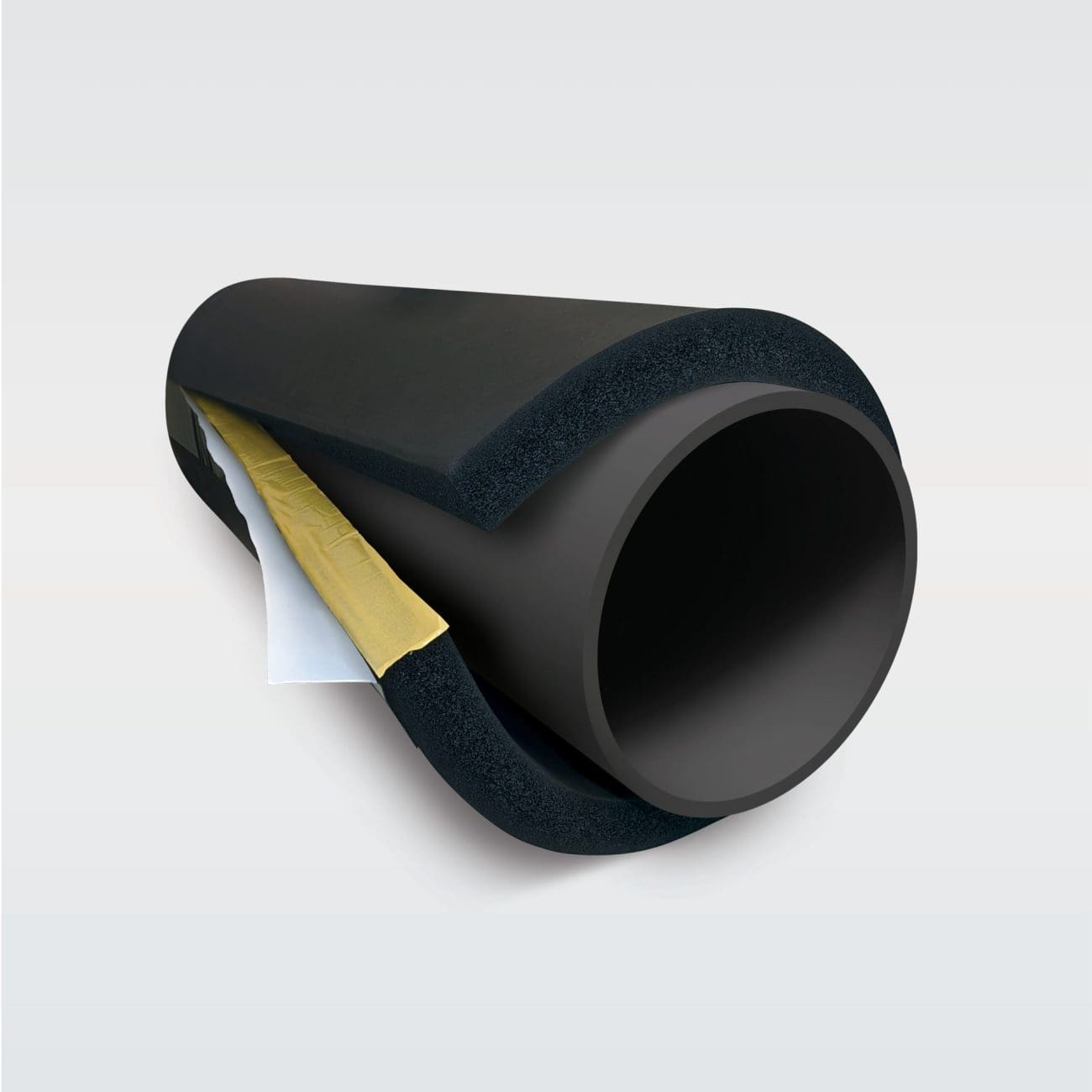
The global elastomeric insulation market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient building solutions and thermal insulation in HVAC, industrial, and plumbing applications. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2029. This expansion is fueled by rising construction activities, stricter energy regulations, and the superior performance characteristics of elastomeric materials—such as low thermal conductivity, moisture resistance, and flexibility. As sustainability and operational efficiency become critical priorities across industries, leading manufacturers are investing in innovative, eco-friendly formulations and expanding their global footprint. In this competitive landscape, nine key players have emerged as leaders, combining technological expertise, extensive product portfolios, and strong distribution networks to capture significant market share.
Top 9 Elastomeric Insulation Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 K
Domain Est. 1998
Website: insulfab.net
Key Highlights: K-FLEX USA is a leading manufacturer of elastomeric and polyethylene based foam products that are easy-to-use and deliver reliable and lasting performance….
#2 Insulflex Corporation Sdn Bhd
Domain Est. 2001 | Founded: 1988
Website: insulflex.com.my
Key Highlights: Insulflex Corporation Sdn Bhd (743287-M) (ICSB) has been a market leader in flexible elastomeric foam insulation since 1988. … Factory: +603-8925-3085 ……
#3 Aerofoam® USA
Domain Est. 2015
Website: aerofoamusa.com
Key Highlights: Aerofoam Thermal Insulation Division is the leading manufacturer of insulation products such as elastomeric insulation and polyolefin insulation in UAE….
#4 nmc technical insulation
Domain Est. 2017
Website: nmc-insulation.com
Key Highlights: NMC, your insulation technology specialist. Dial up your comfort level, dial down your costs and energy consumption – for intact systems and sustainability….
#5 Aerofoam® Insulation Solutions
Website: aerofoam.ae
Key Highlights: Aerofoam® insulation is the premium manufacturer of cross linked polyolefin XLPE foam and NBR elastomeric rubber foam based sheets, tubes and rolls….
#6
Domain Est. 1996
Website: kflex.com
Key Highlights: K-FLEX products are safe to handle, easy to install, available in different sizes and based on innovative and sustainable technologies….
#7 ArmaFlex Overview
Domain Est. 1999
Website: armacell.com
Key Highlights: All closed-cell insulation materials based on elastomeric foam – our standard ArmaFlex product is manufactured worldwide, customised to meet local requirements….
#8 Aeroflex USA
Domain Est. 2000
Website: aeroflexusa.com
Key Highlights: Closed-Cell Elastomeric Foam Insulation uniquely formulated for success in mechanical, refrigeration, HVAC, and plumbing systems….
#9 General Insulation Company
Domain Est. 2001
Website: generalinsulation.com
Key Highlights: A wholesale distributor, providing a full line of sustainable products and solutions for thermal efficiency, condensation/moisture control, and life safety….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Elastomeric Insulation

2026 Market Trends for Elastomeric Insulation
The elastomeric insulation market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by a confluence of sustainability mandates, technological innovation, and shifting global economic dynamics. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
Rising Demand from the HVAC and Plumbing Sectors
The heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), and plumbing industries remain the primary drivers of elastomeric insulation demand. As urbanization accelerates and building standards become more energy-efficient globally, the need for high-performance insulation in commercial, residential, and industrial buildings continues to grow. The proliferation of smart HVAC systems and green building certifications—such as LEED and BREEAM—favors elastomeric materials due to their excellent thermal performance, ease of installation, and low environmental impact.
Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations are increasingly influencing material selection. By 2026, stricter global policies on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and the phase-out of ozone-depleting substances will push manufacturers toward halogen-free, low-emission formulations. Recyclability and the use of bio-based or recycled content in elastomeric insulation are expected to become more prominent, aligning with circular economy goals. Companies investing in eco-friendly production processes will gain a competitive advantage in regulated markets such as the EU and North America.
Expansion in Emerging Economies
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, will remain a high-growth region for elastomeric insulation. Rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and rising energy demands are fueling construction activities. Government initiatives promoting energy efficiency in buildings will further stimulate market expansion. Latin America and the Middle East are also anticipated to see increased adoption due to urban development projects and investments in petrochemical and industrial facilities.
Technological Advancements and Product Innovation
Manufacturers are focusing on enhancing product performance through innovations such as improved fire resistance, extended temperature range tolerance, and enhanced microbial resistance. Nanotechnology integration and advanced polymer formulations are opening avenues for thinner, more efficient insulation materials with superior durability. Smart elastomeric insulation with embedded sensors for real-time temperature and humidity monitoring may begin to emerge in niche applications by 2026, particularly in critical infrastructure and data centers.
Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Volatility
Ongoing fluctuations in the prices of raw materials—especially synthetic rubbers and additives—pose challenges. The industry is responding by diversifying supply chains and exploring alternative feedstocks to mitigate risks. Geopolitical tensions and trade policies will continue to influence material costs and availability, prompting companies to localize production and strengthen regional supply networks.
Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The elastomeric insulation market is expected to witness increased consolidation as larger players acquire niche innovators to expand product portfolios and geographic reach. Competition will intensify on both price and performance, with differentiation increasingly derived from sustainability credentials, technical support, and system integration capabilities.
In summary, the 2026 elastomeric insulation market will be defined by a strong emphasis on sustainability, innovation, and regional growth opportunities, with performance and environmental compliance serving as key competitive differentiators.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Elastomeric Insulation (Quality, IP)
Sourcing elastomeric insulation requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, safety risks, legal disputes, and increased long-term costs. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Performance Issues
Substandard Raw Materials:
Using low-grade synthetic rubber (e.g., NBR or EPDM) or recycled content can compromise physical properties such as flexibility, temperature resistance, and longevity. Inferior materials may degrade faster under UV exposure, moisture, or thermal cycling, leading to premature insulation failure.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes:
Variations in curing, foaming, or thickness control during production result in non-uniform insulation performance. This can cause thermal bridging, condensation, or mold growth, especially in HVAC systems.
Lack of Certification and Testing Data:
Suppliers may claim compliance with standards like ASTM C534 or EN 14304 without providing verifiable test reports. Without third-party certification (e.g., UL, FM, or ISO), buyers risk installing insulation that does not meet fire safety, smoke emission, or thermal performance requirements.
Inadequate Environmental Resistance:
Some elastomeric insulation products are not properly formulated for outdoor use or high-humidity environments. This can result in surface cracking, water absorption, and reduced thermal efficiency over time.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Counterfeit or Imitation Products:
Unscrupulous suppliers may replicate branded elastomeric insulation (e.g., ArmaFlex, K-Flex) without authorization. These counterfeit products often use inferior materials and lack performance validation, posing safety and compliance risks.
Unauthorized Use of Patented Technologies:
Certain formulations, manufacturing processes, or product designs (e.g., antimicrobial additives, low-smoke formulations) are protected by patents. Sourcing from manufacturers who infringe on these patents exposes buyers to legal liability and supply chain disruptions.
Misrepresentation of Brand Affiliation:
Some suppliers falsely claim partnerships or authorization with established brands. This misleads buyers into believing they are purchasing genuine, high-performance products when they are not.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation:
Without proper documentation (e.g., certificates of authenticity, material traceability), it becomes difficult to verify the origin of the product and ensure it is not involved in IP violations.
Mitigation Strategies
- Verify supplier credentials and request independent test reports.
- Require full transparency on material composition and manufacturing origin.
- Conduct due diligence on brand authenticity and IP compliance.
- Work with authorized distributors of reputable manufacturers.
- Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures long-term system efficiency, safety, and legal compliance in elastomeric insulation projects.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Elastomeric Insulation
Product Overview and Handling Requirements
Elastomeric insulation is a flexible, closed-cell foam commonly used for thermal insulation in HVAC, plumbing, and refrigeration systems. Due to its sensitive physical properties, proper handling and storage are critical to maintain performance. The material is susceptible to damage from UV exposure, extreme temperatures, moisture, and physical compression. Always handle rolls and sheets with care using appropriate lifting equipment to avoid kinking or tearing. Use gloves to prevent contamination from oils and dirt, which may compromise adhesive surfaces on pre-coated variants.
Packaging and Transport Specifications
Elastomeric insulation is typically supplied in compressed rolls, pre-slit tubes, or flat sheets, protected by durable plastic wrap or corrugated packaging. During transport, ensure the material remains in its original packaging to guard against moisture, dirt, and mechanical damage. Transport vehicles must be clean, dry, and enclosed to prevent exposure to rain, snow, or direct sunlight. Avoid stacking heavy items on top of insulation packages to prevent permanent compression. Maintain temperatures between 40°F (5°C) and 100°F (38°C) during transit to prevent brittleness or softening.
Storage Conditions and Shelf Life
Store elastomeric insulation in a cool, dry, indoor environment away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Ideal storage conditions are temperatures between 60°F (15°C) and 80°F (27°C) with relative humidity below 65%. Keep material off concrete floors using pallets or racks to prevent moisture absorption. Rolls should be stored vertically when possible to minimize deformation. The typical shelf life is 5–7 years when stored properly; however, inspect material before use for signs of degradation such as cracking, stickiness, or loss of resilience.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Elastomeric insulation products must comply with relevant regional and international standards. In the U.S., look for compliance with ASTM C534 (for elastomeric flexible insulation) and ASTM E84 (surface burning characteristics). Products may also carry UL, FM, or GREENGUARD certifications. Ensure insulation meets low-emission standards (e.g., CDPH Standard Method v1.2) for indoor air quality in commercial and residential applications. Check local building codes for fire safety and VOC requirements. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) must be accessible to all handlers.
International Shipping and Import Regulations
When shipping elastomeric insulation internationally, verify compliance with destination country regulations. Some regions require specific fire ratings (e.g., EN 13501 in the EU) or environmental certifications. Label packages clearly with contents, handling instructions (e.g., “Protect from Moisture,” “Do Not Stack”), and safety information. Complete all required export documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of compliance. Be aware of import duties, customs classifications (e.g., HS Code 3921.90 for certain foam plastics), and any restrictions on chemical content (e.g., REACH, RoHS).
Installation Site Logistics and Best Practices
Coordinate deliveries to match installation schedules to reduce on-site storage time. Store materials on-site in covered, elevated areas protected from weather and construction debris. Unpack insulation only when ready for use to preserve integrity. Train installers on proper cutting, fitting, and sealing techniques to minimize waste and ensure system efficiency. Collect and dispose of off-cuts responsibly—many elastomeric materials are not recyclable through standard municipal programs; consult the manufacturer for disposal or take-back options.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain complete records for all shipments, including batch numbers, production dates, and certificates of conformance. This traceability supports quality assurance and simplifies compliance audits. Provide installers and project managers with product data sheets, installation guides, and warranty information. In commercial projects, retain documentation for the building’s compliance portfolio and LEED or BREEAM certification submissions where applicable.
In conclusion, sourcing elastomeric insulation requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Critical aspects such as thermal efficiency, resistance to moisture and UV exposure, temperature range compatibility, and ease of installation must be evaluated based on the specific application—whether for HVAC systems, plumbing, or industrial use. Additionally, selecting reputable suppliers who provide certified, high-quality materials compliant with industry standards (such as ASTM or UL) is essential to guarantee long-term reliability and safety.
Sustainability and environmental impact are increasingly important considerations, making it beneficial to source insulation with low global warming potential and recyclable or eco-friendly properties. Conducting a total cost analysis—factoring in not only the initial purchase price but also energy savings, maintenance, and lifespan—can lead to more informed procurement decisions.
Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy that balances technical requirements, supplier reliability, and lifecycle value will ensure that elastomeric insulation delivers superior thermal performance, energy efficiency, and operational savings across diverse environments.