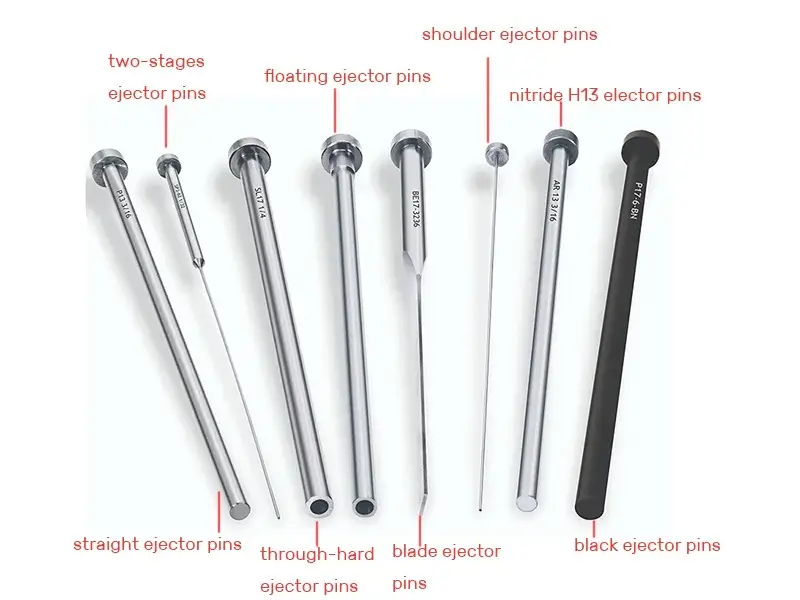
The global ejector pins market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand from injection molding industries, particularly in automotive, consumer electronics, and packaging sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global plastic injection molding market was valued at USD 346.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% from 2023 to 2030—underpinning the increasing need for precision components like ejector pins. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects the industrial molds market, a key end-user segment for ejector pins, to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% during the forecast period 2023–2028. As manufacturing standards evolve toward higher precision and durability, the role of high-quality ejector pins becomes critical in ensuring efficient mold release and minimizing production downtime. With Asia-Pacific emerging as a manufacturing hub and automation on the rise, demand for reliable, wear-resistant ejector pins is escalating. This growing market landscape has intensified competition among manufacturers to deliver innovation in materials, coating technologies, and dimensional accuracy. In this context, we identify the top 9 ejector pins manufacturers shaping the industry through technological advancement, global reach, and consistent product performance.
Top 9 Ejector Pins Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 IMS Company
Domain Est. 1996
Website: imscompany.com
Key Highlights: Applied filters: · Item# 152732. Ejector Pin, H-13, Nitrided Length: 6 OD: 0.125 · Item# 152733. Ejector Pin, H-13, Nitrided Length: 10″ OD: 0.125″ · Item# 152742….
#2 Ejector & Core Pins
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mscdirect.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryMSC Direct offers quality Ejector & Core Pins at a great value. Find premium products to last a lifetime!…
#3 Mold Ejector Pins
Website: uscorepins.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture all types of core pins and many other Mold components such as Pins and Bushings, ejector pins, ejector sleeves, guide pins, and much more….
#4 Ejector Pins
Domain Est. 1996
Website: procomps.com
Key Highlights: Progressive’s ejector pins are engineered and manufactured to meet the growing demands of today’s production tooling industry….
#5 Straight Ejector Pins
Domain Est. 1999
Website: dme.net
Key Highlights: Buy Straight Ejector Pins From DME.net visit us today to get started!…
#6 Economy Ejector Pins
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ppunch.com
Key Highlights: Precision Punch & Tooling offers a complete line of standard stainless steel ejector pins and straight ejector pins made with other materials….
#7 MISUMI Ejector Pins
Domain Est. 2007
Website: us.misumi-ec.com
Key Highlights: Shop MISUMI Ejector Pins at MISUMI. MISUMI offers FREE CAD download, short lead times and competitive pricing. Quote and order online today!…
#8 Ejector pins
Website: nonnenmann.net
Key Highlights: Metric-Nitrided and Metric-Core Ejector Pins, Metric-Nitrided and Metric-Hardened Ejector Sleeves for injection molding and toolmaking….
#9 Performance Alloys PX Ejector Pins
Website: moldstar.com
Key Highlights: PERFORMANCE ALLOYS PX STANDARD STRAIGHT EJECTOR PINS (Steel Nitrided Ejector Pins). CAT NO. PIN DIA, HEAD DIA, HEAD THICK, CAT NO. PIN DIA, HEAD DIA, HEAD…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ejector Pins

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ejector Pins
The global ejector pins market is poised for steady growth and significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving manufacturing demands, material innovations, and the increasing complexity of molded products. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Increased Demand from High-Precision Industries: The automotive, electronics, and medical device sectors are demanding smaller, more intricate, and higher-tolerance components. This necessitates ejector pins with superior precision, consistency, and wear resistance, particularly in micro-molding applications. Expect growth in demand for ultra-fine pins (<1mm diameter) and specialized tip geometries.
-
Material Innovation and Performance Enhancement: The shift towards high-performance engineering plastics (e.g., PEEK, PPS, LCP) and aggressive molding conditions (higher temperatures, pressures) is accelerating the adoption of advanced materials for ejector pins. Trends include:
- Widespread Use of Pre-Hardened & Tool Steels: Materials like H13, S136, and specialized pre-hardened steels offering excellent toughness, polishability, and corrosion resistance will dominate.
- Rise of Coatings and Surface Treatments: Coatings like TiN (Titanium Nitride), TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride), DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon), and specialized nitriding processes will be increasingly adopted to drastically improve wear resistance, reduce friction, prevent galling, and extend pin lifespan, especially in abrasive or high-cycle applications.
- Exploration of Alternative Materials: Research and limited adoption of ceramics or carbide-tipped pins for extreme wear scenarios may emerge, though cost remains a barrier.
-
Focus on Standardization and Quick-Change Systems: To minimize downtime and improve mold changeover efficiency (especially in high-mix/low-volume production), there will be a growing preference for standardized ejector pin systems (e.g., conforming to HASCO, DME standards) and modular quick-change ejector assemblies. This trend enhances productivity and reduces inventory complexity.
-
Integration with Smart Manufacturing (Industry 4.0): While still nascent for individual pins, the broader trend towards smart molds will influence the market. Integration of sensors within ejector sleeves or plates to monitor ejection force, cycle count, temperature, and potential failure (like bending) will gain traction, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization. Data from these sensors can feed into overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) monitoring.
-
Sustainability and Longevity: Manufacturers will prioritize pins with longer service life to reduce waste, replacement frequency, and overall environmental footprint. This drives demand for pins made from durable, recyclable materials (like high-grade tool steels) and robust surface treatments. Efficient manufacturing processes for the pins themselves will also be scrutinized.
-
Geographic Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience: Demand growth will remain strong in Asia-Pacific (driven by China, India, Southeast Asia’s manufacturing hubs), North America (reshoring trends, automotive), and Europe (high-value automotive, medical). However, supply chains will focus on resilience, potentially leading to regionalization of manufacturing or sourcing to mitigate risks, impacting pin suppliers’ strategies.
-
Consolidation and Specialization among Suppliers: The market may see consolidation among smaller players, while leading suppliers will differentiate through offering comprehensive solutions – not just pins, but also technical support, custom engineering, coating services, and integration with mold design software.
In summary, the 2026 ejector pins market will be characterized by a strong emphasis on performance, precision, longevity, and integration. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to leverage advanced materials and coatings, adapt to automation and Industry 4.0 demands, and provide reliable, standardized solutions that enhance overall molding efficiency and product quality.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Ejector Pins (Quality, IP)
Sourcing ejector pins—critical components in injection molding—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to mold failure, production delays, legal disputes, and increased costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Tolerances
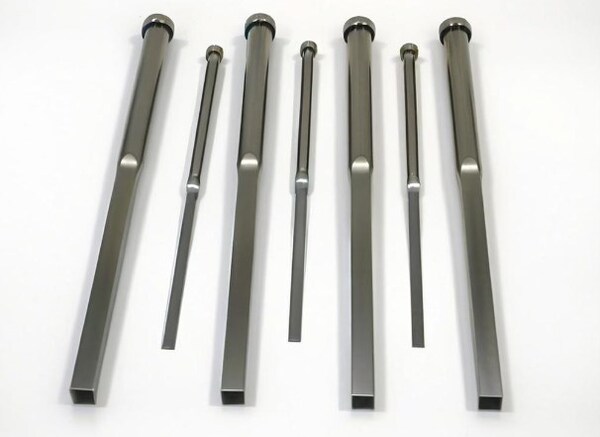
One of the most frequent issues is receiving ejector pins made from substandard materials or manufactured with inconsistent tolerances. Low-quality pins may be made from non-standard steel grades, lack proper heat treatment, or exhibit surface imperfections. This can result in premature wear, galling, or breakage during operation, leading to unplanned downtime and costly mold repairs. Always verify material certifications (e.g., H13, SKD61) and ensure dimensional accuracy per ISO or DIN standards.
Inadequate Surface Finish and Coating
Ejector pins require precise surface finishes (often mirror-polished) and may need specialized coatings like TiN (titanium nitride) to reduce friction and resist corrosion. Sourcing pins without proper surface treatment increases the risk of sticking, scoring, or corrosion in aggressive molding environments. Confirm surface roughness values (e.g., Ra < 0.2 µm) and coating specifications with the supplier to ensure compatibility with your resin and production cycle.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide full traceability, including material test reports (MTRs), heat treatment records, and quality inspection certificates. Sourcing from vendors who cannot provide this documentation increases the risk of counterfeit or non-conforming parts. Ensure your supplier adheres to quality management systems such as ISO 9001 and can supply full documentation upon request.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Using ejector pins that replicate patented designs—such as proprietary geometries, tip profiles, or retention systems—without authorization can lead to IP violations. Some suppliers may offer “compatible” or “generic” versions of branded pins (e.g., DME, Hasco), but these may infringe on design or utility patents. Always verify that the pins you source do not violate third-party IP, especially when reverse-engineered designs are involved.
Misrepresentation of Brand and Origin
Some suppliers falsely advertise pins as being from premium brands or manufactured in specific countries (e.g., Germany, Japan) when they are actually low-cost replicas. This misrepresentation affects performance expectations and may void warranties. Conduct supplier audits or request proof of origin and brand licensing to avoid counterfeit products.
Inconsistent Quality from Low-Cost Suppliers
While cost savings are appealing, sourcing from low-cost suppliers—especially without rigorous vetting—can result in inconsistent quality between batches. This variability undermines mold reliability and longevity. Implement supplier qualification processes, including sample testing and on-site audits, to ensure consistent manufacturing standards.
Overlooking Customization and Application Fit
Standard ejector pins may not suit specialized applications (e.g., high-temperature resins, medical-grade molding). Sourcing without considering application-specific requirements—such as corrosion resistance, non-magnetic properties, or custom tip designs—can lead to functional failure. Work closely with technical suppliers to ensure the pins are engineered for your specific use case.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—through rigorous supplier evaluation, clear specifications, and IP due diligence—companies can ensure reliable mold performance and avoid costly legal and operational setbacks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ejector Pins
Overview
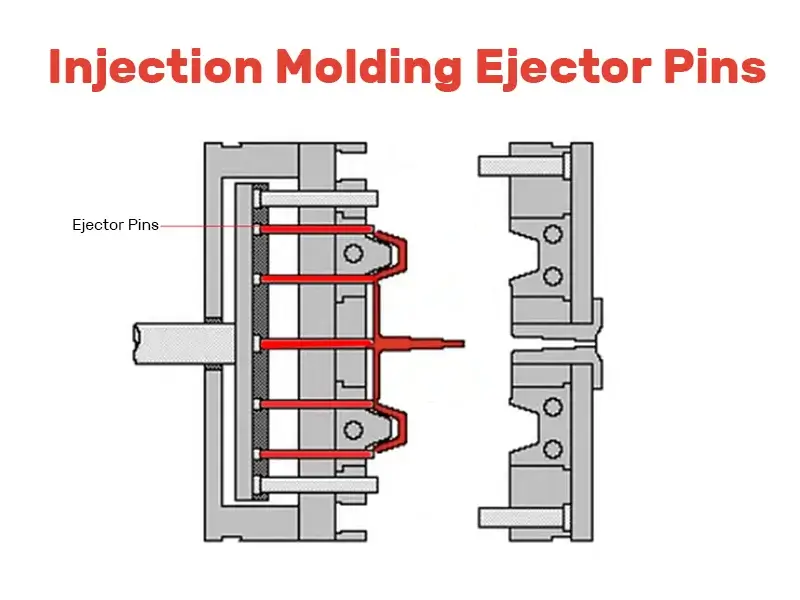
Ejector pins are precision components used in injection molding, die casting, and other manufacturing processes to safely and efficiently remove molded parts from the mold cavity. Proper logistics and compliance management ensures these components meet technical, safety, and regulatory standards across global supply chains.
Classification & Harmonized System (HS) Code
- HS Code: 8480.71.00 (Mold bases and mold parts, including ejector pins, for molding materials)
- Category: Industrial Tooling Components
- Note: Confirm local tariff classifications; some jurisdictions may classify under subcategories based on material (e.g., steel vs. carbide).
Import/Export Regulations
- Export Controls: Generally not subject to ITAR or EAR (U.S. regulations) unless part of a larger controlled system.
- Dual-Use Considerations: Typically non-sensitive, but verify if pins are used in defense-related molds.
- Documentation Required:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin (if claiming preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
- Restricted Destinations: No known broad restrictions, but monitor sanctions lists (e.g., OFAC, EU) for embargoed countries.
Packaging & Handling
- Packaging Standards:
- Individually wrapped or sleeved to prevent scratching.
- Packed in anti-corrosion paper or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) packaging for long-term storage.
- Use rigid containers (plastic trays or wooden crates) for bulk shipments to avoid bending.
- Labeling Requirements:
- SKU/part number
- Material type (e.g., SKD61, H13)
- Hardness rating (e.g., 52–54 HRC)
- Quantity and net weight
- “Fragile – Precision Components” handling labels
- Storage Conditions:
- Dry, climate-controlled environment (40–60% RH).
- Avoid exposure to moisture, acids, or abrasive materials.
Transportation & Freight
- Mode of Transport: Air, ocean, or ground based on urgency and volume.
- Incoterms Recommendations:
- FOB (Free On Board) for cost control on exports.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) when managing full logistics.
- Freight Class: Typically LCL (Less than Container Load) for small batches; FCL for bulk orders.
- Insurance: Cover for loss, damage, and customs delays recommended.
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (EU): Ejector pins are generally exempt as spare parts for industrial machinery (Annex III, Category 11), but verify based on final application.
- REACH (EU): No SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) typically in tool steels, but suppliers should provide compliance declaration.
- REACH SVHC Candidate List: Confirm raw material composition with supplier.
- Prop 65 (California): No known warnings required for standard steel pins.
- China RoHS: Follow labeling requirements if sold as part of a finished product in China.
Quality & Certification
- Standards Compliance:
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management) for manufacturing processes.
- ISO 2859-1 (Sampling procedures for inspection).
- Material Certifications:
- Mill Test Certificate (MTC) per EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2.
- Hardness test reports.
- Tolerances: Typically ±0.01 mm; must conform to customer drawings or DIN 1530 standards.
Customs Clearance
- Duties & Tariffs: Vary by country; leverage free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN) where applicable.
- Customs Broker Engagement: Recommended for complex markets (e.g., Brazil, India).
- Duty Drawback: Possible if pins are used in production of exported goods (check local regulations).
Sustainability & ESG Considerations
- Recyclability: High (tool steels are 100% recyclable).
- Supplier Audits: Ensure ethical labor practices and environmental compliance in the supply chain.
- Carbon Footprint: Optimize shipping routes and consolidate shipments to reduce emissions.
Risk Mitigation
- Supply Chain Diversification: Source from multiple suppliers to avoid disruptions.
- Lead Time Management: Maintain buffer stock for critical tooling operations.
- Counterfeit Prevention: Purchase only from authorized distributors; verify material traceability.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for ejector pins require attention to classification, regulatory alignment, secure packaging, and documentation. Partnering with certified suppliers and experienced freight forwarders ensures smooth international trade and operational reliability. Regular audits and compliance updates are essential to maintain standards across evolving global regulations.
Conclusion on Sourcing Ejector Pins:
Sourcing ejector pins requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, lead time, and supplier reliability. As critical components in injection molding and die-casting processes, ejector pins must meet stringent standards for precision, hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional accuracy to ensure mold performance and longevity. After evaluating various suppliers, materials (such as SKD61, H13, or stainless steel), and manufacturing standards, it is recommended to partner with certified suppliers that offer consistent quality, technical support, and traceability of materials.
Priority should be given to suppliers with proven experience in precision tooling components and those compliant with international standards such as ISO 9001. While cost is a consideration, opting for lower-priced alternatives without verifying quality can lead to increased downtime, maintenance, and reduced mold life. Establishing long-term relationships with reliable vendors, potentially including a mix of domestic and global sources, will enhance supply chain resilience and ensure timely delivery.
In conclusion, a structured sourcing strategy—emphasizing quality assurance, supplier credibility, and total cost of ownership—will optimize performance and reduce operational risks associated with ejector pin failure. Regular evaluation and periodic re-assessment of the supply base will further support continuous improvement in mold reliability and production efficiency.