The global gear motor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for automation, energy efficiency, and precision in industrial and commercial applications. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 102.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 144.6 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by increasing adoption in sectors such as manufacturing, automotive, material handling, and renewable energy. As industries prioritize reliable and high-performance motion control solutions, the role of leading economic gear motor manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. These companies balance cost-efficiency with technological innovation, making advanced drive systems accessible across emerging and developed markets alike. The following list highlights the top 10 econ gear motor manufacturers shaping the competitive landscape through strategic R&D, global supply networks, and scalable product portfolios.
Top 10 Econ Gear Motor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Rossi
Domain Est. 1995
Website: rossi.com
Key Highlights: Gearboxes and electric motors, discover our range. Helical and bevel helical gearmotors. Industrial Gear Units. A wide range of gear reducers, combined with a ……
#2 Dynamatic Technologies Limited
Domain Est. 1997
Website: dynamatics.com
Key Highlights: Dynamatic Hydraulics® specialises in the manufacture of highly engineered hydraulic gear pumps. We are one of the world’s largest manufacturers of hydraulic ……
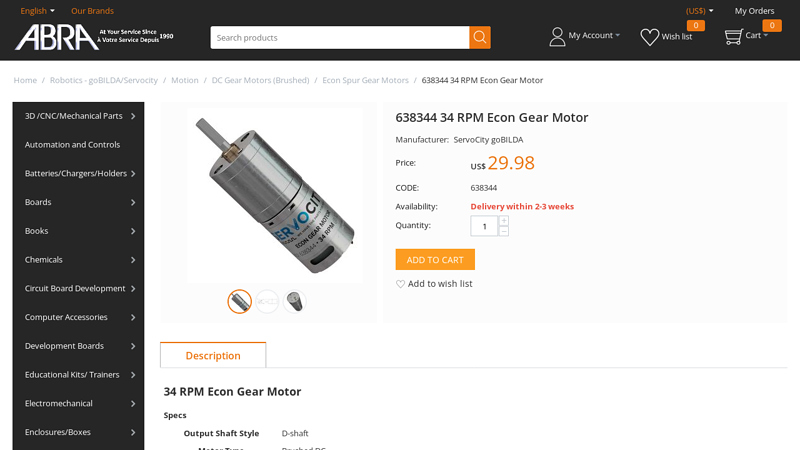
#3 638344 34 RPM Econ Gear Motor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: abra-electronics.com
Key Highlights: 21-day returnsWireless Zigbee/Xbee. 638344 34 RPM Econ Gear Motor. Manufacturer: ServoCity goBILDA. Price: US$29.98. CODE: 638344. Availability: Delivery within 2-3 weeks….
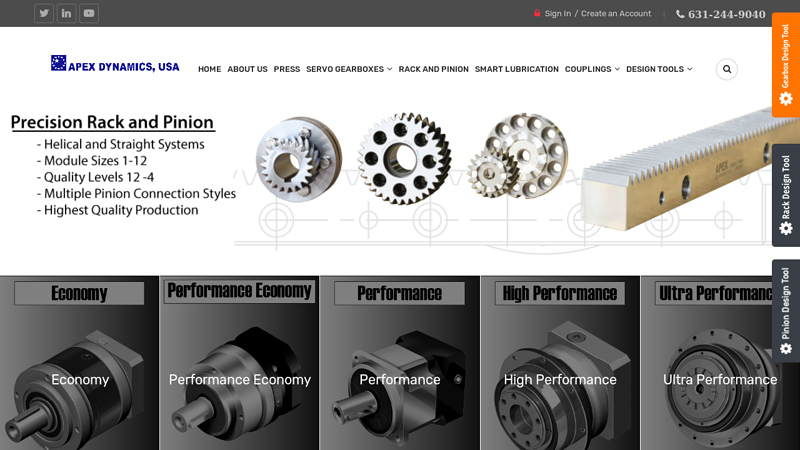
#4 Planetary Gearbox Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2003
Website: apexdynamicsusa.com
Key Highlights: Apex Dynamics is a worldwide name in planetary gearbox manufacturing with over 20 years of accumulated experience producing high-quality components….
#5 Bauer GMC
Domain Est. 2015
Website: bauergmc.com
Key Highlights: Bauer GMC Inc. specializes in innovative and energy-efficient gear drive solutions. We are an official distributor of Bauer gear motors….
#6 ABB Motors and Generators
Domain Est. 1990
Website: new.abb.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to ABB’s Motors and Generators, your ultimate destination for high-efficiency motors and dependable power generators….
#7 34 RPM Econ Gear Motor
Domain Est. 2004
Website: eu.robotshop.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (2) · 30-day returnsThe 34 RPM Econ Gear Motor offers a D-shaft style Brushed DC motor. It provides a speed (No Load at 12 VDC) of 34 rpm and a current (No Load at 1…
#8 WEG
Domain Est. 2004
Website: weg.net
Key Highlights: WEG provides global solutions for electric motors, variable frequency drives, soft starters, controls, panels, transformers, and generators….
#9 Spur Gear Motors
Domain Est. 2017
Website: microdcmotors.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $150 15-day returnsExplore spur gear motors delivering efficient torque and speed for robotics, automation and hobby projects; choose quality gear motors in the …
#10 LEESON Brand
Domain Est. 2021
Website: regalrexnord.com
Key Highlights: The LEESON band spans thousands of alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) motors, gearmotors, washdown and variable-speed control solutions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Econ Gear Motor

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Econ Gear Motor
Based on current industry trajectories, technological advancements, and macroeconomic projections, the second half of 2026 presents a dynamic and largely favorable landscape for Econ Gear Motor. The company is well-positioned to capitalize on several converging trends, though it must also navigate persistent challenges.
1. Accelerated Electrification & Automation (Primary Growth Driver)
* Industrial Automation Surge: H2 2026 will see continued strong demand for automation across manufacturing, logistics (especially e-commerce fulfillment centers), and food & beverage processing. Econ Gear Motor’s core products are essential components in conveyors, robotic arms, packaging machinery, and material handling systems. The push for efficiency, labor cost mitigation, and resilience will drive capital expenditure in automation, directly benefiting Econ.
* EV & EV Infrastructure Boom: The electric vehicle market is expected to reach new adoption milestones by 2026. Econ Gear Motors are critical in EV production lines (robotic welding, assembly) and increasingly within charging infrastructure (cooling pumps, actuation in chargers, automated parking systems in charging hubs). This represents a significant and growing market segment.
* Renewable Energy Expansion: Onshore and offshore wind turbine maintenance platforms, solar panel tracking systems, and hydroelectric plant operations increasingly rely on robust, reliable gear motors. The global push for decarbonization ensures sustained investment in these sectors, creating steady demand.
2. Sustainability & Energy Efficiency as Core Demands (Value Differentiation)
* Regulatory & Customer Pressure: Stricter global energy efficiency standards (e.g., IE4 becoming baseline, push towards IE5) and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) mandates will be paramount. Econ Gear Motor’s focus on high-efficiency product lines (e.g., IE4/IE5 compliant motors, optimized gear designs reducing losses) will be a major competitive advantage. Customers will prioritize total cost of ownership (TCO), where energy savings dominate.
* Demand for “Green” Solutions: Beyond efficiency, demand for motors with longer lifespans, recyclable materials, and lower environmental impact during manufacturing will grow. Econ’s ability to demonstrate sustainable practices and offer eco-designs will enhance brand value and market share.
3. Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization (Operational Imperative)
* Shift from “Just-in-Time” to “Just-in-Case”: Geopolitical tensions and recent disruptions have made resilient supply chains non-negotiable. H2 2026 will see customers prioritizing suppliers with diversified sourcing, regional manufacturing/warehousing (e.g., nearshoring to North America, Europe, or Southeast Asia), and robust inventory management. Econ’s ability to demonstrate supply chain security will be a key differentiator, potentially allowing for premium pricing.
* Localization Pressure: Trade policies and customer demands will favor local production. Econ may need to evaluate or expand regional manufacturing or assembly hubs to serve key markets efficiently and reduce logistics risks/costs.
4. Digitalization & Smart Motor Integration (Emerging Opportunity)
* Rise of IIoT & Predictive Maintenance: Integration of sensors (vibration, temperature, current) into gear motors for condition monitoring will become more common. While Econ may not be a pure-play IIoT company, offering motors compatible with or easily integrated into predictive maintenance systems (e.g., standardized interfaces, data output) will add significant value.
* Demand for “Smart” Components: Customers seek motors that enable better process control and data analytics. Econ could explore partnerships with sensor/IoT platform providers or develop basic monitoring capabilities within its product range to meet this demand.
5. Persistent Challenges & Competitive Pressures
* Raw Material Volatility: Prices for copper, steel, and rare earth elements (for permanent magnets in some motors) remain susceptible to geopolitical and economic fluctuations. Econ’s procurement strategy and potential for material substitution (e.g., ferrite magnets where feasible) will be crucial for margin protection.
* Intense Competition: The gear motor market remains competitive, with established global players and agile regional manufacturers. Price pressure will persist, making Econ’s focus on reliability, efficiency, and service critical for differentiation beyond just cost.
* Skilled Labor Shortage: Automation demand is outpacing the availability of skilled engineers and technicians for integration and maintenance. Econ can leverage this by offering enhanced technical support, training programs, and potentially more plug-and-play solutions.
Strategic Implications for Econ Gear Motor (H2 2026 Focus):
- Double Down on Efficiency: Prioritize R&D and marketing for IE4/IE5 compliant and ultra-efficient gear motor solutions. Quantify energy savings for customers.
- Enhance Supply Chain Agility: Invest in regional distribution centers, diversify key component suppliers, and implement advanced inventory forecasting tools to ensure reliability.
- Target High-Growth Sectors: Actively pursue opportunities in EV manufacturing/infrastructure, renewable energy, and automated logistics solutions.
- Embrace Digital Connectivity: Develop or partner on solutions enabling basic motor health monitoring and data integration, moving beyond purely mechanical components.
- Strengthen Sustainability Narrative: Formalize and communicate eco-design initiatives, recyclability, and manufacturing sustainability efforts to meet customer ESG requirements.
- Invest in Service & Support: Counter skill shortages by offering superior technical support, remote diagnostics, and training, enhancing customer loyalty.
Conclusion:
H2 2026 offers significant growth potential for Econ Gear Motor, driven by unstoppable trends in automation, electrification, and sustainability. Success will hinge on Econ’s ability to leverage its core strengths in efficiency and reliability while proactively adapting to demands for supply chain resilience, digital integration, and demonstrable sustainability. By focusing on high-value, high-growth applications and differentiating through performance and service, Econ is well-positioned to capture market share in the latter half of 2026.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Economical Gear Motors (Quality and IP)
Sourcing cost-effective gear motors is essential for many industrial and commercial applications, but choosing overly economical options can lead to significant risks—particularly concerning quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these pitfalls helps in making informed procurement decisions.
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
Low-cost gear motors often use substandard materials such as inferior-grade gears, weak housing, or low-efficiency bearings. These compromises lead to premature wear, increased downtime, and higher total cost of ownership due to frequent replacements and maintenance.
Inaccurate or Inflated Performance Specifications
Budget gear motors may be advertised with misleading torque, speed, or efficiency ratings. These exaggerated claims can result in system underperformance, design failures, or safety hazards, especially in precision applications.
Lack of Protection Ratings (IP Inadequacy)
Many economical motors do not meet required Ingress Protection (IP) standards. An IP65 rating may be claimed when the motor only achieves IP54, leaving it vulnerable to dust and moisture—leading to internal damage and reduced lifespan in harsh environments.
Non-Compliance with International Standards
Cheap gear motors may not comply with critical standards such as CE, UL, or ISO. This not only affects performance and safety but can also result in legal liabilities or difficulties in global market access.
Counterfeit or Clone Products
Some low-cost suppliers offer gear motors that mimic well-known brands, infringing on intellectual property rights. Using such products exposes businesses to legal risk, warranty issues, and unpredictable performance due to unlicensed design replication.
Limited or No Technical Support and Documentation
Economical suppliers often provide incomplete datasheets, lack CAD models, or offer minimal technical support. This makes integration into systems difficult and increases engineering time and risk during installation and troubleshooting.
Short or No Warranty and Poor After-Sales Service
Many budget gear motors come with limited or voidable warranties. Combined with poor customer service, this makes resolving defects or failures time-consuming and costly.
Supply Chain and Long-Term Availability Risks
Low-cost manufacturers may lack stable production capabilities. This increases the risk of supply interruptions, making it difficult to source replacement units or maintain consistent product lines over time.
Hidden Total Cost of Ownership
While the initial purchase price is low, poor reliability, higher energy consumption, and frequent maintenance can dramatically increase operational costs over the motor’s lifecycle—offsetting any upfront savings.
Lack of Traceability and Quality Control
Economical gear motors often come from manufacturers with weak quality management systems. The absence of traceability (e.g., batch numbers, certifications) makes it difficult to address quality issues or conduct root cause analysis when failures occur.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Econ Gear Motor
Product Classification and HS Code
Econ Gear Motors are typically classified under Harmonized System (HS) Code 8501.31 or 8501.32, depending on motor type and power output. Confirm the exact HS code based on product specifications (e.g., AC/DC, voltage, horsepower) to ensure accurate customs declarations. Always refer to the latest tariff schedule of the destination country, as classifications may vary slightly by region.
Export Documentation Requirements
Ensure the following documents are prepared for every shipment:
– Commercial Invoice (with detailed product description, value, and country of origin)
– Packing List (itemizing contents, weights, and dimensions per package)
– Bill of Lading (for sea freight) or Air Waybill (for air freight)
– Certificate of Origin (if required by trade agreement or destination country)
– Technical Datasheets (to support classification and compliance)
All documents must be accurate, consistent, and signed where required.
Packaging and Labeling Standards
Package Econ Gear Motors securely to prevent damage during transit. Use moisture-resistant materials and include internal bracing for heavy components. Label each package with:
– Product name and model number
– Net and gross weight
– Handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”)
– Manufacturer and consignee information
– Compliance markings (e.g., CE, RoHS, if applicable)
Ensure barcodes or SKU labels are scannable and durable.
Regulatory Compliance (CE, RoHS, REACH)
Econ Gear Motors exported to the European Union must comply with:
– CE Marking: Demonstrates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– RoHS (2011/65/EU): Restricts the use of hazardous substances (e.g., lead, mercury, cadmium).
– REACH (EC 1907/2006): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
Verify compliance through internal testing or third-party certification, and maintain Technical Files for audit purposes.
Shipping and Freight Options
Choose shipping method based on delivery urgency and cost:
– Air Freight: Faster (3–7 days), higher cost, ideal for urgent or lightweight shipments.
– Sea Freight: Cost-effective for large volumes, longer transit (20–45 days), requires proper containerization.
– Land Transport: For regional distribution within contiguous countries (e.g., EU, North America).
Partner with certified freight forwarders experienced in industrial machinery logistics.
Import Duties and Taxes
Research import tariffs, VAT, and applicable taxes in the destination country. Duties vary by HS Code and trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-South Korea FTA). Use Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP) clearly in contracts to define responsibility for duties and taxes. Consider duty drawback programs or bonded warehouses where available.
Product Safety and EMC Compliance
Ensure Econ Gear Motors meet Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC Directive 2014/30/EU) and Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) requirements in applicable markets. Perform EMC testing to avoid interference with other devices. Retain test reports and conformity declarations for regulatory inspections.
Battery and Motor-Specific Regulations
If Econ Gear Motors include integral batteries (e.g., for brake systems), comply with IATA/IMDG regulations for lithium-ion batteries. Ship with proper UN38.3 testing certification, state of charge ≤30%, and use approved packaging marked with Class 9 hazard labels.
Recordkeeping and Audit Preparedness
Maintain digital and physical records of all export transactions for a minimum of 5 years (longer in some jurisdictions). Include:
– Export licenses (if required)
– Compliance certifications
– Shipping documents
– Internal compliance checklists
Regular internal audits help ensure ongoing adherence to trade regulations.
Restricted Parties and Embargo Screening
Screen all buyers, suppliers, and intermediaries against government restricted party lists (e.g., U.S. OFAC, EU Sanctions List, BIS Denied Persons List) before shipment. Implement automated screening tools to flag high-risk entities and prevent violations of economic sanctions.
After-Sales Support and Warranty Compliance
Provide clear warranty terms aligned with local consumer protection laws (e.g., UK Consumer Rights Act, EU Consumer Sales Directive). Include multilingual user manuals and contact details for technical support. Track warranty claims to identify potential compliance or product performance issues.
Conclusion: Sourcing EC on Gear Motor
After a comprehensive evaluation of technical requirements, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and long-term reliability, sourcing EC (electronically commutated) gear motors presents a strategic advantage for energy-efficient and precision-driven applications. EC gear motors offer superior energy efficiency, precise speed control, low maintenance, and extended service life compared to traditional AC or DC alternatives.
Careful supplier selection—prioritizing quality certifications, technical support, scalability, and proven industry experience—ensures reliable performance and integration into end systems. Although the initial investment may be higher, the total cost of ownership is significantly reduced due to lower energy consumption and maintenance costs.
In conclusion, sourcing EC gear motors aligns with sustainability goals, enhances operational efficiency, and supports advanced automation needs. A well-structured procurement strategy focused on performance, reliability, and lifecycle value will ensure optimal returns and future-proofing of engineering systems.