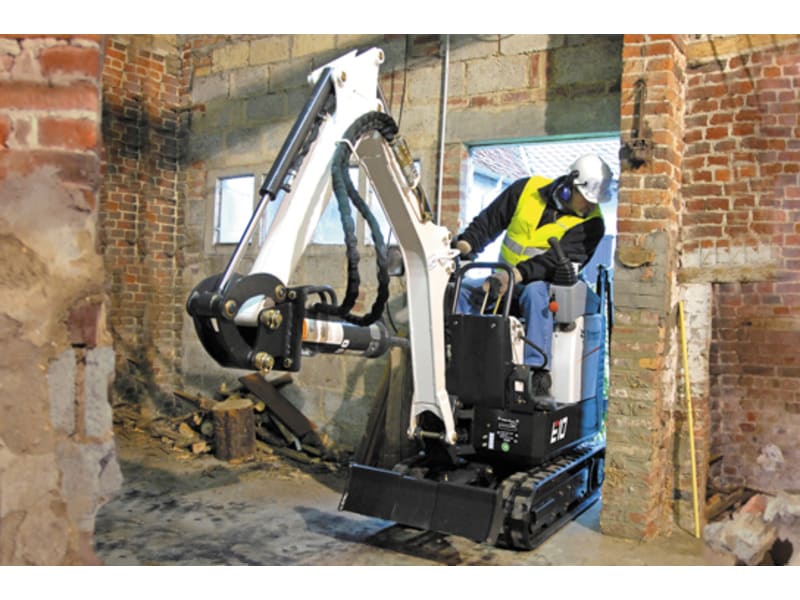
The global compact excavator market, including E10-class mini excavators, is experiencing robust growth driven by rising infrastructure development, urbanization, and demand for equipment suitable for tight urban worksites. According to Mordor Intelligence, the mini excavator market was valued at USD 13.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by increased adoption in residential construction, landscaping, and utility installation—applications where E10 models excel due to their maneuverability and minimal ground disturbance. As demand for compact, efficient machinery rises, manufacturers are investing heavily in electric and fuel-efficient models to meet emissions regulations and customer preferences. Based on market presence, technological innovation, sales volume, and customer reviews, the following five companies have emerged as leading E10 excavator manufacturers shaping this expanding segment.
Top 5 E10 Excavator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 E10 Compact (Mini) Excavator (Specs, Pricing & More)
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bobcat.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $99 30-day returnsWith a retracted track width of 28 in., the ultra-compact E10 compact mini excavator accesses jobsites where hand labor is your only other opti…
#2 Bobcat E10 Compact Excavator
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bobcatofhouston.com
Key Highlights: Explore the Bobcat E10 Compact Excavator. Ultra-compact size, smooth hydraulics and versatile attachments ideal for tight access digging and precision work….
#3 Bobcat E10 Mini Excavator
Domain Est. 2004
Website: brokentractor.com
Key Highlights: The Bobcat E10 Mini Excavator is a nimble and compact machine built for efficient performance in tight spaces. Introduced in 2019, it features a zero-tail ……
#4 Bobcat E10 Micro Digger
Domain Est. 2011
Website: adaremachinery.com
Key Highlights: Bobcat E10z | Most popular micro digger on the market. The new Bobcat E10z micro digger delivers big performance without compromising on size….
#5 ITT Bobcat Of celebrates manufacturing 10000 Bobcat mini
Domain Est. 2024
Website: ittdynamics.com
Key Highlights: Bobcat Of celebrates the manufacture of the 10,000th unit of the Bobcat E10 mini-excavator in the same year as the brand’s tenth anniversary….
Expert Sourcing Insights for E10 Excavator
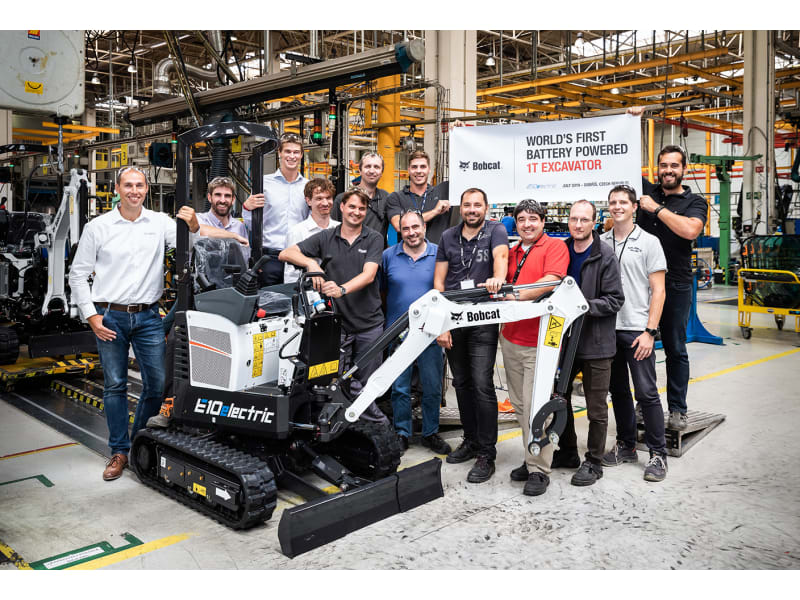

H2: 2026 Market Trends for E10 Excavators
By 2026, the market for E10-class mini excavators (typically 1-2 ton operating weight) is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, regulatory pressures, and shifting customer demands. Here’s a breakdown of the key trends expected to shape this segment:
1. Accelerated Electrification
- Dominant Trend: Electric E10 excavators will move from niche offerings to mainstream products. Stricter emissions regulations (especially in the EU, UK, and major US cities) and tightening noise ordinances will be primary drivers.
- Technology Maturation: Battery technology will improve, offering longer run times (potentially matching or exceeding diesel counterparts for typical urban jobs), faster charging, and lower costs. Swappable battery systems will become more common.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): While upfront costs may remain higher, the significantly lower operating costs (electricity vs. diesel, reduced maintenance) will make electric models increasingly attractive, especially for rental fleets and urban contractors.
- Market Share: Expect major manufacturers (Takeuchi, Kubota, Wacker Neuson, Bobcat, Yanmar, Hyundai) to have robust electric E10 lines, capturing a growing share (potentially 25-40% in regulated markets) of new sales.
2. Enhanced Connectivity & Telematics
- Standardization: Telematics (machine health, location, usage, fuel/battery levels, idle time) will become standard equipment, not an option, driven by fleet management demands and preventative maintenance.
- Advanced Diagnostics: AI-powered analytics will predict component failures and optimize service schedules, minimizing downtime.
- Remote Monitoring & Security: Real-time monitoring via smartphone apps and enhanced anti-theft features (geofencing, remote disable) will be standard, crucial for high-value electric assets.
- Data-Driven Services: OEMs will leverage data to offer predictive maintenance contracts, usage-based insurance, and performance optimization services.
3. Focus on Urbanization & Compact Efficiency
- “Zero Tail Swing” (ZTS) as Standard: The ability to work in confined spaces (backyards, alleys, inside buildings) will remain paramount. True ZTS designs will be the dominant configuration.
- Ultra-Compact Designs: Expect continued innovation in reducing overall machine footprint and tail swing radius without sacrificing stability or power.
- Low Noise & Vibration: Essential for early morning/late-night work in residential areas and indoor applications (e.g., basement work, retail). Electric models inherently excel here, but diesel models will also incorporate advanced noise-dampening technologies.
4. Increased Automation & Operator Assistance
- Semi-Automation: Features like automated digging (depth/grade control), automatic dozing, and intelligent swing will become more prevalent, improving efficiency and reducing operator skill requirements.
- Collision Avoidance: Proximity sensors and basic obstacle detection systems will start appearing, enhancing safety in congested worksites.
- Remote Operation: While full autonomy is distant, basic remote control capabilities (especially for electric models) may emerge for hazardous or repetitive tasks.
5. Sustainability & Circular Economy
- Material Focus: Increased use of recycled materials in manufacturing and designs optimized for easier end-of-life disassembly and recycling.
- Battery Lifecycle Management: Established processes for battery recycling, remanufacturing, and second-life applications (e.g., stationary storage) will become critical for electric models.
- Sustainable Operations: Rental fleets will prioritize low-emission (electric) machines, and customers will increasingly factor a machine’s environmental impact into purchasing decisions.
6. Rental Market Dominance & Fleet Flexibility
- Rental Growth: The high upfront cost of advanced (especially electric) E10s will further solidify the rental channel’s dominance. Fleets will need to offer a diverse mix of diesel and electric models.
- Fleet Management Tech: Rental companies will heavily invest in telematics and fleet management software to optimize utilization, maintenance, and customer service.
- Subscription Models: Potential emergence of “as-a-service” models, offering a specific machine with maintenance, insurance, and potentially battery swaps included.
7. Competitive Landscape Intensification
- New Entrants: Specialized electric construction equipment startups may target the E10 segment, challenging established players.
- OEM Differentiation: Competition will focus on battery performance, charging speed, telematics capabilities, service network, and overall TCO proposition. Partnerships (e.g., OEMs with battery tech firms) will be common.
- Price Pressure: As technology matures and competition increases, prices for both electric and advanced diesel models will face downward pressure.
Conclusion:
The E10 excavator market in 2026 will be defined by the convergence of electrification, digitalization, and urbanization. Electric models will be a major force, driven by regulations and TCO. Connectivity will be ubiquitous, enabling smarter operations and fleet management. Machines will be designed for maximum efficiency and minimal environmental impact in dense urban environments. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to deliver reliable, connected, and increasingly electric machines with compelling TCO, while rental companies and end-users adapt to this rapidly evolving technological and operational landscape. The “mini” excavator will be a major player in the construction industry’s sustainable and digital future.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing an E10 Excavator (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a mini excavator like the E10 model—especially from less-regulated markets—exposes buyers to significant risks related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial to avoid costly failures, safety hazards, and legal complications.
Poor Build Quality and Substandard Components
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing E10 excavators from unverified suppliers is inferior build quality. Many manufacturers use low-grade steel, undersized hydraulic components, and unreliable engines to cut costs. These compromises lead to premature wear, frequent breakdowns, and reduced machine lifespan. Buyers may receive units with poor welds, misaligned tracks, or inconsistent paint finishes—indicators of lax manufacturing standards. Additionally, subpar hydraulic systems can result in poor performance, leaks, or complete failure under normal operating conditions.
Misrepresentation of Specifications and Branding
Numerous suppliers falsely advertise their machines as equivalent to well-known brands (e.g., “E10 equivalent to Kubota” or “CAT performance”) without meeting the engineering or performance benchmarks. This misrepresentation can extend to engine power, dig depth, and operating weight. In extreme cases, counterfeit branding or logos may be used, misleading buyers into thinking they are purchasing genuine equipment. Such practices not only compromise performance but also void potential warranty claims and resale value.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
A major ethical and legal concern in sourcing generic E10 excavators is IP violation. Many low-cost manufacturers replicate the design,外观, and technical features of branded machines without licensing or authorization. This includes copying patented components, control layouts, and even proprietary hydraulic systems. Purchasing such machines may indirectly support IP theft, and in some jurisdictions, buyers could face reputational or legal risks—especially if the equipment is used in regulated industries or exported across borders.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if the initial price appears attractive, the long-term cost of ownership can skyrocket due to inadequate after-sales service. Generic E10 models often lack reliable dealer networks, technical documentation, or access to genuine spare parts. When breakdowns occur, sourcing compatible components becomes a challenge, leading to extended downtime. Unlike OEMs, many no-name manufacturers do not provide service manuals, training, or remote diagnostics, leaving operators stranded.
Inadequate Safety and Compliance Standards
Budget E10 excavators may not meet international safety or emissions standards (e.g., CE, EPA, or ISO certifications). Missing or poorly implemented safety features—such as ROPS/FOPS, emergency shutoffs, or proper lighting—pose serious risks to operators. Furthermore, non-compliant machines may be denied entry at ports or prohibited from use on certain job sites, resulting in financial and operational setbacks.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence: verify supplier credentials, request third-party inspections, demand compliance documentation, and prioritize vendors with transparent manufacturing practices. Avoiding the lowest-priced options often pays off in reliability, safety, and long-term value.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for E10 Excavator
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the transport, operation, and maintenance of the E10 Excavator. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, legal compliance, and operational efficiency.
Transportation and Shipping
Ensure the E10 Excavator is prepared for safe and legal transport. Secure all moving parts, lower the bucket to the carrier, and disengage all hydraulics. Use appropriate low-bed trailers or flatbed trucks with sufficient weight capacity—verify the E10’s operating weight and dimensions to select compliant transport equipment. Confirm load securement meets regional regulations (e.g., U.S. DOT FMCSA, EU Directive 2015/719) using rated tie-down straps or chains. Obtain necessary over-dimensional load permits if required due to size or weight.
Import/Export Documentation
For international movement, prepare complete customs documentation including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin. Confirm the E10 Excavator’s HS (Harmonized System) code—typically under 8429.52 for hydraulic excavators—to determine applicable tariffs and import duties. Include EPA or CE compliance documentation as required by destination country. Verify adherence to trade regulations such as U.S. EAR or EU dual-use controls if applicable.
Environmental and Emissions Compliance
The E10 Excavator must comply with local emissions standards. In the U.S., confirm it meets EPA Tier 4 Final emission requirements. In the EU, it should be certified under Stage V of the EU Non-Road Mobile Machinery (NRMM) Regulation (EU) 2016/1628. Maintain emissions compliance documentation and ensure exhaust after-treatment systems (e.g., DPF, SCR) are properly maintained. Avoid operation in regions with anti-idling laws or low-emission zones without proper certification.
Operator Certification and Training
Only trained and certified operators should operate the E10 Excavator. Comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1926.602 in the U.S. or equivalent national standards (e.g., UK LOLER, Canada OH&S). Provide documented training covering machine controls, safety procedures, hazard awareness, and emergency protocols. Retain training records for auditing purposes.
On-Site Safety and Operational Compliance
Conduct daily pre-operation inspections in accordance with manufacturer guidelines. Comply with site-specific safety plans, including traffic control, underground utility checks (call 811 in the U.S.), and slope stability assessments. Use required personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensure the excavator is equipped with operational ROPS (Roll-Over Protective Structure), FOPS (Falling Object Protective Structure), and backup alarms. Adhere to local regulations regarding noise, dust control, and working near public areas.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to ensure reliability and regulatory compliance. Keep detailed records of all servicing, repairs, and part replacements. Maintain logs for fluid disposal to comply with environmental regulations (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.). Used oil and filters must be handled and disposed of by licensed waste management providers.
Regional Regulatory Considerations
Verify compliance with country- or region-specific requirements. For example:
– North America: Comply with ANSI/SAE B77.1 for safety signage and machine guarding.
– European Union: Ensure CE marking and provide an EU Declaration of Conformity.
– Australia/New Zealand: Meet requirements under the Work Health and Safety (WHS) Regulations and AS 2627 standards.
Always consult local authorities and regulatory bodies to confirm up-to-date compliance obligations before deployment.
In conclusion, sourcing an E10 excavator involves a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors, including supplier reliability, equipment specifications, pricing, after-sales support, and compliance with regional regulations. The E10 class mini excavator is ideal for compact and urban construction projects due to its maneuverability, low ground pressure, and versatility. When sourcing, it is essential to partner with reputable manufacturers or authorized dealers—such as Volvo, Caterpillar, or Kobelco—who provide genuine parts, warranties, and technical support. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership, availability of service networks, and resale value will ensure long-term operational efficiency and return on investment. Proper due diligence in sourcing the E10 excavator will lead to reliable performance, reduced downtime, and successful project execution.