The global e-beam welding equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining solutions in aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global electron beam welding market size was valued at USD 617.8 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the need for clean, deep-penetration welds in advanced materials and complex geometries, particularly in high-tech industrial applications. As manufacturers seek greater automation, vacuum efficiency, and process repeatability, leading e-beam welding equipment providers are advancing their technologies to meet stringent quality and throughput requirements. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers stand out for their innovation, global reach, and comprehensive service offerings. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 10 e-beam welding equipment manufacturers shaping the future of precision welding.
Top 10 E Beam Welding Equipment Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
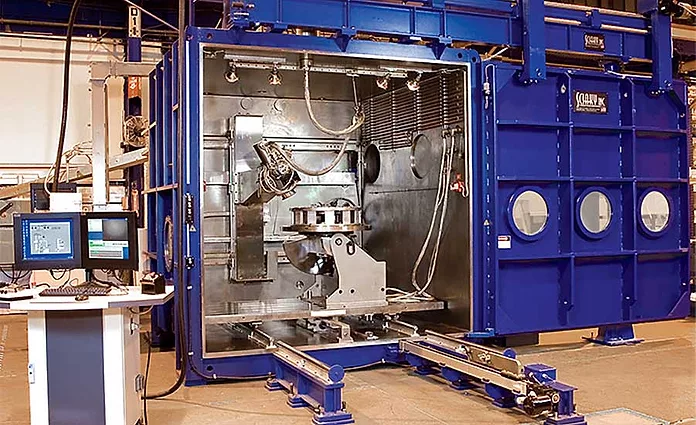
#1 Sciaky, Inc.
Founded: 1939
Website: sciaky.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1939, Sciaky is the worldwide leader in industrial 3D metal printing technology and the most trusted name in electron beam welding….
#2 Electron Beam Welding
Website: ptreb.com
Key Highlights: PTR manufactures and services Electron Beam Welders and provides electron beam welding job shop services in the US with the most modern EB welding machines….
#3 Electron Beam Welding Solutions
Website: sst-ebeam.com
Key Highlights: As a global medium-sized company, we are one of the leading developers and manufacturers of electron beam machines….
#4 Electron Beam Equipment
Website: electronbeamwelding.com
Key Highlights: Electron Beam Engineering Services (EBES) provides electron beam welding and laser beam welding systems and weld tooling accessories….
#5 Electron Beam Welding, LLC
Founded: 1966
Website: electronbeamweldinginc.com
Key Highlights: A leading edge electron beam welding company since 1966, we partner with our customers to provide high performance quality results….
#6 EB Industries: Electron Beam Welding
Website: ebindustries.com
Key Highlights: We are the preeminent supplier of Electron Beam Welding, Laser Beam Welding, and Laser Hermetic Sealing in North America. All industries served, NADCAP, ……
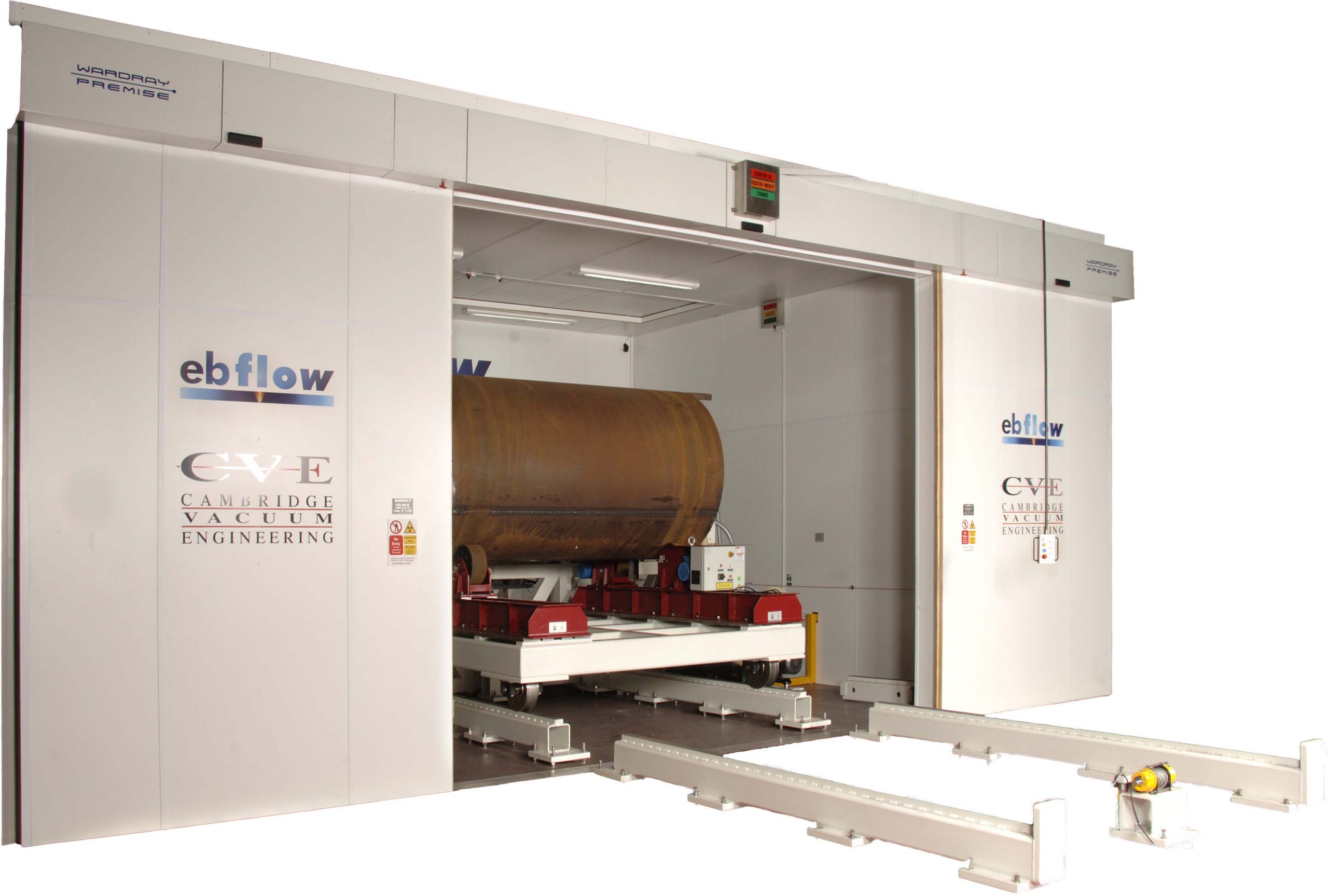
#7 Cambridge Vacuum Engineering
Website: camvaceng.com
Key Highlights: ELECTRON BEAM WELDING MACHINES. Electron beam welding (EBW) is a fusion welding process that uses a high-velocity electron beam to join two materials ……
#8 Electron Beam Welding Associates
Website: ebwelding.com
Key Highlights: Our electron beam welding services are useful in producing parts for all types of engines. We have proficiency in electron beam welding pressure vessels, ……
#9 Electron Beam Welding Experts
Website: ebpglobal.com
Key Highlights: EBP is Europe’s most experienced electron beam welding specialist. As an increasing number of our customers have asked us to provide the hardware for their ……
#10 Electron Beam Welder
Website: electronbeamwelder.net
Key Highlights: Electron beam welder is a relatively sophisticated welding equipment that uses the principle of high-speed moving electron beam bombardment of the workpiece ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for E Beam Welding Equipment
H2: 2026 Market Trends for E-Beam Welding Equipment
The global e-beam (electron beam) welding equipment market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising demand for high-precision joining solutions, and shifts toward automation and sustainability across key industries. Below is an analysis of the major market trends expected to shape the e-beam welding equipment sector in 2026:
-
Increased Adoption in Aerospace and Defense
E-beam welding’s ability to produce deep, narrow, and distortion-free welds makes it indispensable in aerospace and defense applications. By 2026, growing investments in next-generation aircraft, space exploration vehicles, and hypersonic technologies will drive demand for high-integrity welding solutions. OEMs are increasingly integrating e-beam systems into production lines for turbine blades, rocket engines, and structural components, favoring vacuum environments for contamination-free welds. -
Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Battery Manufacturing
The rise of the electric vehicle industry is creating new opportunities for e-beam welding. By 2026, e-beam systems are expected to be more widely adopted for welding battery packs, power electronics, and high-strength EV drivetrain components. The process’s precision and minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ) are ideal for joining dissimilar and heat-sensitive materials used in battery modules, contributing to enhanced safety and performance. -
Advancements in Automation and Integration with Industry 4.0
E-beam welding systems are increasingly being integrated with robotics, real-time monitoring, and digital twin technologies. By 2026, smart e-beam welding cells equipped with AI-driven process optimization, predictive maintenance, and IoT connectivity will become standard in advanced manufacturing facilities. This shift enhances repeatability, reduces downtime, and supports high-mix, low-volume production environments. -
Expansion of Non-Vacuum and Local Vacuum Systems
While traditional e-beam welding requires full vacuum chambers—limiting throughput and increasing costs—non-vacuum and local vacuum e-beam technologies are gaining traction. These innovations allow for larger workpieces and continuous processing, especially in automotive and heavy industrial applications. By 2026, improvements in electron beam control and pump efficiency are expected to make localized vacuum systems more cost-effective and accessible. -
Regional Market Shifts and Capacity Expansion
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, is projected to lead market growth due to rapid industrialization and government support for high-tech manufacturing. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, especially in aerospace and medical device sectors. Equipment manufacturers are localizing production and service networks to reduce lead times and support after-sales service, enhancing competitiveness. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
As industries prioritize carbon footprint reduction, e-beam welding is gaining favor for its energy efficiency compared to traditional arc welding. The process generates minimal waste and often eliminates the need for filler materials. By 2026, equipment manufacturers will emphasize energy recovery systems, recyclable components, and reduced helium usage (in sensors), aligning with global ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. -
Material Innovation Driving Demand
The use of advanced materials—such as titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and refractory metals—in high-performance applications is boosting the need for e-beam welding. These materials are often difficult to weld using conventional methods, but e-beam’s high energy density enables reliable joints. R&D in additive manufacturing hybrids (e.g., e-beam wire feed) is also opening new applications. -
Competitive Landscape and Technological Differentiation
By 2026, the market will see intensified competition among key players like TRUMPF, Siemens, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and Atlas Technologies. Differentiation will center on software integration, ease of operation, and modular designs. Smaller innovators are emerging with compact, desktop-sized e-beam systems for research and prototyping, expanding market reach beyond large industrial users.
In summary, the 2026 e-beam welding equipment market will be shaped by technological innovation, sector-specific demand from aerospace and EVs, and the integration of digital manufacturing ecosystems. As precision, reliability, and sustainability become critical, e-beam welding is expected to transition from a niche process to a cornerstone of advanced industrial production.
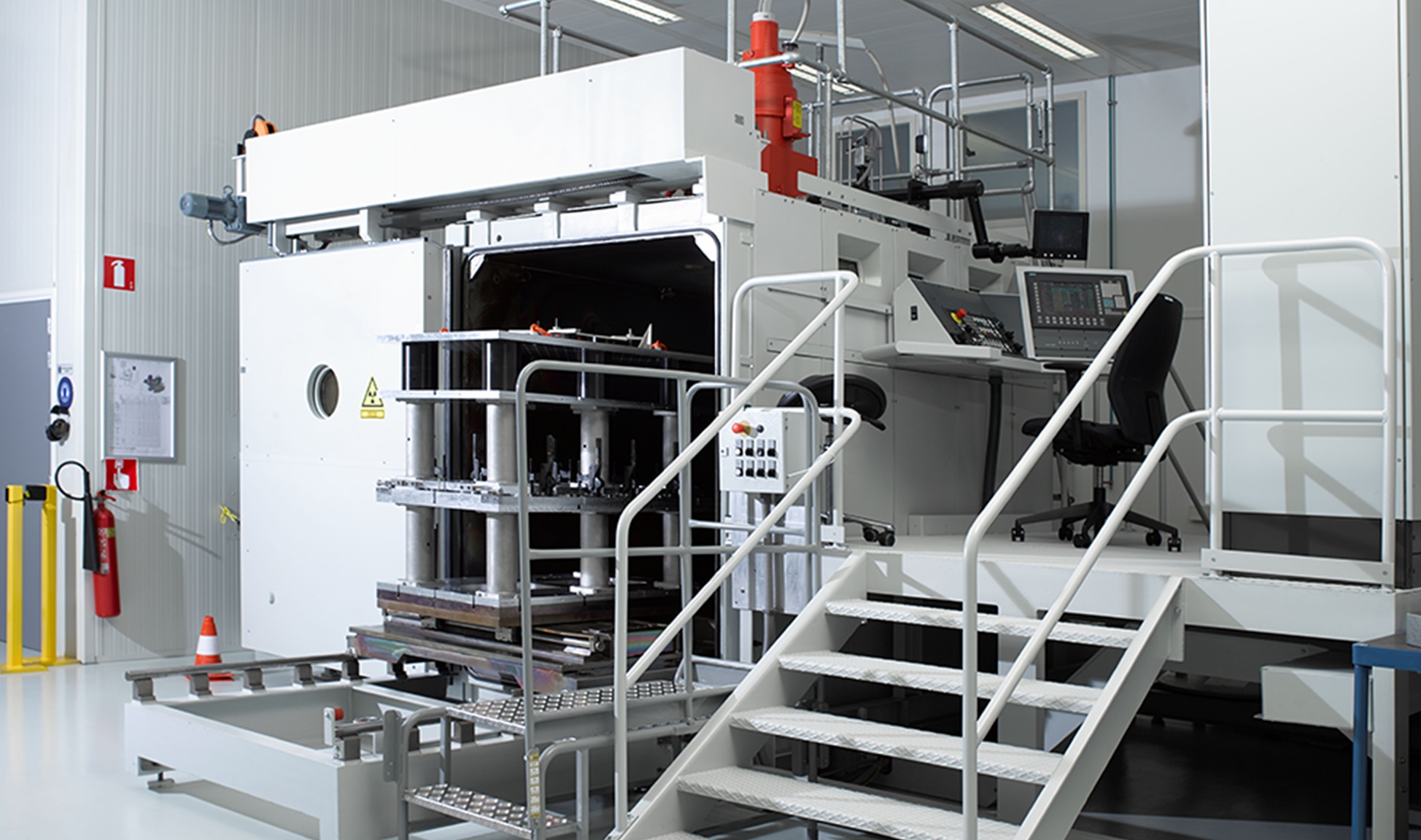

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing E-Beam Welding Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing electron beam (E-beam) welding equipment involves significant technical, financial, and legal considerations. Overlooking critical factors related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to costly failures, operational delays, and legal disputes. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Equipment Quality and Performance
One of the most significant risks when sourcing E-beam welding systems—especially from less-established suppliers or emerging markets—is receiving equipment that does not meet required performance, safety, or reliability standards.
- Inadequate Beam Stability and Control: Low-quality systems may suffer from inconsistent beam focus, power fluctuations, or poor vacuum integrity, leading to defective welds and high scrap rates.
- Substandard Vacuum Systems: E-beam welding requires high-vacuum environments. Poorly engineered vacuum chambers or pumps can result in contamination, arcing, and unreliable weld quality.
- Insufficient After-Sales Support: Some suppliers lack local service networks or technical expertise, resulting in extended downtime and increased maintenance costs.
- Hidden Defects and Non-Compliance: Equipment may appear functional during demonstration but fail to meet industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASME, CE) or lack proper certifications, raising safety and compliance concerns.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence: request third-party inspections, review customer references, and perform factory acceptance tests (FAT) before shipment.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement and Lack of Licensing
E-beam welding technology incorporates proprietary designs, control software, and process know-how. Sourcing from unverified suppliers increases the risk of inadvertently acquiring counterfeit, cloned, or IP-infringing equipment.
- Use of Unauthorized Software or Firmware: Some suppliers may use pirated or reverse-engineered control systems, which can lead to instability, lack of updates, and legal liability for the end user.
- Replicated Core Components: Critical components such as electron guns, high-voltage power supplies, or deflection systems may be illicitly copied from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), compromising performance and exposing buyers to IP litigation.
- Ambiguous IP Ownership: Contracts may fail to clarify whether process-specific software, automation interfaces, or custom tooling are licensed or owned by the buyer, limiting future scalability or modifications.
- Export Control and Compliance Risks: Advanced E-beam systems may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR). Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers can result in customs seizures or regulatory penalties.
To protect against IP-related pitfalls:
– Verify the supplier’s IP rights and request documentation proving legal use of all software and components.
– Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
– Work with legal counsel to assess compliance with international trade and technology transfer laws.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure the acquisition of reliable, compliant, and legally sound E-beam welding equipment that supports long-term manufacturing success.
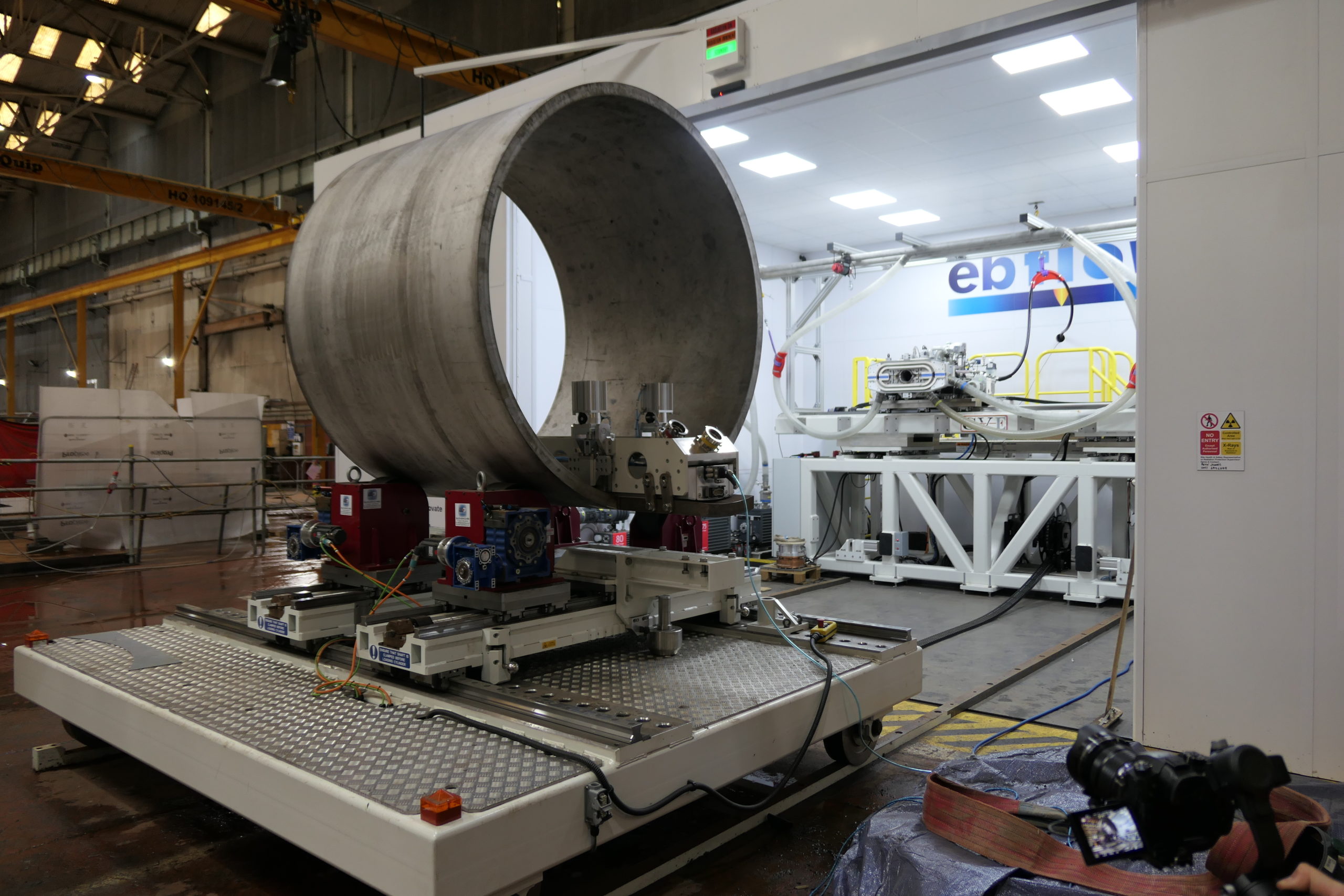

Logistics & Compliance Guide for E Beam Welding Equipment
Equipment Handling and Transportation
E Beam welding equipment is highly sensitive and requires careful handling during transportation. Due to its vacuum chamber, high-voltage components, and precision electron optics, the system must be transported in a controlled environment. Always use original packaging or custom crating with shock-absorbing materials. Ensure the equipment remains upright and protected from moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. Coordinate with certified freight handlers experienced in delicate industrial machinery, and avoid abrupt movements or vibrations during transit.
Site Preparation and Installation Requirements
Prior to delivery, the installation site must meet specific structural, electrical, and environmental criteria. The floor must support the equipment’s weight (typically several tons) and provide vibration isolation. Electrical requirements include stable high-voltage power supply (often 480V 3-phase), proper grounding, and dedicated circuits to prevent interference. A clean, climate-controlled environment with temperature and humidity control is essential. Adequate space for maintenance access, radiation shielding, and vacuum pump systems must also be ensured.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
E Beam welding systems are subject to strict regulatory requirements due to ionizing radiation and high-voltage hazards. Compliance with standards such as 21 CFR 1020.40 (FDA/CDRH in the U.S.) and IEC 60601-1 for electrical safety is mandatory. Operators must implement a radiation protection program, including shielding design certification, interlock systems, and routine radiation surveys. Local occupational safety regulations (e.g., OSHA) require documented safety procedures, operator training, and emergency protocols.
Import/Export Controls and Documentation
E Beam welding equipment may be subject to international trade controls due to dual-use technologies. Verify export classification under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) as applicable. Required documentation includes commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and technical specifications. For imports, ensure compliance with customs regulations in the destination country, including conformity assessments (e.g., CE marking in the EU) and potential import permits.
Operational Licensing and Registration
In many jurisdictions, operating an E Beam welding system requires formal registration with national radiation protection authorities (e.g., NRC or state agencies in the U.S.). Facilities must obtain a license or registration certificate, which often involves submitting a facility diagram, safety protocols, and radiation monitoring plans. Regular inspections and equipment audits may be required. Maintain up-to-date records of compliance, personnel training, and maintenance logs to satisfy regulatory audits.
Maintenance, Calibration, and Recordkeeping
Scheduled maintenance and calibration are critical for compliance and performance. Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for vacuum systems, electron guns, and high-voltage components. Calibration of beam alignment, voltage, and current controls must be performed by qualified technicians using traceable standards. Maintain detailed records of all maintenance, repairs, radiation surveys, and component replacements for audit purposes and regulatory reporting.
Conclusion for Sourcing Electron Beam (E-Beam) Welding Equipment:
Sourcing electron beam welding equipment is a strategic decision that requires careful evaluation of technical specifications, production requirements, and long-term operational goals. E-beam welding offers unmatched precision, deep penetration, and minimal distortion, making it ideal for high-integrity applications in aerospace, defense, medical devices, and advanced manufacturing. When selecting equipment, key considerations include vacuum chamber size, beam power, control systems, automation compatibility, and vendor support.
A thorough assessment of suppliers—emphasizing reliability, service capabilities, training, and compliance with safety and regulatory standards—is essential to ensure optimal performance and return on investment. Additionally, integrating e-beam technology should align with existing manufacturing workflows and future scalability needs. By choosing the right equipment and partner, organizations can achieve superior weld quality, enhanced productivity, and a competitive advantage in demanding markets.