The global acetone market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as pharmaceuticals, construction, and chemical manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global acetone market was valued at USD 11.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 3.5% from 2024 to 2029. A significant portion of this demand comes from dry acetone, a high-purity variant essential in precision cleaning, electronics manufacturing, and laboratory applications due to its low water content and superior solvent properties. With increasing industrialization and stricter quality standards in sectors requiring contamination-free solvents, the need for reliable dry acetone manufacturers has intensified. As the market expands, key players are investing in production capacity and purity optimization to meet evolving customer requirements. Here’s a look at the top five dry acetone manufacturers leading the charge in quality, innovation, and global supply.
Top 5 Dry Acetone Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Acetone
Domain Est. 2020
Website: ohanachemco.com
Key Highlights: Acetone from Ohana Chem Cooffers high purity and fast evaporation, making it the trusted solvent choice for coatings, adhesives, cleaning, and industrial ……
#2 Acetone
Domain Est. 1995
Website: fishersci.com
Key Highlights: Acetone is a colorless, volatile, and flammable organic solvent with a distinct sweet odor. It occurs naturally in plants and the environment….
#3 ACETONE
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sunnysidecorp.com
Key Highlights: ACETONE. Acetone is a highly effective thinner and remover for epoxy resins, ink, adhesives, and lacquers. It thins and cleans fiberglass resins….
#4 Purchase Acetone (Dry Solvent) in bulk …
Domain Est. 2000
Website: pure-chemical.com
Key Highlights: Acetone (Dry Solvent) is a versatile and high-purity solvent used extensively in laboratories for analytical and preparative work….
#5 Mg Chemicals 434
Domain Est. 2020
Website: rapiroy.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.5 (145) Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store. New $29.17….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Dry Acetone
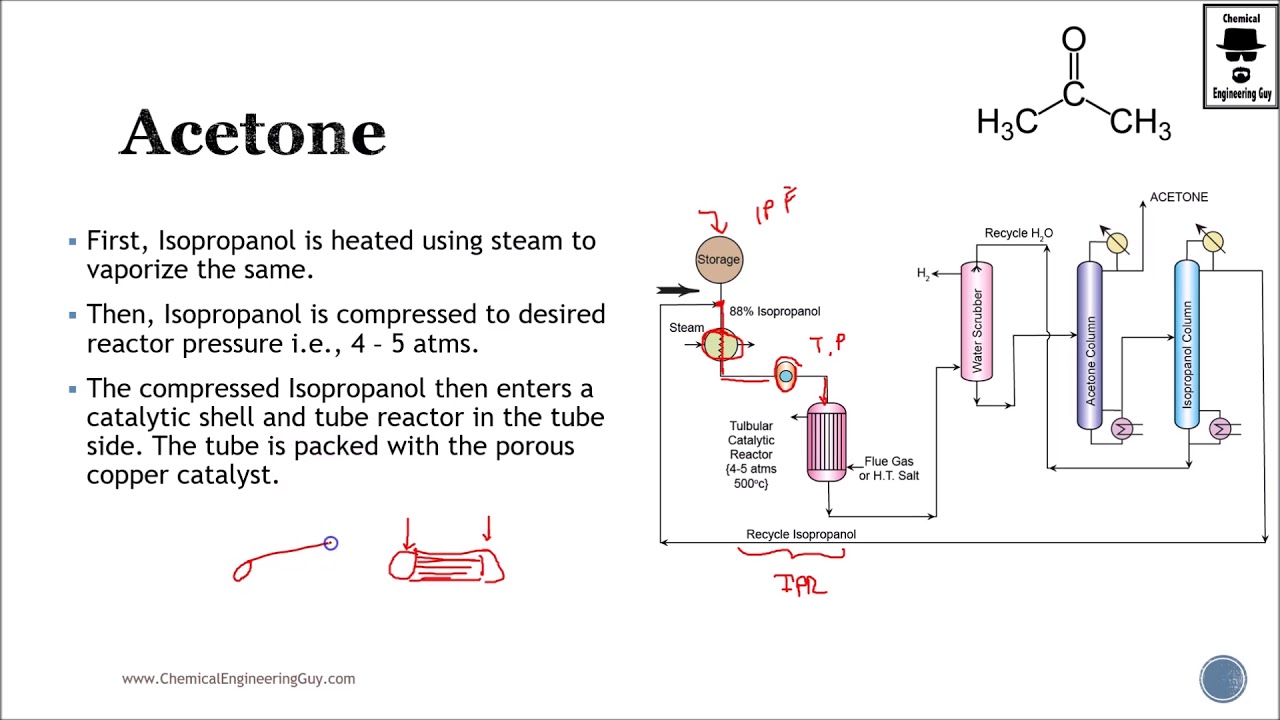
As of now, we are still in 2024, and specific market data for the year 2026 is inherently forward-looking and speculative. However, using H2 (second half) trends and projections from 2023–2024 as a foundation, we can analyze and forecast likely developments in the dry acetone market through 2026. Below is a structured analysis based on industry drivers, supply-demand dynamics, regional trends, and macroeconomic factors.
Dry Acetone Market Trends Outlook: H2 2023 – 2026 Forecast
1. Market Overview
Dry acetone (high-purity acetone, typically ≥99.5%) is a critical solvent used across pharmaceuticals, electronics, cosmetics, and chemical manufacturing. It differs from technical-grade acetone due to stricter impurity controls, making it essential in high-sensitivity applications.
2. Key Drivers Influencing 2026 Trends
-
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Expansion
The global pharmaceutical sector, particularly in emerging markets (India, China, Southeast Asia), is projected to grow at a CAGR of ~6–8% through 2026. Dry acetone is a key solvent in drug synthesis and purification. Increasing R&D investments and biosimilar production are boosting demand. -
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry Growth
H2 2023 saw a recovery in semiconductor markets after the 2022 downturn. With AI, 5G, and IoT driving chip demand, dry acetone is essential for wafer cleaning and photoresist stripping. The Asia-Pacific region (especially Taiwan, South Korea, and China) remains the largest consumer. -
Regulatory Pressure and Purity Standards
Stricter environmental and safety regulations (e.g., REACH in EU, EPA guidelines in U.S.) are pushing manufacturers toward higher-purity solvents. This favors dry acetone over lower-grade alternatives, supporting market value growth. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Post-pandemic and geopolitical tensions (e.g., U.S.-China trade dynamics) have accelerated regional supply chain reconfiguration. By 2026, we expect increased regional production of dry acetone in North America and Europe to reduce dependence on Asian imports.
3. Supply-Side Developments
-
Production Capacity Additions
Major chemical producers (e.g., INEOS, Shell, Jubilant Ingrevia) have announced capacity expansions in H2 2023–H1 2024. These will come online by 2025–2026, improving supply stability but potentially leading to moderate price softening in late 2026. -
Feedstock Cost Volatility
Acetone is primarily a co-product of phenol production (via cumene process). Crude oil and propylene price fluctuations impact phenol/acetone economics. With H2 2024 showing stabilized energy prices, 2026 is expected to see relatively stable input costs, supporting predictable dry acetone pricing.
4. Regional Market Trends (2026 Outlook)
-
Asia-Pacific
Dominates global consumption (~55–60%). Growth in India’s pharmaceutical exports and China’s specialty chemical sector will sustain demand. However, environmental crackdowns may constrain supply, creating import opportunities for U.S. and EU suppliers. -
North America
Shale gas-driven chemical renaissance supports domestic acetone production. Demand from biotech and advanced electronics will rise. By 2026, North America may become a net exporter of dry acetone, especially to Latin America. -
Europe
Slower industrial growth but strong demand from high-end pharmaceuticals and green chemistry initiatives. Emphasis on circular economy may drive investment in acetone recycling technologies, affecting net demand.
5. Price Trends and Market Sentiment
- H2 2023–H1 2025: Tight supply and strong demand led to price increases (~5–10% YoY).
- H2 2025–2026: As new capacity stabilizes, prices are expected to plateau or see slight declines (~2–3%).
- Average FOB price for dry acetone in 2026 is projected at $1,100–$1,300/ton, depending on region and purity grade.
6. Emerging Opportunities
-
Sustainable and Bio-Based Acetone
R&D in bio-acetone (from fermentation of biomass) is gaining momentum. While still niche, pilot plants in the U.S. and EU could scale by 2026, appealing to ESG-focused buyers. -
Digital Supply Chains and On-Demand Manufacturing
Adoption of digital platforms for solvent procurement and just-in-time delivery models will grow, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
7. Risks to 2026 Outlook
- Geopolitical disruptions (e.g., Middle East tensions affecting petrochemical flows).
- Recessionary pressures in major economies reducing industrial output.
- Regulatory changes in chemical handling (e.g., potential reclassification under new EPA rules).
Conclusion: 2026 Dry Acetone Market Outlook (H2 Perspective)
The dry acetone market in 2026 is expected to be stable and moderately growing, supported by strong end-use demand in pharma and electronics. While supply will improve due to new capacity, demand in high-tech and life sciences sectors will maintain a balanced market. Regional diversification and sustainability trends will shape strategic investments.
Forecast Summary (2026):
– Global Market Size: ~$3.8–4.2 billion
– Demand Growth: ~4.5% CAGR (2023–2026)
– Key Growth Regions: India, U.S., South Korea
– Trend: Shift toward high-purity, traceable, and sustainably produced dry acetone
Stakeholders should focus on quality differentiation, supply chain resilience, and sustainability to capture value in the evolving 2026 landscape.
When sourcing Dry Acetone, especially under the quality standards referenced by H2 (commonly indicating high-purity, anhydrous, or technical grade suitable for sensitive applications such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, or chemical synthesis), several common pitfalls can impact both quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Below is a breakdown of these pitfalls using the H2 quality context:
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
a. Inadequate Dryness / Moisture Content
- Pitfall: “Dry” acetone must have very low water content (typically < 50 ppm). Suppliers may claim “anhydrous” without proper certification or testing.
- H2 Context: H2-grade acetone must meet strict moisture limits. Accepting material without Karl Fischer titration data risks process inefficiency (e.g., in Grignard reactions or HPLC).
- Mitigation: Require COA (Certificate of Analysis) with moisture content verified by standardized methods.
b. Impurity Profile Misrepresentation
- Pitfall: Acetone may contain aldehydes (e.g., acetaldehyde), alcohols, or organic peroxides—especially if stored improperly or near UV light.
- H2 Context: H2 specifications often include limits on key impurities. Suppliers may not test for all relevant contaminants.
- Mitigation: Specify impurity thresholds in procurement agreements and conduct batch testing.
c. Stabilizer Misuse
- Pitfall: Some acetone is stabilized with compounds like BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene) to prevent peroxide formation. This may interfere with sensitive processes.
- H2 Context: H2-grade acetone is typically unstabilized. Receiving stabilized acetone unknowingly affects downstream use (e.g., in spectroscopy or synthesis).
- Mitigation: Explicitly request unstabilized acetone and verify via COA.
d. Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Quality
- Pitfall: Different production batches may vary in purity due to changes in feedstock or process.
- H2 Context: H2 implies consistency. Variability can disrupt R&D reproducibility or manufacturing.
- Mitigation: Work with suppliers who practice strict quality control and offer long-term supply agreements with fixed specs.
e. Packaging and Contamination Risks
- Pitfall: Use of inappropriate containers (e.g., non-inert liners, reused drums) introduces leachables or moisture.
- H2 Context: H2-grade materials should be packaged in airtight, moisture-resistant containers (e.g., nitrogen-blanketed HDPE bottles or stainless steel cylinders).
- Mitigation: Audit supplier packaging protocols and request inert gas capping.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
a. Reverse Engineering via Material Sourcing
- Pitfall: Using a unique or specialized dry acetone in a proprietary process may allow competitors to deduce formulations or process conditions by analyzing the input chemicals.
- H2 Context: If your process depends on a specific H2-grade acetone (e.g., ultra-low metals), sourcing openly may reveal process sensitivity.
- Mitigation: Use confidentiality agreements (CDAs) with suppliers; consider dual sourcing or blending to obscure specs.
b. Supplier as a Single Point of Disclosure
- Pitfall: A supplier may inadvertently or intentionally disclose your purchasing patterns or volume, indicating scale of operations or process needs.
- H2 Context: High-purity acetone procurement in large volumes may signal advanced R&D or production scale.
- Mitigation: Use intermediaries or distributors; avoid custom labeling that identifies end-user.
c. Lack of IP Clauses in Supply Agreements
- Pitfall: Standard supply contracts may not protect your use case or innovations developed using the acetone.
- H2 Context: If you develop a novel process using H2 acetone, ensure supplier agreements do not claim joint ownership or rights to improvements.
- Mitigation: Include IP ownership clauses stating that all process innovations remain your sole property.
d. Grey Market or Diverted H2-Grade Material
- Pitfall: H2-grade acetone may be diverted from original supply chains and resold through unauthorized channels, increasing risk of adulteration and loss of traceability.
- IP Risk: If a competitor sources the same “H2” acetone from a grey market, they might reverse-engineer your process.
- Mitigation: Source directly from manufacturer; use track-and-trace systems; audit supply chain.
Best Practices Summary (H2-Grade Dry Acetone)
| Area | Best Practice |
|——|—————|
| Quality Assurance | Require COA with moisture < 50 ppm, impurity profile, and stabilization status |
| Supplier Vetting | Audit supplier GMP/GLP compliance and manufacturing processes |
| Packaging | Specify nitrogen-purged, sealed containers with desiccants |
| IP Protection | Execute CDAs, avoid revealing end-use, secure IP rights in contracts |
| Supply Chain | Use direct sourcing; avoid grey markets; consider dual sourcing |
Conclusion:
Sourcing H2-grade Dry Acetone requires diligence not only in ensuring consistent chemical quality but also in protecting intellectual property throughout the supply chain. A holistic approach combining technical specifications, supplier audits, and legal safeguards is essential to avoid common pitfalls.
H2: Logistics and Compliance Guide for Dry Acetone
Dry acetone is a highly flammable, volatile organic solvent widely used in laboratories, industrial cleaning, and chemical synthesis. Due to its physical and chemical properties, the logistics and compliance requirements for handling, storing, transporting, and disposing of dry acetone are strictly regulated to ensure safety and environmental protection. This guide outlines key considerations under major regulatory frameworks.
1. Chemical Identification and Properties
- Chemical Name: Acetone (dry, anhydrous)
- CAS Number: 67-64-1
- UN Number: UN 1090
- Hazard Class: 3 (Flammable Liquid)
- Packing Group: II (Medium danger)
- Boiling Point: 56°C (133°F)
- Flash Point: -20°C (-4°F) – highly flammable
- Autoignition Temperature: 465°C (869°F)
- Vapor Density: 2.0 (heavier than air)
- Solubility: Miscible with water
2. Regulatory Compliance Overview
a. Globally Harmonized System (GHS)
Dry acetone is classified under GHS as:
- Flammable Liquid Category 2 (H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapor)
- Acute Toxicity (Inhalation) Category 4 (H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness)
Label elements must include:
– Flame pictogram (GHS02)
– Signal word: “Danger”
– Hazard statements: H225, H336
– Precautionary statements (e.g., P210: Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames; P304+P340: IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air)
b. U.S. Regulations (OSHA, DOT, EPA)
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910.106: Flammable liquid storage and handling standards.
– DOT 49 CFR: Regulates transportation:
– Shipping name: “Acetone”
– UN 1090, Class 3, PG II
– Required labels: Flammable liquid, Class 3
– Placarding required for bulk shipments (>119 gallons)
– EPA Regulations:
– Listed as a Hazardous Air Pollutant (HAP) under the Clean Air Act
– RCRA: Not listed as a hazardous waste per se, but waste acetone may be regulated under F003 if mixed with other solvents
c. International Regulations
– IMDG Code (Maritime): UN 1090, Class 3, PG II – requires proper stowage, segregation, and documentation.
– IATA DGR (Air): Forbidden for passenger aircraft; allowed on cargo aircraft with limitations (e.g., max 350 L per package, inner packaging ≤ 1 L).
– ADR (Road, Europe): Class 3, UN 1090, PG II – requires orange panels, driver training (ADR certification), and vehicle labeling.
3. Storage Requirements
- Containers: Use approved flammable liquid safety cans or UN-rated drums (e.g., steel drums with proper closure).
- Storage Area:
- Flammable storage cabinets (FM/OSHA-compliant) for quantities over 25 gallons.
- Segregated from oxidizers, acids, and ignition sources.
- Well-ventilated, temperature-controlled (<30°C recommended).
- Bonded and grounded if transferring large volumes.
- Secondary Containment: Required for bulk storage (e.g., spill pallets capable of holding 110% of largest container).
4. Handling and Use Precautions
- Use only in well-ventilated areas or with local exhaust ventilation.
- Avoid open flames, sparks, static discharge—use intrinsically safe equipment.
- Wear appropriate PPE:
- Chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile or neoprene)
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Flame-resistant lab coat
- Respiratory protection if vapor levels exceed OSHA PEL (1,000 ppm TWA)
- Prohibit eating, drinking, or smoking in handling areas.
5. Transportation Guidelines
- Packaging: Must meet UN performance standards (e.g., 1A1, 1H1 drums).
- Marking & Labeling: Proper shipping name, UN number, hazard labels (Class 3 flammable), orientation arrows.
- Documentation: Safety Data Sheet (SDS) required; shipping papers must include proper description.
- Segregation: Do not transport with oxidizers (e.g., nitric acid, peroxides) or strong bases.
- Driver Training: Personnel must be hazmat certified (DOT HAZMAT endorsement).
6. Emergency Response
- Spill Response:
- Evacuate area, eliminate ignition sources.
- Use spark-proof tools and explosion-proof equipment.
- Absorb with inert material (vermiculite, sand); do not flush into drains.
- Collect in approved hazardous waste container.
- Fire Response:
- Use alcohol-resistant foam, CO₂, or dry chemical extinguishers.
- Cool exposed containers with water spray.
- Firefighters should wear full SCBA and protective gear.
- First Aid:
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical attention if drowsiness or dizziness occurs.
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water.
- Eye Contact: Flush with water for 15 minutes; seek medical advice.
- Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting; rinse mouth and seek immediate medical help.
7. Waste Disposal
- Waste acetone is typically regulated as a hazardous waste under RCRA (F003) if spent or mixed.
- Dispose through licensed hazardous waste handlers.
- Never pour down the drain or into the environment.
- Maintain manifest records for disposal tracking.
8. Documentation and Training
- Maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheet (SDS) – Section 14 covers transport information.
- Train employees on:
- Hazards of acetone
- Safe handling and storage
- Emergency procedures
- DOT/OSHA compliance (annual refresher required)
- Keep records of training, inspections, and spill incidents.
Conclusion
Dry acetone requires careful attention to logistics and compliance due to its flammability and health hazards. Adherence to OSHA, DOT, EPA, and international transport regulations ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and environmental protection. Always consult the latest SDS and local regulations before handling or transporting dry acetone.
Note: Regulations may vary by jurisdiction. Always verify local, state, and national requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing dry acetone requires careful consideration of purity, supplier reliability, and intended application. Dry acetone, typically anhydrous with less than 0.1% water content, is essential for sensitive laboratory procedures, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and certain industrial processes where water can interfere with reactions or product quality. To ensure consistent quality, it is crucial to work with reputable chemical suppliers who provide detailed specifications, Certificates of Analysis (CoA), and proper packaging to prevent moisture absorption during storage and transport. Additionally, evaluating factors such as regulatory compliance, packaging size, cost-effectiveness, and logistics will help establish a reliable supply chain. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy ensures the availability of high-purity dry acetone, supporting operational efficiency and product integrity.