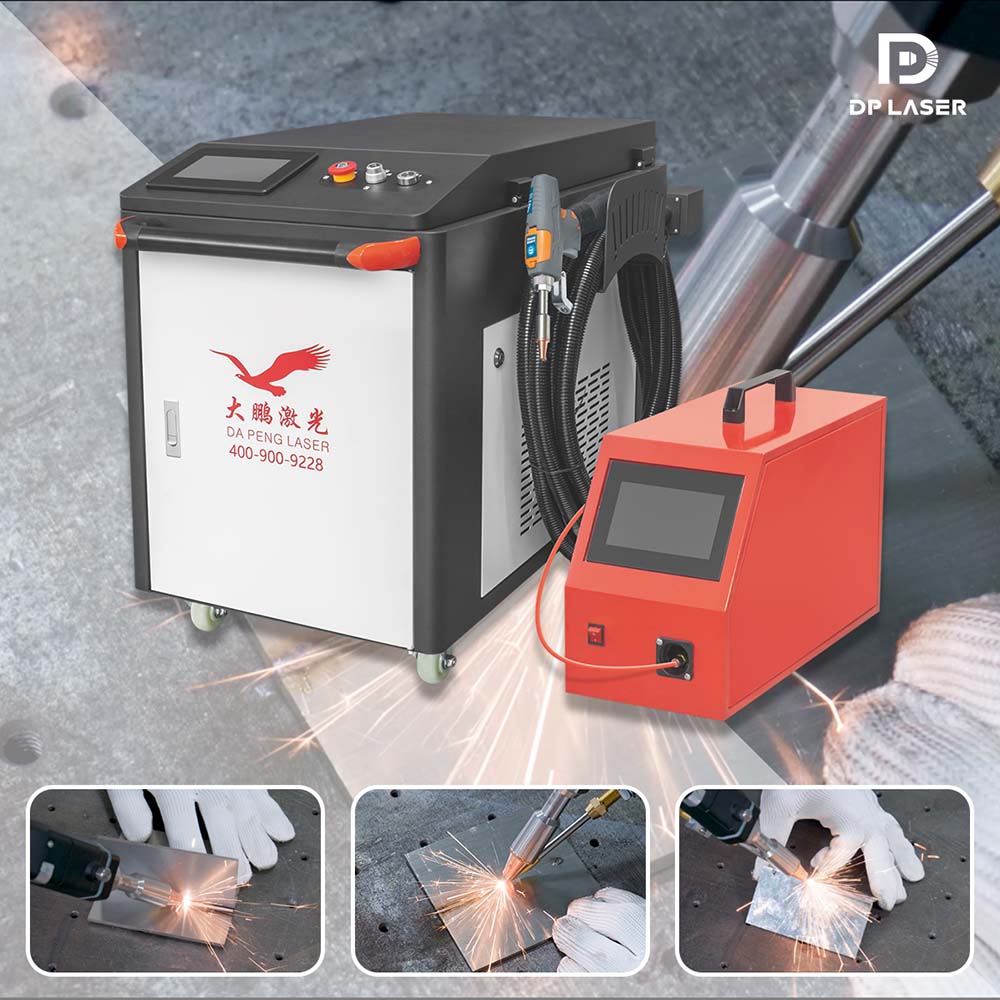
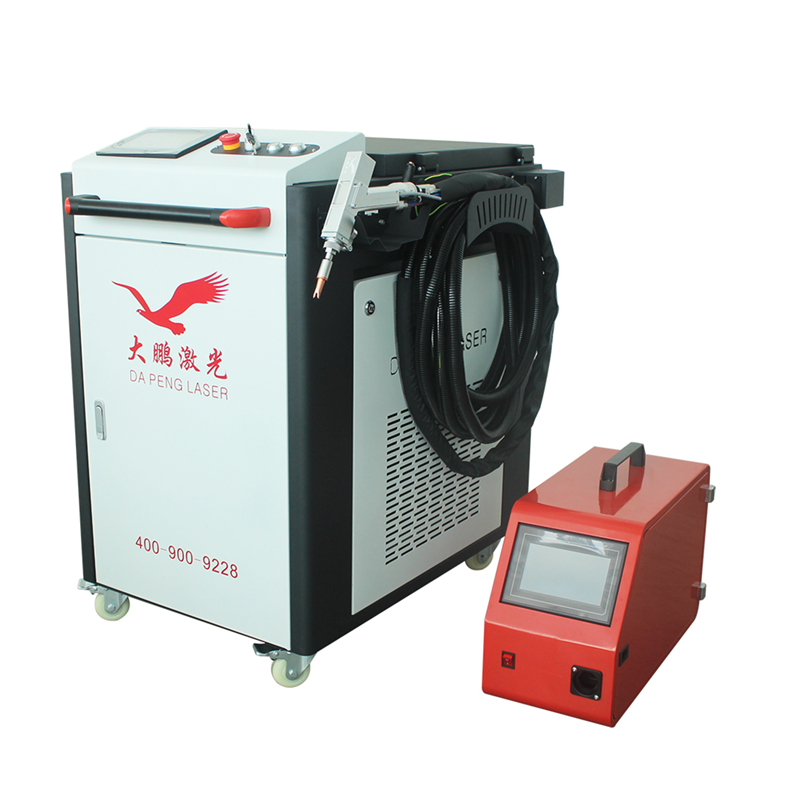
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining technologies across automotive, electronics, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 3.56 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in fiber and diode-pumped (DP) laser technologies, which offer superior beam quality, energy efficiency, and integration capabilities in automated production lines. As demand for DP laser welding systems rises, particularly in high-accuracy applications, key manufacturers are scaling production and driving down costs to capture expanding market share. Based on pricing competitiveness, production capacity, and technological innovation, the following three manufacturers have emerged as leaders in offering cost-effective DP laser welding solutions without compromising performance.
Top 3 Dp Laser Welding Price Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Machine – Laser Equipment Manufacturer
Website: dplaser.com
Key Highlights: DPLASER is a leading manufacturer & factory of industrial laser welding, laser cutting, laser marking and laser cleaning machines….
#2 DP Laser
Website: dplaser.cn
Key Highlights: DP Laser offers a comprehensive range of high-quality laser cutting and welding machines for various applications.Visit our website to explore our products ……
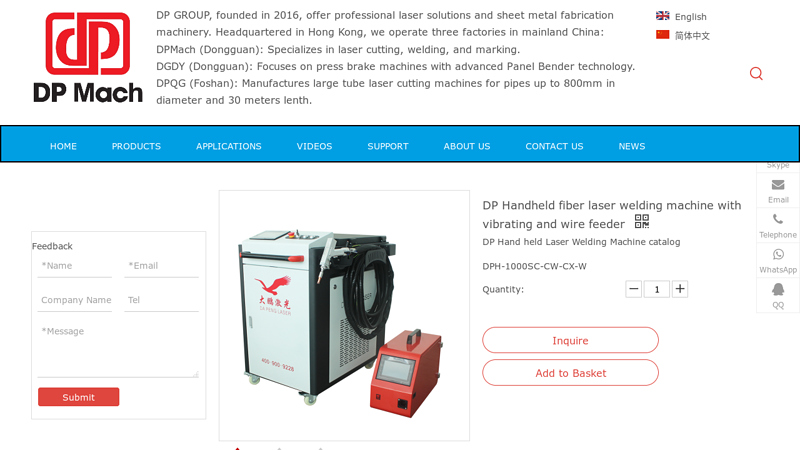
#3 DP Handheld fiber laser welding machine with vibrating and wire …
Website: dplasers.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (94) DP Handheld fiber laser welding machine with vibrating and wire feeder offered by China manufacturer Dapeng Laser, over 11 years experience, CE certified ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Dp Laser Welding Price

H2: 2026 Market Trends for DP Laser Welding Machine Prices
The market for Diode-Pumped (DP) laser welding machines is expected to experience notable shifts by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing industrial automation, and evolving global supply chains. The price trends for DP laser welding equipment in 2026 will be shaped by several interrelated factors:
-
Technological Innovation and Efficiency Gains
By 2026, continued improvements in diode laser efficiency, beam quality, and system integration are expected to enhance performance while reducing manufacturing costs. As DP lasers become more energy-efficient and require less maintenance compared to older lamp-pumped systems, economies of scale and mature production processes will contribute to moderate price reductions—especially in mid-range industrial models. -
Increased Competition and Market Expansion
The growing number of manufacturers—particularly in China, South Korea, and Europe—is intensifying competition. This competitive landscape is likely to exert downward pressure on prices, especially for standardized DP laser welding units. At the same time, premium systems featuring AI-driven controls, real-time monitoring, and high-precision welding capabilities may maintain or even increase in price due to added value and specialized applications in aerospace, medical devices, and electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing. -
Rising Demand in High-Growth Industries
The automotive and clean energy sectors are projected to be primary drivers of demand. With the global push toward electric vehicles, DP laser welding is becoming essential for battery pack assembly and lightweight material joining. This surge in demand may initially stabilize or slightly increase prices for high-power, reliable systems. However, as production scales and automation becomes widespread, prices are expected to gradually decline from 2025 into 2026. -
Supply Chain and Raw Material Costs
Fluctuations in the cost of critical components—such as laser diodes, optics, and rare-earth materials—may impact pricing. Geopolitical factors and trade policies could influence supply chain stability. However, by 2026, increased localization of manufacturing and second-source suppliers are expected to mitigate some of these risks, contributing to more predictable and stable pricing. -
Regional Pricing Variations
In North America and Western Europe, DP laser welding machines may command higher prices due to regulatory compliance, service support, and integration with Industry 4.0 systems. In contrast, Asian markets—especially China and India—are likely to offer competitively priced units, accelerating adoption in small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and influencing global benchmark pricing downward.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the average price of DP laser welding machines is projected to decline slightly for standard models due to technological maturity and market competition, while high-end,智能化 (intelligent) systems may see stable or rising prices. Overall, the market will shift toward greater affordability and accessibility, supporting broader industrial adoption and innovation across advanced manufacturing sectors.
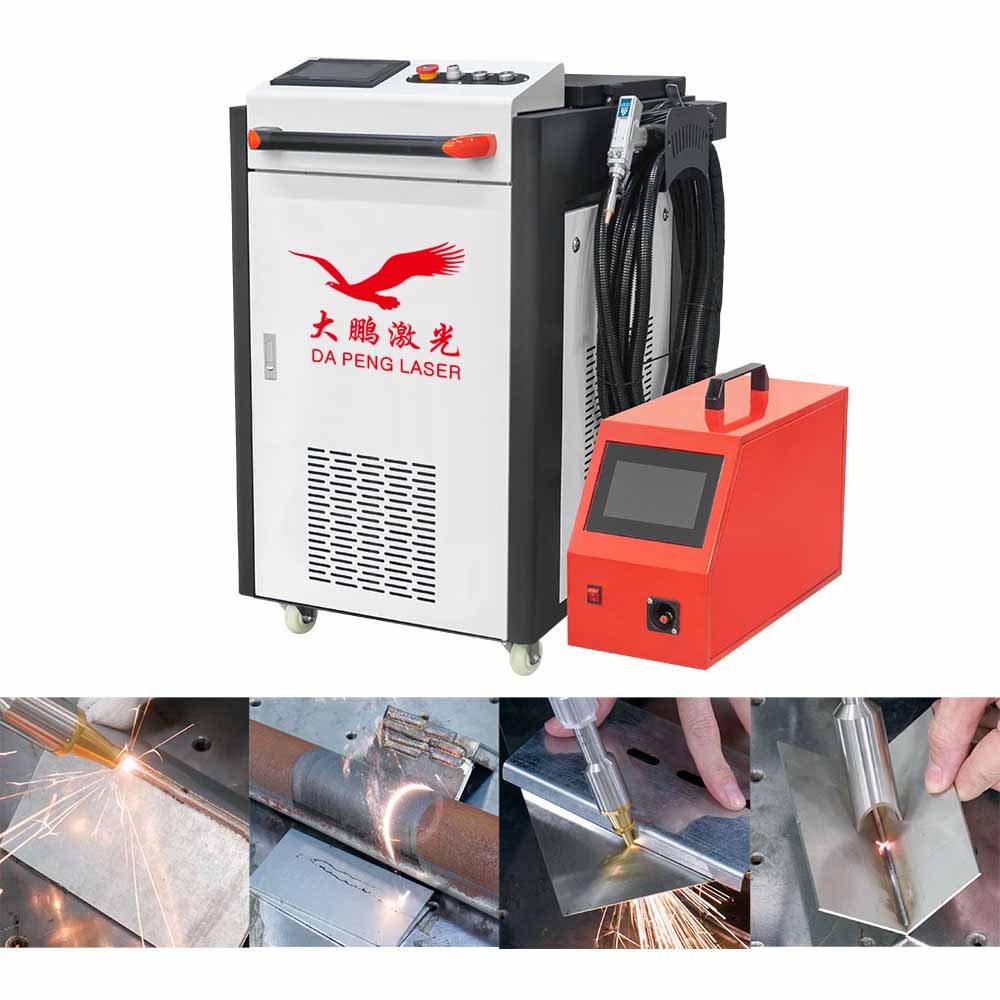

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing DP Laser Welding Machines (Price, Quality, and IP Risks)
Sourcing DP (Diode Pumped) laser welding machines from global suppliers—especially from regions like China—can offer cost advantages, but it also comes with significant risks related to price, quality, and intellectual property (IP). Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for making informed procurement decisions.
1. Hidden Costs Behind Low Initial Prices
Many suppliers advertise attractively low prices to win business, but additional costs often emerge later. These may include:
– Shipping, import duties, and customs clearance fees.
– Installation, training, and commissioning charges not included in the quote.
– Cost of spare parts, maintenance kits, or software updates.
– Currency fluctuations or payment terms that affect the final cost.
Tip: Always request a total cost of ownership (TCO) breakdown before finalizing a purchase.
2. Inconsistent or Substandard Quality
Low-cost machines may use inferior components (e.g., lower-grade optics, unstable cooling systems, or unreliable motion control), leading to:
– Reduced welding precision and repeatability.
– Frequent breakdowns and high downtime.
– Shorter machine lifespan and increased maintenance costs.
Tip: Require third-party inspection reports or conduct on-site factory audits. Test machines with real production samples before shipment.
3. Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate laser power, beam quality (M²), or automation capabilities. For example:
– Advertised 500W lasers may deliver only 400W stable output.
– Software features like “AI-assisted welding” may be basic pre-programmed routines.
Tip: Insist on live demonstrations or video validation using standardized test materials.
4. Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Overseas suppliers may lack local service teams, leading to:
– Long wait times for technical support.
– Difficulty sourcing compatible spare parts.
– Language and time zone barriers.
Tip: Verify the supplier’s global service network and request a service-level agreement (SLA).
5. Intellectual Property (IP) and Technology Risks
When customizing or co-developing laser systems, there is a risk of:
– Unauthorized replication or resale of your designs or processes.
– Use of counterfeit or unlicensed software/firmware in the machine.
– Weak contractual IP protections in supplier agreements.
Tip: Use strong NDAs and clear IP clauses in contracts. Consider working with suppliers in jurisdictions with enforceable IP laws.
6. Regulatory and Compliance Gaps
Machines may not meet safety or emissions standards required in your country (e.g., CE, FDA, or laser safety Class 1 certification). Non-compliant machines can be blocked at customs or create workplace safety hazards.
Tip: Confirm compliance with local regulations and request certified documentation.
Conclusion
While cost is an important factor, sourcing DP laser welding machines based solely on price can lead to long-term operational and financial setbacks. A balanced approach—emphasizing verified quality, reliable support, and protected IP—is essential for sustainable manufacturing success.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for DP Laser Welding Machines
When importing or exporting DP Laser Welding Machines, navigating logistics and compliance requirements is essential to ensure smooth delivery, avoid delays, and remain legally compliant. This guide outlines key considerations for international trade involving DP Laser Welding equipment.
Import and Export Regulations
DP Laser Welding Machines may be subject to export controls and import restrictions due to their classification under dual-use technologies. Before shipping, verify the Harmonized System (HS) code—typically 8456.20 for laser cutting and welding machines. Check if the destination country requires import licenses or permits. Certain high-powered laser systems may fall under national security or technology transfer regulations (e.g., U.S. EAR or EU Dual-Use Regulation). Always confirm compliance with both origin and destination country laws.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is crucial to protect sensitive optical and electronic components during transit. Use custom wooden crates with internal foam or shock-absorbing materials to prevent vibration and impact damage. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators. Include desiccants to control humidity. Secure all moving parts and disassemble delicate optics if required. Ensure the packaging meets international standards (e.g., ISPM 15 for wooden materials).
Shipping and Transportation Options
Choose between air, sea, or land freight based on urgency, cost, and destination. Air freight is recommended for time-sensitive deliveries, especially for high-value units. Sea freight is cost-effective for bulk shipments but requires longer lead times. Use reputable freight forwarders experienced in handling industrial machinery. Ensure the equipment is insured for its full value during transit. Provide detailed shipping documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading or air waybill.
Customs Clearance Procedures
Prepare all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including a commercial invoice with declared value, product description, and HS code. Include a certificate of origin if required for tariff preferences. For laser equipment, customs may require technical specifications (e.g., laser power, wavelength) to assess classification and safety compliance. Be prepared for inspections—ensure the machine is easily accessible for examination. Delays can occur if documentation is incomplete or inconsistent.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
DP Laser Welding Machines must comply with safety standards in the destination market. In the U.S., this includes FDA/CDRH regulations for laser products (21 CFR 1040.10). In the EU, compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and CE marking is mandatory. Machines should include safety interlocks, warning labels, and proper laser classification labels (e.g., Class 4). Provide user manuals in the local language and ensure all technical files are available for regulatory audits.
After-Sales Support and Warranty Logistics
Plan logistics for spare parts, technical support, and warranty service. Maintain an inventory of critical components in key regions to reduce downtime. Clearly define warranty terms, including coverage for shipping costs and repair turnaround times. Train local technicians or partner with certified service providers to offer on-site support. Provide compliance documentation (e.g., conformity certificates) to customers for their own regulatory filings.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
At end-of-life, DP Laser Welding Machines must be disposed of in accordance with environmental regulations such as the EU’s WEEE Directive or local e-waste laws. The machines may contain hazardous materials (e.g., batteries, optical components). Provide customers with disposal guidelines and support take-back programs where applicable. Maintain records of responsible recycling or disposal to meet corporate sustainability goals.
Conclusion on Sourcing DP Laser Welding Machine Pricing
After evaluating various suppliers, market trends, and pricing structures for DP (Diode Pumped) laser welding machines, it is evident that pricing is influenced by several key factors including laser power output, brand reputation, technical specifications, level of automation, after-sales support, and regional market conditions. While competitive pricing can be found from manufacturers in regions like China, particularly for mid-range industrial models, it is crucial to balance cost considerations with machine reliability, precision, and long-term serviceability.
Pricing for standard DP laser welding systems typically ranges from $15,000 to $50,000, with higher-end or customized models exceeding this range. Direct sourcing from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) often provides better value compared to purchasing through intermediaries, though local distributors may offer advantageous service and warranty terms.
In conclusion, while initial cost is an important factor, the total cost of ownership — including maintenance, training, uptime, and technical support — should guide the sourcing decision. Conducting thorough due diligence, requesting product demonstrations, and obtaining detailed quotes from multiple vetted suppliers will ensure optimal value, performance, and return on investment when sourcing DP laser welding equipment.