The global double-ridged horn antenna market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing, defense, aerospace, and telecommunications applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the RF and microwave antenna market—which includes double-ridged horn antennas—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by rising deployment of 5G infrastructure and stringent regulatory requirements for EMC testing across electronic devices. Grand View Research further supports this trajectory, estimating that the global antenna market will expand at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2022 to 2030, with specialty antennas like double-ridged horn models benefiting from their broadband capabilities and consistent performance across wide frequency ranges. As industries demand greater accuracy in signal measurement and interference testing, leading manufacturers are innovating to deliver high-gain, ultra-wideband solutions. Below are the top 10 double-ridged horn antenna manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape.
Top 10 Double-Ridged Horn Antenna Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 EMC Horn Antenna Rentals
Domain Est. 1996
Website: atecorp.com
Key Highlights: 7-day returnsEMC horn antennas emit RF for radiated immunity testing. Rent double ridged, high gain, waveguide antennas covering 1 – 18 GHz and 18 ……
#2 Double Ridged Horn Antennas
Domain Est. 2003
Website: rfspin.com
Key Highlights: Robust and high-performance double ridged horn antennas designed for outdoor environments deliver exceptional broadband accuracy with superior weather ……
#3 Double
Domain Est. 2013
Website: horn.ft-rf.com.tw
Key Highlights: Double Ridged Horn Antennas are suitable for both transmitting and receiving purposes, with applications: – Antenna measurement; – Communication systems; – ……
#4 Double
Domain Est. 2014
Website: theemcshop.com
Key Highlights: Double-ridged horn antennas are in stock and available for immediate shipment. The EMC Shop specializes in radiated immunity and emissions testing….
#5 A-RWH-1560 Double Ridged Horn Antenna
Domain Est. 2016
Website: store.rotkee.com
Key Highlights: In stock 14-day returnsDouble Ridge Guide Horns is a broadband antenna that offers excellent performance over the frequency range of 1500 MHz to 6000 MHz….
#6 Double
Website: schwarzbeck.info
Key Highlights: Linear polarized double ridge broadband horn antenna for receive and transmit applications made of aluminium. An optional 7/16 connector is available for high ……
#7 Double Ridge Guide Horn Antennas
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ahsystems.com
Key Highlights: AH Systems Double Ridge Guide Horns are broadband antennas that offer excellent performance over the frequency range of 170 MHz to 40 GHz….
#8 R&S®HF907 double
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rohde-schwarz.com
Key Highlights: The linearly polarized R&S®HF907 double-ridged waveguide horn antenna is a broadband, compact transmitting and receiving antenna for the frequency range from ……
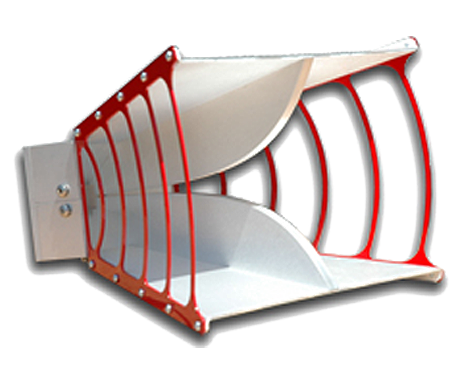
#9 3115 Double
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ets-lindgren.com
Key Highlights: ETS-Lindgren’s Model 3115 Double-Ridged Guide Horn Antenna has excellent gain and VSWR characteristics, it is small and portable with a length of 24.4 cm ……
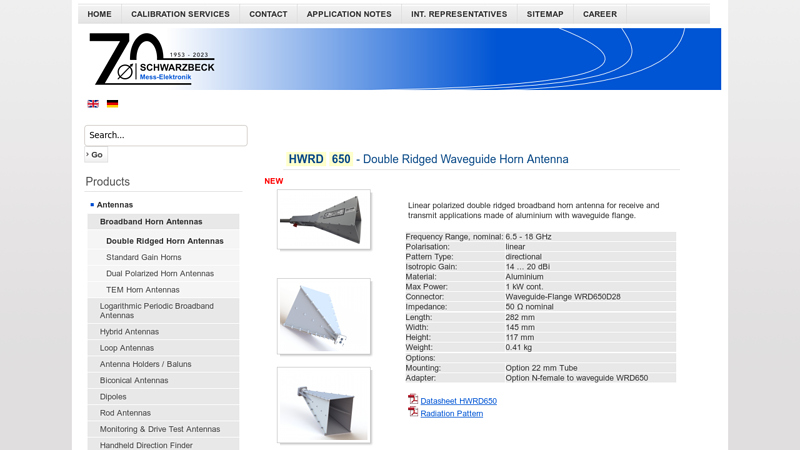
#10 HWRD 650
Website: schwarzbeck.de
Key Highlights: Linear polarized double ridged broadband horn antenna for receive and transmit applications made of aluminium with waveguide flange….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Double-Ridged Horn Antenna

2026 Market Trends for Double-Ridged Horn Antennas
The double-ridged horn antenna (DRHA) market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by increasing demands for high-performance, broadband electromagnetic solutions across defense, commercial, and research sectors. These antennas, valued for their wide bandwidth, high gain, and linear polarization across a broad frequency range, are becoming increasingly critical components in advanced electronic systems. Key trends shaping the market in 2026 include:
Growing Adoption in 5G and mmWave Testing
As 5G networks expand into higher mmWave bands (24 GHz and above), the need for precise over-the-air (OTA) testing of devices and base stations intensifies. Double-ridged horn antennas, with their ability to cover wide frequency bands efficiently, are essential in anechoic chamber testing for beamforming validation, antenna pattern measurements, and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) assessments. By 2026, demand is expected to rise significantly from telecom equipment manufacturers and test laboratories investing in next-generation validation infrastructure.
Expansion in Defense and Electronic Warfare (EW) Applications
Defense modernization programs worldwide are accelerating investments in electronic warfare, radar warning receivers (RWR), and signal intelligence (SIGINT) systems. DRHAs are ideal for wideband signal reception and jamming due to their consistent performance across multiple frequency bands. In 2026, government contracts and defense spending will continue to drive market growth, particularly in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, where electronic warfare capabilities are being prioritized.
Rising Demand in EMC and Regulatory Testing
Stringent electromagnetic compatibility regulations across industries—especially automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics—are fueling the need for reliable broadband antennas. Double-ridged horn antennas are standard in EMC testing setups due to their predictable gain and radiation patterns. With electric vehicles (EVs), IoT devices, and autonomous systems proliferating, compliance testing volumes are expected to surge by 2026, reinforcing DRHA demand in certified test labs.
Technological Advancements and Miniaturization
Manufacturers are focusing on improving DRHA performance through advanced materials (e.g., lightweight composites), enhanced ridge profiles, and integrated calibration features. A key trend by 2026 will be the development of compact, broadband DRHAs suitable for field deployment and portable test systems. Innovations in additive manufacturing may also enable custom horn geometries optimized for specific frequency ranges, reducing production costs and time.
Increased Competition and Regional Market Growth
While established players in the U.S. and Europe dominate the high-end DRHA market, emerging manufacturers in Asia (particularly China and South Korea) are gaining traction with cost-effective alternatives. This competitive landscape will drive innovation and pricing pressures in 2026. Additionally, growing R&D investments in countries like India and Japan will contribute to regional market expansion.
In summary, the double-ridged horn antenna market in 2026 will be characterized by robust growth fueled by technological advancements, stringent regulatory requirements, and expanding applications in communications, defense, and testing. Stakeholders who invest in high-performance, adaptable DRHA solutions will be well-positioned to capitalize on these emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Double-Ridged Horn Antennas: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing double-ridged horn antennas (DRHAs) for EMC testing, antenna measurement, or research applications requires careful attention to avoid compromising performance, compliance, or legal integrity. Below are critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) that buyers often encounter.
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Material Substitution
One of the most prevalent pitfalls is receiving antennas with substandard construction due to cost-cutting measures. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior materials—such as aluminum alloys with poor conductivity or plating that degrades quickly—leading to inconsistent performance and shortened lifespan. Poorly machined ridges or misaligned waveguide sections cause impedance mismatches, increased VSWR, and distorted radiation patterns. These flaws undermine measurement accuracy, especially in calibrated EMC environments where traceability and repeatability are essential.
Inadequate or Falsified Calibration Data
Many vendors offer DRHAs with calibration files, but these can be generic, outdated, or even fabricated. Buyers may receive antennas with calibration data not traceable to accredited laboratories, or worse, data copied from another unit. Without valid, unit-specific calibration certificates (preferably ISO 17025 accredited), the antenna’s performance across frequency bands cannot be trusted. This is particularly problematic for compliance testing, where regulatory bodies require demonstrable measurement uncertainty and traceability.
Lack of Shielding and RF Leakage
Cheaply manufactured DRHAs often lack proper electromagnetic shielding in the housing or feed section. This can result in RF leakage, causing unwanted coupling and measurement errors. Grounding points may be poorly implemented, increasing susceptibility to external noise and degrading signal integrity. In EMI testing, such deficiencies can lead to false emissions readings or mask genuine interference, compromising test validity.
Intellectual Property Infringement and Reverse-Engineered Designs
Some suppliers offer DRHAs at suspiciously low prices because they are reverse-engineered copies of patented designs from reputable manufacturers. These clones may infringe on existing IP, exposing end users to legal liability—especially in regulated industries or export-controlled applications. Using counterfeit or IP-infringing equipment can void test certifications and damage organizational credibility. It also supports unethical manufacturing practices that undercut innovation.
Absence of Design Documentation and Support
Reputable manufacturers provide detailed technical documentation, including mechanical drawings, S-parameters, gain plots, and warranty terms. Sourcing from obscure suppliers often results in missing or incomplete documentation, making integration and troubleshooting difficult. Lack of engineering support further complicates deployment, especially when anomalies arise during testing or system validation.
Non-Compliance with Industry Standards
DRHAs used in EMC testing must comply with standards such as ANSI C63.4, CISPR 16-1-4, or MIL-STD-461. Off-brand antennas may not meet these specifications, even if marketed as compliant. Without third-party verification or test reports, buyers risk investing in equipment that fails audit requirements or produces non-acceptable measurement results.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should source DRHAs from established manufacturers with verifiable quality control processes, transparent calibration practices, and a clear IP posture. Due diligence—including requesting accreditation certificates, reviewing test reports, and verifying warranty and support terms—is essential to ensure long-term reliability and regulatory compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Double-Ridged Horn Antenna
Overview
This guide provides essential logistics and compliance information for the proper handling, transportation, import/export, and regulatory adherence associated with Double-Ridged Horn Antennas. These antennas are commonly used in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing, broadband signal transmission, and RF measurement applications, requiring careful attention to technical specifications and regulatory controls.
Export Classification (ECCN/HTS)
Double-Ridged Horn Antennas may be subject to export control regulations due to their use in high-frequency testing and potential dual-use applications.
– Export Control Classification Number (ECCN): Typically classified under ECCN 3A999 or 3A001 of the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL), depending on frequency range and technical capabilities. Antennas operating above 31.8 GHz or designed for military use may require stricter controls.
– Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) Code: Commonly falls under HTS 8526.91.00 or 8517.62.00, depending on intended use and configuration. Confirm with local customs authority for accurate classification.
– License Requirements: A license may be required for export to embargoed or restricted countries. Utilize the Commerce Department’s SNAP-R system for license applications if necessary.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure the antenna meets international and regional regulatory standards for electromagnetic equipment:
– FCC (USA): Must comply with Part 15 or Part 2 if integrated into a system. Standalone antennas are generally exempt but associated test systems may require certification.
– CE Marking (EU): Must meet directives such as RED (Radio Equipment Directive 2014/53/EU) and EMC Directive (2014/30/EU) if marketed or used within the European Union.
– RoHS & REACH: Confirm the antenna’s materials comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization of Chemicals) regulations, particularly for EU shipments.
– ISED (Canada): Antennas used in radio systems must adhere to RSS-Gen and applicable standards under Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada.
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging ensures product integrity during shipping and storage:
– Use anti-static, foam-lined containers to protect the antenna’s delicate ridged waveguide structure.
– Include desiccant packs in packaging for humid environments to prevent internal corrosion.
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators.
– Avoid direct hand contact with the aperture to prevent contamination or damage to internal surfaces.
Transportation Guidelines
Follow best practices for domestic and international shipping:
– Air Freight: Declare contents accurately; no special hazardous material classification is typically required, but documentation must reflect ECCN if applicable.
– Ground/Sea Freight: Secure the antenna to prevent movement; use pallets with edge protectors for bulk shipments.
– Temperature & Humidity: Store and transport within 0°C to 40°C and 10% to 80% non-condensing humidity to avoid material degradation.
Documentation Requirements
Maintain accurate records for compliance and traceability:
– Commercial Invoice with detailed product description, ECCN/HTS codes, value, and country of origin.
– Packing List specifying quantity, weight, and dimensions.
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC) for CE, FCC, or other relevant standards, if applicable.
– Export License or License Exception Authorization (e.g., LVS, NLR) when required.
– End-User Statement or Technology Transfer Agreement for dual-use items in sensitive regions.
Import Considerations
Be aware of destination-specific requirements:
– Verify import duties, VAT, and local certification needs (e.g., KC Mark for South Korea, CCC for China).
– Some countries may require pre-shipment inspection or local representative registration.
– Ensure antenna frequencies do not exceed permitted civilian use limits in the destination country.
Disposal & Environmental Compliance
At end-of-life, follow environmental regulations:
– Recycle metal components (typically aluminum or brass) through certified e-waste programs.
– Adhere to WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directive in the EU.
– Do not dispose of in regular landfill due to metal content and potential coatings.
Summary
Double-Ridged Horn Antennas require meticulous attention to export controls, regulatory standards, and handling protocols. Always verify classification codes, maintain proper documentation, and ensure compliance with destination country regulations to avoid delays or penalties. Consult with a qualified compliance officer or legal expert when shipping to high-risk or sanctioned regions.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Double-Ridged Horn Antenna
In conclusion, sourcing a double-ridged horn antenna requires careful consideration of technical specifications, application requirements, and supplier reliability. These antennas are widely used in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing, broadband measurements, and signal monitoring due to their wide frequency coverage and consistent performance across bands. When selecting a supplier, factors such as frequency range, gain, VSWR, power handling, polarization, and calibration options must align with the intended use case.
Reputable manufacturers like Schwarzbeck, TDK RF Solutions, ETS-Lindgren, and Aaronia AG offer high-quality, calibrated antennas suitable for precision applications, though at a higher cost. Alternatively, cost-effective options from select Chinese manufacturers may meet budget constraints but often require additional verification for performance and durability.
Ultimately, the choice depends on balancing performance needs, regulatory compliance, and budget. Investing in a well-calibrated, certified antenna from a trusted supplier ensures measurement accuracy, repeatability, and long-term reliability—critical for R&D, compliance testing, and field operations. Proper due diligence during the sourcing process will lead to a successful integration of the double-ridged horn antenna into the intended system.