The global demand for high-performance insulation materials has surged in recent years, driven by rising energy efficiency standards, growing construction activities, and increased focus on sustainable building practices. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global insulation materials market was valued at USD 55.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is further fueled by innovations in thermal insulation technologies, including the adoption of double faced insulation—known for its dual-layered design that enhances thermal resistance and simplifies installation in both residential and commercial applications. As industries ranging from construction to HVAC seek materials that balance performance with cost-efficiency, manufacturers specializing in double faced insulation are positioned at the forefront of this growth. The following list highlights the top nine manufacturers leading the charge in innovation, scalability, and market reach across this dynamic sector.
Top 9 Double Faced Insulation Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Styrofoam™ Brand XPS Insulation
Domain Est. 1987
Website: dupont.com
Key Highlights: Its unique closed-cell structure and rigid foam board technology enables XPS to meet core thermal, moisture, air and vapor performance requirements. The history ……
#2 ThermaFiber Mineral Wool Insulation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: owenscorning.com
Key Highlights: Thermafiber is the leading manufacturer of mineral wool insulation. As the pioneers of perimeter fire containment, we have over 89 years of experience….
#3 Rmax Insulation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rmax.com
Key Highlights: Rmax Polyiso is your one step, continuous Insulation solution. Reduces construction time • Saves labor and material • Reduces carbon footprint….
#4 Double Reflective Insulation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: reflectixinc.com
Key Highlights: The Reflectix Double Reflective Insulation is the most versatile, widely-distributed, energy-efficient product that we manufacture….
#5 FI-FOIL® Reflective Insulation Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fifoil.com
Key Highlights: Based in Florida, FI-FOIL® is your leading source for sustainable, high-value, advanced performance reflective insulation products and systems….
#6 1. Energy Saver Double Layer Wall
Domain Est. 1996
Website: silvercote.com
Key Highlights: Energy Saver Double Layer is a high R-value insulation system with reduced air infiltration. Bright Finished Appearance, Vapor Retarder, Formaldehyde Free….
#7 Fiberglass Insulation
Domain Est. 1997
Website: jm.com
Key Highlights: Johns Manville Formaldehyde-free™ fiberglass insulation provides thermal and accoustical control for both vertical and horizontal applications….
#8 R-TECH Insulation Panels
Domain Est. 1998
Website: insulfoam.com
Key Highlights: R-Tech Panels are an engineered rigid insulation consisting of a superior closed-cell, lightweight and resilient expanded polystyrene (EPS) with advanced ……
#9 Radiant Barrier Product Selection Guide
Domain Est. 2006
Website: radiantguard.com
Key Highlights: Our radiant barriers and reflective insulation products are available for purchase online by homeowners, retail store operators, resellers, installers, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Double Faced Insulation
H2: Emerging Market Trends for Double-Faced Insulation in 2026
As the global construction, manufacturing, and energy efficiency sectors evolve, double-faced insulation—a versatile thermal and acoustic insulation material with adhesive or reflective coatings on both sides—is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by sustainability mandates, technological advancements, and shifting regulatory landscapes, several key market trends are expected to shape the demand, innovation, and competitive dynamics of the double-faced insulation industry.
-
Increased Demand from Green Building Initiatives
By 2026, global green building standards such as LEED, BREEAM, and energy performance certifications (e.g., Energy Performance Certificates in Europe) will continue to drive demand for high-efficiency insulation materials. Double-faced insulation, particularly products with low-emissivity (low-e) foils and high R-values, will be increasingly adopted in residential, commercial, and industrial constructions aiming for net-zero energy use. The reflective properties of double-faced insulation improve thermal performance, helping buildings meet stringent energy codes. -
Growth in Retrofitting and Renovation Projects
With aging infrastructure and rising energy costs, many countries will prioritize building retrofitting. Double-faced insulation is well-suited for retrofit applications due to its thin profile, ease of installation, and dual functionality (insulation and vapor barrier). By 2026, government incentives in regions like North America and the EU for energy-efficient retrofits will boost market penetration, especially in attic, wall, and HVAC duct insulation applications. -
Technological Innovation in Material Composition
Advancements in material science will lead to next-generation double-faced insulation incorporating phase-change materials (PCMs), aerogels, or bio-based foams. These innovations will enhance thermal performance while reducing environmental impact. Additionally, smart insulation variants—integrating sensors or responsive coatings—may emerge, offering real-time monitoring of temperature and moisture levels, appealing to smart building ecosystems. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Pressure
Environmental regulations targeting embodied carbon and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions will push manufacturers toward eco-friendly formulations. By 2026, double-faced insulation made from recycled materials (e.g., post-consumer PET or mineral wool) or with bio-based adhesives will gain traction. Certifications like EPD (Environmental Product Declaration) and Cradle to Cradle will become differentiators in competitive markets. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Urbanization in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East will fuel construction growth, increasing demand for cost-effective, high-performance insulation. Countries like India, Indonesia, and Saudi Arabia—with large-scale infrastructure and cooling demands—will adopt double-faced reflective insulation to reduce HVAC loads in hot climates. Localized manufacturing and partnerships will emerge to meet regional specifications and reduce supply chain dependencies. -
Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
As solar panel installations grow, double-faced insulation will play a supportive role in building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) and solar thermal systems. Its reflective backing can enhance heat management behind panels, improving efficiency and durability. By 2026, integrated building envelopes combining insulation, solar tech, and ventilation will drive demand for multifunctional materials like double-faced insulation. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Volatility
Persistent fluctuations in the prices of aluminum (used in reflective facers) and petrochemicals (for foam cores) will prompt manufacturers to diversify sourcing and invest in recycling loops. Nearshoring and regional production hubs may expand to mitigate geopolitical risks and reduce carbon footprints associated with transportation.
Conclusion
By 2026, the double-faced insulation market will be shaped by sustainability imperatives, technological innovation, and expanding applications across retrofit, new construction, and renewable energy sectors. Companies that prioritize energy efficiency, circularity, and smart functionality will lead the market, capturing opportunities in both developed and emerging economies. Strategic investments in R&D, eco-certifications, and value-added solutions will be critical to maintaining a competitive edge.
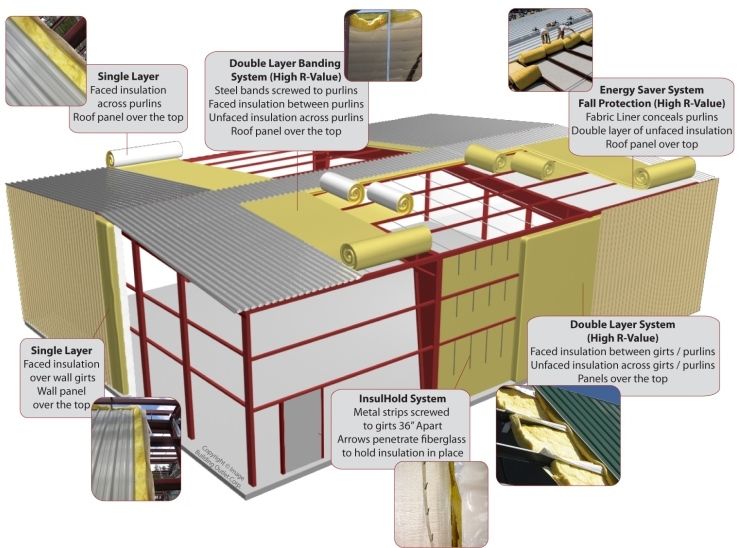
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Double-Faced Insulation (Quality, IP)
Sourcing double-faced insulation—typically a composite material like foil-faced fiberglass or foam board with adhesive backing—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, compliance risks, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing double-faced insulation is receiving substandard materials that fail to meet technical specifications. This includes variations in thickness, inadequate adhesive strength, inconsistent facing lamination, or poor thermal resistance (R-value). Low-quality facings may delaminate over time or degrade under UV exposure, compromising the insulation’s effectiveness. Buyers often face this when working with less-reputable suppliers who prioritize cost over consistency, leading to field failures and costly rework.
Misrepresentation of Fire and Safety Ratings
Suppliers may inaccurately claim fire resistance, smoke development, or flame spread ratings (e.g., ASTM E84, UL 723). Some sourced materials might not have undergone proper third-party testing, or certifications may be outdated or falsified. Using insulation that doesn’t meet local building codes can result in failed inspections, liability issues, or safety hazards. Always verify test reports and ensure the exact product model has been certified.
Inadequate Moisture and Vapor Barrier Integrity
Double-faced insulation often serves as a vapor retarder. A common pitfall is sourcing material where the foil or polymer facing has micro-perforations, pinholes, or weak seams, reducing its effectiveness as a moisture barrier. This can lead to condensation within wall or roof assemblies, promoting mold growth and structural damage. Quality control during manufacturing is critical—inspect samples and request permeability (perm) ratings backed by lab data.
IP Infringement Through Copycat Products
Many double-faced insulation products incorporate proprietary technologies, such as specialized adhesives, reflective coatings, or composite structures protected by patents or trademarks. Sourcing generic or “compatible” versions from certain regions—especially without proper due diligence—risks infringing on IP rights. Using counterfeit or reverse-engineered materials can result in legal action, shipment seizures, or reputational damage. Always confirm that the supplier has the right to manufacture and sell the product, and request IP indemnification where possible.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Low-cost suppliers may not provide full material traceability, test reports, or safety data sheets (SDS). This becomes a major issue during audits, warranty claims, or litigation. Without proper documentation, proving compliance with green building standards (e.g., LEED) or environmental regulations (e.g., formaldehyde emissions) becomes impossible. Ensure suppliers offer complete product documentation and batch traceability.
Overlooking Regional Compliance Requirements
Insulation products must comply with regional building codes and environmental regulations (e.g., California Title 24, EU CE marking, REACH). A common mistake is assuming a product approved in one market is suitable elsewhere. Sourcing without verifying local compliance can delay projects or result in non-conforming installations. Confirm that the insulation meets all applicable standards for the target market.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—through supplier vetting, third-party testing, and legal review of IP rights—buyers can ensure they source high-quality, compliant, and legally sound double-faced insulation.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Double Faced Insulation
Double faced insulation—typically composed of a fiberglass or mineral wool core with reinforced facing on both sides—is widely used in HVAC, building envelopes, and industrial applications for thermal and acoustic performance. Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure product integrity, worker safety, and adherence to environmental and transportation standards. This guide outlines key considerations for handling, shipping, storing, and complying with regulations when working with double faced insulation.
Product Handling and Packaging
Double faced insulation is sensitive to moisture, compression, and physical damage. Proper packaging is critical to maintain performance and appearance.
- Protective Wrapping: Insulation should be factory-wrapped in moisture-resistant plastic film with end caps or cardboard protectors to prevent edge damage.
- Palletization: Bundles must be securely strapped and banded to pallets to prevent shifting during transit. Use edge protectors to avoid crushing.
- Labeling: Each bundle or pallet must include product identification, R-value, facing type (e.g., FSK, ASJ), fire rating, lot number, and handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Do Not Stack”).
Transportation and Shipping
Transporting double faced insulation requires planning to prevent damage and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Weather Protection: Always use enclosed or covered trailers to protect against rain, snow, and high humidity. Avoid open flatbeds unless adequately tarped.
- Load Securing: Use straps, load bars, or dunnage to prevent shifting. Avoid over-stacking, which can compress lower layers and degrade insulation performance.
- Temperature Considerations: While most double faced insulation is not temperature-sensitive, prolonged exposure to extreme cold may make facings brittle. Avoid freezing conditions when possible.
Storage Requirements
Improper storage can lead to moisture absorption, mold, or physical damage.
- Indoor Storage: Store in a dry, well-ventilated warehouse. Elevate pallets off the floor using wood or plastic pallets to prevent ground moisture uptake.
- Moisture Control: Maintain relative humidity below 70%. Avoid storage near plumbing leaks or exterior doors.
- Stacking Limits: Follow manufacturer guidelines. Typically, do not stack more than 3–4 high to prevent bottom-layer compression.
- Shelf Life: Most double faced insulation has an indefinite shelf life if stored properly, but inspect periodically for signs of moisture, pests, or facing delamination.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to environmental, safety, and building code regulations.
- Fire Safety Standards: Verify insulation meets ASTM E84 (Surface Burning Characteristics) and ASTM E96 (Water Vapor Transmission). Common facings like FSK-25 must carry a flame spread index ≤25 and smoke-developed index ≤50.
- Indoor Air Quality (IAQ): Comply with ASTM C1071 and ASTM C553. Some products may need to meet low-emission standards (e.g., California 01350) for use in sensitive environments.
- Fiber Content Regulations: Fiberglass and mineral wool insulation must comply with OSHA PEL (Permissible Exposure Limit) and ACGIH TLV (Threshold Limit Value) for airborne fibers. Provide worker safety data sheets (SDS) and implement dust control during installation.
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: For international shipments, confirm that facing materials (e.g., adhesives, coatings) are free from restricted substances under EU regulations.
- Building Codes: Ensure product meets local energy codes (e.g., IECC, ASHRAE 90.1) for thermal resistance (R-value) and proper application methods.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- Recyclability: Fiberglass and mineral wool are recyclable. Coordinate with suppliers or waste handlers for end-of-life material recovery.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Look for insulation with high recycled content (e.g., up to 80% in some fiberglass products) and third-party certifications like GREENGUARD Gold or LEED compliance.
- Packaging Waste: Minimize plastic wrap where possible and recycle stretch film and cardboard.
Worker Safety and Training
- PPE Requirements: Installers must wear NIOSH-approved respirators, gloves, long sleeves, and eye protection to reduce skin and respiratory irritation.
- Training: Provide training on safe handling, cutting, and disposal procedures. Emphasize avoiding inhalation of fibers and proper cleanup techniques.
- First Aid: Post first aid procedures for fiber exposure (e.g., flushing eyes, washing skin).
Documentation and Traceability
- Material Test Reports (MTRs): Maintain MTRs for each batch, including thermal, fire, and vapor performance data.
- Certificates of Compliance (CoC): Obtain CoCs confirming adherence to ASTM, UL, or other relevant standards.
- Chain of Custody: Track insulation from manufacturer to job site to support warranty claims and quality audits.
By following this logistics and compliance guide, stakeholders can ensure safe, efficient handling of double faced insulation while meeting all regulatory and performance requirements. Always consult manufacturer specifications and local regulations for project-specific compliance.
Conclusion on Sourcing Double-Faced Insulation
Sourcing double-faced insulation requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, cost efficiency, and long-term sustainability. After evaluating various suppliers, material types (such as foil-faced fiberglass, foam, or reflective insulation), and technical specifications—including R-value, vapor barrier properties, and fire resistance—it is evident that selecting the right product hinges on the specific application, whether for HVAC systems, building envelopes, or industrial installations.
Partnering with reputable manufacturers who offer certified, consistent-quality products ensures compliance with industry standards and building codes. Additionally, considerations such as environmental impact, recyclability, and ease of installation contribute to the overall value proposition. Establishing long-term supplier relationships can lead to improved lead times, volume discounts, and access to technical support.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of double-faced insulation involves a thorough assessment of technical needs, supplier reliability, and total cost of ownership. A well-informed procurement strategy not only enhances energy efficiency and thermal performance but also supports project timelines and sustainability goals. Regular market review and engagement with multiple suppliers will ensure continued access to innovative, high-performing insulation solutions.