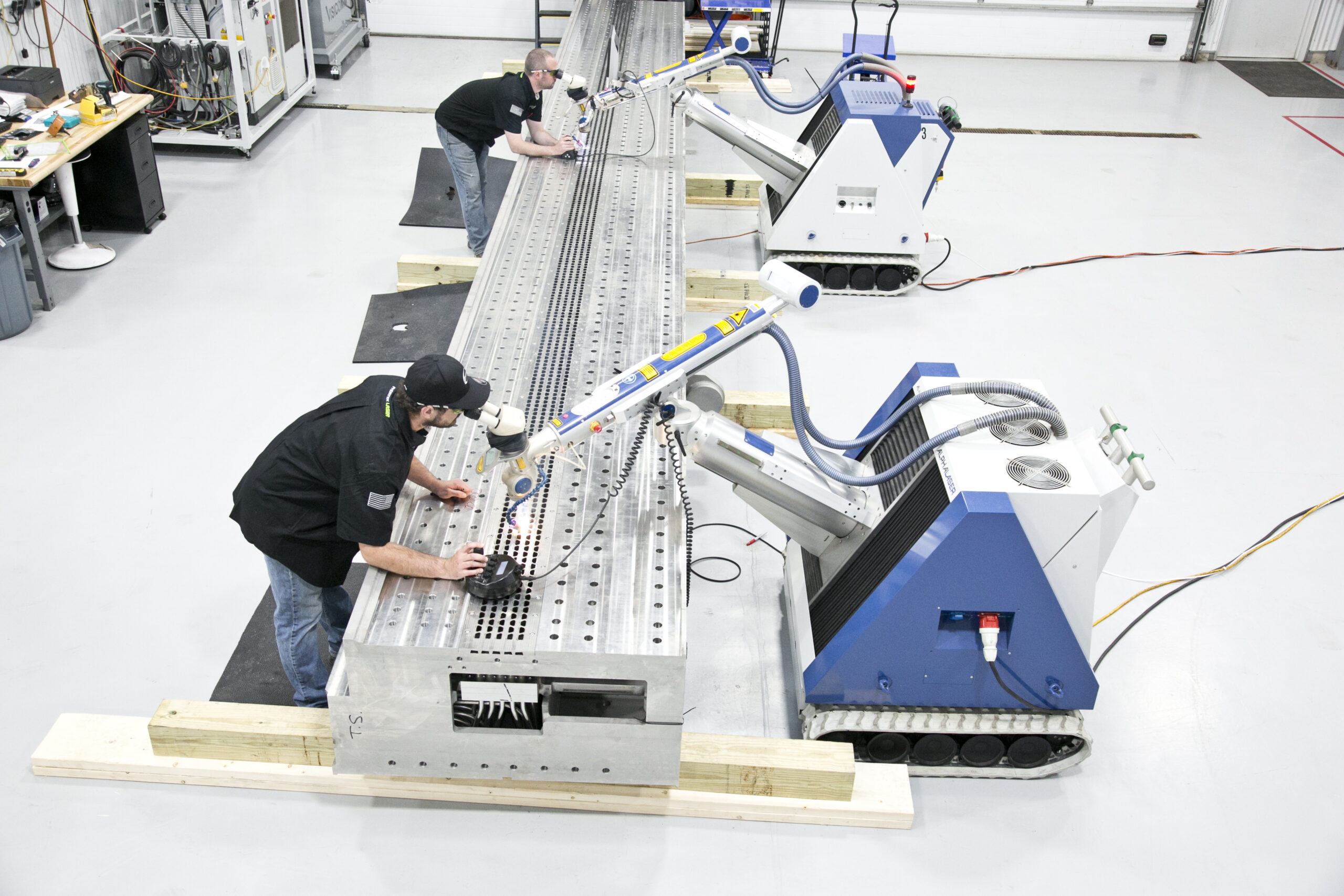
The global laser welding equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the laser welding market was valued at USD 4.87 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 7.63 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising adoption of automation in production lines, and the need for high-speed, low-distortion welding solutions. As demand intensifies, manufacturers specializing in laser welding systems are scaling innovation and production capacity to capture a share of this expanding market. Below is a data-driven review of the top 10 laser welder manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Do Laser Welders Work Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered by the most experienced engineers and ……
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a pioneer in the field of mobile laser welding, ALPHA LASER GmbH offers a wide range of high-quality laser welding devices. This includes laser welding ……
#4 A New World Of Laser Welding ⋆ Alpha Laser U.S.
Website: alphalaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser welders for laser welding, cutting, cladding and hardening. Industrial lasers from Alpha Laser U.S. with new capabilities and fewer limitations….
#5 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding solutions can be seamlessly integrated into almost any manufacturing environment to maximize your operation’s productivity….
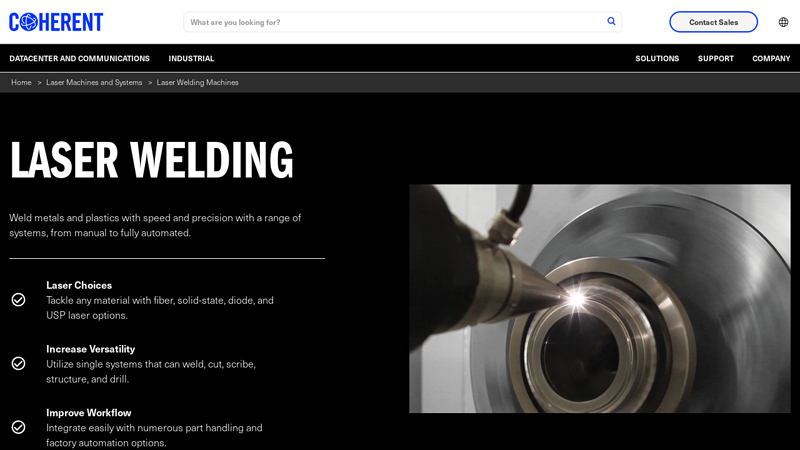
#6 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Our laser welders are cost-effective solutions that meet needs common to industries as diverse as medical device manufacturing and automotive manufacturing – ……
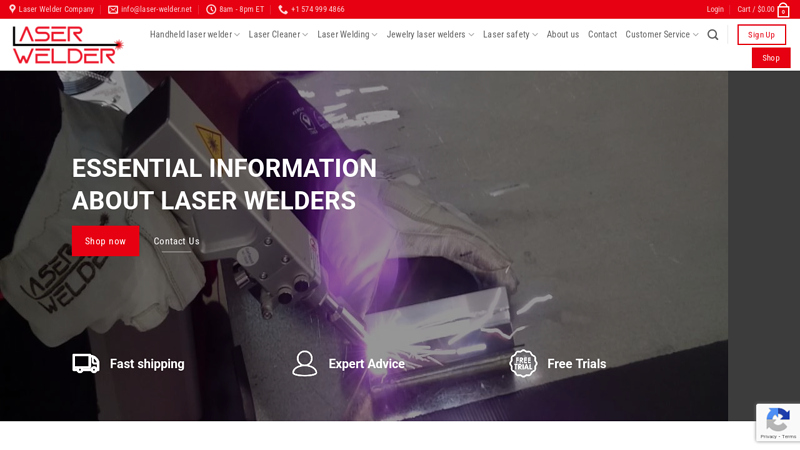
#7 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: All our laser welders are continuous wave fiber laser based due to their excellent performance to cost ratio, high efficiency and high power output. Continuous ……
#8 Miller Electric enters the world of hand
Website: thefabricator.com
Key Highlights: Miller Electric sees laser weldi*ng not as a simple alternative to conventional welding, but as a tool for companies to boost productivity while ……
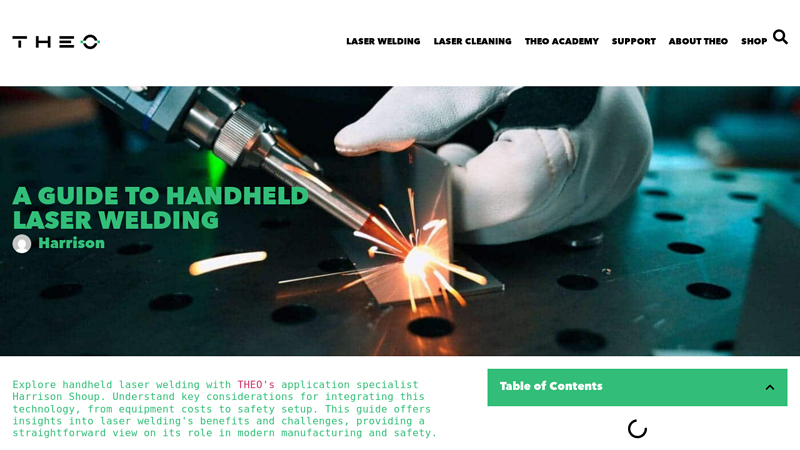
#9 A Guide to Handheld Laser Welding
Website: theo.inc
Key Highlights: This guide offers insights into laser welding’s benefits and challenges, providing a straightforward view on its role in modern manufacturing and safety….
#10 The 15 Best Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers in the US
Website: kuntailaser.com
Key Highlights: A laser welding machine is a state-of-the-art manufacturing tool that employs concentrated laser beams to fuse materials….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Do Laser Welders Work
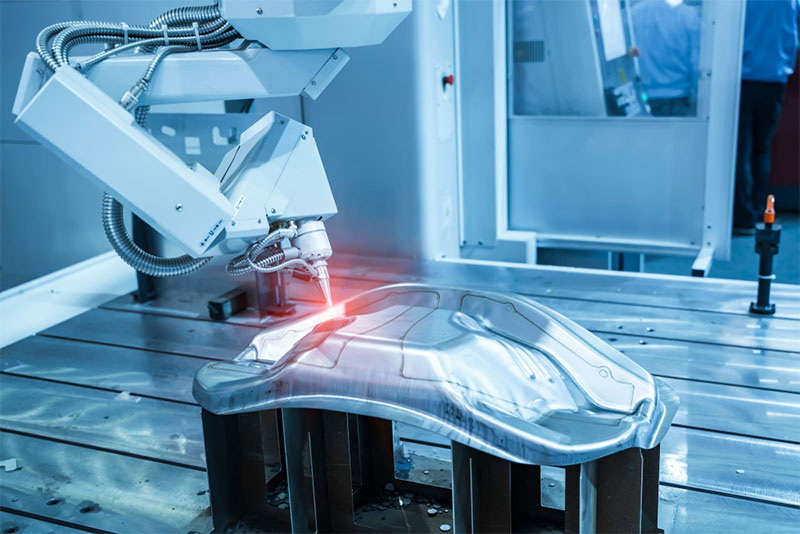

H2: 2026 Market Trends for “Do Laser Welders Work”
As we approach 2026, the query “Do laser welders work?” reflects growing consumer and industrial interest in the efficacy, reliability, and practical applications of laser welding technology. This interest is not just theoretical—market trends indicate a robust expansion in adoption across multiple sectors, validating that yes, laser welders do work, and they are increasingly becoming essential tools in advanced manufacturing.
-
Increased Industrial Adoption
By 2026, laser welding systems are projected to see significant penetration in automotive, aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and consumer electronics. The precision, speed, and consistency of laser welders make them ideal for high-volume production with minimal material distortion. Companies are investing heavily in automation-integrated laser welding solutions, confirming their functional effectiveness and long-term viability. -
Advancements in Fiber Laser Technology
Fiber lasers now dominate the market due to their efficiency, lower maintenance, and improved beam quality. By 2026, these systems are expected to account for over 70% of industrial laser welding deployments. Enhanced cooling systems, smarter controls, and modular designs have made laser welders more reliable and easier to use, directly addressing earlier skepticism about their practicality. -
Expansion into SMEs and Light Manufacturing
Originally limited to large-scale operations, laser welding is becoming accessible to small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The drop in equipment costs and the rise of compact, user-friendly systems mean more businesses are asking, “Do laser welders work for smaller operations?”—and the answer is increasingly yes. Plug-and-play systems with intuitive interfaces reduce the skill barrier, making laser welding a feasible alternative to traditional methods like MIG or TIG. -
Growing Emphasis on Sustainability and Efficiency
Laser welding consumes less energy and produces less waste compared to conventional welding techniques. As sustainability becomes a core business imperative, industries are turning to laser solutions to meet environmental goals. By 2026, regulatory pressures and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) standards are expected to further drive adoption, reinforcing the technology’s functional and economic value. -
Rise of Hybrid and Smart Welding Systems
Integration with AI, IoT sensors, and real-time monitoring allows laser welders to self-optimize parameters and detect defects instantly. These smart systems improve yield and reduce rework, proving not only that laser welders work, but that they work better when connected and intelligent. Predictive maintenance and data analytics enhance uptime and productivity, making laser welding a cornerstone of Industry 4.0. -
Consumer and DIY Market Curiosity
While professional-grade systems dominate, there’s growing interest in entry-level laser welders for hobbyists and metal fabricators. Online forums and review platforms frequently address the question “Do laser welders work for thin metals or home shops?” With improved safety features and portable designs, consumer confidence is rising—though expectations are tempered by realistic assessments of power and application limits.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market trend is clear: laser welders not only work—they are transforming modern manufacturing. The persistent inquiry “Do laser welders work?” is gradually shifting from doubt to demand, as real-world performance, technological maturity, and economic benefits solidify their role across industries. With ongoing innovation and broader accessibility, laser welding is poised to become the standard rather than the exception.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Laser Welders (Quality, IP Protection)
Sourcing laser welders, especially from international or unfamiliar suppliers, involves significant risks related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these factors can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing laser welders is receiving equipment that fails to meet promised performance standards. Low-cost suppliers may cut corners on components such as laser diodes, cooling systems, or control software, resulting in inconsistent weld quality, frequent breakdowns, or shortened machine lifespan. Without rigorous quality control processes—such as ISO certification or third-party inspection reports—buyers risk investing in underperforming machines that disrupt production and increase maintenance costs.
Lack of Transparency in Technical Specifications
Many suppliers provide vague or inflated technical data, such as maximum laser power, beam quality (M² factor), or duty cycle. Some may advertise peak power instead of continuous output, misleading buyers about actual capabilities. Without access to detailed, verifiable specifications and performance test data, purchasers may end up with a system unsuitable for their specific applications, especially in high-precision industries like medical device or aerospace manufacturing.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Laser welding systems require regular maintenance and occasional component replacement. Sourcing from suppliers without established local support networks can lead to prolonged downtime when issues arise. A common pitfall is discovering too late that spare parts are either unavailable, excessively priced, or require long lead times. Ensure the supplier offers comprehensive service agreements, training, and a clear plan for technical support before finalizing procurement.
Inadequate Intellectual Property Protection
When sourcing laser welders—particularly custom or integrated systems—there’s a risk of IP infringement or misappropriation. Some manufacturers may use reverse-engineered components or unlicensed software, exposing the buyer to legal liability. Additionally, if you’re providing proprietary designs or integration specs, ensure robust contracts are in place with non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clear IP ownership clauses to prevent unauthorized use or replication of your technology.
Non-Compliance with Safety and Regulatory Standards
Laser systems are subject to strict international safety regulations (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety, CE, FDA). Sourcing from uncertified manufacturers may result in equipment that doesn’t comply with local regulations, posing safety risks and potentially leading to fines or operational shutdowns. Always verify that the laser welder meets relevant regional safety and emissions standards and comes with proper documentation and certification.
Hidden Costs in Integration and Calibration
While the initial purchase price may seem competitive, additional costs often emerge during installation, calibration, and integration with existing production lines. Some suppliers do not include on-site commissioning or alignment services, requiring third-party experts at added expense. Ensure the quote covers full turnkey delivery, including system calibration, safety interlocks, and integration support, to avoid budget overruns.
By carefully evaluating supplier credibility, demanding verifiable quality assurances, and protecting intellectual property through legal safeguards, businesses can mitigate these common pitfalls and ensure a reliable, compliant, and high-performing laser welding solution.
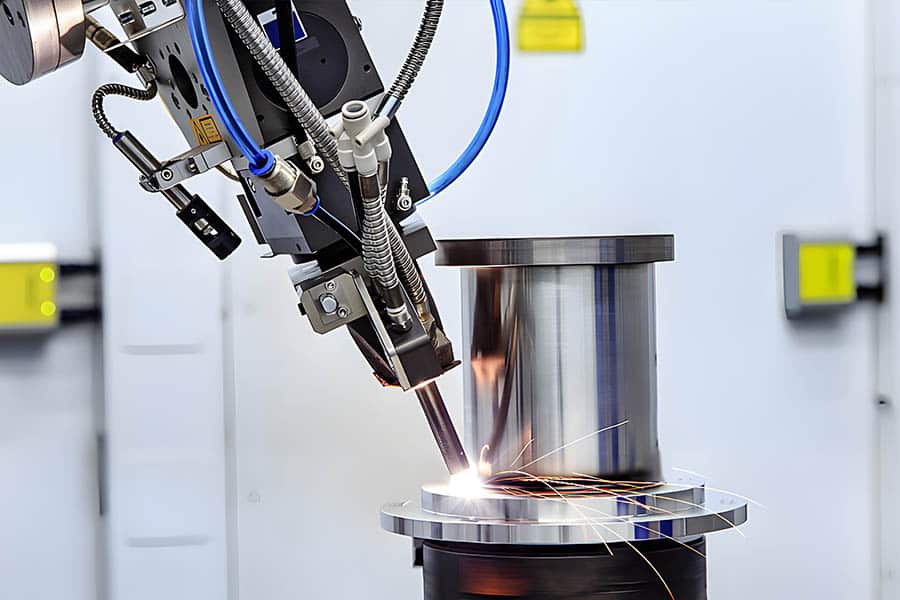

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Welders
When deploying or operating laser welders in industrial or manufacturing environments, understanding both logistical requirements and compliance standards is essential for safety, efficiency, and legal adherence. This guide outlines key considerations in logistics and regulatory compliance for laser welding operations.
1. Equipment Transportation and Installation
Proper logistics begin with the safe transport and setup of laser welding systems:
- Packaging & Handling: Ensure laser welders are shipped in manufacturer-approved, shock-resistant packaging with proper labeling, including fragile and sensitive equipment indicators.
- Site Preparation: Verify facility readiness—adequate floor space, power supply (voltage, phase, grounding), cooling systems (chillers), and ventilation before installation.
- Qualified Personnel: Use certified technicians for unpacking, assembly, and calibration to avoid damage and ensure optimal performance.
2. Regulatory Compliance Standards
Laser welders must comply with national and international safety and performance regulations:
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1 / ANSI Z136.1): Classify lasers according to output power and implement appropriate engineering controls (e.g., enclosures, interlocks) based on laser class (typically Class 4 for industrial welders).
- Occupational Safety (OSHA, EU Directive 2006/25/EC): Ensure workplace exposure limits for laser radiation are met. Provide protective equipment and control access to laser operation zones.
- Electrical Compliance (CE, UL, CSA): Confirm equipment meets regional electrical safety standards for the country of operation.
3. Workplace Safety & Hazard Control
Mitigate risks associated with laser welding processes:
- Laser Hazard Zones: Designate controlled areas with warning signs, interlocks, and emergency stop mechanisms.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Require laser-safe eyewear with appropriate optical density, flame-resistant clothing, and face shields.
- Fume Extraction: Install local exhaust ventilation systems to capture hazardous fumes and particulates (e.g., metal oxides).
4. Training & Operational Procedures
Ensure personnel are properly trained and operations are standardized:
- Operator Certification: Train staff on laser safety, equipment operation, and emergency procedures. Maintain training records.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and enforce documented workflows for startup, operation, maintenance, and shutdown.
- Maintenance Logs: Keep detailed records of servicing, calibration, and repairs to ensure reliability and compliance audits.
5. Environmental & Waste Management
Address environmental impacts and disposal protocols:
- Waste Materials: Safely collect and dispose of metal residues, filters, and consumables in accordance with local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, REACH).
- Energy Efficiency: Optimize power usage and consider energy-efficient models to reduce carbon footprint and operational costs.
6. Documentation & Auditing
Maintain compliance through proper documentation:
- Compliance Certificates: Keep copies of equipment certifications (CE, FDA, etc.) and safety approvals on file.
- Inspection Records: Conduct regular safety audits and equipment inspections to ensure ongoing compliance with regulations.
- Incident Reporting: Establish protocols for reporting and investigating laser-related incidents or near-misses.
By adhering to these logistics and compliance guidelines, organizations can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient operation of laser welding systems across various industrial applications.
Conclusion: Do Laser Welders Work?
Yes, laser welders are highly effective and represent a significant advancement in modern welding technology. They offer precise, clean, and consistent welds with minimal heat distortion, making them ideal for high-accuracy applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. Their ability to weld thin materials, dissimilar metals, and complex geometries gives them a distinct advantage over traditional welding methods.
While the initial investment in laser welding equipment can be high and requires skilled operators, the long-term benefits—such as increased productivity, reduced post-processing, and superior weld quality—often justify the cost. Advances in fiber laser technology have also improved reliability and efficiency, making laser welders more accessible and practical for a wider range of manufacturing environments.
In conclusion, laser welders not only work effectively but are increasingly becoming the preferred choice for precision welding applications where quality, speed, and automation are critical.