The global DNA purification kit market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for genomic research, personalized medicine, and advancements in molecular biology techniques. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 4.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.3% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the market could surpass USD 7.8 billion by 2030, fueled by increasing adoption of biotechnological tools in diagnostics and pharmaceutical development. This growth reflects a heightened need for high-throughput, reliable, and scalable nucleic acid extraction solutions across academic, clinical, and industrial laboratories. As innovation accelerates and competition intensifies, several key manufacturers have emerged as leaders in providing efficient, standardized, and application-specific DNA purification kits. Below is a data-informed overview of the top 10 DNA purification kit manufacturers shaping the future of genomic workflows.
Top 10 Dna Purification Kit Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 sbeadex Nucleic Acid Purification Technology
Domain Est. 1999
Website: biosearchtech.com
Key Highlights: The sbeadex Livestock DNA Purification Kit contains all of the components necessary to perform high-quality DNA purification. We offer our standard livestock ……
#2 Nucleic Acid Purification
Domain Est. 2020
Website: revvity.com
Key Highlights: Revvity provides a unique and efficient method for isolating nucleic acids based on chemagic technology established over 25 years….
#3 Nucleic Acid Purification
Domain Est. 1992
Website: neb.com
Key Highlights: Monarch nucleic acid purification kits provide fast and reliable isolation and purification of high-quality DNA and RNA from a variety of sample types….
#4 Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit
Domain Est. 1993
Website: promega.com
Key Highlights: The Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a simple, solution-based method for isolation of DNA from white blood cells, tissue culture cells, animal ……
#5 DNA
Domain Est. 1997
Website: qiagen.com
Key Highlights: Our trusted DNA purification kits ensure high yields of high-quality DNA free of contaminants and inhibitors. Streamlined DNA extraction protocols ……
#6 DNA Isolation Kits
Domain Est. 1998
Website: norgenbiotek.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsExtract Cell-Free DNA and Genomic DNA with our high-quality Purification kits. Optimize DNA Clean-Up for PCR and NGS with our kits….
#7 DNA
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mn-net.com
Key Highlights: Combining selective purification technologies and chemistries, we offer a comprehensive range of specialized DNA isolation kits for a broad range of ……
#8 Geneaid Biotech Ltd
Domain Est. 2002
Website: geneaid.com
Key Highlights: New Kit in Store: Magnetic Beads Blood gDNA Extraction Plate Kit (MBP096). MBP096 was designed for high-throughput purification of high-quality of genomic DNA ……
#9 DNA Products, Kits & Free Samples
Domain Est. 2002
Website: zymoresearch.com
Key Highlights: A complete portfolio of DNA stabilization, DNA purification, and DNA clean-up products for the simple and rapid recovery of high-yield, ……
#10 TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit
Domain Est. 2005
Website: en.tiangen.com
Key Highlights: The TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit provides a fast and easy silica-based format for DNA purification. The kit simplifies the purification of DNA from a wide range ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Dna Purification Kit
H2: Emerging Market Trends for DNA Purification Kits in 2026
As the global biotechnology and life sciences sectors continue to expand, the DNA purification kit market is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by advancements in genomic research, personalized medicine, and point-of-care diagnostics, several key trends are expected to shape the industry landscape.
-
Increased Demand from Precision Medicine and Genomics Research
By 2026, the proliferation of precision medicine initiatives and large-scale genomic projects—such as population genomics and cancer genomics—will drive robust demand for high-throughput and high-yield DNA purification kits. Researchers will require kits capable of efficiently isolating DNA from diverse sample types, including blood, saliva, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues, and circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA). This demand will favor suppliers offering automation-compatible, scalable solutions. -
Shift Toward Automation and Integrated Workflows
Laboratory automation is becoming a cornerstone of modern molecular biology. In 2026, DNA purification kits will increasingly be designed for seamless integration with liquid handling robots and next-generation sequencing (NGS) platforms. Vendors will emphasize compatibility with automated systems to improve reproducibility, reduce human error, and increase throughput—especially in clinical diagnostics and pharmaceutical R&D settings. -
Growth in Point-of-Care and Field-Deployable Applications
With rising interest in rapid diagnostics and decentralized testing, there will be growing demand for portable, rapid DNA extraction kits. These kits will be optimized for use in resource-limited settings, veterinary clinics, and field research, featuring simplified protocols, ambient-stable reagents, and minimal equipment requirements. Innovations in lateral flow and microfluidic-based purification will gain traction. -
Emphasis on Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
Environmental concerns will influence product development, with manufacturers focusing on reducing hazardous chemical use (e.g., phenol-chloroform), minimizing plastic waste, and offering recyclable packaging. By 2026, leading brands are expected to highlight their sustainability credentials as a competitive advantage, particularly in Europe and North America where regulatory and consumer pressures are stronger. -
Expansion of Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa will emerge as high-growth regions due to increased government funding for life sciences, rising biotech startups, and expanding healthcare infrastructure. Localized production and distribution partnerships will allow multinational companies to cater to regional needs while reducing costs and delivery times. -
Technological Innovations in Purification Chemistry
Advancements in magnetic bead-based and silica membrane technologies will continue to dominate, but newer approaches such as enzyme-based lysis, microfluidic purification, and nanoparticle-enabled DNA capture will gain validation. These innovations will offer higher purity, faster processing, and better recovery of low-concentration samples—critical for single-cell genomics and liquid biopsy applications. -
Rise of Custom and Niche Kits
Market segmentation will intensify, with vendors offering specialized kits tailored for specific applications—such as microbiome analysis, epigenetics (e.g., methylation-preserving extraction), or forensic DNA isolation. Customization and private labeling services will become standard offerings to meet the needs of academic, clinical, and industrial customers. -
Consolidation and Competitive Dynamics
The market will likely see increased mergers and acquisitions as major players like Thermo Fisher Scientific, Qiagen, Promega, and Bio-Rad seek to broaden their portfolios and strengthen supply chains. At the same time, innovative startups leveraging AI-driven reagent design or novel purification methods may disrupt the market by offering cost-effective alternatives.
In summary, the DNA purification kit market in 2026 will be characterized by technological sophistication, application-specific innovation, and a strong push toward automation and sustainability. Companies that adapt to these evolving demands—particularly in high-growth sectors like oncology, infectious disease testing, and synthetic biology—will be best positioned for long-term success.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing DNA Purification Kits: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing DNA purification kits is a critical step for laboratories engaged in molecular biology, genomics, and diagnostics. While these kits offer convenience and standardization, several pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can compromise research integrity, regulatory compliance, and commercial outcomes.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Kit Performance
One of the most frequent issues is batch-to-batch variability in kit performance. Poor quality control during manufacturing can lead to inconsistent DNA yield, purity (A260/A280 and A260/A230 ratios), and integrity. This inconsistency may result in failed downstream applications such as PCR, sequencing, or cloning, wasting valuable samples and time.
Substandard Reagents and Materials
Lower-cost kits, especially from lesser-known suppliers, may use inferior reagents (e.g., contaminated lysis buffers, inefficient binding matrices) or low-quality consumables (e.g., spin columns with inconsistent flow rates). These compromises can lead to low recovery, co-purification of inhibitors, or cross-contamination.
Lack of Validation for Specific Sample Types
Many kits are optimized for common samples like blood or cultured cells but may underperform with challenging inputs such as FFPE tissues, soil, or plant material. Sourcing a kit without verifying its validation data for your specific sample type risks poor DNA extraction efficiency and degraded results.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Reputable suppliers provide detailed Certificates of Analysis (CoA), lot-specific testing data, and full ingredient disclosure. Kits lacking this documentation make troubleshooting difficult and raise concerns about traceability—especially critical in regulated environments like clinical diagnostics or GMP facilities.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Technologies
Many DNA purification kits incorporate patented technologies (e.g., silica-membrane binding, magnetic bead formulations, or specific lysis chemistries). Sourcing kits from vendors who do not license these technologies can expose end users to IP infringement risks, particularly in commercial or diagnostic applications.
Ambiguous IP Warranties and Indemnification
Some suppliers do not provide clear IP indemnification, leaving customers legally vulnerable if a third party asserts patent claims related to the kit’s use. This is especially critical for biotech companies developing IVDs or therapeutics, where freedom-to-operate analyses are essential.
Counterfeit or Grey Market Kits
Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or grey market channels increases the risk of receiving counterfeit products that may infringe IP and lack quality assurance. These kits often bypass regulatory oversight and may not meet safety or performance standards.
Unclear Field-of-Use Restrictions
Certain kit licenses may restrict usage to research-only (RUO) and prohibit use in clinical or commercial settings. Overlooking these restrictions can lead to regulatory non-compliance and invalidation of data used for submissions to agencies like the FDA or EMA.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Choose Reputable Suppliers: Prioritize vendors with established quality systems (e.g., ISO 13485 certification) and transparent manufacturing practices.
- Request Validation Data: Ask for performance data relevant to your sample type and application.
- Review IP Terms: Examine licensing agreements and ensure the supplier provides IP indemnification where needed.
- Verify Distribution Channels: Purchase directly from the manufacturer or authorized distributors to avoid counterfeits.
- Conduct Pilot Testing: Evaluate kits with your specific workflows before large-scale procurement.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP considerations, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, compliant, and sustainable DNA purification workflows.
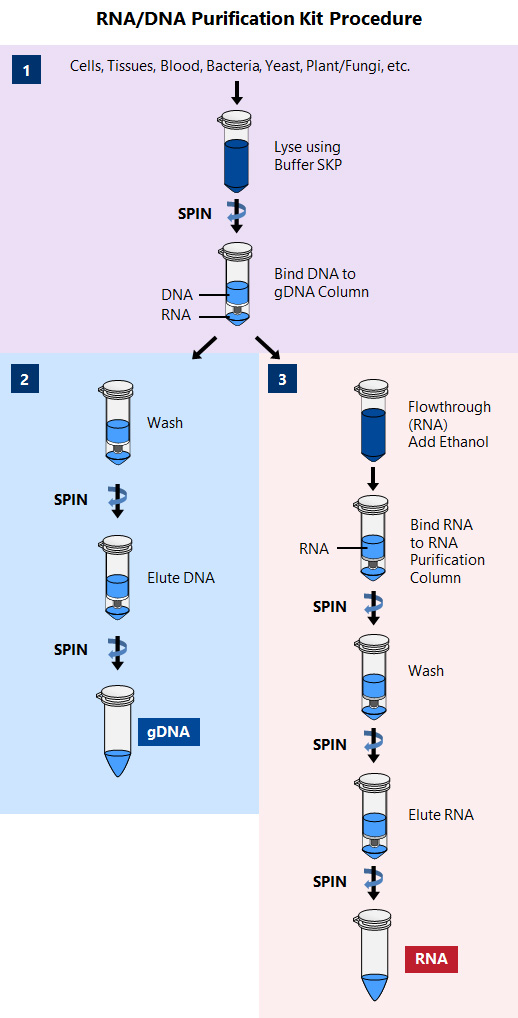
Logistics & Compliance Guide for DNA Purification Kit
This guide outlines the essential logistics and regulatory compliance considerations for the safe handling, storage, transportation, and use of a DNA Purification Kit. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, user safety, and compliance with international and local regulations.
1. Storage and Handling
- Temperature Requirements: Store the kit at 2–8°C (refrigerated) upon receipt. Avoid freezing unless specified in the product insert. Lyophilized components may have different requirements—verify with the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Light Sensitivity: Protect light-sensitive reagents (e.g., certain buffers or dyes) by storing in original packaging or amber bottles. Avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or UV light.
- Humidity Control: Store in a dry environment to prevent degradation of desiccants and reagents, particularly silica-based spin columns.
- Shelf Life: Observe expiration dates printed on each component. Do not use kits or individual reagents past their expiration date. Monitor for signs of contamination or precipitation.
2. Transportation
- Cold Chain Management: Ship using validated cold chain logistics (e.g., refrigerated packaging with ice packs or dry ice for long distances). Ensure temperature does not exceed 8°C during transit. Use temperature data loggers when possible.
- Packaging Standards: Use insulated shipping containers with adequate cushioning. Follow IATA and IMDG regulations if shipping internationally or by air/sea.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with “Keep Refrigerated,” “Do Not Freeze,” and “Biological Substances, Category B” (if applicable). Include handling instructions and contact information.
3. Regulatory Compliance
- Classification: Most DNA Purification Kits are classified as Diagnostic or Research-Use-Only (RUO) products and are not intended for diagnostic procedures unless specifically certified.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Confirm compliance with EU regulations governing chemical substances (REACH) and restriction of hazardous substances (RoHS). Safety Data Sheets (SDS) must be available.
- GHS Compliance: All chemical components (e.g., ethanol, guanidine salts) must be labeled according to the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) with hazard pictograms, signal words, and precautionary statements.
- FDA & USP (USA): Kits intended for clinical use may require FDA 510(k) clearance or approval. Research-use-only kits must carry appropriate disclaimers per 21 CFR 809.10.
- Import/Export Controls: Be aware of CITES, dual-use, or biosecurity regulations if shipping across borders. Some genetic material handling tools may be subject to national biosafety laws.
4. Safety and Handling Precautions
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear gloves, lab coat, and safety goggles when handling kit components. Use in a well-ventilated area or fume hood if working with volatile solvents.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of biohazardous waste (e.g., samples, used tips) according to local biohazard protocols. Chemical waste (e.g., ethanol, chaotropic salts) must be segregated and disposed of following environmental regulations (e.g., EPA guidelines).
- Spill Management: In case of spillage, neutralize with appropriate absorbent, decontaminate surfaces with 10% bleach or commercial DNA decontamination solution, and dispose of waste as hazardous material.
5. Documentation and Traceability
- Batch Tracking: Maintain records of lot numbers, expiration dates, and storage conditions for quality control and audit purposes.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Ensure up-to-date SDS are accessible for all chemical reagents included in the kit.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and follow SOPs for kit usage, storage, and disposal. Train all personnel accordingly.
6. Special Considerations
- Biosafety Level (BSL): Perform DNA purification from human or pathogenic samples in appropriate BSL-2 or higher containment facilities, depending on sample origin.
- Ethical & Legal Use: Ensure compliance with genetic privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) when processing human-derived samples. Obtain proper informed consent where required.
By following this guide, laboratories and distributors can ensure the safe, compliant, and effective use of DNA Purification Kits across the supply chain and end-user environment. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions and local regulatory requirements for specific applications.
Conclusion:
After evaluating various options for sourcing a DNA purification kit, it is evident that selecting the right product involves balancing factors such as yield, purity, ease of use, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Commercial kits offer consistent performance, time savings, and reliability, making them ideal for routine laboratory workflows and high-throughput applications. Among the available suppliers, kits from reputable manufacturers demonstrate superior DNA recovery and minimal contamination, ensuring downstream compatibility with PCR, sequencing, and other molecular biology techniques.
While in-house or non-kit methods may reduce costs, they often require more time, expertise, and quality control. Therefore, purchasing a well-validated DNA purification kit from a trusted supplier is recommended for ensuring reproducible and high-quality results. Based on performance, reliability, and value for money, sourcing from established providers such as Qiagen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, or Zymo Research is advisable, depending on specific laboratory needs and budget constraints.
In conclusion, investing in a high-quality DNA purification kit enhances experimental accuracy and efficiency, ultimately supporting robust and reliable genetic analysis.